The anatomy of these magnificent creatures is a blend of elegance and strength, showcasing a remarkable design that supports their unique abilities. From the powerful limbs to the graceful neck, every aspect plays a crucial role in their functionality and performance.
In this exploration, we will delve into the various components that contribute to their overall structure. Each section highlights the significance of individual elements, illustrating how they work together harmoniously.
By comprehensively examining these features, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the ultimate form and function of equines, enriching our understanding of their remarkable biology.
Understanding Horse Anatomy
Grasping the structure and function of equine physiology is essential for anyone involved in the care and management of these magnificent animals. A thorough comprehension enables better training, health maintenance, and overall interaction, fostering a harmonious relationship between humans and these graceful creatures.
Key Systems
The anatomy encompasses various systems that work in unison to support the animal’s needs. From locomotion to respiration, each system plays a vital role in overall functionality.
| System | Function |
|---|---|
| Muscular | Facilitates movement and support |
| Cardiovascular | Delivers oxygen and nutrients |
| Digestive | Processes food and absorbs nutrients |
| Respiratory | Enables gas exchange |
Importance of Anatomy Knowledge
A deep understanding of equine structure ultimately aids in recognizing signs of health issues, improving training techniques, and ensuring the well-being of these animals. Knowledge of anatomy is indispensable for effective veterinary care and optimal performance in various equestrian disciplines.
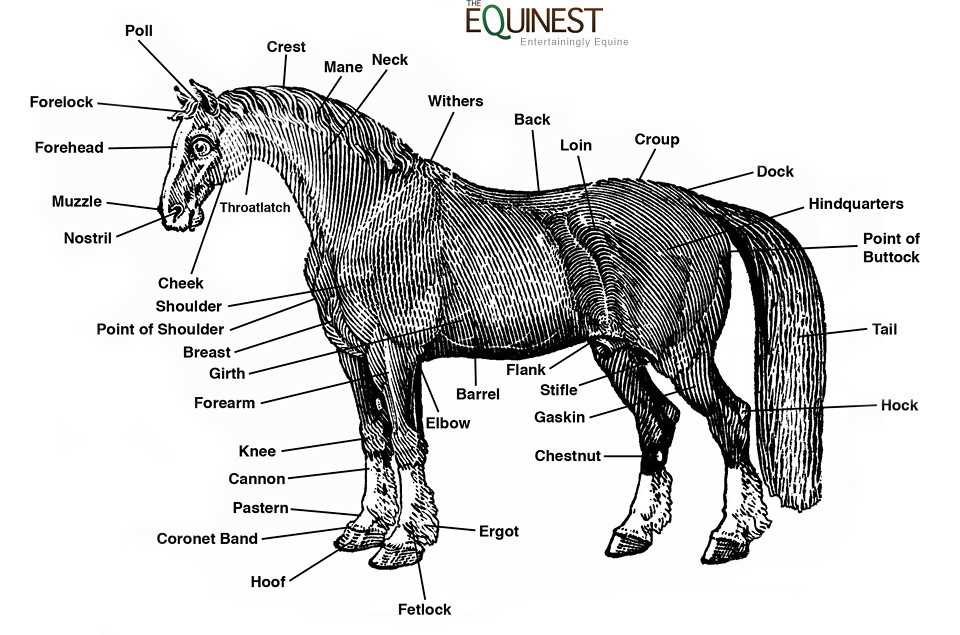
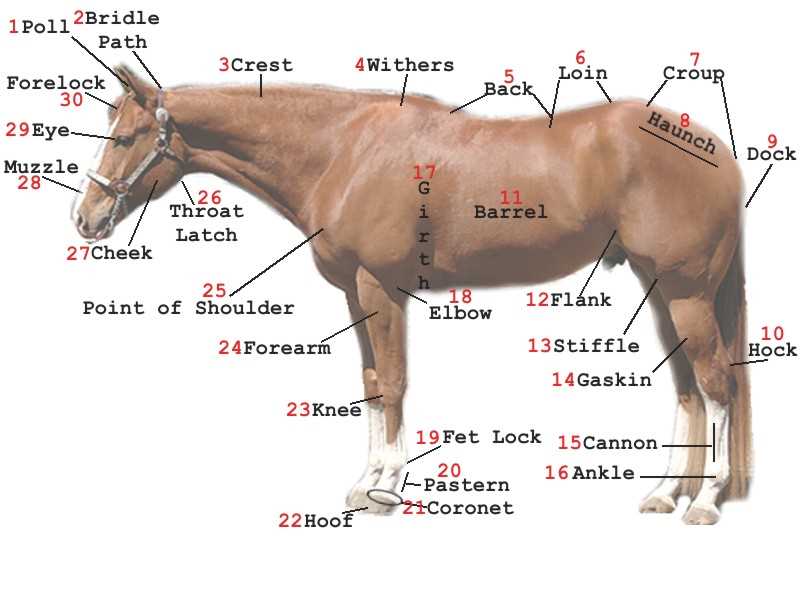
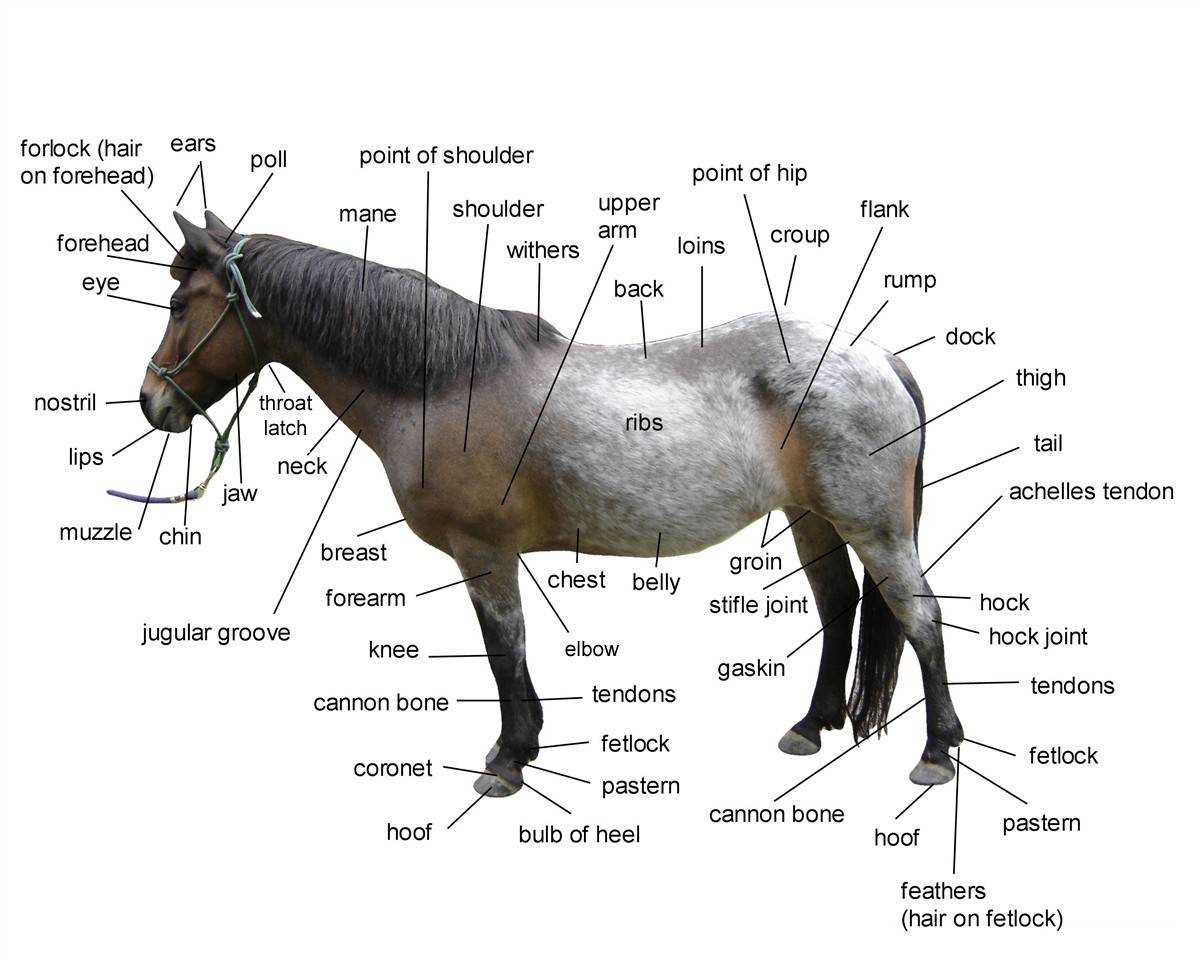
Key External Features of Horses
The anatomy of equines showcases a variety of distinctive characteristics that contribute to their grace and functionality. Understanding these elements is essential for appreciating their beauty and utility.
