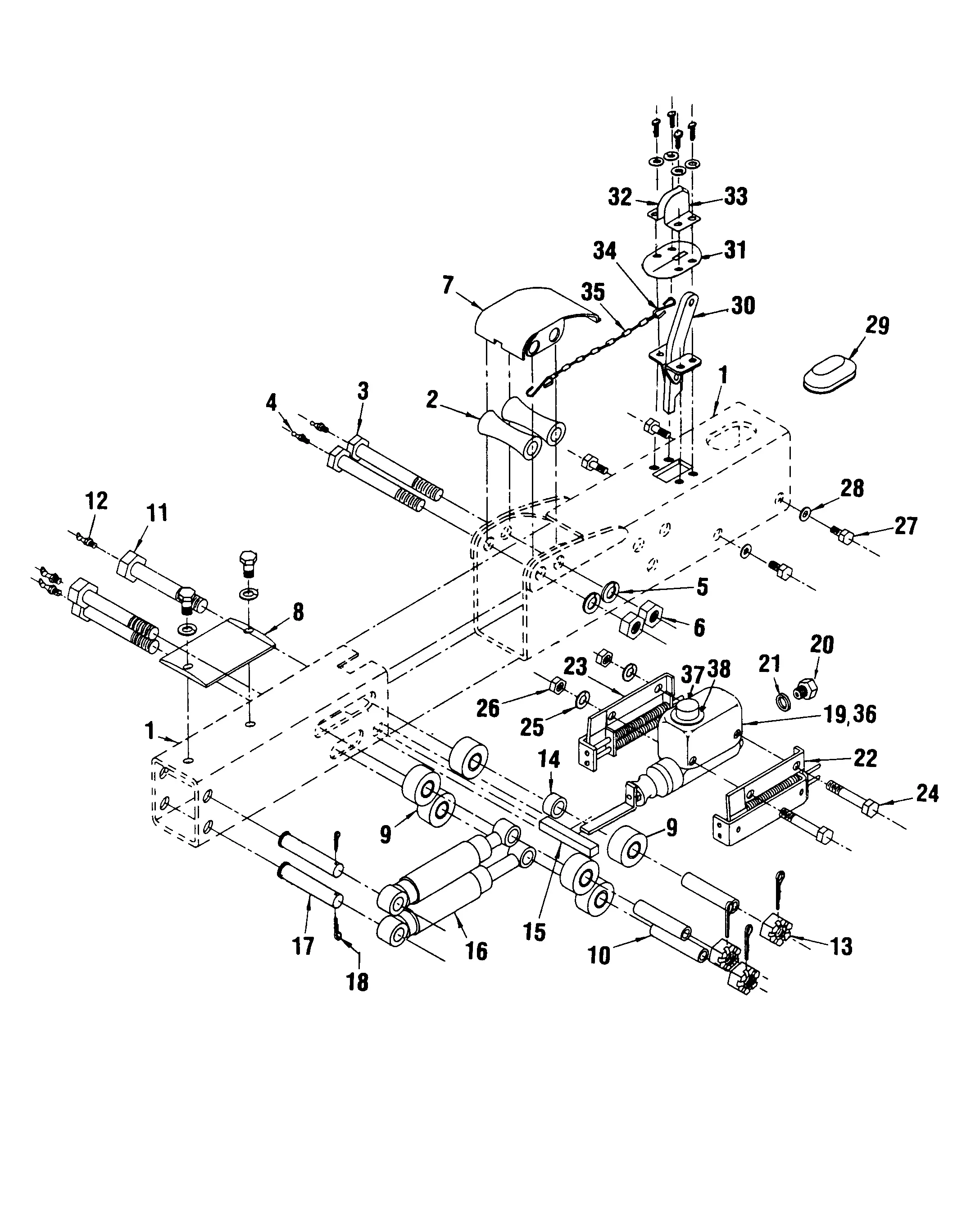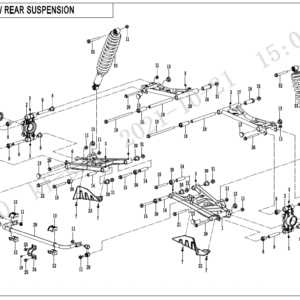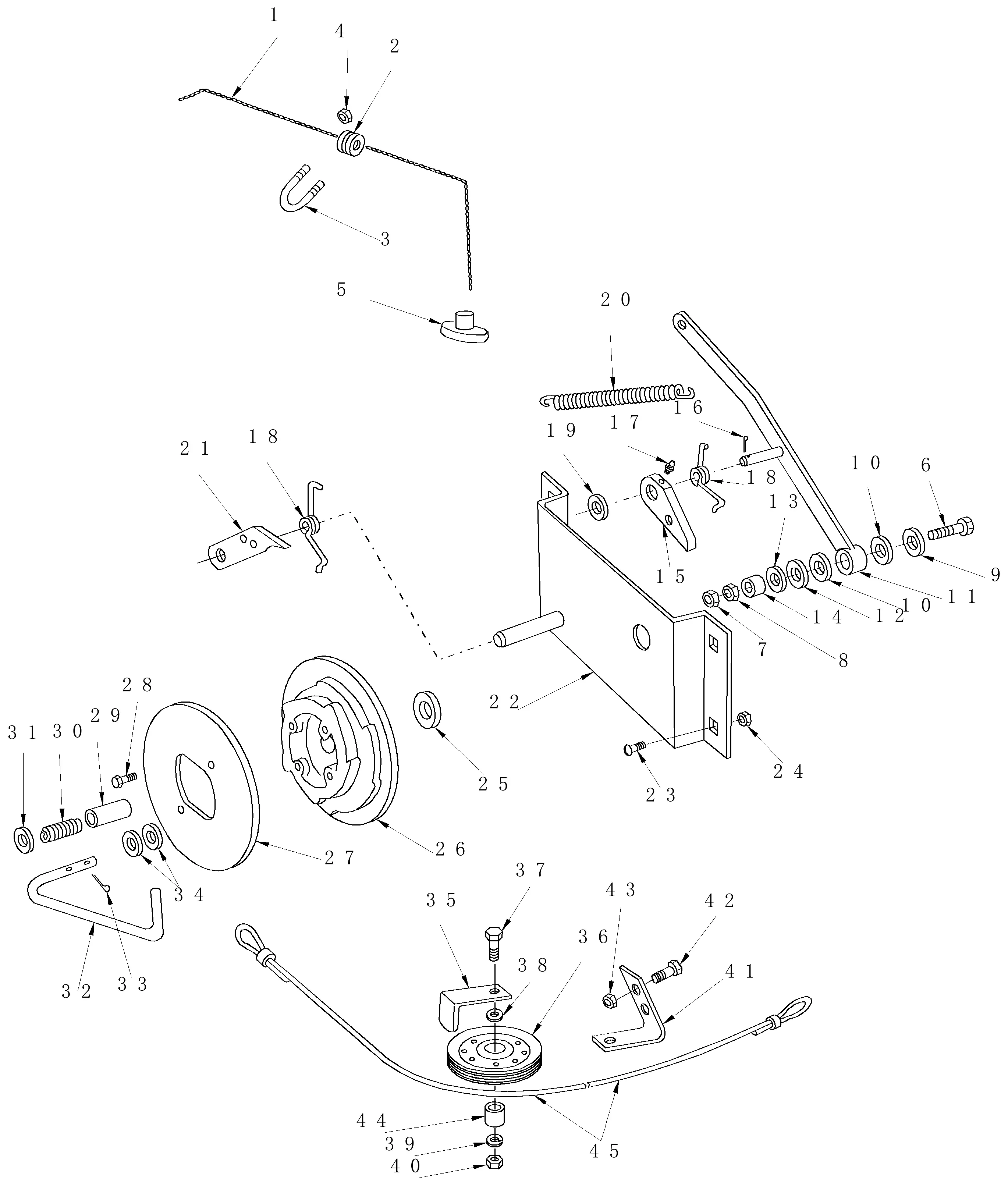
In the world of agriculture, efficient machinery plays a critical role in managing daily operations. Each machine consists of a variety of components, working together to ensure smooth functionality in the field. Familiarity with these elements can greatly aid in maintaining and repairing equipment, minimizing downtime and enhancing productivity.
Whether you are dealing with older models or more modern systems, knowing the layout of key mechanisms helps streamline routine inspections and necessary adjustments. Identifying essential components and their interconnections allows users to address potential issues before they escalate, keeping equipment running effectively.
Comprehensive guides to machinery configurations are valuable resources, especially when it comes to replacing or adjusting individual elements. With a clear understanding of the internal structure, operators can approach tasks more confidently, ensuring every part is in optimal working order.
Overview of H&S Manure Spreader Components
The equipment in question consists of various integral elements that work together to ensure efficient material distribution across fields. These components are specifically designed to handle heavy loads, providing reliability and durability in demanding agricultural environments.
- Frame and Chassis: The sturdy foundation supports the entire machine, offering stability during transportation and operation.
- Conveyor System: A robust mechanism that moves the material from the storage area towards the distribution system, ensuring a consistent flow.
- Distribution Mechanism: This part handles the even spread of material over the field, ensuring uniform coverage and effective usage of the load.
- Power Transmission: Includes chains, gears, and drive shafts that connect the power source to the moving parts, ensuring smooth operation.
- Tires and Axles: Heavy-duty wheels and axles provide mobility, allowing the machine to navigate different terrains with ease.
Key Functions of the Manure Spreader
The equipment plays a critical role in efficiently distributing organic materials across agricultural fields. By ensuring an even application, it contributes to enhancing soil quality and optimizing crop yields. Understanding its primary operations helps in achieving better performance and longevity.
