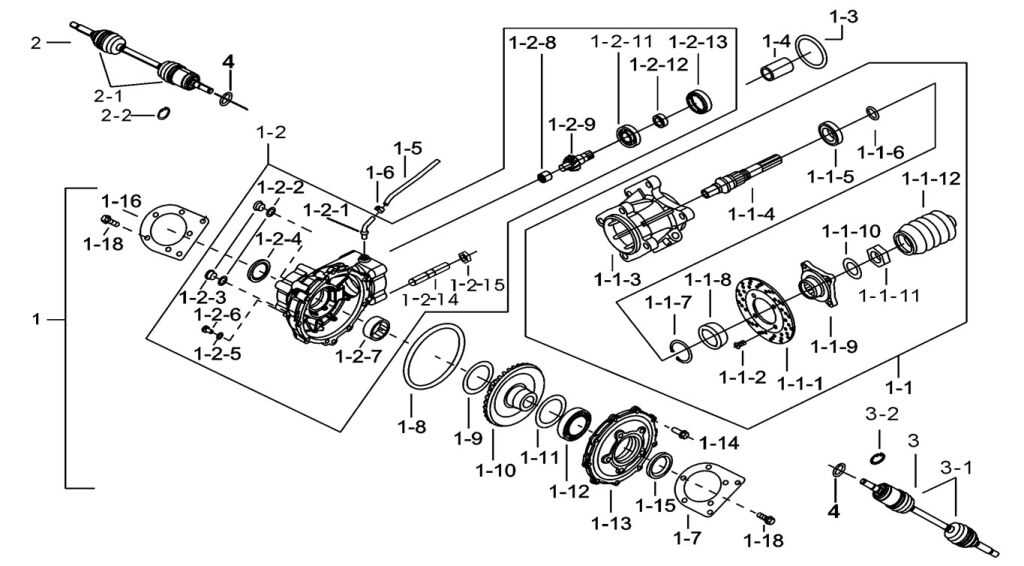
In the realm of mechanical engineering, there exists a critical assembly of elements that work in harmony to facilitate the smooth operation of various machinery. Each element plays a distinct role, contributing to the overall functionality and efficiency of the system. A profound grasp of these elements is essential for anyone involved in design, maintenance, or innovation within this field.
The intricate relationship among these components is vital for achieving desired outcomes. When one considers how these elements interact, it becomes evident that their synergy is what enables complex processes to unfold seamlessly. A thorough examination reveals the necessity of each component, highlighting their unique contributions to the overarching system.
Moreover, understanding the configuration and functionality of each element allows engineers to optimize performance and troubleshoot issues effectively. By dissecting the assembly into its fundamental components, professionals can identify areas for improvement and ensure the longevity of the entire mechanism. This knowledge is not merely academic; it translates directly into practical applications that enhance productivity and reliability in various industries.
Understanding Differential Diagrams
This section explores the essential elements and relationships that illustrate complex systems. By analyzing these representations, one can uncover the intricate interactions between various components, leading to a deeper comprehension of how they function together.
The Significance of Visual Representations
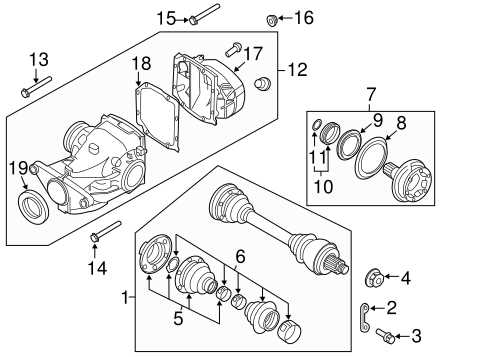
Visual aids serve as crucial tools for interpreting relationships within a system. They provide clarity, allowing for a quicker grasp of the underlying principles at play. When utilized effectively, these illustrations enhance communication and facilitate collaborative problem-solving.
