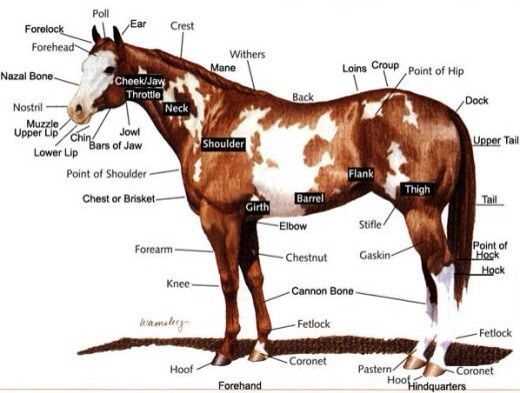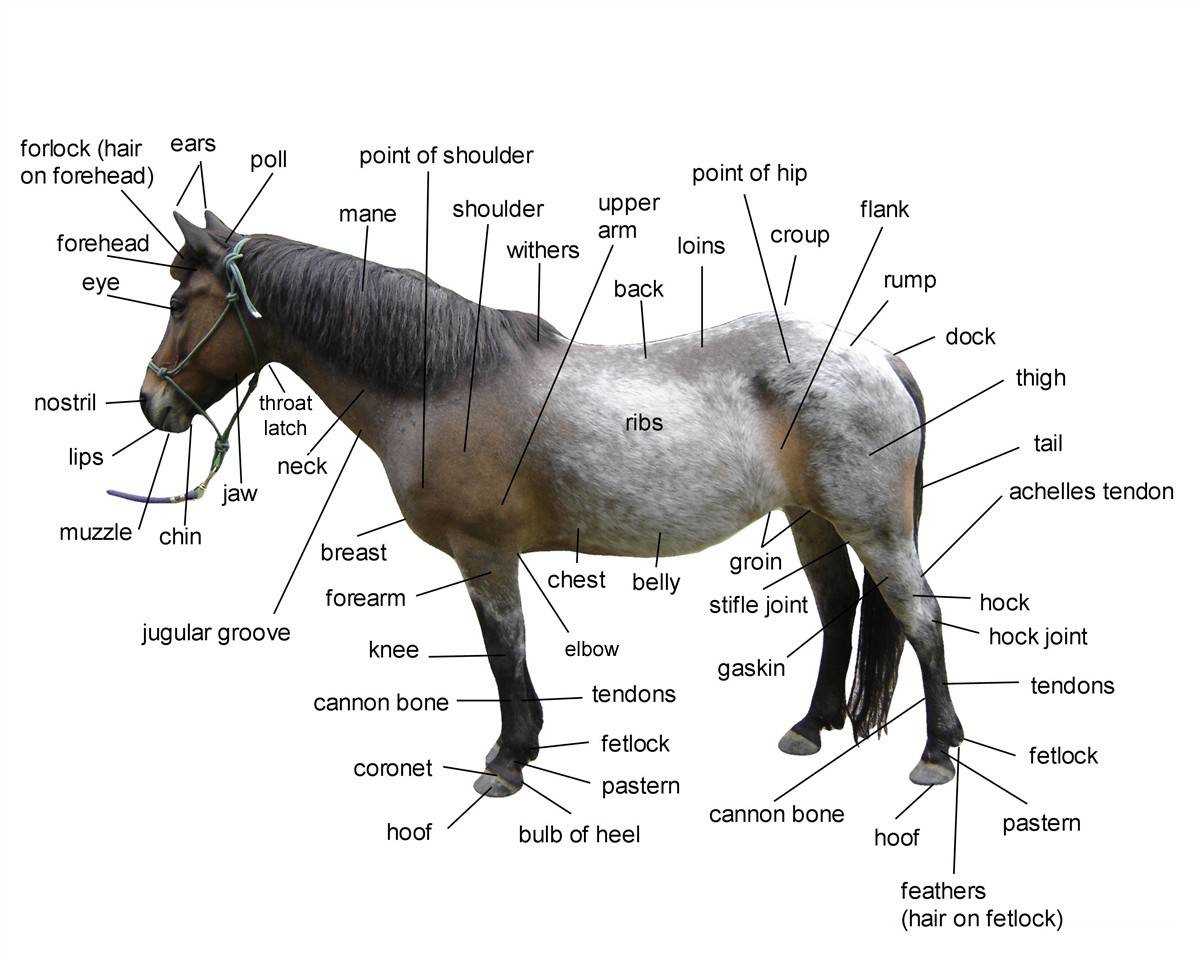
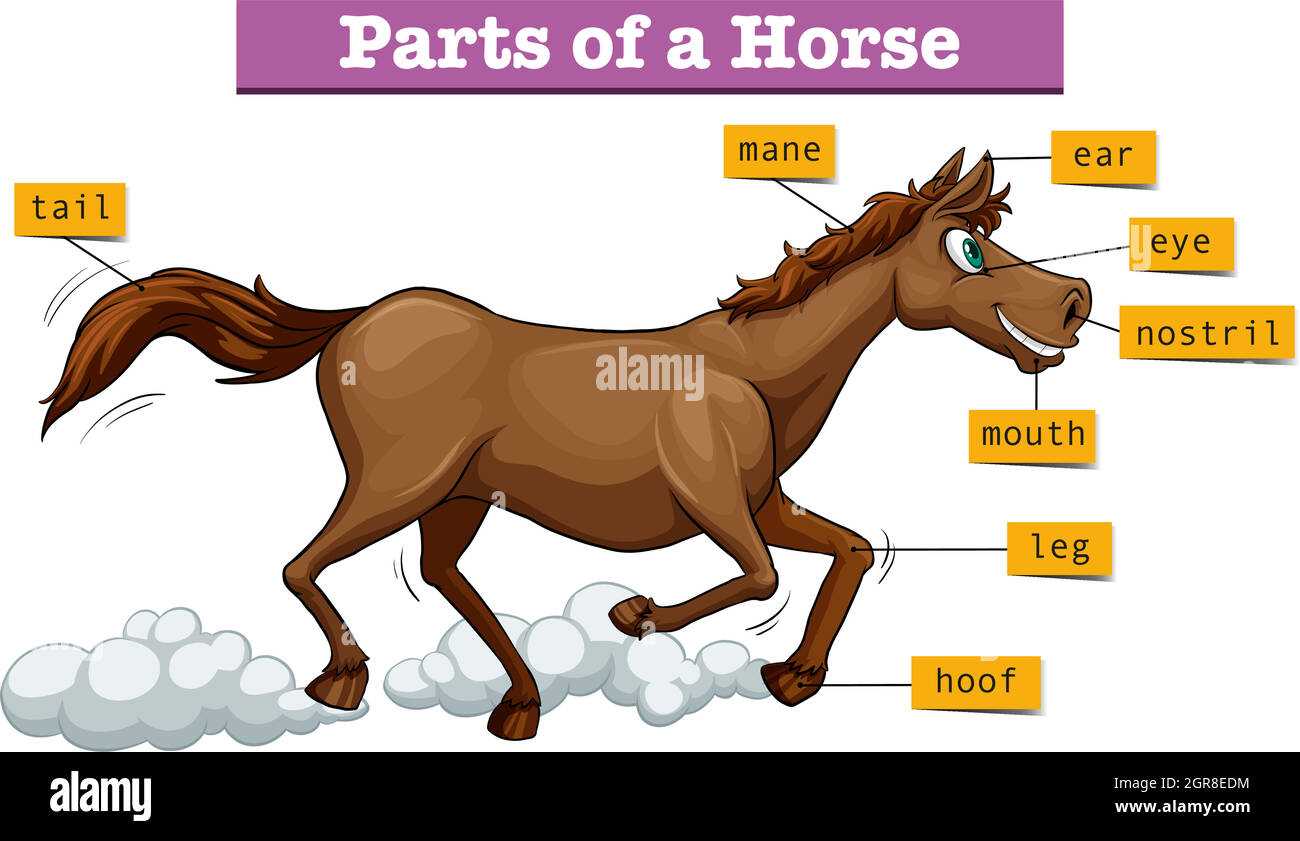
The intricate structure of this noble animal reveals a complex system of various regions, each serving its own unique function. Understanding these areas is crucial for those studying the anatomy and physiology of this graceful being.
