
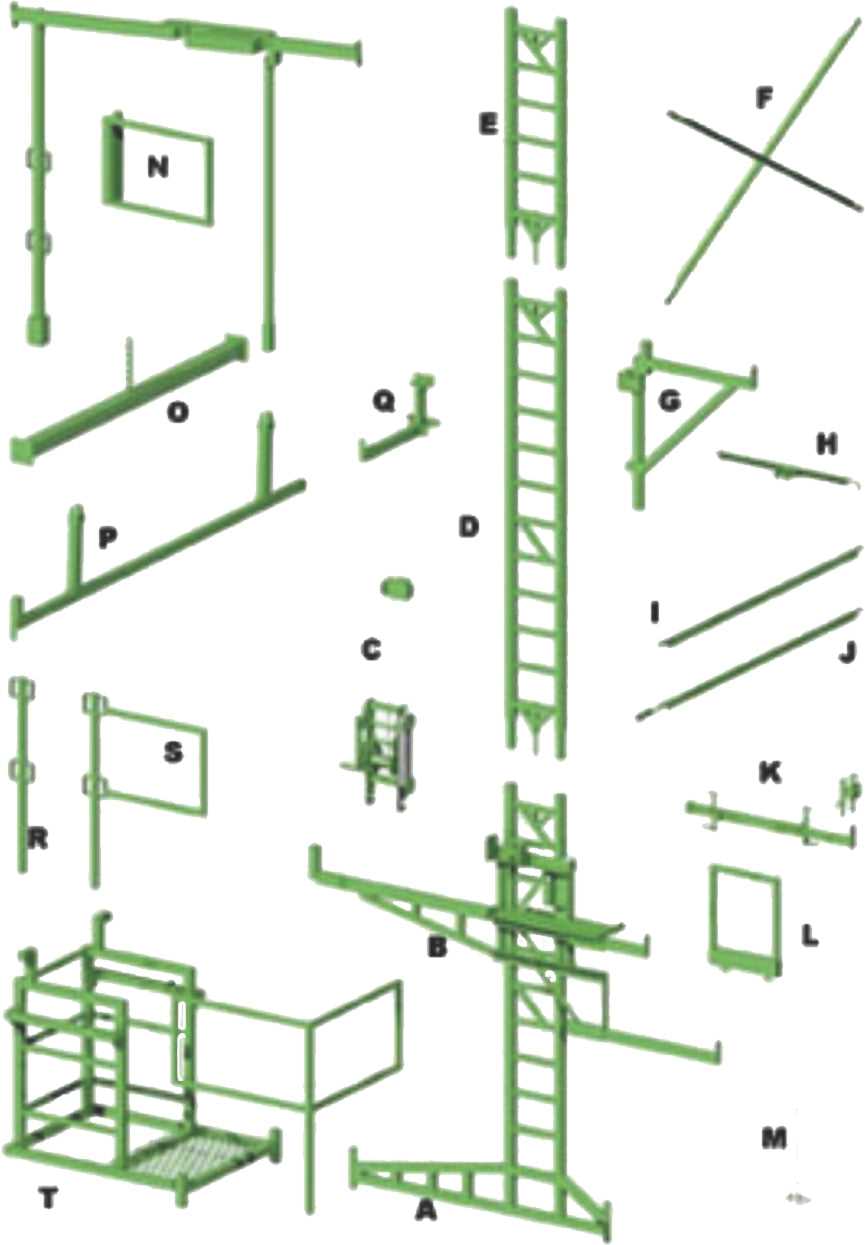
The construction industry relies heavily on modular systems that provide essential support and safety during building projects. This intricate framework enables workers to operate at various heights while ensuring stability and reliability. A thorough grasp of the individual elements that make up these systems is vital for both safety and efficiency.
Each segment of the structure plays a crucial role in the overall integrity of the assembly. From vertical supports that bear weight to horizontal beams that create platforms, understanding their functions is fundamental for effective project management. Knowledge of how these components interact allows for better planning and execution, minimizing risks associated with construction activities.
Moreover, the choice of materials and design impacts not only the performance but also the safety standards of the entire operation. As projects vary in scale and complexity, recognizing the specific attributes of each component can lead to enhanced safety protocols and optimized workflows. Thus, delving into the intricacies of these vital building blocks is essential for anyone involved in the industry.