Key Components to Consider
Focusing on fundamental elements is vital for a comprehensive understanding. Each symbol and connection holds meaning, contributing to the ultimate interpretation. Recognizing these nuances allows one to delve into the intricacies of the overall framework.
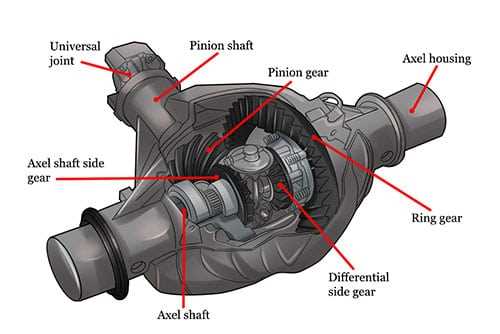
Key Components of Differential Systems
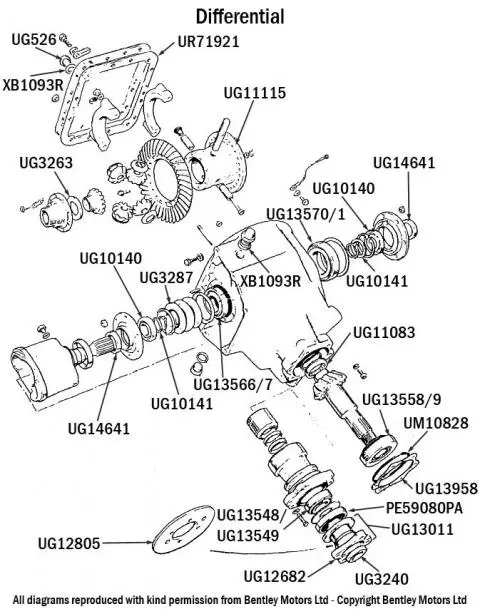
Understanding the essential elements that make up complex systems is crucial for analyzing their behavior and functionality. Each component plays a vital role in how the overall mechanism operates, contributing to its efficiency and effectiveness. By examining these critical components, one can gain insights into the dynamics at play and the interactions that drive performance.
1. Inputs: The initial factors that influence the system are known as inputs. These may include external forces, signals, or conditions that trigger responses within the framework. They set the stage for how the system will react and evolve over time.
2. State Variables: These are the fundamental parameters that define the current status of the system. They provide a snapshot of its condition and are essential for understanding how the system will respond to changes in inputs. Monitoring state variables allows for effective control and prediction of behavior.
3. Governing Equations: The relationships between different elements are described through mathematical formulations. These equations illustrate how inputs and state variables interact, guiding the evolution of the system. They serve as the backbone of the analytical framework, allowing for simulation and analysis.
4. Outputs: The results of the system’s operation are known as outputs. These reflect how well the system is performing in relation to its intended purpose. Analyzing outputs helps to assess the overall effectiveness and to identify areas for improvement.
5. Feedback Mechanisms: Feedback loops are crucial for maintaining stability and enhancing performance. They allow the system to adjust based on the difference between expected and actual outputs, ensuring that it remains responsive and adaptive to changing conditions.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of these vital components provides a foundation for effective analysis and optimization of complex systems, enabling practitioners to design and implement more efficient and robust solutions.
Types of Differential Diagrams Explained
Understanding the various representations of systems is crucial for effective analysis and communication. Each representation serves unique purposes and offers different insights, allowing users to visualize relationships and functions within complex frameworks.
Key Variations

- Flowcharts: Used to represent processes and workflows, illustrating steps and decision points.
- Block Schematics: Simplified versions that showcase the main components and their interactions without intricate details.
- Signal Flow Graphs: Focus on the flow of signals, highlighting dependencies and transfers between elements.
- Function Block Diagrams: Emphasize the functional aspects, showcasing how inputs and outputs relate through defined operations.
Applications
- Engineering: Often utilized to design and optimize systems.
- Education: Aids in teaching complex concepts through visual means.
