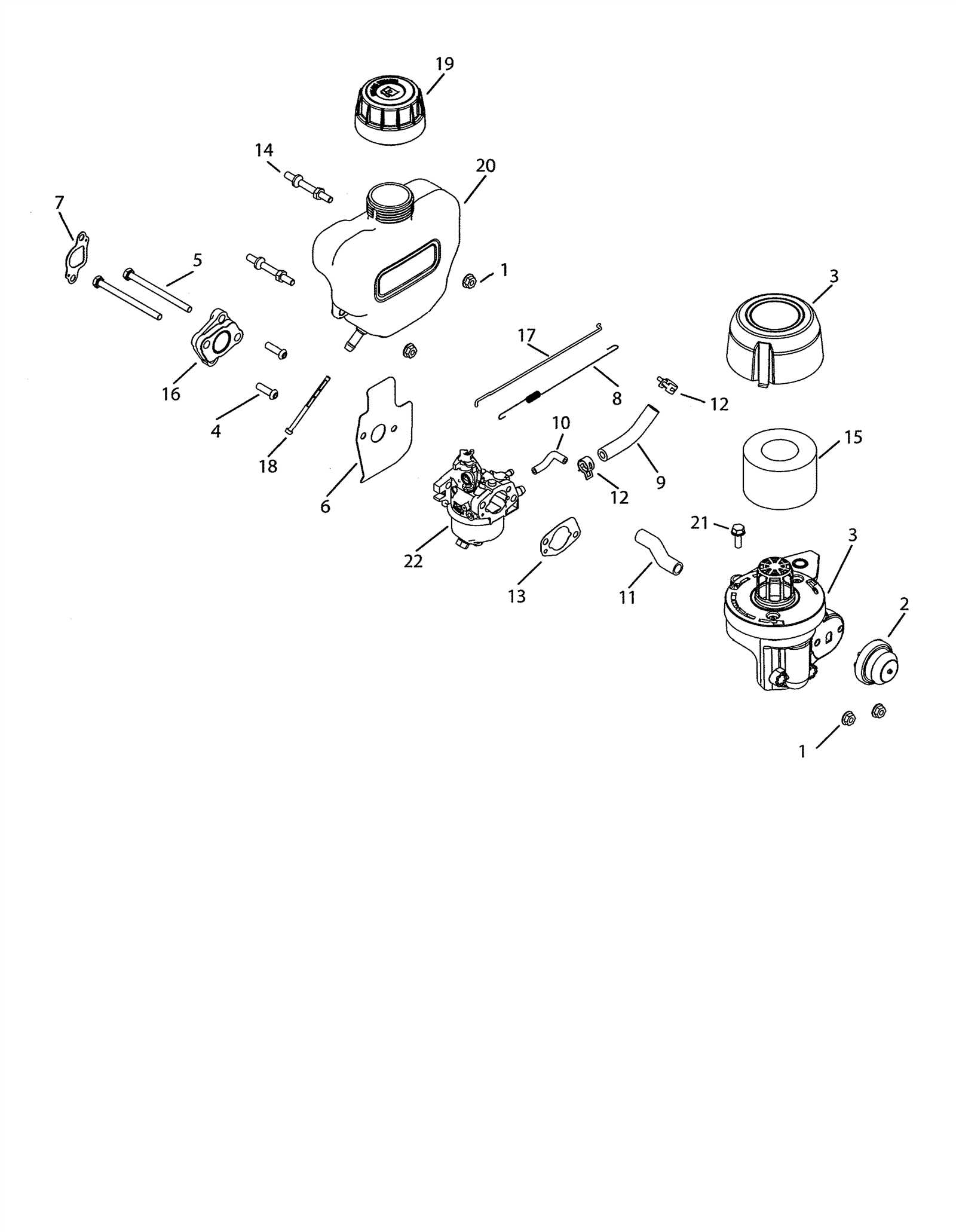
The efficient operation of grass cutting machinery relies heavily on the intricate components that make up its fuel delivery system. These elements work in harmony to ensure that the engine runs smoothly, providing the power necessary for effective grass trimming. A clear understanding of these components can enhance maintenance practices and improve the overall performance of the equipment.
