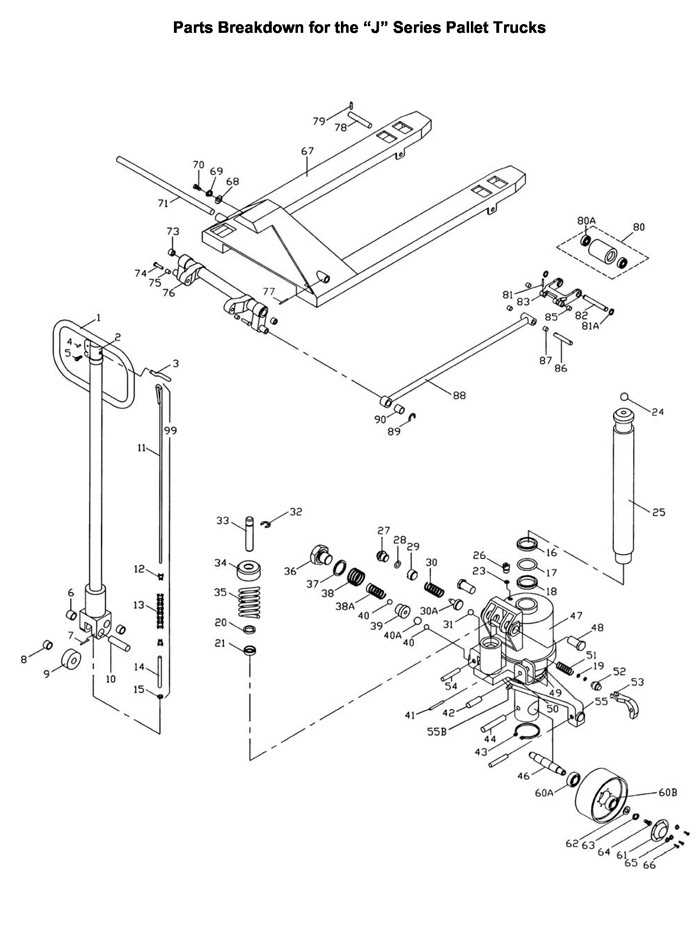
Understanding the intricate structure of various mechanical systems can be essential for ensuring proper maintenance and repairs. This guide is designed to offer a detailed look at the specific elements that make up complex machinery, helping users identify and understand the key components involved in its functionality.
In the following sections, you’ll find an organized breakdown of various units, highlighting their roles and how they connect to the larger structure. Whether you’re troubleshooting an issue or simply seeking to learn more about the internal workings, this information will provide valuable insights.
We also delve into the assembly and disassembly processes, ensuring that even those with minimal experience can follow along and gain a deeper understanding of each piece’s contribution to the overall operation.
Understanding the Key Components of Crown PTH50
Each manual pallet truck is composed of several fundamental elements that contribute to its smooth operation and efficiency. These mechanical structures ensure reliable performance, ease of movement, and proper load handling. Identifying and familiarizing yourself with these elements is essential for maintenance, troubleshooting, and effective use of the equipment.
Handle and Lever Mechanism: The control system that allows the operator to lift, lower, and steer the unit is crucial. It includes a lever that releases the hydraulic system and directs the movement of the entire unit.
Hydraulic Pump: At the heart of the lifting mechanism is the hydraulic pump. This system is responsible for generating the force needed to raise heavy loads off the ground, providing smooth lifting action.
Forks: The long, sturdy arms extending from the frame are designed to support the weight of pallets and other loads. Their design and strength ensure that loads are balanced and transported securely.
Wheels and Rollers: This unit’s mobility is enabled
Handle Assembly Breakdown and Maintenance Tips
The handle system plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient operation. Understanding the individual components of the handle and their functionality can help prolong the lifespan of your equipment. Regular maintenance is essential to prevent common wear and tear, ensuring that the system continues to operate safely and effectively.
Key Components of the Handle System
The handle system consists of several interconnected elements. The grip section provides the user with a secure hold, while the lever mechanism ensures smooth operation when lifting or maneuvering. Additionally, the linkage connects the handle to the rest of the system, transferring the necessary force for movement.