- Project Management: Assists in outlining project workflows and responsibilities.
- Software Development: Helps in visualizing data flows and interactions between modules.
Applications in Engineering and Design
Innovative problem-solving methods play a crucial role in various fields of engineering and design. These methods allow engineers and designers to predict behavior, optimize performance, and improve overall system efficiency. By applying specific principles, professionals can model complex systems and analyze how different factors influence performance, ensuring the development of more reliable and functional solutions.
Structural Analysis and Optimization
In structural engineering, advanced methodologies are employed to study forces and their effects on physical structures. Through simulations, engineers can identify weaknesses, predict potential failures, and refine the structural elements to achieve maximum strength while minimizing material usage. This contributes to the creation of safer buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure.
Control Systems and Automation
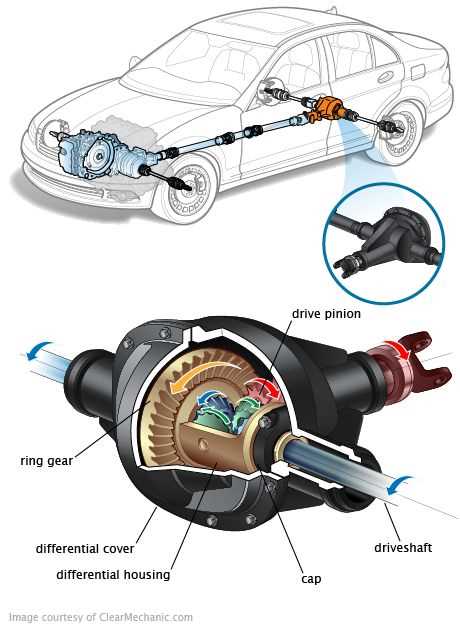
In automation and control systems, predictive models enable the accurate adjustment of processes. These models help engineers design control strategies that ensure optimal operation of machinery, systems, and processes across various industries. By understanding how certain parameters interact, engineers can enhance efficiency, stability, and precision in automated systems.
How to Create a Differential Diagram

Crafting a visual representation to illustrate relationships and variations can significantly enhance understanding and communication. This process involves several key steps to ensure clarity and effectiveness in conveying the intended message.
Step-by-Step Approach
Begin by identifying the key elements you wish to compare or contrast. Gather relevant data and insights to support your visual. Next, sketch a rough layout to organize your information logically. Use simple shapes to represent each component, ensuring they are distinct and easily recognizable.
Refinement and Presentation
Once the initial draft is complete, refine your work by enhancing visual appeal. Utilize color coding to signify different categories and emphasize critical points. Finally, ensure that the final product is easy to read and interpret, making adjustments based on feedback from peers if necessary.
In summary, creating an effective visual tool requires careful planning, thoughtful design, and iterative refinement. By following these steps, you can develop a powerful visual aid that communicates complex relationships clearly and effectively.
Common Mistakes in Diagramming
Creating visual representations can be challenging, and several pitfalls can undermine their effectiveness. Identifying and avoiding these errors is crucial for ensuring clarity and accuracy in communication.
- Lack of Clarity: Overly complex visuals can confuse rather than inform. It’s essential to keep representations straightforward and focused on the key message.
- Inconsistent Symbol Usage: Using different symbols or styles for similar elements can lead to misunderstanding. Consistency is key to maintaining coherence.
- Ignoring the Audience: Failing to consider the knowledge level of the audience can result in overly technical or overly simplistic visuals. Tailor the content to suit the viewers’ needs.
- Poor Layout: An unorganized arrangement can distract from the main points. A logical flow and strategic placement of elements enhance readability.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, one can significantly improve the quality and impact of visual representations, leading to better communication and understanding.
