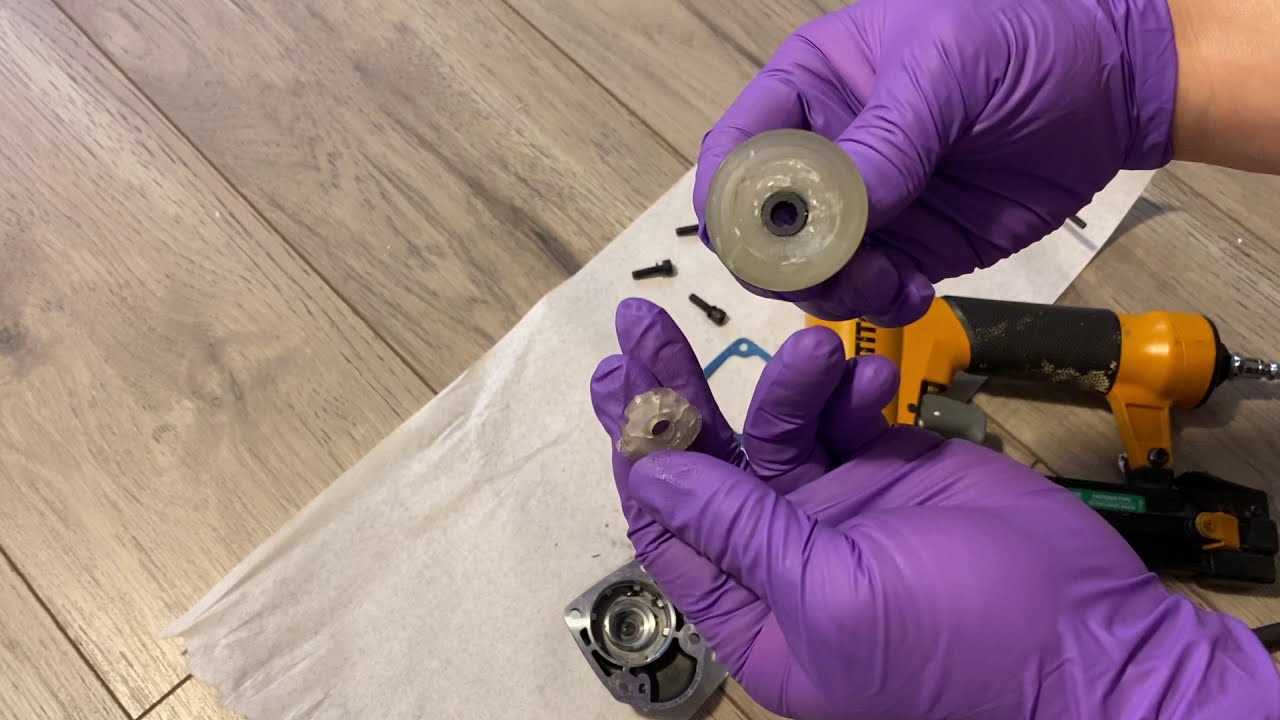

When it comes to understanding the inner workings of certain devices, having a clear illustration of the main elements is key. Knowing how each piece functions within the entire system helps users not only maintain their tools efficiently but also troubleshoot any potential issues with ease.
This guide explores the core elements and their relationships within a specific tool. It provides a comprehensive look at each element’s role and how they fit together to form a reliable and functional system. With this knowledge, users will be able to ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of their equipment.
By following this overview, readers will gain a deeper understanding of how everything fits and works seamlessly. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, this breakdown will provide valuable insights into the detailed construction and assembly process.
