Houses
The Role of Valve Mechanisms
Valve mechanisms play a crucial role in systems designed for water management and delivery. Their function extends beyond simply controlling flow; they are essential in ensuring regulated pressure, allowing precise distribution, and enabling secure shutdown when necessary. Understanding the structure and functionality of these mechanisms can significantly enhance the efficiency and reliability of water systems.
| Valve Type |
Primary Function |
Benefits |
| Gate Valve |
Controls flow by lifting or lowering a gate within the pathway. |
Offers full-flow access when open, reducing friction loss. |
| Ball Valve |
Utilizes a rotating ball with a central hole to allow or block flow. |
Quick to operate and provides reliable shut-off. |
| Check Valve |
Permits flow in a single direction, preventing backflow. |
Reduces water hammer and protects system integrity. |
| Pressure-Relief Valve |
Releases excess pressure to maintain safe operating levels. |
Prevents over-pressurization, safeguarding system components. |
Materials Used in Hydrant Construction
The choice of materials in the fabrication of these essential components significantly influences their durability and functionality. A variety of substances are utilized to ensure these devices can withstand environmental challenges while maintaining their operational efficiency.
Cast Iron is frequently employed due to its exceptional strength and resistance to corrosion. This material can endure harsh weather conditions and the wear and tear associated with frequent use, making it a reliable option for long-lasting construction.
Brass is another popular choice, known for its anti-corrosive properties and aesthetic appeal. This alloy not only provides resilience against elements but also offers a certain level of visual appeal, which can be important in urban settings.
Aluminum has gained traction as a lightweight alternative, offering ease of installation and maintenance. This material is also resistant to rust, enhancing its suitability for various environments.
Rubber components are essential for ensuring seals and joints are watertight. The flexibility and resilience of rubber allow for effective sealing against leaks, which is crucial for the overall performance of these devices.
In summary, the combination of these materials contributes to the efficiency, longevity, and reliability of these crucial components, ensuring they meet the demands of public safety and infrastructure requirements.
Why Fire Hydrant Caps Matter
The protective covers on essential water supply fixtures play a crucial role in ensuring efficient access and safety during emergencies. These components are designed to provide secure sealing while also allowing for quick and easy removal when necessary. Understanding their significance can enhance public awareness and preparedness.
Key Functions of Protective Covers
- Accessibility: These fixtures must be readily accessible for emergency responders, ensuring that time is not wasted in critical situations.
- Prevention of Contamination: The covers prevent debris and contaminants from entering the water supply, maintaining its quality.
- Durability: High-quality materials are used to withstand environmental conditions, ensuring longevity and reliability.
Importance of Maintenance
Regular checks and maintenance of these protective components are essential to ensure their functionality. Neglect can lead to rust, corrosion, or other forms of damage, which may impede performance when needed the most.
- Inspect for visible damage.
- Ensure easy operation during emergencies.
- Replace any worn or broken components promptly.
Maintenance Essentials for Fire Hydrants
Regular upkeep of critical infrastructure elements is vital to ensure their reliability and functionality. This involves a series of essential tasks designed to prolong the lifespan of these systems and guarantee their readiness for emergency situations. Effective maintenance helps to identify potential issues before they escalate, thereby promoting safety and efficiency.
Visual Inspections: Routine checks should be conducted to assess the overall condition of the units. Look for any signs of corrosion, damage, or wear that may hinder performance. Pay special attention to moving components, ensuring they operate smoothly and without obstruction.
Cleaning Procedures: Keeping the external surfaces clear of debris, dirt, and vegetation is essential for accessibility. Regular cleaning not only enhances visibility but also prevents long-term damage from buildup. It is advisable to use appropriate cleaning agents that do not harm the materials.
Lubrication: Regular application of suitable lubricants to moving parts is crucial. This minimizes friction and ensures smooth operation. Proper lubrication schedules should be established based on usage frequency and environmental conditions.