Maintenance Tips
To keep the handle in optimal condition, periodic checks are necessary. Ensure the pivot points are lubricated to reduce friction and wear. Tighten any loose bolts or screws in the linkage to prevent wobbling. Regularly inspect the grip for signs of damage, replacing it if
Fork Frame Parts and Their Functions
The structure supporting the forks plays a vital role in ensuring smooth and efficient material handling. Each component within this assembly is designed for a specific purpose, contributing to the overall stability, control, and safety during operations.
- Main Fork Frame: This is the core element that provides the backbone of the lifting system, bearing the weight of the load and distributing pressure evenly across the structure.
- Support Beams: Reinforce the frame, offering additional stability and preventing bending or twisting under heavy loads.
- Fork Mounting Brackets: Secure the forks in place, ensuring they remain aligned and firmly attached to the frame for safe and controlled lifting.
- Guide Rollers: Assist in the smooth upward and downward movement, reducing friction and wear between the moving parts of the assembly.
- Locking Pins: Provide the necessary safety feature to hold the forks securely at desired heights, preventing accidental slipping
Wheel Configuration and Replacement Procedures
Proper maintenance of the wheeled assembly is essential for ensuring smooth operation and extended longevity. This section outlines the general structure of the wheels, focusing on their arrangement and the recommended steps for replacing them when necessary. Regular inspection and timely replacements are key to maintaining the functionality and efficiency of the unit.
Wheel Arrangement Overview
The wheels are positioned to provide optimal stability and maneuverability, facilitating seamless movement across various surfaces. Each wheel is strategically mounted to ensure balance and reduce wear during operation. Pay attention to the alignment and attachment points, as improper installation can cause uneven wear and affect the overall performance.
Step-by-Step Replacement Instructions
When it’s time to replace a wheel, ensure the device is secured on a stable surface. Begin by loosening the fasteners that hold the wheel in place. Carefully remove the old wheel, making sure to check for any signs of damage or excessive wear on the mounting area. Once inspected, position the new wheel, aligning it properly with the attachment points. Secure the fasteners tightly, ensuring that the wheel rotates freely but is firmly held in place. Regular lubrication may also be applied to reduce friction and enhance mobility.
Note: Always use appropriate tools and follow manufacturer guidelines for safety and accuracy when performing any replacement procedures.
Hydraulic System Overview for Optimal Performance
The hydraulic system plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient operation of material handling equipment. Understanding its core components and maintaining proper functionality are key to achieving reliable performance. This section outlines the essential elements of the hydraulic mechanism, emphasizing its role in lifting and maneuvering heavy loads with precision and control.
At the heart of the hydraulic system is a pump that generates the necessary pressure to move fluid through a network of hoses and valves. This pressurized fluid enables the movement of cylinders, which translate the fluid power into mechanical force. The smooth operation of these components is critical to the overall efficiency of the equipment.
Proper maintenance, such as regular fluid checks and ensuring that seals and hoses are in good condition, is vital to avoid leaks and pressure drops. Keeping the system clean and free from debris also contributes to its longevity and optimal functionality. Regular inspections and timely replacement of worn-out components will help maintain consistent hydraulic performance.
Detailed View of the Pump Unit Components

The pump unit plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient operation of the machinery. A closer examination reveals various essential elements that work together to achieve optimal performance. Each of these components is integral to the overall functioning of the system, contributing to the smooth transfer of fluids and ensuring reliability under demanding conditions.
The hydraulic motor is a key element, responsible for driving the pump and enabling the movement of hydraulic fluid. It operates with a combination of precision and power, ensuring that the entire system maintains the required pressure levels for effective performance. Alongside it, the valve assembly governs the flow of fluid, directing it to the appropriate areas and allowing for control over the pressure and direction of the fluid.
The pump housing provides a protective structure for the internal mechanisms, safeguarding them from external wear and tear. It is designed to withstand high pressures and ensure that the fluid remains contained within the system. Additionally, the seals and gaskets prevent leaks and ensure that fluid integrity is maintained during operation, contributing to the longevity and efficiency of the unit.
Finally, the gear assembly works seamlessly with the rest of the components to ensure smooth motion and high efficiency. It is designed for durability, capable of handling the stress and wear from constant usage, while maintaining precision in its function.
Safety Features and Associated Parts
When operating any material handling equipment, safety should be the top priority. To ensure smooth and secure operations, various safety mechanisms are integrated into these machines, each playing a crucial role in minimizing risks. These safety components are designed to protect both the operator and the equipment from potential hazards, ensuring optimal performance under controlled conditions.