Familiarizing oneself with the layout and function of these vital mechanisms allows for better troubleshooting and repair. By grasping how each element interacts within the fuel system, users can identify issues more effectively and carry out necessary adjustments or replacements. This knowledge ultimately leads to longer-lasting and more reliable performance during use.
In this guide, we will explore the various components involved in the fuel system of grass cutting machinery, offering insights into their specific roles and relationships. Understanding these features will empower users to optimize their equipment and ensure its readiness for any lawn care task.
Lawn Mower Carburetor Components Overview
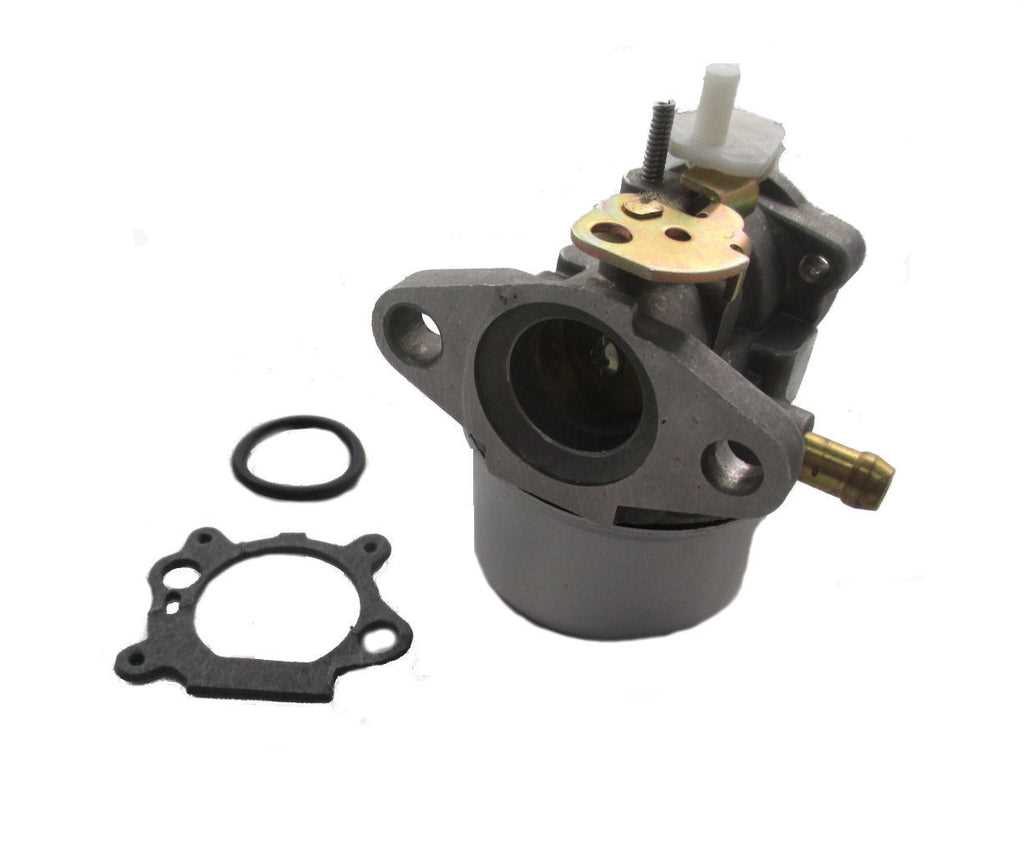

This section provides a detailed examination of the essential elements that constitute a fuel delivery mechanism in small engines. Understanding these components is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring optimal performance of the machine.
Key Components
The primary elements involved in the fuel delivery process include the float chamber, needle valve, and jet. Each of these plays a vital role in regulating the fuel flow and maintaining the appropriate mixture for combustion. The float chamber stores the fuel, while the needle valve controls its entry. The jet, on the other hand, disperses the fuel into the airflow, facilitating an efficient combustion process.