Head: The head is a prominent feature, characterized by a long muzzle and expressive eyes, which enhance their communication and perception of surroundings.
Neck: A muscular neck supports the head and aids in balance, allowing for agile movements and postures that are vital during activities like jumping and racing.
Body: The torso, robust and well-proportioned, provides the necessary strength for locomotion and endurance, reflecting the animal’s health and fitness.
Legs: Long, powerful limbs are crucial for speed and agility, featuring strong bones and joints that withstand rigorous activity.
Tail: The flowing tail serves multiple purposes, including communication and protection against insects, contributing to the overall elegance.
Coat: The coat varies in color and texture, providing insulation and protection from environmental elements, while also serving as a canvas for expressive markings.
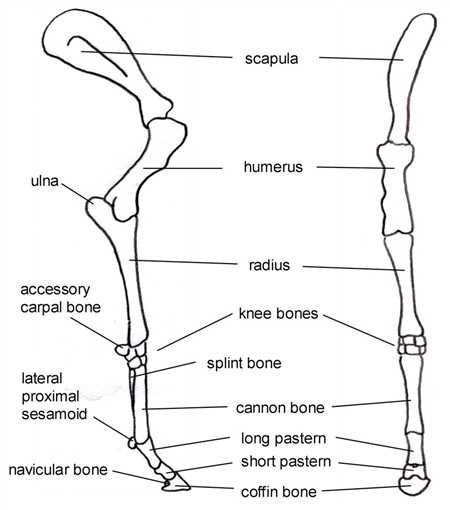
Importance of Equine Skeletal Structure
The framework of an equine body plays a crucial role in its overall functionality and performance. This complex system not only provides support but also enables movement, balance, and agility, making it essential for various activities and tasks. Understanding its significance can lead to better care and training practices.
Functionality and Performance
