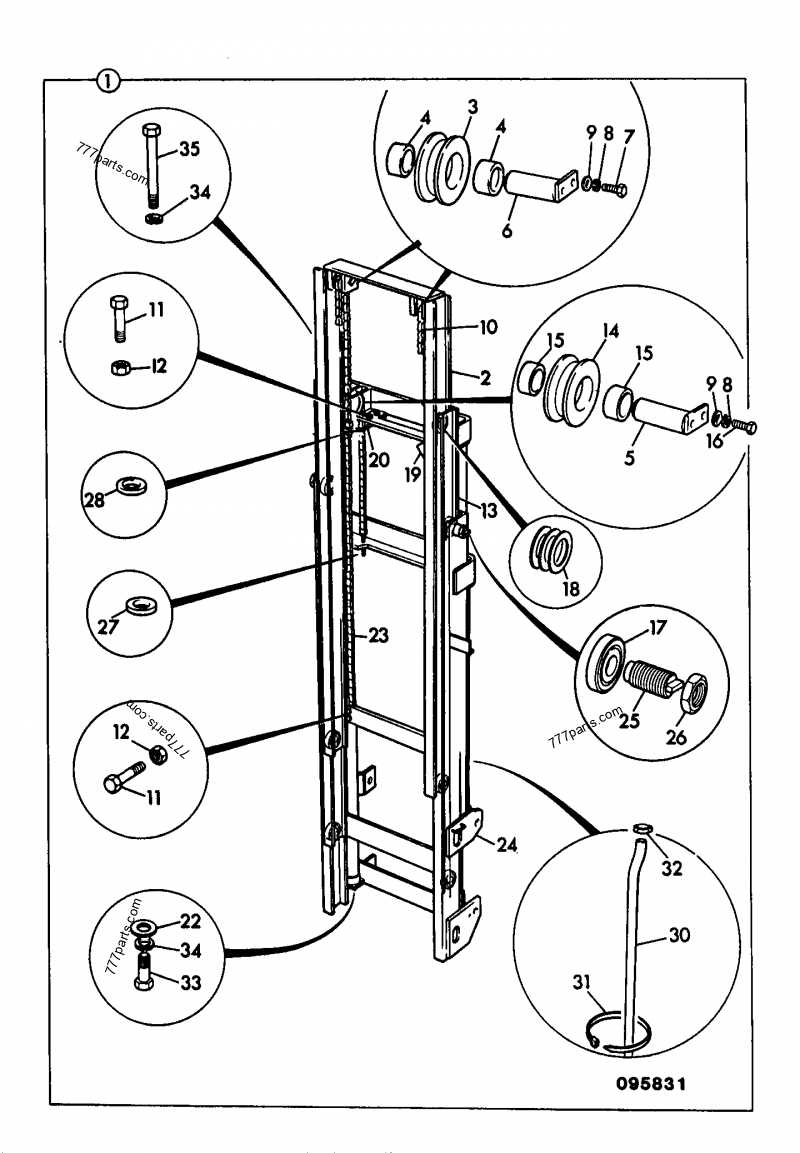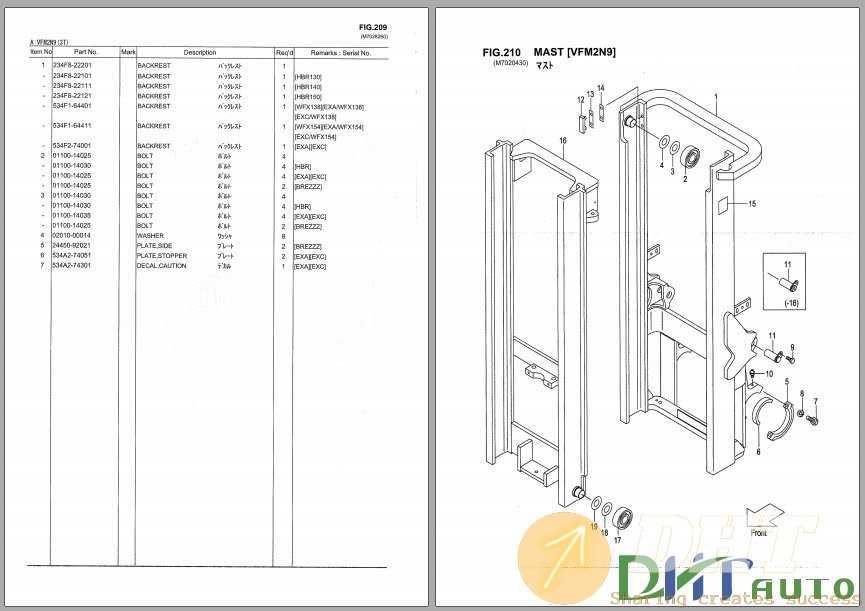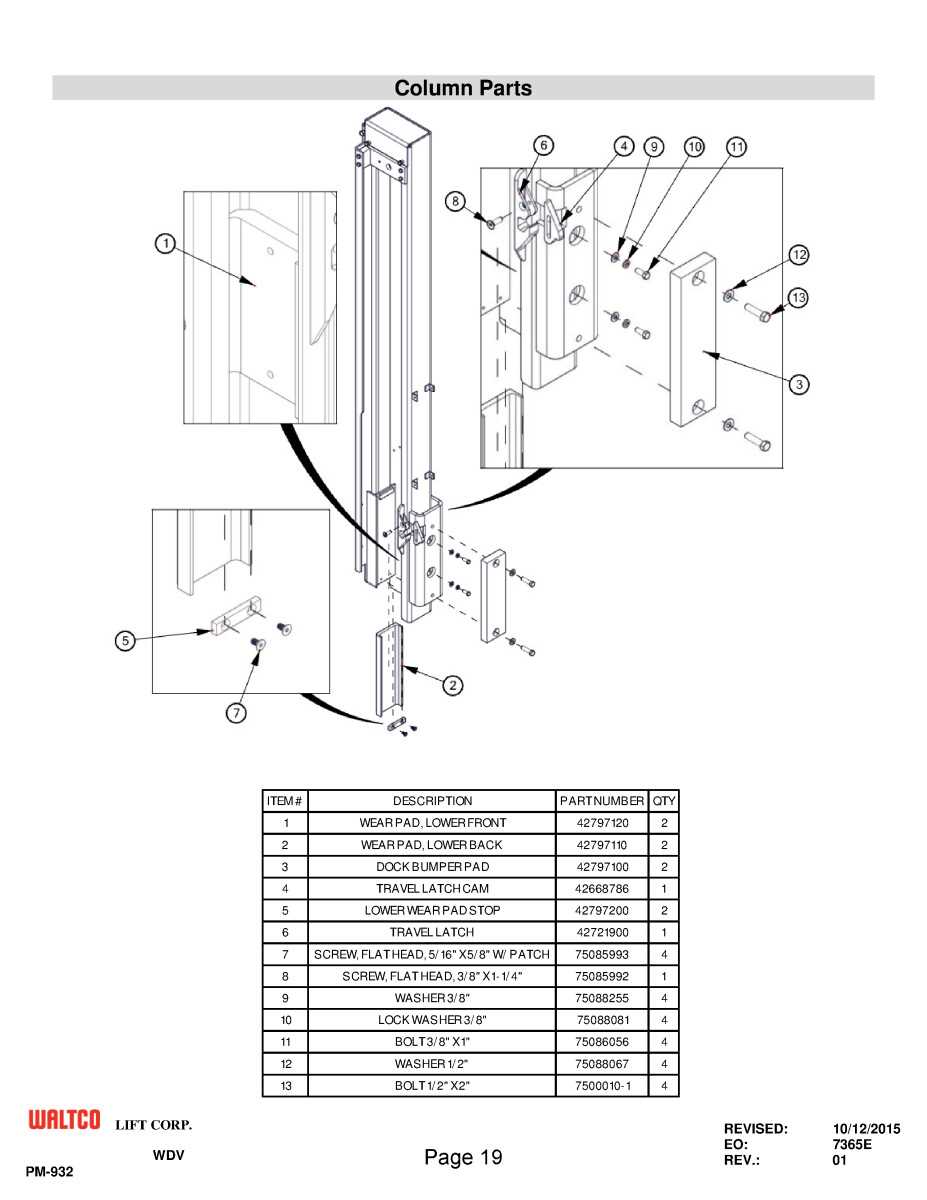
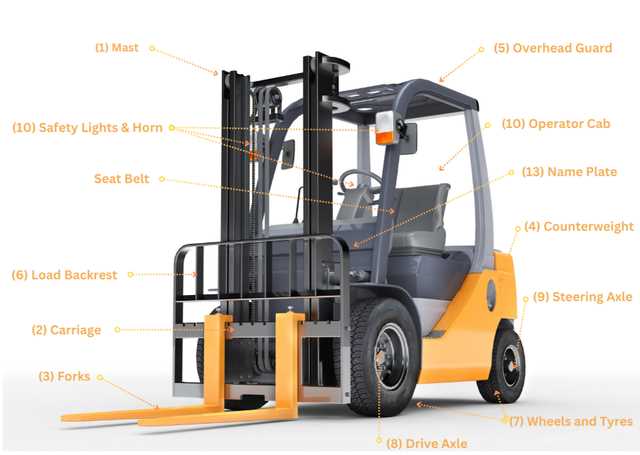
Vertical lifting equipment is essential in a wide range of industrial applications, ensuring efficient handling and transportation of heavy loads. The core structure responsible for this vertical motion is made up of interconnected elements designed to provide stability and smooth operation. These elements work in unison to support movement, ensuring safety and precision during use.
Each component plays a critical role in maintaining balance and control, allowing the lifting mechanism to operate effectively under various conditions. Understanding the layout and function of these elements is essential for proper maintenance, repair, and optimal performance of the equipment.
By exploring the specific interactions between these elements, one can gain deeper insight into the engineering behind these systems. This knowledge not only improves operational efficiency but also helps in identifying potential issues before they escalate into more significant problems.