Functionality and Maintenance
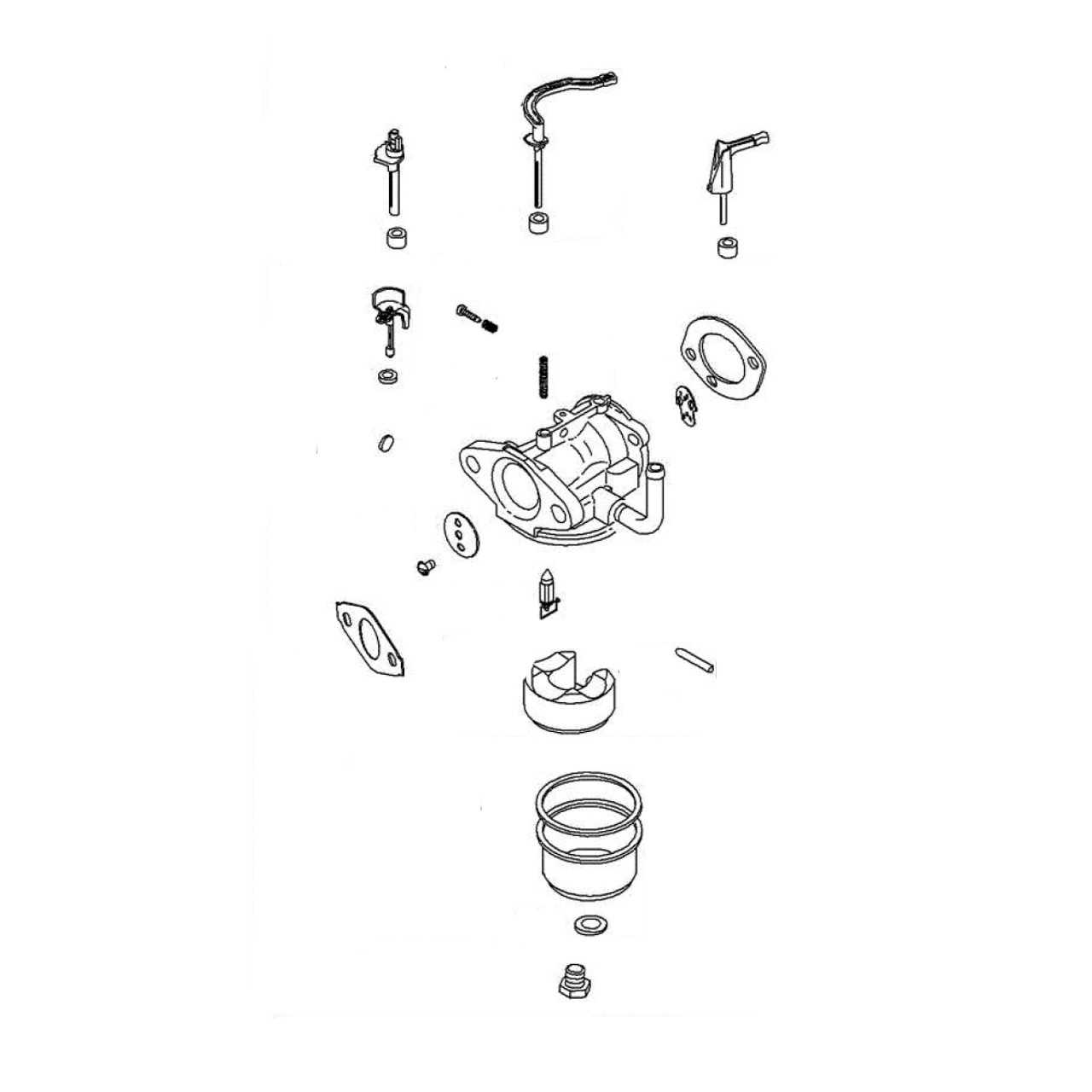
Proper functionality of these components is essential for the overall efficiency of the engine. Regular inspection and cleaning of the float chamber and jet can prevent issues related to clogging and fuel delivery. Ensuring the needle valve operates smoothly is also critical, as it directly affects the fuel level in the chamber.
Understanding Carburetor Functionality

The component responsible for mixing air and fuel in an engine plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance. It regulates the flow of fuel and air, allowing the engine to operate efficiently across various conditions. Understanding how this mechanism works can significantly enhance maintenance and troubleshooting efforts.
