The inner workings of a two-wheel vehicle rely on numerous interconnected elements, each playing a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and efficient ride. These elements, both large and small, are designed to work together seamlessly, creating a harmonious system that provides balance, speed, and control. In this section, we will explore the various components that make this possible.
Whether you are looking to maintain, upgrade, or simply familiarize yourself with the individual mechanisms that keep your vehicle moving, a clear understanding of these elements is essential. We will cover key systems responsible for motion, steering, and stability, giving you a comprehensive overview of how everything functions together.
From the framework to the tiniest connectors, each piece is carefully engineered for performance and durability. This guide aims to provide clarity on how these essential components fit together, ensuring your machine operates at its best.
Understanding the Components of Giant Bicycles
When exploring the structure of modern two-wheelers, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the various elements that ensure smooth and efficient performance. Each element plays a vital role in delivering a seamless riding experience, and understanding their function can help with maintenance and customization.
- Frame: The main structure that supports the entire build, often designed to balance strength and lightness.
- Handlebars: These provide control and steering, available in various styles to suit different riding preferences.
- Wheels: Key for movement, these components are typically designed for durability and optimal traction on different surfaces.
- Drivetrain: The system responsible for transferring power from the rider’s motion to the wheels, including multiple gear mechanisms.
- Brakes: Safety-critical elements that ensure controlled stopping power, offered in various designs such as disc or rim types.
- Saddle: The seat designed for rider comfort, often adjustable to meet specific ergonomic needs.
Knowing the purpose and interaction of each element can significantly improve both your riding experi
The Role of Frame Structure in Bike Design
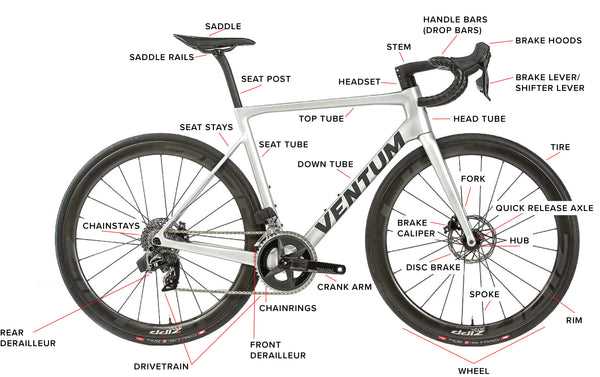
The frame is a critical element in the overall design of two-wheeled vehicles, providing both the foundation and support for other components. Its structure impacts the machine’s performance, comfort, and durability. Understanding how different shapes and materials affect the strength and flexibility of the frame is essential in creating a well-balanced riding experience.
Impact on Performance
Frame geometry plays a significant role in determining speed, stability, and control. The angles, lengths, and materials used in its construction influence how the rider interacts with the vehicle during movement. For instance, a more rigid frame often allows for better speed, while a flexible one provides enhanced comfort over uneven terrain.
Materials and Design Choices
The choice of material is crucial to balancing weight and durability. Aluminum, steel, and carbon fiber are commonly used, each offering unique advantages. The right combination of material and structure ensures the frame can handle both everyday use and more demanding conditions without compromising the user’s comfort.
| Material | Advantages | Common Use |
|---|
| Gear Type | Description | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Speed | A basic system with a single gear ratio. Simple and easy to maintain. | Flat terrain, city commuting |
| Multi-Speed | A more complex arrangement with multiple gears for varied conditions. | Hilly areas, long-distance rides |
| Internal Hub | Enclosed gears offering smooth shifting and lower maintenance. | Urban environments, casual riding |
Brake Technology and Safety Enhancements

Modern advancements in braking systems have greatly improved overall performance and rider safety. With ongoing innovations, braking mechanisms are now more responsive, providing better control in a variety of conditions. These updates not only enhance stopping power but also contribute to a smoother, more reliable experience during rapid deceleration.
Key Features: Recent technological improvements focus on optimizing pressure distribution and reducing wear, ensuring longer durability. In addition, these systems incorporate precision engineering to minimize the risk of skidding, allowing for safer maneuvering at high speeds.
Another crucial aspect is the integration of materials that offer improved friction and heat dissipation, which further prevents overheating during prolonged use. These developments are designed to enhance overall reliability and provide riders with the confidence to navigate both urban and off-road environments safely.
Seat and Saddle Adjustments for Comfort

Ensuring the seat is properly adjusted is essential for a comfortable and efficient ride. Small changes in positioning can significantly affect posture, balance, and overall ease during long distances. In this section, we’ll cover the key factors that contribute to making the seat setup more tailored to individual preferences and needs.
Height Adjustments
The seat height is a critical element for ensuring proper alignment with the pedals and reducing strain on the knees. A properly adjusted seat height allows for efficient energy transfer and minimizes discomfort over time.
- Start by sitting in a neutral position and placing the heel on the pedal at its lowest point.
- If the leg is fully extended with the heel on the pedal, the height is approximately correct.
- A slight bend in the knee when the ball of the foot is on the pedal should be maintained.
Position and Tilt
Equally important to height is the forward-backward position and tilt of the saddle. These factors influence the overall body posture and how weight is distributed across the seat.
The Importance of Proper Pedal Placement
Correct positioning of foot supports is crucial for enhancing performance and comfort during cycling. Ensuring that these components are aligned appropriately can significantly impact the efficiency of energy transfer, reduce the risk of injury, and improve the overall riding experience. This section delves into the significance of optimal placement and its effects on various aspects of cycling.
Enhancing Efficiency
When foot supports are placed correctly, energy generated by the rider is transmitted more effectively to the propulsion mechanism. This efficiency allows for smoother rides and better speed control, particularly on challenging terrains. Misalignment can lead to wasted energy and increased fatigue.
Reducing Injury Risks

Improper placement can contribute to discomfort and injuries, particularly in the knees and hips. Aligning foot supports according to individual biomechanics helps in maintaining a natural posture, thus minimizing the risk of strain and overuse injuries.
| Placement Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Foot Position | Directly affects power output and comfort |
| Cleat Alignment | Influences pedal stroke efficiency |
| Height Adjustment | Prevents knee pain and improves leverage |
Maintenance Tips for Giant Bicycle Parts
Proper upkeep of your two-wheeled transport is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Regular attention to various components ensures a smooth and enjoyable ride. Here are some effective strategies to keep your equipment in excellent condition.
| Component | Maintenance Tips |
|---|---|
| Brakes | Inspect pads regularly for wear and replace them if they are less than 1/4 inch thick. Adjust the alignment for effective stopping power. |
| Chain | Lubricate the chain every few weeks, especially after riding in wet conditions. Clean it with a degreaser to remove dirt buildup. |
| Tires | Check tire pressure weekly and maintain it according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Inspect for any punctures or wear patterns. |
| Gear Shifters | Test shifting performance frequently. Adjust cables and derailleur settings to ensure smooth transitions between gears. |
| Frame | Clean the frame regularly to prevent rust and corrosion. Inspect for cracks or damage, especially after rough rides. |