Understanding the Forklift Mast Mechanism
The vertical lifting system is a critical component that allows heavy loads to be raised and lowered with precision. This system is designed to handle substantial weight while maintaining stability and balance during the lifting process. Its structure is engineered to ensure smooth and controlled movements, making it essential for efficient operation.
Key elements within this mechanism work together to provide seamless vertical motion. Various interconnected components are responsible for transferring power and ensuring that the platform moves in unison with the operator’s commands. These parts are engineered for durability and efficiency, playing a vital role in the system’s overall functionality.
Operational efficiency depends on how well these elements are maintained and adjusted. Understanding their role and ensuring regular checks can significantly improve the longevity and reliability of the equipment.
Key Components of Lifting System

The lifting mechanism in industrial machinery plays a crucial role in vertical movement and safe load handling. This section highlights the essential elements that work together to ensure smooth and efficient operation, allowing for the movement of materials in various environments.
Main Framework Elements
The core structure supports the entire assembly, providing stability during lifting and lowering processes. It is designed to bear the weight and distribute forces evenly, preventing imbalance and ensuring durability. Key structural elements include the vertical tracks, stabilizing beams, and connecting joints that allow for seamless movement.
Power and Motion Control
The lifting system relies on hydraulic components and control mechanisms that provide the necessary force to elevate and lower loads. These elements include cylinders, chains, and control valves that manage the speed and direction of movement. The hydraulic circuit is crucial in converting pressure into motion, enabling the equipment to function effectively in various operational conditions.