Software Tools for Differential Diagrams
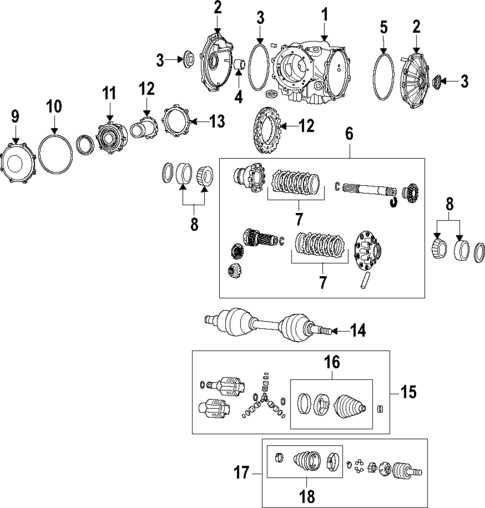
In the realm of visual representation, utilizing the right software can significantly enhance the clarity and effectiveness of complex relationships. Various applications offer specialized features tailored to streamline the creation and analysis of these visual models.
Popular Software Solutions
- Lucidchart – A versatile platform for creating a wide range of visuals with collaborative features.
- Microsoft Visio – Known for its comprehensive tools, ideal for professionals seeking precision.
- Draw.io – A free, user-friendly option that integrates seamlessly with various cloud services.
- SmartDraw – Offers extensive templates and automation tools to expedite the design process.
Key Features to Consider
- Intuitive Interface – Ensures ease of use, making the design process efficient.
- Collaboration Tools – Enables team members to work together in real-time.
- Integration Capabilities – Allows compatibility with other software and data sources.
- Customizable Templates – Provides a starting point that can be tailored to specific needs.
Best Practices for Effective Communication
Effective interaction is crucial in any environment, whether personal or professional. Clear exchanges foster understanding and collaboration, ensuring that messages are conveyed and received accurately. Implementing strategies that enhance this process can lead to more productive relationships and outcomes.
1. Listen Actively: Engaging in active listening allows individuals to fully comprehend the speaker’s message. This involves not only hearing the words but also understanding the underlying emotions and intentions. Nodding, summarizing, and asking clarifying questions can enhance this practice.
2. Be Clear and Concise: When conveying information, clarity is key. Use straightforward language and avoid jargon unless it is well-understood by the audience. Keeping messages concise helps prevent misunderstandings and maintains the listener’s attention.
3. Tailor Your Message: Adapt your communication style based on the audience. Consider their background, knowledge level, and preferences. This customization ensures that the message resonates and is easily digestible.
4. Utilize Nonverbal Cues: Body language, facial expressions, and eye contact significantly impact how messages are perceived. Being aware of these nonverbal signals can enhance the overall communication experience, reinforcing spoken words.
5. Provide Feedback: Encouraging a two-way dialogue fosters an environment of openness. Offering constructive feedback shows that you value the other person’s input and are committed to improving the exchange.
6. Stay Open-Minded: Being receptive to different viewpoints encourages a richer discussion. A willingness to consider alternative perspectives can lead to innovative solutions and a deeper understanding of the topic at hand.
Incorporating these strategies into daily interactions can significantly improve the quality of communication, resulting in more effective collaborations and relationships.
Future Trends in Diagramming Techniques
The evolution of visual representation methodologies is poised to transform how we communicate complex information. As technology advances, we can anticipate innovative approaches that enhance clarity and engagement. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning is set to streamline the creation process, making it more intuitive and adaptive to user needs.
Moreover, the rise of collaborative platforms will foster real-time interaction, enabling teams to co-create and refine visuals seamlessly. Augmented reality and virtual reality technologies will further immerse users, offering dynamic ways to explore intricate concepts. As we move forward, the ultimate goal remains to simplify understanding while enriching the user experience.
In addition, the emphasis on data-driven insights will likely drive the demand for visuals that can effectively convey analytical information. With the growing importance of storytelling in presentations, we may see a shift towards more narrative-focused representations, blending aesthetics with functionality to captivate audiences. The future holds exciting possibilities for enhancing how we convey ideas visually.