The skeletal framework serves as a foundation for muscles and connective tissues, facilitating efficient motion. A well-structured system allows for optimal performance in activities ranging from racing to jumping, contributing to athletic prowess.
Health and Care Considerations
Maintaining a healthy structure is vital for longevity and well-being. Issues such as misalignments or injuries can severely impact mobility and quality of life, underscoring the importance of regular veterinary care and proper training methods.
| Aspect | Importance |
|---|---|
| Support | Foundation for muscles and organs |
| Movement | Facilitates agility and speed |
| Balance | Enhances stability and coordination |
| Health | Prevents injuries and disorders |
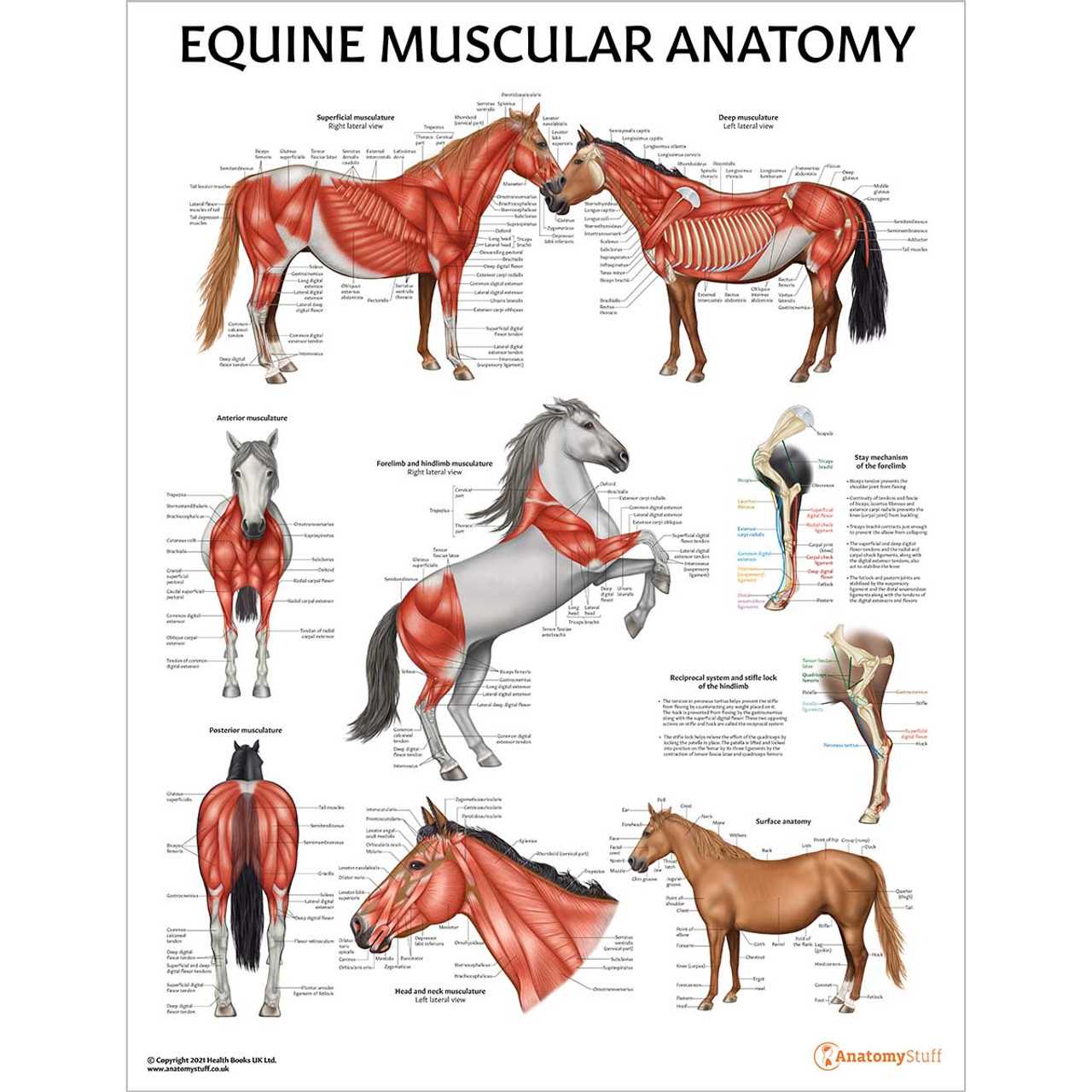
Muscle Groups in Horse Movement
The efficiency of movement in equines relies heavily on the intricate interplay of various muscle groups. These muscles work in unison to facilitate actions such as running, jumping, and turning, all of which require strength, flexibility, and coordination. Understanding these muscle systems is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring the well-being of these magnificent creatures.
Key Muscle Groups
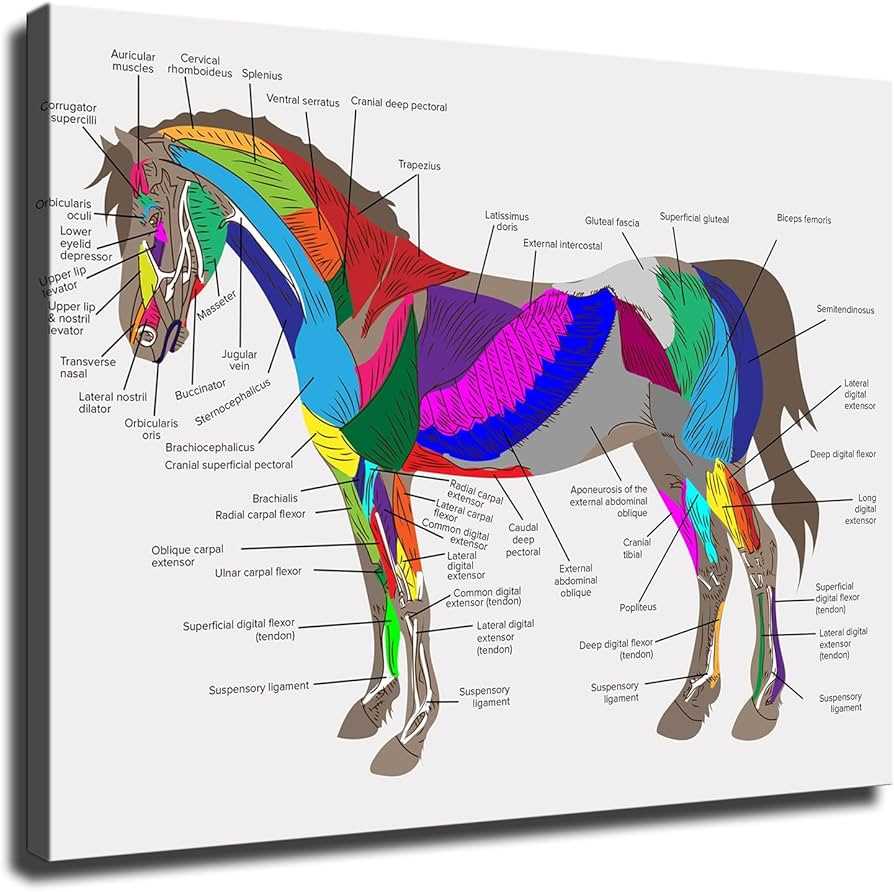
- Forelimb Muscles:
- Shoulder Muscles: Crucial for lifting and extending the front legs.