Overview of Key Components
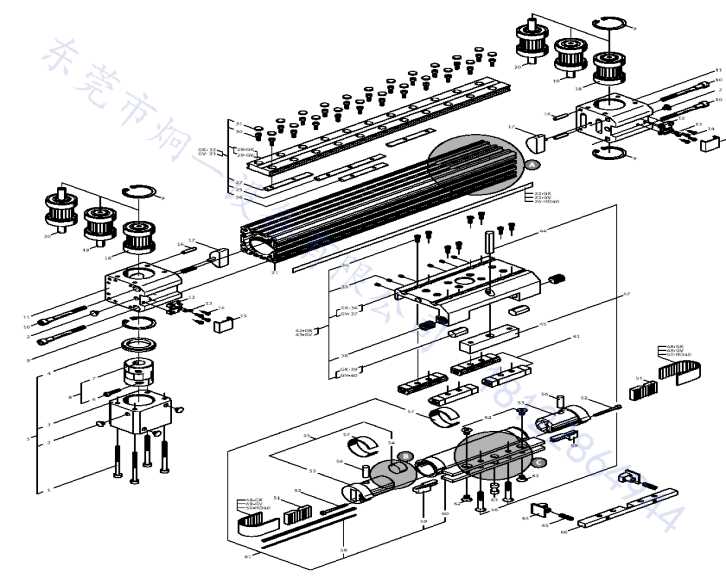
Understanding the core elements of this device is essential for ensuring smooth operation and longevity. Each piece works in harmony, contributing to the overall functionality, and recognizing their roles can aid in troubleshooting or maintenance.
Main Structural Elements
The framework includes several interconnected parts, each designed for durability and precision. The primary structure supports the internal mechanisms, providing stability and protection for the delicate components within.
Functional Mechanisms
At the heart of the operation are several key mechanisms responsible for efficient performance. These include elements that control movement, trigger action, and ensure safety during use. Proper maintenance of these mechanisms ensures consistent and reliable functionality.
Exploring the Trigger Mechanism
The actuation system in this tool plays a crucial role in controlling its operation. It is responsible for initiating the release of energy, allowing the device to perform its intended function. Understanding how this component works can provide deeper insights into the overall performance and reliability of the tool.
The trigger mechanism is designed with multiple elements that interact to ensure smooth and precise control. Each element plays a specific role in the functionality, providing safety and efficiency during use. Let’s examine how these components interact and how they contribute to the mechanism’s reliability.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Trigger Lever | Controls the engagement, initiating the cycle when pressed. |
| Safety Lock | Prevents accidental actuation, ensuring the tool operates only when intended. |
| Return Spring | Resets the mechanism to its default position after each cycle. |
| Valve Assembly | Regulates air or energy flow, enabling the operation when the trigger is pressed. |
By understanding each component’s role, users can better appreciate how the system works, allowing for proper maintenance and troubleshooting if needed.
Air Compression System Breakdown
The air compression system plays a vital role in ensuring consistent operation by supplying the necessary pressure for various functions. This section provides an in-depth look into how the system generates and regulates airflow, focusing on its essential mechanisms and components.
Main Components
- Compressor Unit: The central mechanism that generates air pressure through mechanical compression.
- Air Tank: A storage reservoir that holds pressurized air, ensuring a steady supply when needed.
- Pressure Valve: Regulates the flow of compressed air, maintaining a balanced output.
- Air Filter: Prevents dust and debris from entering the system, safeguarding internal components.
How It Works
- Air enters the compressor, where it is compressed to the desired pressure.
- The pressurized air is stored in the tank, ready for use.
- As the pressure reaches a certain level, the valve opens to release controlled amounts of air for various tasks.
- The filter ensures that no external particles interfere with the system’s performance.
Understanding the Nail Loading System
The nail loading system is a critical component in ensuring efficient operation of fastening tools. Proper alignment and placement of fasteners allow for smooth functioning and reliable performance during various applications. To maintain consistent output and avoid jams or misfires, it is essential to understand the process behind inserting and securing the fasteners correctly within the designated chamber.
By following the appropriate steps for loading, the tool can deliver fasteners smoothly without interruptions, ensuring precise results with each use. Mastering this system allows for a more efficient workflow and minimizes the chance of operational issues, keeping the tool ready for action.
Guide to the Safety Features
Ensuring secure operation is critical when working with any pneumatic tool. Understanding the key protective mechanisms can significantly reduce the risk of accidents. This guide highlights the crucial elements designed to prevent unintentional harm and enhance user control during operation.