Each section of its body is designed with purpose, from the powerful limbs that provide speed and strength, to the finely tuned regions responsible for balance and movement. By exploring these features, one gains deeper insights into the animal’s agility and endurance.
Whether you are a veterinarian, trainer, or simply an enthusiast, gaining knowledge of these detailed features enhances your understanding and appreciation of the creature’s form and function.
Horse Parts Diagram
Understanding the anatomy of this majestic creature is essential for anyone involved in its care or training. By learning the key regions of the body, one can better assess its health, identify areas of strength, and address potential issues. This knowledge is fundamental in both riding and veterinary practices, ensuring effective communication between professionals and caretakers.
| Body Region | Function |
|---|---|
| Head | Responsible for sensory input and guidance. |
| Neck | Provides balance and flexibility, aiding in movement. |
| Legs | Key to mobility, these are powerful and resilient, allowing for speed and agility. |
| Back | Supports the rider and absorbs shocks during movement. |
Anatomy of a Horse’s Head
The structure of this animal’s head is a fascinating blend of functionality and form, designed to accommodate essential tasks such as feeding, breathing, and sensory perception. The unique configuration plays a key role in overall body coordination and communication.
Key Structural Features
Among the primary elements are the prominent facial bones and muscular systems, which support movement and expression. The placement of various sensory organs, like the large eyes and nostrils, allows for enhanced awareness and adaptability in diverse environments.
Functional Aspects
Each section of the head serves a distinct purpose, contributing to the animal’s ability to interpret and react to its surroundings. From powerful jaw muscles that assist in chewing to the flexible neck that provides wide motion, these features work together seamlessly.
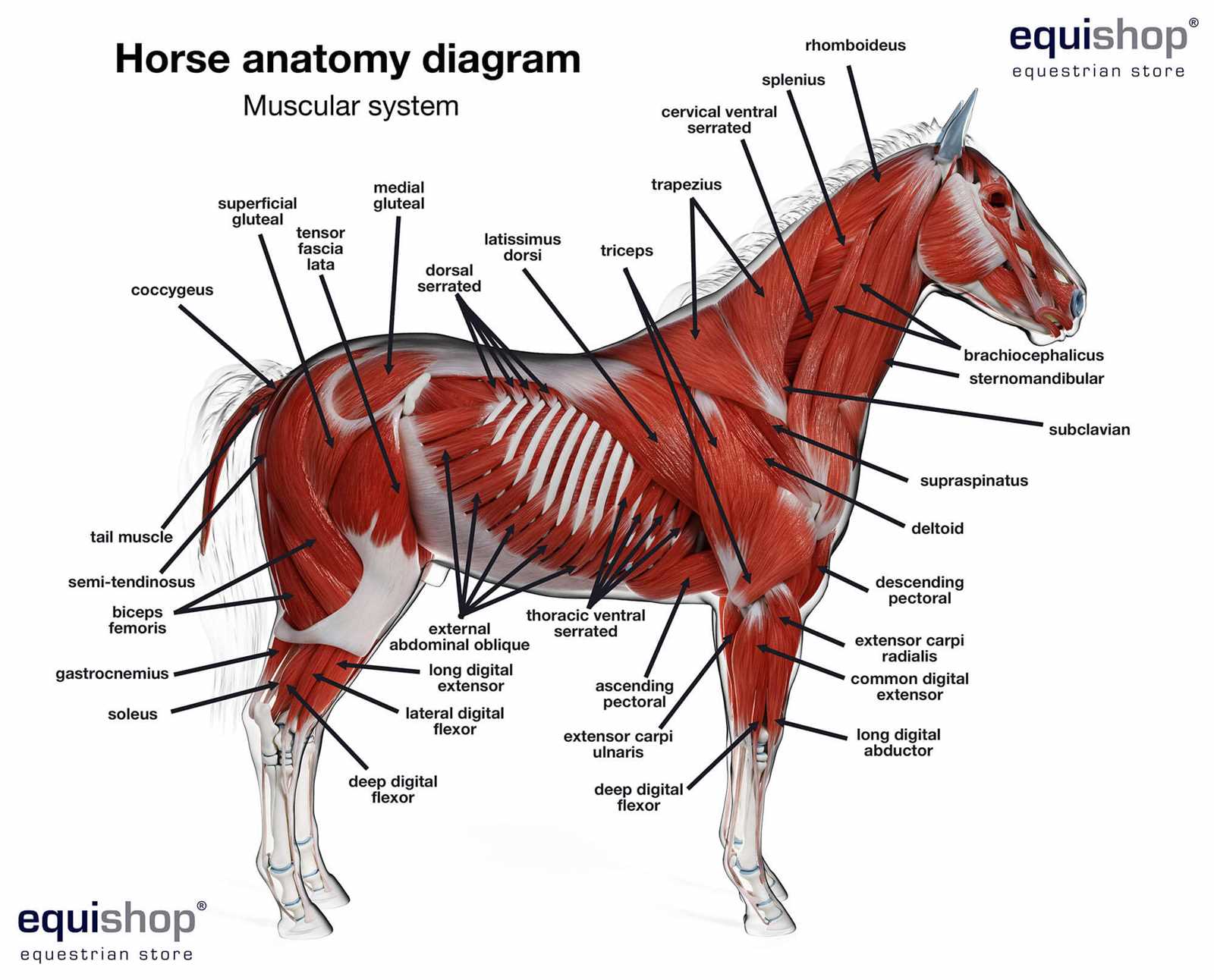
Understanding the Horse’s Muscular Structure
The muscular system plays a crucial role in enabling movement and maintaining posture. It consists of a complex network of fibers working in unison to control various motions, from subtle shifts to powerful strides. The arrangement of these tissues is intricately designed to provide both strength and flexibility, allowing for a wide range of physical activities.
Key muscle groups are responsible for different functions, whether it’s supporting locomotion or stabilizing the body during rest. Each region has its own specific purpose, contributing to the overall fluidity and efficiency of movement. Studying these muscle patterns provides insight into how mobility and endurance are achieved.
Skeletal Framework of Equine Limbs