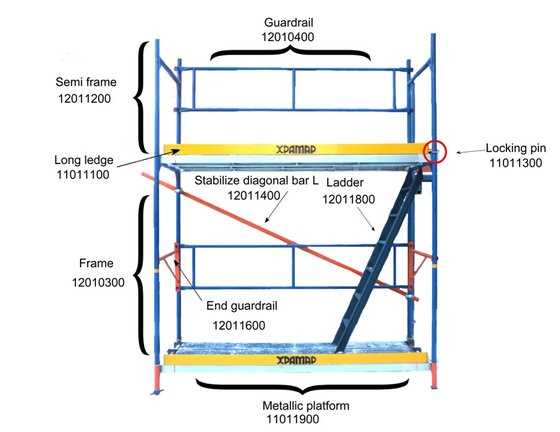
Understanding Scaffold Diagram Components
In the construction realm, a comprehensive grasp of the visual representations of structural frameworks is essential. These illustrations serve to clarify the various elements that come together to support and ensure the integrity of a building. Each component plays a pivotal role, contributing to the overall stability and functionality of the project.
Key Elements of Structural Illustrations
When analyzing these visual aids, it is important to recognize the fundamental components that they include:
- Support Structures: These foundational elements bear the weight and provide stability.
- Connecting Components: Pieces that link different sections together, ensuring cohesion.
- Safety Features: Items designed to protect workers and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Access Points: Areas that allow movement and entry for personnel and materials.
Importance of Each Component
Understanding the significance of each element can greatly enhance project efficiency and safety:
- Weight Distribution: Properly placed supports prevent structural failure.
- Stability Assurance: Connecting elements enhance rigidity and reduce swaying.
- Compliance Adherence: Safety features mitigate risks associated with construction.
- Operational Flow: Access points facilitate smooth movement throughout the site.
By familiarizing oneself with these components, stakeholders can ensure better planning, execution, and safety throughout the building process.
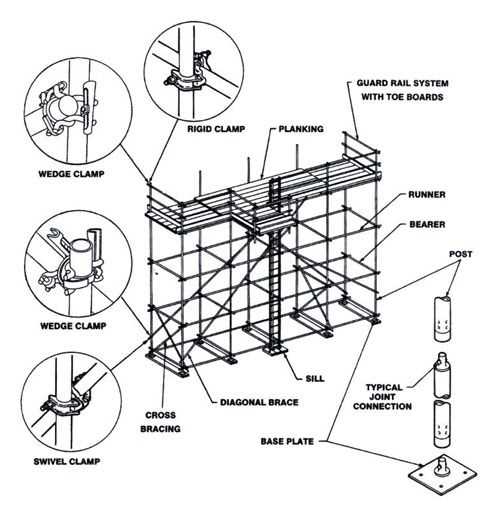
Types of Scaffolding Systems
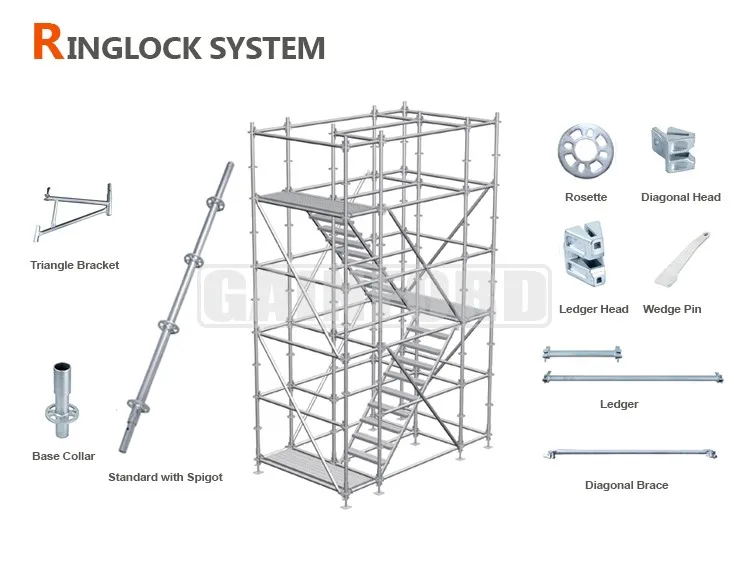
In construction and maintenance, various support structures play a crucial role in ensuring safety and efficiency. These frameworks are designed to provide elevated platforms for workers, tools, and materials, facilitating a range of tasks at height. Understanding the different varieties of these systems is essential for selecting the appropriate solution for specific projects.