Primary Safeguards
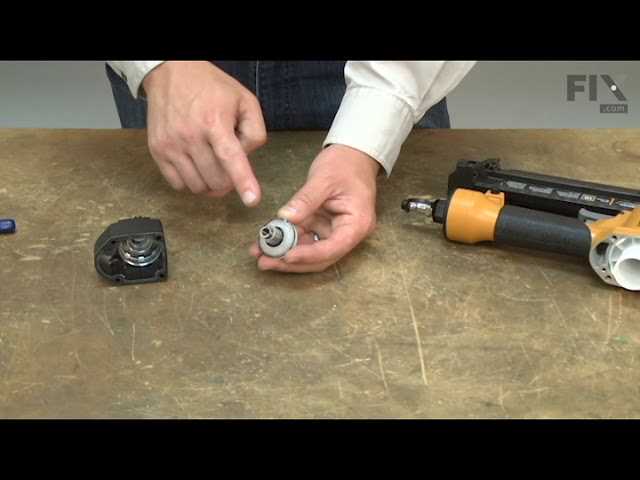

The device incorporates several preventive measures that must be engaged for it to function. These include a system to avoid misfires and a lockout feature that restricts operation when certain conditions aren’t met. Both mechanisms work together to enhance operator safety and maintain control in challenging environments.
Trigger and Contact Mechanism
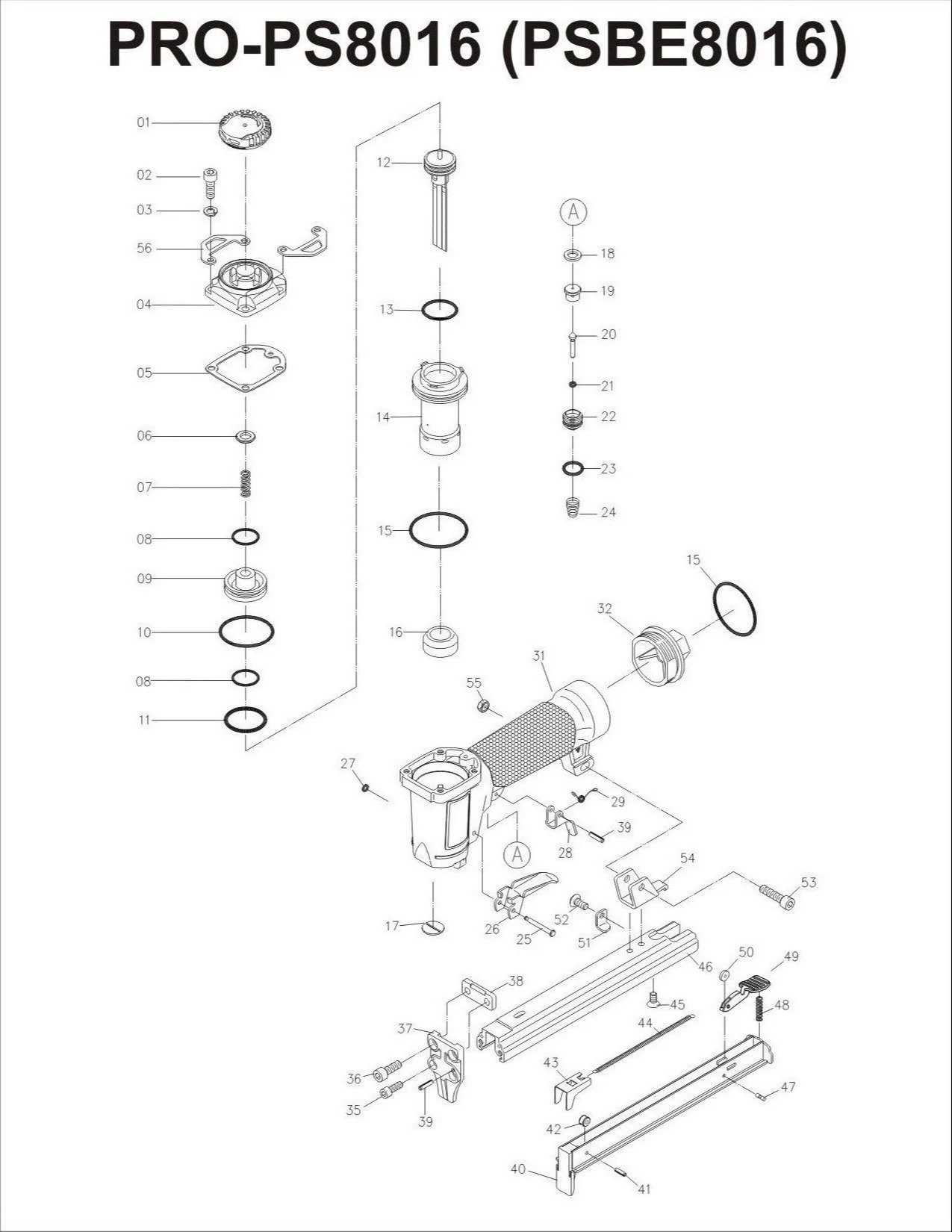
The actuation system is essential for ensuring only intentional actions result in tool engagement. The trigger works alongside a contact element, which must be fully depressed before any action is taken. This prevents accidental discharges and ensures the tool operates only when positioned correctly.