The key safety features in these machines are built to prevent accidents and provide warnings during unsafe situations. These mechanisms can include protective guards, emergency stop systems, and monitoring devices that actively track the machine’s performance. Every element serves to enhance user safety by preventing malfunctions and enabling immediate intervention in the case of an emergency.
- Emergency Stop System: A quick-access emergency button that halts machine operation to prevent accidents in critical moments.
- Warning Lights: Indicators that alert the operator of any irregularities or risks that may require attention.
- Speed Regulation: Controls that ensure the machine does not exceed safe operating speeds, reducing the risk of loss of control.
- Load Monitoring: Sensors that prevent the lifting or moving of loads that exceed the machine’s capacity.
- Operator Presence Detection: Systems that automatically stop the equipment if the operator leaves the designated safe area.
Each of these safety systems is directly connected to specific mechanical or electronic elements of the equipment. Regular maintenance and checks are essential to ensure that these systems remain functional and reliable. Neglecting any part of the safety system can result in significant risks, potentially leading to equipment failure or operator injury.
Understanding the function of each safety component and its role in overall machine reliability allows operators to maintain a secure working environment. It is critical to familiarize oneself with these features to both prevent accidents and optimize the machine’s efficiency and lifespan.
Compatibility of Crown PTH50 Replacement Parts

When seeking to replace essential components of lifting equipment, ensuring proper compatibility between the new elements and the existing machinery is critical. Incompatibility can result in reduced functionality, increased wear and tear, and safety hazards. This section explores how to assess the suitability of replacement components for the specific model in question, while emphasizing the importance of maintaining high performance and longevity.
Evaluating Quality and Fit
Before selecting new components, it’s important to verify that they meet the necessary standards in terms of quality and design. Many manufacturers produce components that can serve as direct substitutes, but quality differences may exist between original and aftermarket products. Precision in fitting ensures that the equipment operates efficiently, preventing unnecessary strain on the system and extending the lifespan of the machine.
Third-Party Compatibility Considerations
While original components are often recommended for optimal performance, third-party options may also be suitable if they meet the same specifications. In such cases, it is essential to carefully review technical documents to determine whether the replacements adhere to the necessary standards. Consulting with professionals or relying on certified sellers can mitigate the risks of using non-standardized products.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with PTH50 Parts
When working with a particular material handling equipment, issues with individual components are common. Identifying and addressing these problems early can significantly improve the performance and longevity of the device. In this section, we will explore some of the most frequent malfunctions and how to efficiently resolve them.
Unresponsive Movement
One of the most common issues is when the equipment does not respond to user commands, leading to a halt in its operation. This could be due to problems with the drive assembly or electrical connections. Begin by inspecting the motors and controllers for any signs of damage or wear. Ensure that all wiring is properly connected and not frayed. If the issue persists, a thorough check of the battery connections and charging system may be necessary to rule out power failure.
Uneven Lifting or Lowering
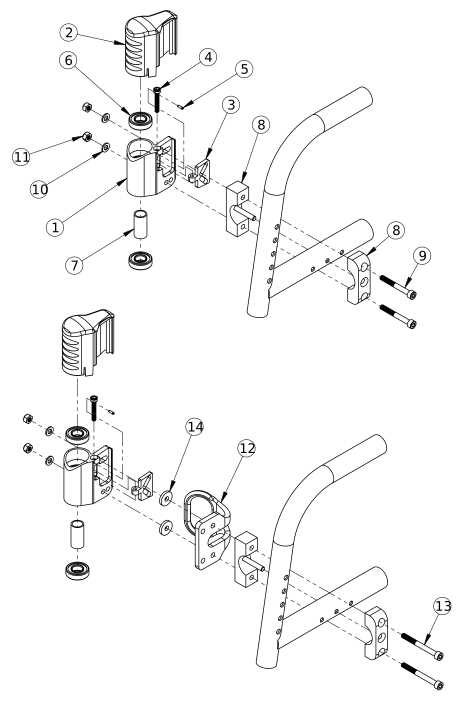
Another frequent concern involves uneven lifting or lowering actions. This can often be traced back to issues with hydraulic systems or malfunctioning actuators. Inspect the hydraulic fluid levels and look for any signs of leaks in the hoses. Additionally, check the lift cylinders and their seals to ensure they are functioning correctly. Proper maintenance of these elements can prevent further damage and restore smooth performance.