Traditional Frameworks
Traditional frameworks, often composed of metal or wood, are widely used due to their versatility and ease of assembly. They consist of a series of poles and boards that create stable working surfaces. These structures can be adapted to fit various building shapes and heights, making them ideal for both residential and commercial projects. The straightforward design allows for quick setup and dismantling, providing a reliable option for temporary use.
Modular Systems
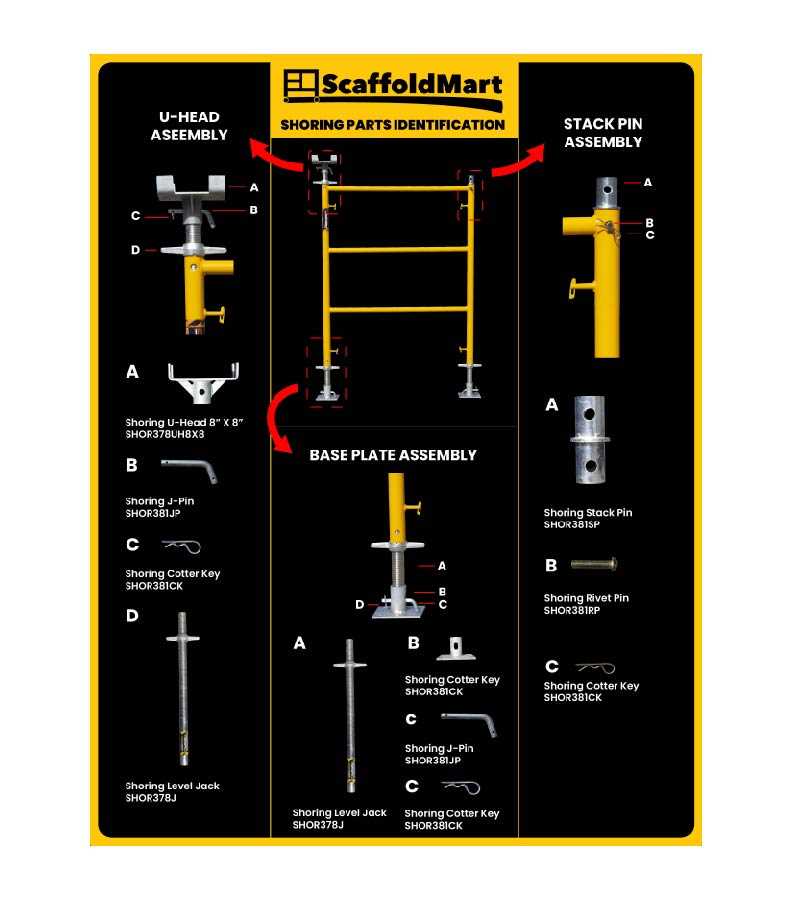
Modular systems offer a more advanced approach, utilizing prefabricated components that can be easily connected and