The complex structure of these limbs supports the animal’s movement and stability. Each bone, from the upper sections to the lower extremities, plays a crucial role in facilitating both speed and strength, making it an efficient system for motion and balance. Understanding the arrangement of bones within the limbs helps to grasp how they contribute to overall mobility and endurance.
| Bone | Function | |
|---|---|---|
| Scapula | Acts as a base for muscle attachment, aiding in limb movement. | |
| Humerus | Connects to the shoulder and forearm, allowing for extensive movement. | |
| Radius | Provides structural support and forms part of the forelimb’s primary framework. | |
| Carpus | Functions like a wrist, allowing flexibility and shock absorption. | |
| Femur | The major bone of the hind limb, crucial for strength and propulsion. |
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Nostrils | Entry point for air; helps filter and warm incoming air. |
| Trachea | Transports air to and from the lungs. |
| Lungs | Primary site for gas exchange; oxygen is absorbed, and carbon dioxide is expelled. |
| Diaphragm | Muscle that aids in the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity, facilitating breathing. |
Understanding these essential components and their functions helps to appreciate the importance of a healthy respiratory system in maintaining the vitality of these remarkable animals.
Nervous System and Sensory Organs in Horses
The intricate network responsible for coordinating actions and processing information plays a crucial role in the life of these majestic creatures. Understanding this complex system reveals how they interact with their environment and respond to various stimuli. This section delves into the components that make up this vital system, emphasizing their functions and significance in maintaining the overall health and well-being of the animals.
Components of the Nervous System
The nervous system comprises two main divisions: the central and peripheral systems. Each plays a unique role in how information is transmitted and processed. The central part consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral section includes all other nerves branching throughout the body. This division ensures a quick response to external factors and internal conditions.
Function of Sensory Organs
Sensory organs enable these creatures to perceive their surroundings. They include structures that detect sound, light, touch, taste, and smell. Each organ is specialized, contributing to the animal’s ability to react to potential threats and navigate through various environments. Understanding these organs highlights their importance in everyday activities, from foraging for food to avoiding dangers.
| Type of Organ | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Eyes | Vision | Located on either side of the head |
| Ears | Hearing | Positioned on the top of the head |
| Nostrils | Smell | At the end of the muzzle |
| Skin receptors | Touch | Throughout the body |
| Tongue | Taste | Inside the mouth |