| Feature | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Lockout Mechanism | Prevents operation under improper conditions | Reduces the risk of misfires |
| Trigger Safety | Requires user engagement before activation | Prevents accidental triggering |
| Contact Safety | Ensures tool operates only when properly positioned | Enhances control and safety |
Examining the Magazine Assembly
The magazine assembly plays a crucial role in the operation of fastener tools, ensuring efficient loading and delivery of fasteners. Understanding its components and functionality is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section delves into the various elements that comprise the assembly and their significance in overall performance.
Key Components of the Magazine Assembly

- Feed Mechanism: This component is responsible for the seamless movement of fasteners from the magazine to the tool’s firing mechanism. It ensures that each fastener is positioned correctly for reliable operation.
- Spring Tension: Springs maintain the necessary pressure on the fasteners, allowing for consistent feeding and preventing jamming. Proper spring tension is vital for optimal functionality.
- Magazine Housing: The outer casing of the assembly protects internal components and provides a structured pathway for fasteners. It is designed for durability and ease of access during maintenance.
- Loading Slot: This feature allows for quick and easy replenishment of fasteners, ensuring minimal downtime during tasks.
Maintenance Tips for the Magazine Assembly
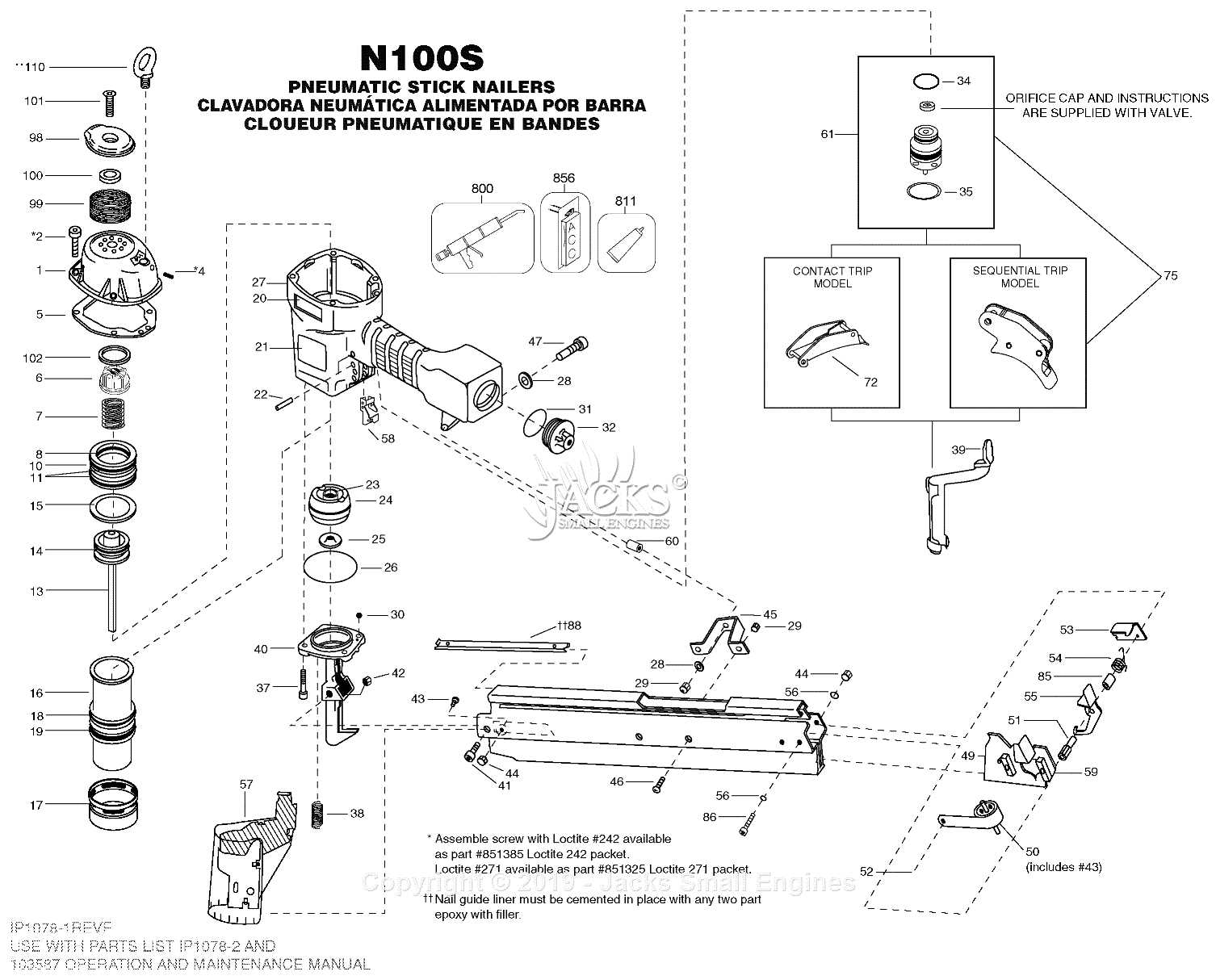
- Regularly inspect the feed mechanism for wear and debris to ensure smooth operation.
- Check spring tension and replace any worn springs to maintain proper functionality.
- Clean the magazine housing to prevent buildup that could hinder performance.
- Lubricate moving parts as recommended by the manufacturer to enhance efficiency.
Understanding these components and maintenance tips can significantly improve the performance and longevity of the tool. Regular attention to the magazine assembly can prevent common issues and enhance overall productivity in fastening tasks.
Maintenance Tips for Internal Parts
Ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your equipment requires regular attention to its internal components. Proper maintenance not only enhances performance but also reduces the likelihood of unexpected failures. Here are some essential practices to consider for the upkeep of these vital elements.