reconfigured. This flexibility allows for rapid assembly and disassembly, making them particularly suitable for large-scale operations where time efficiency is critical. Additionally, these systems often incorporate safety features and can be customized to meet specific requirements, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Materials Used in Scaffold Construction
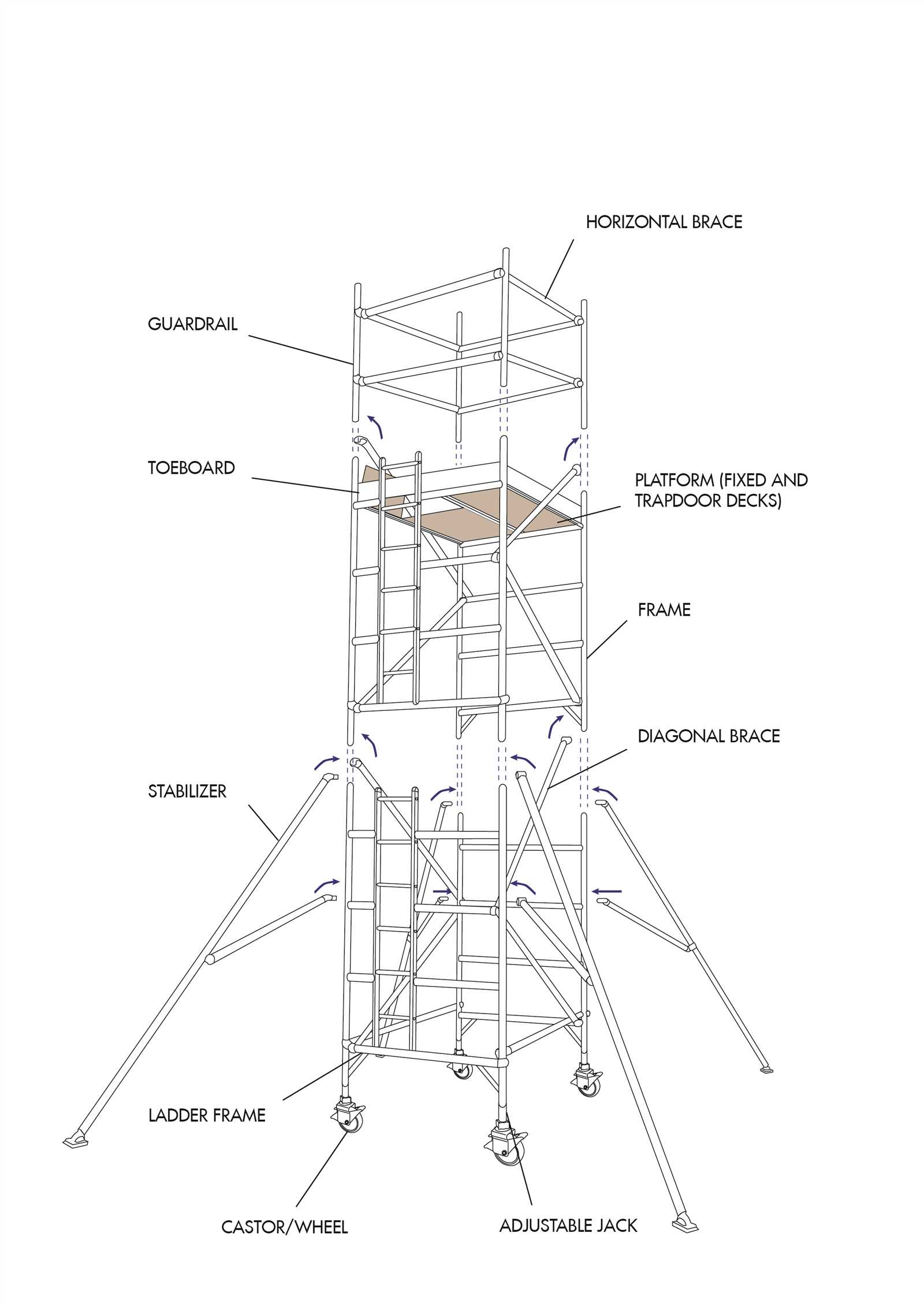
The selection of materials is crucial for ensuring safety, durability, and efficiency in temporary structures used for construction projects. Different options cater to specific needs, impacting overall performance and adaptability on site.