Efficient Material Distribution
One of the primary roles of this tool is to evenly distribute materials over a wide area. This is essential for preventing over-concentration in specific spots and promoting balanced soil nutrient levels.
- Ensures uniform coverage
- Reduces manual labor
- Increases productivity in large fields
Optimized Flow Control
The machinery allows users to regulate the flow rate of the material being spread, ensuring that the amount applied matches the specific needs of the land. This control minimizes waste and maximizes the effectiveness of the distribution.
- Adjustable speed settings
- Customizable distribution patterns
- Improved operational efficiency
How to Identify Worn-Out Parts
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of your equipment. Over time, certain components may begin to degrade, which can lead to inefficiencies or even breakdowns. Knowing how to recognize early signs of wear can help prevent costly repairs and downtime.
One of the first indicators of aging components is unusual noise during operation. If the machinery begins to make grinding or squeaking sounds, it’s a clear sign that something may be deteriorating internally. Additionally, decreased efficiency, such as slower movement or reduced output, often points to mechanical issues that need attention.
Another sign to watch for is visual damage. Cracks, rust, or noticeable deformation of any mechanical elements typically indicate wear. Pay close attention to areas that experience high stress or friction, as these are more prone to damage. Regularly inspecting these sections can prevent further complications.
If you notice increased vibration or instability during use, it may suggest that key components are loosening or wearing out. This can result in misalignment, which should be addressed promptly to avoid more significant damage.
Lastly, leaks or unusual fluid levels in hydraulic or lubrication systems are red flags. Deteriorating seals or connections may cause these issues, signaling that it’s time to replace the faulty components before they fail completely.
Understanding the Gearbox Mechanism
The gearbox is an essential component in any agricultural machinery, responsible for efficiently transferring power from the engine to various operational systems. Its role is crucial in ensuring the proper synchronization of mechanical parts, allowing for smooth and reliable operation in demanding field conditions.
Key Components of the Gearbox
At the heart of the gearbox mechanism are gears, shafts, and bearings. The gears are designed to manage torque and speed, with each gear ratio tailored to specific performance needs. Shafts are responsible for transmitting power, while the bearings reduce friction and provide smooth rotation. Together, these elements ensure the machinery can handle various loads without failure.
How the Gearbox Functions
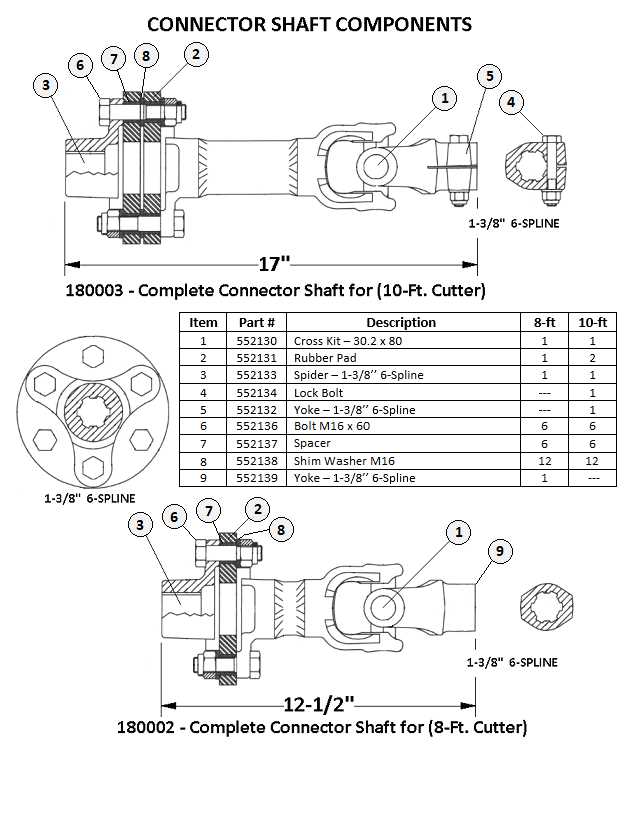
When power is delivered from the engine, the gearbox adjusts the torque and rotational speed through a series of gear shifts. The operator can control the speed and power output by selecting the appropriate gear. This precise control allows for optimal performance under different working conditions, maximizing efficiency and minimizing wear on the equipment.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Regular upkeep of agricultural equipment ensures its efficiency and extends its operational life. By following proper maintenance procedures, you can prevent costly repairs and avoid unexpected breakdowns. Consistent attention to key components is essential for keeping your machinery in optimal condition.
Key Areas to Monitor
To maintain the longevity of your machinery, it’s crucial to check certain parts regularly. These areas tend to face the most wear and tear, and proactive care will help keep your equipment running smoothly for years.
| Component | Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Bearings | Lubricate to reduce friction | Every 6 months |
| Chains | Inspect for wear and tension | Monthly |
| Hydraulic Lines | Check for leaks and replace if necessary |