- Forearm Muscles: Aid in the flexion and extension of the forelimb.
- Chest Muscles: Support movement and balance during strides.
- Hindlimb Muscles:
- Thigh Muscles: Provide power for propulsion and support during motion.
- Calf Muscles: Important for the push-off phase during running.
- Gluteal Muscles: Help with hip extension and overall stability.
Role in Motion
Each muscle group contributes to a specific aspect of locomotion:
- Propulsion: The hindlimb muscles generate the primary force necessary for forward movement.
- Stability: Core and shoulder muscles maintain balance, especially during turns and jumps.
- Flexibility: Muscles around joints allow for a range of motion, crucial for agility and speed.
A thorough understanding of these muscle systems can enhance training methods, leading to improved performance and reduced risk of injury in these agile athletes.
Internal Organs and Their Functions

The inner workings of an equine creature play a vital role in its overall health and performance. Understanding these essential systems provides insight into their well-being and how they maintain life.
- Heart: Pumps blood, supplying oxygen and nutrients throughout the body.
- Lungs: Facilitate breathing, exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- Liver: Processes nutrients and detoxifies harmful substances.
- Kidneys: Filter blood, removing waste and regulating fluid balance.
- Stomach: Breaks down food, initiating the digestive process.
- Intestines: Absorb nutrients and water while eliminating waste.
Each of these systems collaborates to ensure vitality and functionality, contributing to the creature’s ultimate capacity for endurance and strength.
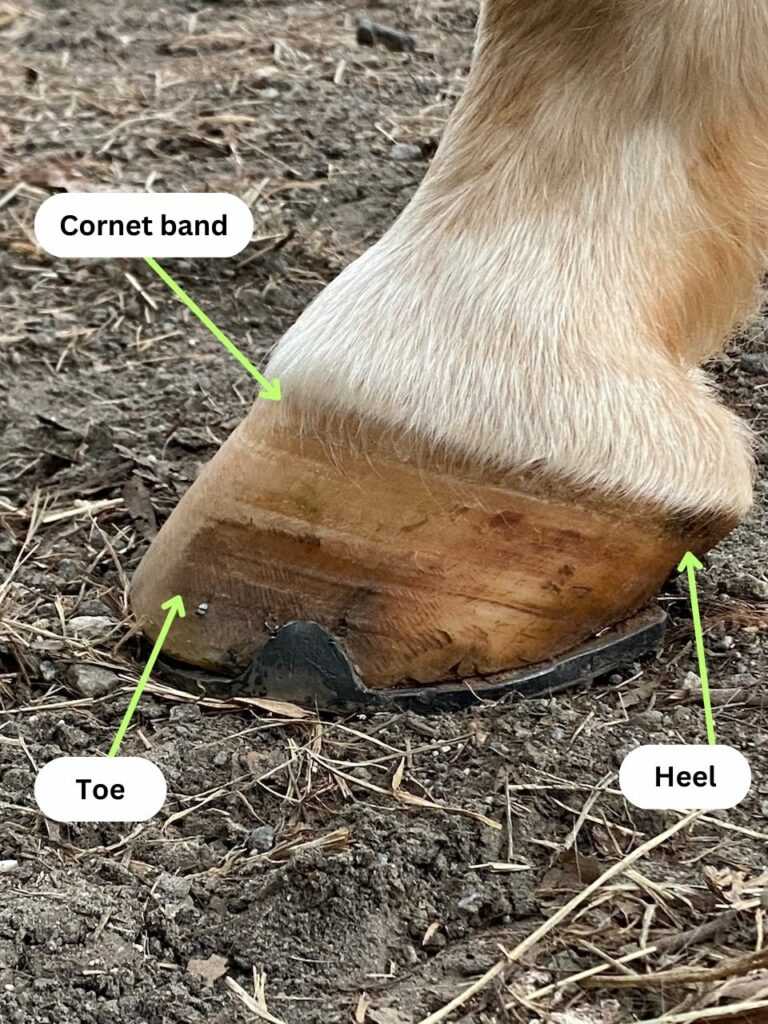
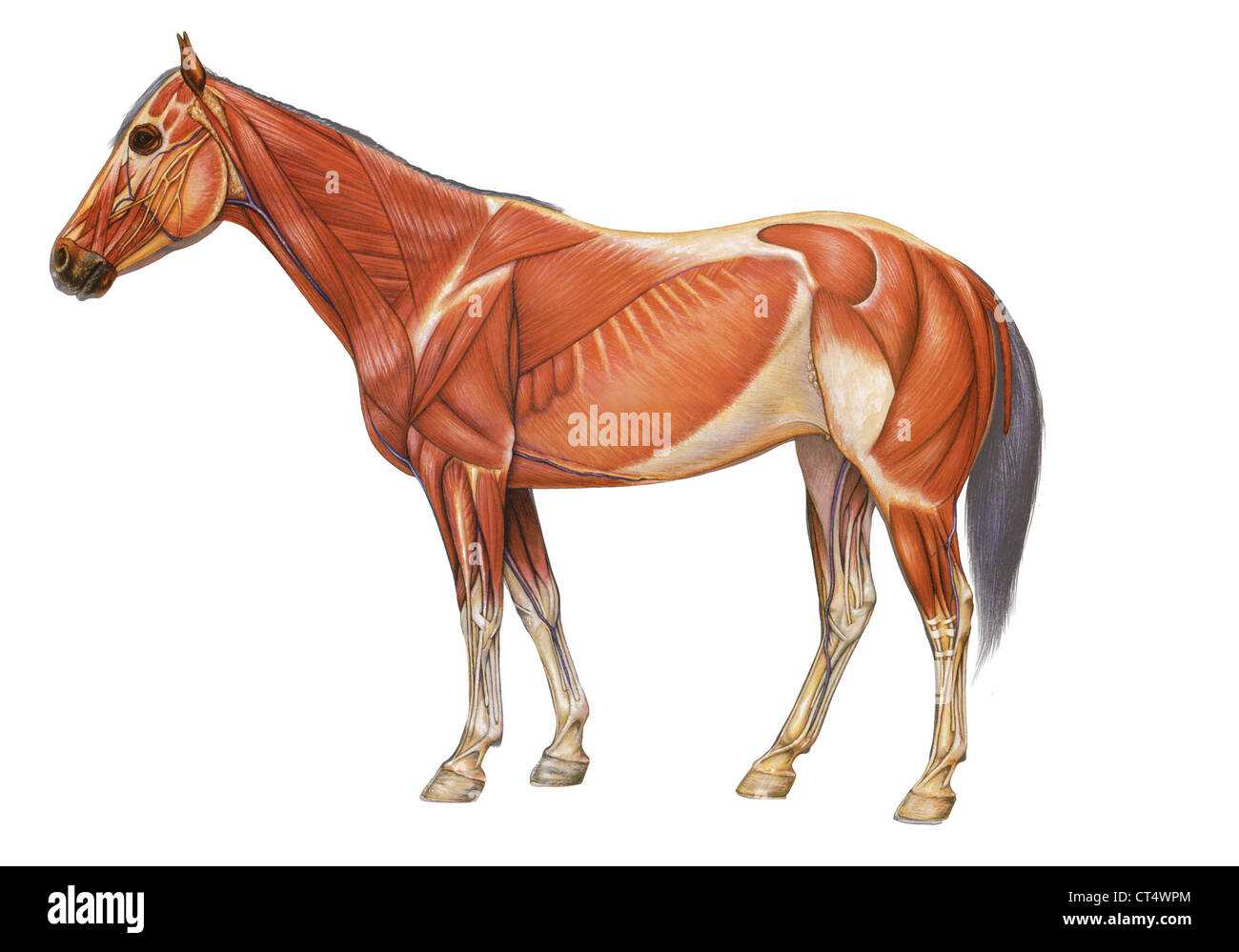
Role of Hooves in Horse Health
The condition of a certain crucial body structure significantly impacts overall well-being and performance. These essential components serve not only as a foundation but also as a protective barrier against various environmental challenges.