Commonly Utilized Materials
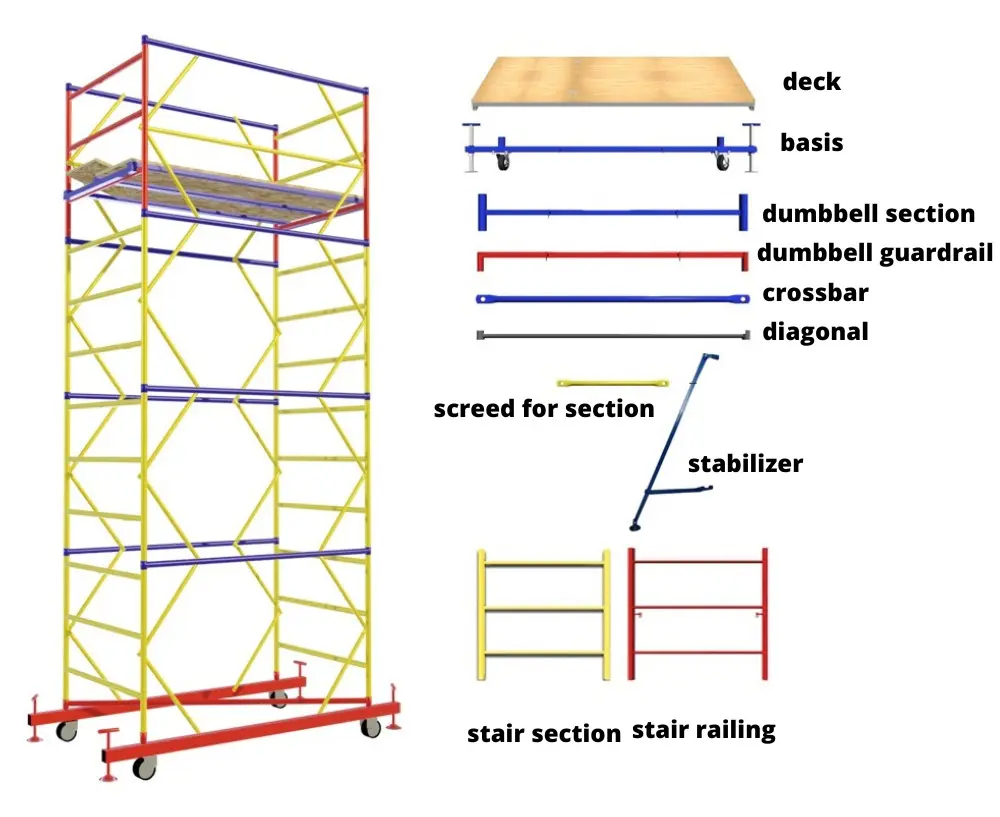
Several materials are prevalent in the creation of these structures, each offering distinct advantages:
| Material | Properties |
|---|---|
| Steel | High strength, durability, resistant to weathering |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, easy to handle |
| Wood | Cost-effective, easy to work with, renewable resource |
Environmental Considerations
Choosing eco-friendly materials contributes to sustainability. Recycled steel and sustainably sourced timber minimize the environmental impact, making them ideal for modern construction practices.
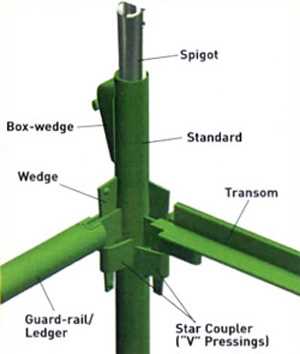
Safety Features in Scaffolding Design
Ensuring the well-being of workers during construction activities is paramount. A robust structure that supports personnel and materials must integrate essential safety mechanisms. These elements are crucial for minimizing risks and providing a secure working environment at elevated heights.
Effective safety features in construction frameworks can be categorized into several key areas:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Load Capacity | Designed to support specified weights without compromising stability, ensuring the framework remains secure under pressure. |
| Guardrails | Installed at strategic points to prevent falls, these barriers are vital for protecting workers on upper levels. |
| Non-slip Surfaces | Textured materials used on walking platforms to reduce the likelihood of slips and enhance grip during wet conditions. |
| Inspection Tags | Visible markers that indicate the status of the structure, ensuring regular checks are conducted for safety compliance. |
| Stabilizers | Additional components that reinforce stability, helping to prevent tipping or shifting during use. |
Incorporating these safety features not only promotes compliance with regulatory standards but also fosters a culture of safety among workers. Continuous assessment and improvement of these elements are essential for maintaining high safety standards in construction environments.