Functional Testing: Periodically testing the operational capabilities of the systems is essential. This includes flow tests to ensure adequate pressure and functionality during emergencies. Any irregularities detected during testing should be addressed promptly.
Record Keeping: Maintaining accurate logs of inspections, repairs, and maintenance activities is necessary for effective management. Documentation helps in tracking the history and condition of each unit, facilitating better decision-making for future upkeep efforts.
Implementing these maintenance essentials not only enhances the reliability of the infrastructure but also fosters community safety. A proactive approach to upkeep can significantly reduce the risk of failures during criti
Standard Types of Fire Hydrants
Understanding the various categories of external water sources is crucial for effective emergency response. These crucial components differ in design, functionality, and application, tailored to meet the diverse needs of urban and rural environments. Each type plays a significant role in ensuring rapid access to water during critical situations.
One prevalent variety is the wet barrel model, commonly found in warmer climates. It features a design that allows water to be readily available, minimizing the need for draining during the off-season. This type typically includes multiple outlets for simultaneous use.
In contrast, the dry barrel variant is engineered for areas that experience freezing temperatures. Its innovative structure keeps water below the frost line, preventing freezing and ensuring functionality year-round. When activated, the water flows from the top of the barrel, making it a reliable option in colder regions.
Another significant type is the pumper, designed specifically for fire response units. This variant incorporates a large opening for rapid water access and can connect to various hoses and equipment, facilitating efficient firefighting efforts.
Lastly, the standpipe system serves as a fixed source of water, often integrated into buildings for quick access by fire departments. These systems can be utilized with hoses and other firefighting tools, ensuring a consistent water supply during emergencies.
Identifying External Hydrant Features
Understanding the visible characteristics of water access points is essential for effective management and maintenance. These features play a crucial role in ensuring that these units can be easily recognized and accessed during emergencies. Each component contributes to the overall functionality, and familiarizing oneself with these elements enhances preparedness and response efficiency.
Surface Markings: The exterior often includes various markings that indicate the unit’s specifications. These may include the manufacturer’s name, model number, and relevant pressure ratings, which are vital for assessing the capabilities of the installation.
Connection Points: Noticeable connections are present, designed for interfacing with hoses or other equipment. Understanding the different types of connections can assist in determining compatibility with emergency response tools.
Accessibility Features: Many installations incorporate handles or levers that are designed for easy operation. These features are essential for ensuring that the equipment can be quickly and effectively utilized in urgent situations.
Color Coding: The coloring of these installations often conveys important information regarding water flow and pressure. Recognizing these color codes is essential for making informed decisions in critical scenarios.
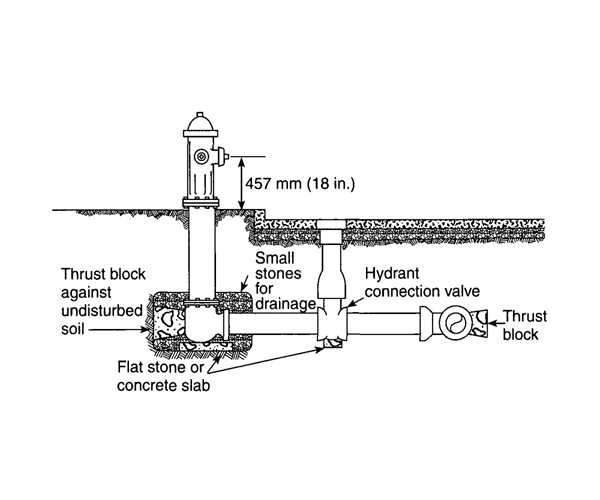
Drainage Systems: Some units are equipped with drainage mechanisms to prevent water accumulation, which can lead to damage or functional issues. Familiarity with these systems aids in regular maintenance checks.
By paying attention to these external characteristics, individuals can better prepare for their effective utilization during critical times.
|