Maintaining optimal health of these structures is vital for numerous reasons:
- Shock absorption: They help in reducing the impact during movement.
- Balance: Properly cared for, they enhance stability and coordination.
- Traction: They provide necessary grip, crucial for agility and speed.
- Circulation: Healthy structures promote better blood flow in the limbs.
Regular care, including trimming and cleaning, is essential for preventing common issues:
- Thrush: A bacterial infection that can develop in damp conditions.
- Laminitis: A painful condition affecting the sensitive tissues inside.
- Cracks: These can lead to severe complications if not addressed.
Overall, the significance of these vital elements cannot be overstated; they are fundamental to achieving ultimate health and performance. Regular veterinary check-ups and proper hoof care are crucial for ensuring long-term well-being.
Common Health Issues in Horses
Understanding the typical ailments that affect equines is essential for any caretaker or enthusiast. These conditions can vary widely in severity and impact, making early detection and treatment crucial for maintaining overall well-being.
Respiratory Problems are among the most frequently encountered issues. Conditions such as heaves and pneumonia can significantly affect breathing, leading to distress and decreased performance. Regular monitoring of a steed’s breathing patterns can help in identifying these concerns early.
Lameness is another prevalent challenge, often caused by injuries or conditions like arthritis. This issue not only hampers movement but can also indicate underlying health problems. Maintaining proper hoof care and ensuring appropriate exercise can mitigate some risks associated with lameness.
Digestive Disorders, including colic and laminitis, are critical health concerns that require immediate attention. These ailments can arise from dietary changes or stress, and their symptoms may escalate rapidly. Providing a balanced diet and minimizing abrupt changes in feeding routines are vital preventive measures.
Skin Issues such as dermatitis and parasites are common as well. Regular grooming and skin inspections can help detect these problems early, enabling timely intervention. Keeping living areas clean and using preventive treatments can significantly reduce the risk of infestations.
By being aware of these common health concerns, caretakers can take proactive steps to ensure the vitality and happiness of their equine companions.
Comparing Horse Breeds and Anatomy
The diverse world of equine species presents a fascinating opportunity to explore variations in structure and function across different breeds. Each type exhibits unique traits shaped by purpose, environment, and breeding practices. Understanding these distinctions enhances our appreciation for these majestic animals.
Variations in Structure
The anatomical features of equines can vary significantly among breeds. Key aspects include:
- Body Size: Some breeds, like the Shire, are known for their large stature, while others, such as the Arabian, are more compact.
- Head Shape: Breeds differ in head proportions; thoroughbreds often have elongated heads, whereas ponies might display shorter, broader heads.
- Leg Length: Speed-oriented breeds usually possess longer legs for greater stride length.
Functional Adaptations
In addition to structural variations, different breeds have evolved specific adaptations that cater to their roles:
- Sporting Purposes: Breeds like the Quarter Horse excel in agility and speed for competitive events.
- Work Roles: Draft breeds are bred for strength and endurance, ideal for heavy labor.
- Riding Styles: Certain breeds are preferred for various riding disciplines, reflecting their training and temperament.
By comparing the anatomical and functional traits of these remarkable creatures, one can gain insights into how evolution and selective breeding have shaped their roles in human society.