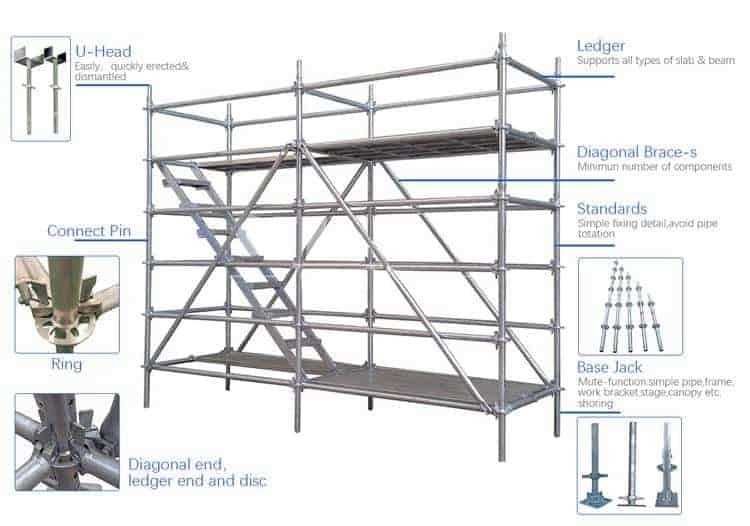
Common Applications of Scaffold Diagrams
Visual representations play a crucial role in various fields, serving as essential tools for communication, analysis, and understanding. These structures help organize complex information, making it easier to convey ideas and processes to different audiences.
Here are some common areas where these visual frameworks are applied:
- Construction and Engineering:
- Planning project timelines and workflows
- Identifying structural components and their interactions
- Facilitating safety assessments and inspections
- Education:
- Supporting curriculum design and lesson planning
- Enhancing student understanding of complex concepts
- Promoting collaborative learning through visual aids
- Healthcare:
- Streamlining patient care processes
- Visualizing treatment protocols and workflows
- Facilitating interdisciplinary collaboration among healthcare providers
- Business and Management:
- Mapping organizational structures and roles
- Visualizing project management methodologies
- Enhancing strategic planning and decision-making
These frameworks not only simplify complex information but also foster collaboration and clarity across various sectors, proving their value in effective communication and problem-solving.
Inspection and Maintenance Guidelines
Regular assessment and upkeep of temporary structures are crucial to ensure safety and efficiency on construction sites. Implementing systematic procedures can prevent accidents and prolong the lifespan of the equipment.
It is essential to establish a routine inspection schedule. This includes daily checks, weekly assessments, and comprehensive evaluations at regular intervals. Key focus areas should include:
- Structural integrity
- Connection points
- Surface conditions
- Wear and tear
- Load capacities
During inspections, personnel should adhere to the following guidelines:
- Inspect all components for visible damage or deformation.
- Check that all fasteners are secure and appropriately torqued.
- Verify that safety devices are functional and in place.
- Ensure that platforms are clear of debris and other hazards.
- Document findings and take corrective actions as needed.
Maintenance practices play a vital role in sustaining performance. Recommended actions include:
- Cleaning components regularly to prevent rust and corrosion.
- Lubricating moving parts to ensure smooth operation.
- Replacing any worn or damaged items immediately.
- Updating safety equipment as regulations change.
By adhering to these inspection and maintenance protocols, stakeholders can create a safer working environment and enhance the reliability of their temporary structures.
Benefits of Proper Scaffolding Planning
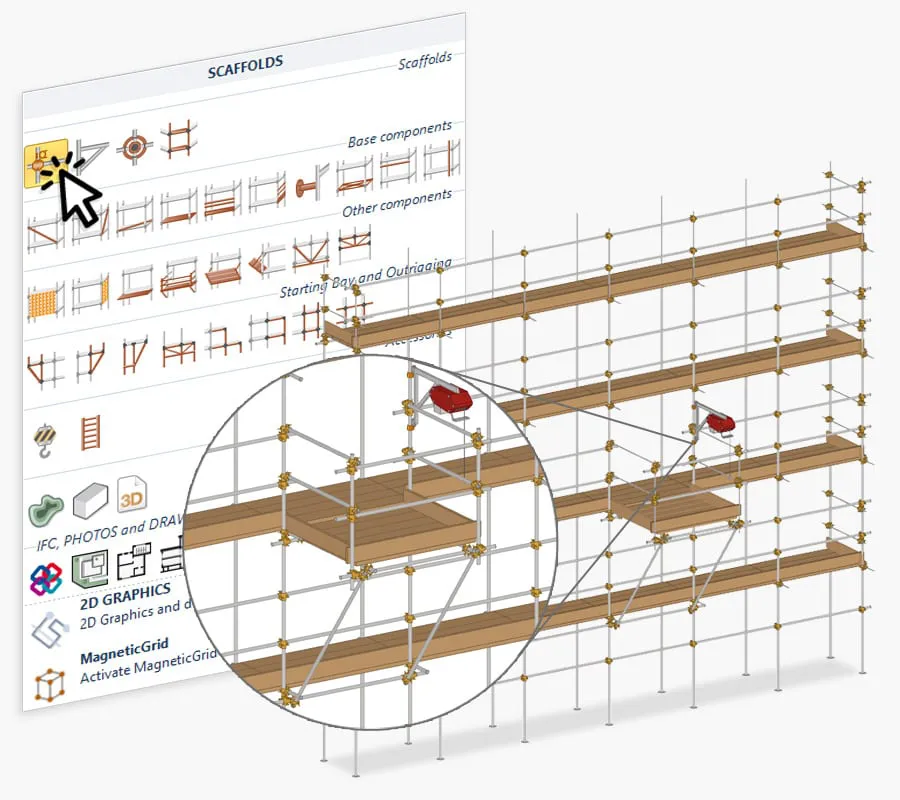
Effective preparation and organization play a crucial role in ensuring the success and safety of any construction project. Thoughtful arrangement not only streamlines workflows but also enhances safety protocols, ultimately leading to a more efficient and productive environment.