- Regular Cleaning: Dust and debris can accumulate inside machinery, leading to blockages and wear. Use compressed air or a soft brush to remove contaminants.
- Lubrication: Many internal mechanisms rely on lubrication to function smoothly. Apply appropriate lubricants to moving parts as specified by the manufacturer.
- Inspection: Periodically check for signs of wear or damage. Look for cracks, corrosion, or unusual sounds during operation, which may indicate that components need replacement.
- Calibration: Keeping internal systems properly calibrated ensures optimal performance. Regularly check settings and adjust them according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Component Replacement: If any part shows significant wear or malfunction, replace it promptly to avoid further damage. Use genuine replacement components for compatibility and reliability.
- Documentation: Maintain a log of all maintenance activities, including cleaning schedules, lubrication, and parts replaced. This helps in tracking performance over time.
By following these guidelines, you can prolong the life of your machinery and ensure it operates at peak efficiency, minimizing downtime and enhancing productivity.
Common Issues with Firing Mechanism
The firing mechanism is crucial for the proper functioning of any fastening tool. Understanding the common problems that may arise can help users troubleshoot effectively and maintain optimal performance. These issues often stem from wear and tear, improper maintenance, or manufacturing defects, leading to operational difficulties that can hinder productivity.
Some frequent complications include misfires, jams, and inconsistent firing power. These problems can result from various factors, including incorrect loading of fasteners, debris accumulation, or mechanical failures. It is essential to identify and address these issues promptly to ensure safe and efficient operation.
| Issue | Possible Causes | Recommended Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Misfire | Incorrect fastener type, insufficient air pressure | Verify fastener specifications, check air supply |
| Jamming | Debris blockage, improperly loaded fasteners | Clean the mechanism, reload fasteners correctly |
| Inconsistent Firing | Worn parts, inadequate lubrication | Inspect and replace worn components, apply proper lubrication |