| Component | Function | |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Tracks | Guide and support the upward and downward movement | |
| Hydraulic Cylinders | Generate force to lift and lower loads |
| Aspect | Importance |
|---|---|
| Material Quality | Enhances durability and strength |
| Regular Inspections | Identifies wear and prevents accidents |
| Lubrication | Reduces friction and extends lifespan |
How Tilt Cylinders Operate in Forklifts
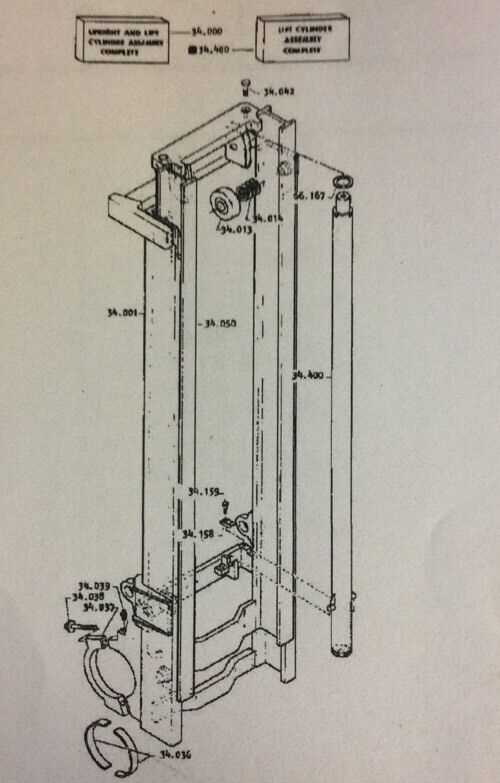
The mechanism responsible for the tilting action in lifting machines plays a crucial role in enhancing their versatility. These hydraulic devices allow for the adjustment of the angle of the lifting platform, enabling operators to position loads accurately and safely. Understanding the functionality of these components is essential for effective operation and maintenance.
Mechanics of Operation
The tilting system consists of two main hydraulic cylinders that work in tandem. When hydraulic fluid is pumped into one of the cylinders, it creates pressure that extends the cylinder, causing the platform to tilt backward. Conversely, releasing fluid from that cylinder and directing it into the other allows for a forward tilt. This controlled movement is vital for balancing loads during transportation and ensuring stability.
Importance of Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of these hydraulic mechanisms are vital to prevent failures and ensure optimal performance. Checking for leaks, ensuring proper fluid levels, and examining the integrity of the seals can significantly prolong the lifespan of the system and enhance safety during operation. Proper care not only improves efficiency but also protects the equipment from unnecessary wear and tear.
Rollers: Purpose and Maintenance
Rollers play a crucial role in enhancing the functionality and efficiency of lifting machinery. These components facilitate smooth movement, ensuring stability and support during operations. Their design is aimed at reducing friction and wear, contributing to the overall performance of the equipment.
Regular maintenance is essential to prolong the lifespan of rollers and prevent potential malfunctions. Proper care involves routine inspections, lubrication, and timely replacement of worn-out parts. Below is a table outlining key maintenance practices:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Weekly | Check for any visible damage or wear. |
| Lubrication | Monthly | Apply appropriate lubricant to reduce friction. |
| Replacement | As Needed | Replace any rollers showing signs of significant wear. |
| Alignment Check | Quarterly | Ensure rollers are properly aligned for optimal performance. |
Common Issues with Mast Components
The efficiency and reliability of lifting equipment are often compromised by various challenges related to its structural elements. Understanding these common issues is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety during operation. Below are some prevalent concerns that can arise within the essential components of this equipment.
| Issue | Description | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Wear and Tear | Over time, the mechanical elements can experience degradation due to continuous use, leading to reduced performance. | Regular inspections and timely replacement of worn components. |
| Misalignment | Improper alignment can cause uneven loading, leading to operational inefficiencies and increased wear. | Frequent checks and adjustments to ensure correct positioning. |
| Hydraulic Leaks | Leaks in hydraulic systems can result in loss of power and functionality, affecting overall operations. | Routine maintenance to identify and repair leaks promptly. |
| Rust and Corrosion | Exposure to moisture and harsh environments can lead to rust, weakening structural integrity. | Protective coatings and regular cleaning to prevent corrosion. |