Here are some key advantages of meticulous planning:
- Enhanced Safety: Careful consideration of the layout minimizes risks, helping to prevent accidents and injuries on site.
- Improved Efficiency: Well-structured setups facilitate smoother operations, allowing workers to move freely and access necessary tools and materials without delay.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Strategic planning can reduce waste and minimize unnecessary expenses, optimizing resource allocation.
- Compliance with Regulations: Proper organization ensures adherence to safety standards and legal requirements, mitigating potential liabilities.
- Better Communication: Clear layout designs enhance coordination among team members, fostering collaboration and reducing misunderstandings.
In summary, taking the time to plan meticulously not only safeguards personnel but also contributes to the overall efficiency and success of construction endeavors.
Challenges in Scaffold Implementation
Implementing temporary support structures in construction projects presents a range of difficulties that can impact safety, efficiency, and overall project timelines. From ensuring structural integrity to managing workforce dynamics, these challenges require careful planning and execution to mitigate risks and enhance productivity.
Common Issues Faced
Among the various hurdles, some of the most frequently encountered issues include the following:
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Safety Concerns | Ensuring the safety of workers during setup and use is paramount, as improper assembly can lead to accidents. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating the complex landscape of local regulations and standards can complicate the implementation process. |
| Material Availability | Delays in sourcing materials can halt progress and impact project timelines. |
| Workforce Training | Inadequate training of personnel can lead to improper handling and increased risks on-site. |
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges
To address these obstacles effectively, companies can adopt several strategies, including rigorous training programs, thorough risk assessments, and regular inspections to ensure compliance and safety. By prioritizing these elements, the implementation process can be streamlined, leading to safer and more efficient construction practices.
Future Trends in Scaffolding Technology
The landscape of temporary structures is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and the need for enhanced safety and efficiency. As industries adapt to modern challenges, innovative solutions are emerging that promise to redefine how these frameworks are designed, manufactured, and utilized.
One of the most significant trends is the integration of smart technology into construction frameworks. This includes the use of sensors and IoT devices that monitor structural integrity in real-time, ensuring safety and reducing the risk of accidents. Furthermore, advancements in materials science are leading to lighter, more durable options that can support heavier loads while being easier to assemble and dismantle.
Another notable trend is the move towards sustainability. The industry is increasingly adopting eco-friendly materials and practices, such as recycling and reusing components, which not only minimizes waste but also lowers the carbon footprint of projects. Innovations in modular construction are also gaining traction, allowing for quicker assembly and disassembly while enhancing flexibility on job sites.
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Smart Technology Integration | Incorporating sensors and IoT for real-time monitoring of structure integrity. |
| Advanced Materials | Using lighter and more durable materials for improved load-bearing capabilities. |
| Sustainability Practices | Adopting eco-friendly materials and recycling components to reduce waste. |
| Modular Construction | Facilitating quicker assembly and flexibility with modular design approaches. |
As these trends continue to develop, the future of temporary frameworks will likely see improved efficiency, safety, and environmental consciousness, setting new standards for the construction industry as a whole.