Illustrating Horse Anatomy for Education
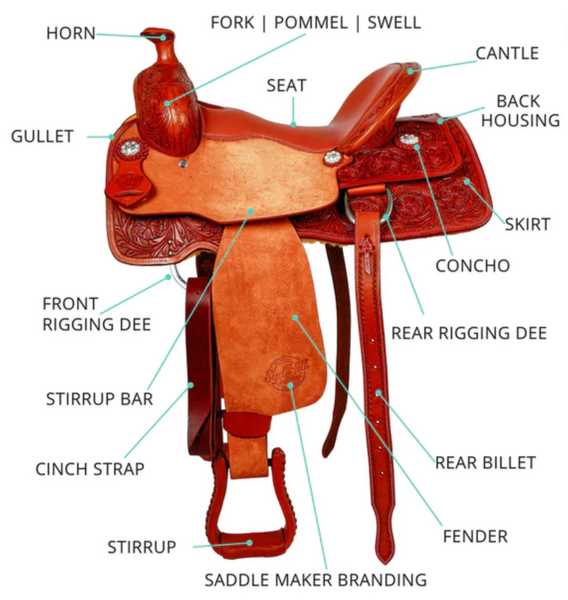
Understanding the structure and function of equine anatomy is essential for students and enthusiasts alike. This knowledge enhances appreciation for these magnificent animals and informs practices in care, training, and veterinary medicine. By exploring the intricate systems that comprise the equine form, learners can gain insights into movement, behavior, and health.
The Importance of Visual Learning
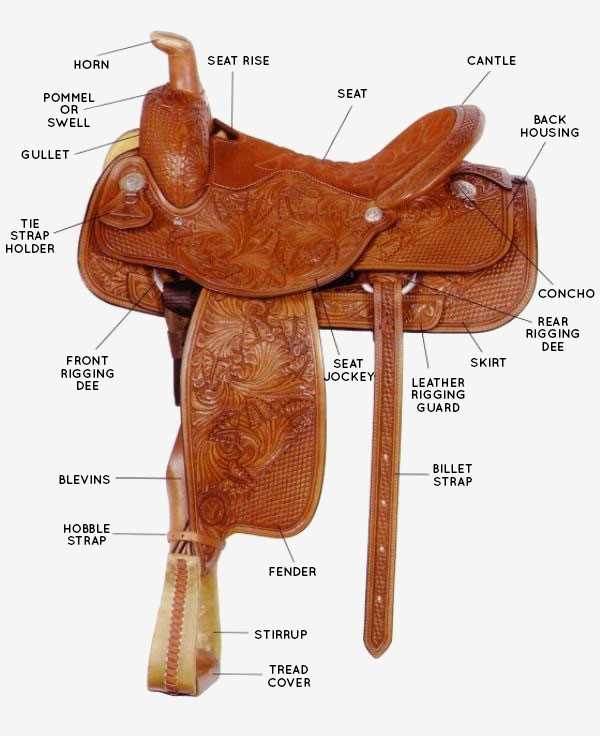
Visual representations serve as powerful tools in the educational journey. They allow individuals to grasp complex concepts through clear imagery, fostering a deeper understanding of how various components interact. Utilizing well-crafted illustrations can bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, making the study of equine structure both engaging and accessible.
Key Components in Focus
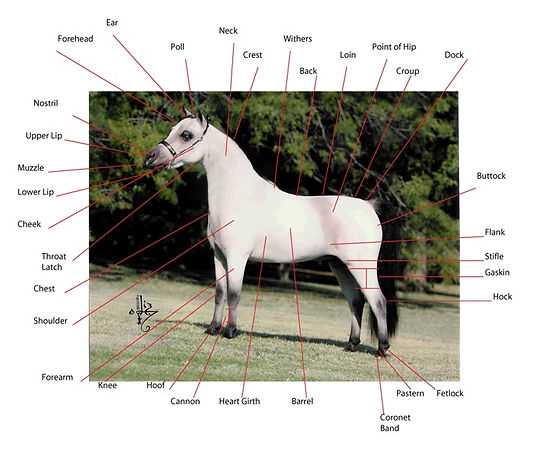
Focusing on essential systems such as the muscular, skeletal, and circulatory frameworks provides a comprehensive overview of equine physiology. Each system plays a vital role in the overall functionality and well-being of the animal. Detailed visuals highlighting these areas can enhance retention and stimulate further inquiry into specific topics of interest, ultimately contributing to a richer educational experience.