At its core, this device operates by creating a vacuum that draws fuel from a reservoir into the air stream. As air flows through the inlet, the reduction in pressure causes fuel to be atomized and mixed with the incoming air. This process is vital for achieving the right mixture for combustion, impacting both power output and emissions.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Air-Fuel Mixture | Regulates the ratio of air to fuel for efficient combustion. |
| Atomization | Breaks down fuel into tiny droplets for better mixing with air. |
| Throttle Control | Adjusts the amount of air and fuel entering the engine, influencing power output. |
| Idle Adjustment | Maintains a stable operation when the engine is running at low speeds. |
Common Issues with Carburetors

Fuel delivery systems are essential components that can encounter various complications affecting their performance. Understanding these common challenges can aid in maintaining optimal functionality and ensuring a smooth operation.
1. Fuel Flow Problems: Inadequate fuel flow can lead to engine stalling or difficulty starting. This may result from blockages in the fuel line, a malfunctioning pump, or contaminated fuel. Regular inspection and cleaning can help prevent these issues.
2. Air Leaks: Leaks in the intake system can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to erratic engine behavior. Identifying and sealing these leaks is crucial for maintaining the correct mixture for efficient combustion.
3. Improper Mixture: An incorrect air-fuel ratio can cause poor performance, including excessive smoke or engine overheating. Adjustments may be necessary to achieve the proper mixture for the specific engine requirements.
4. Sticking Components: Moving parts within the system can become stuck due to dirt, varnish, or wear. Regular cleaning and lubrication are vital to ensure these components operate freely and efficiently.
5. Corrosion: Over time, moisture can lead to rust and corrosion within the system, impacting overall functionality. Using high-quality fuel and storing equipment in a dry environment can help mitigate this issue.
Being aware of these common challenges allows for timely interventions and maintenance, ensuring longevity and reliability of the fuel delivery systems.
Essential Tools for Repairs
When it comes to maintaining and fixing various machinery, having the right equipment is crucial. The appropriate tools not only ensure efficient work but also enhance safety during the repair process. Below is a list of necessary implements that every technician should have on hand for effective servicing.
Basic Hand Tools
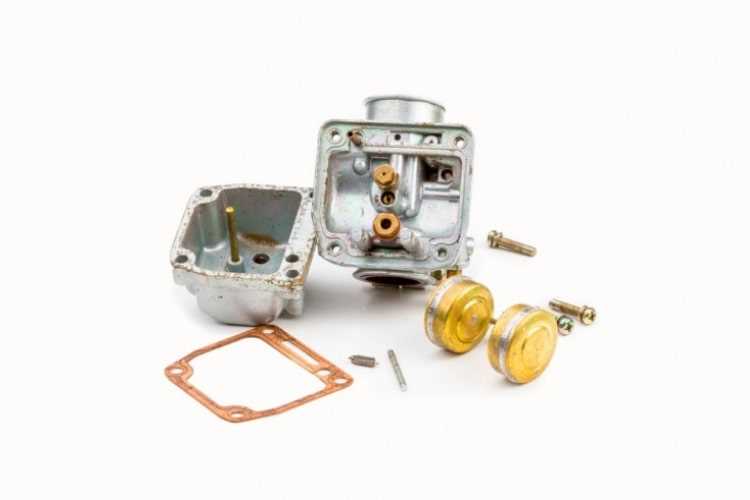

Essential hand tools form the backbone of any repair kit. These implements are versatile and can be used for a range of tasks. Common examples include:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Wrenches | Used for tightening or loosening nuts and bolts. |
| Screwdrivers | Ideal for driving screws into various surfaces. |
| Pliers | Helpful for gripping and bending materials. |
| Socket Set | Provides versatility in accessing fasteners in tight spaces. |
Specialized Equipment
Alongside basic tools, specialized equipment can significantly enhance repair efficiency. These tools are tailored for specific tasks and make complex jobs more manageable:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Torque Wrench | Ensures that fasteners are tightened to the correct specifications. |
| Multimeter | Used for measuring voltage, current, and resistance in electrical components. |
| Compression Tester | Assesses the condition of internal components by measuring pressure. |
| Fuel Line Tool | Facilitates the quick disconnection and connection of fuel lines. |
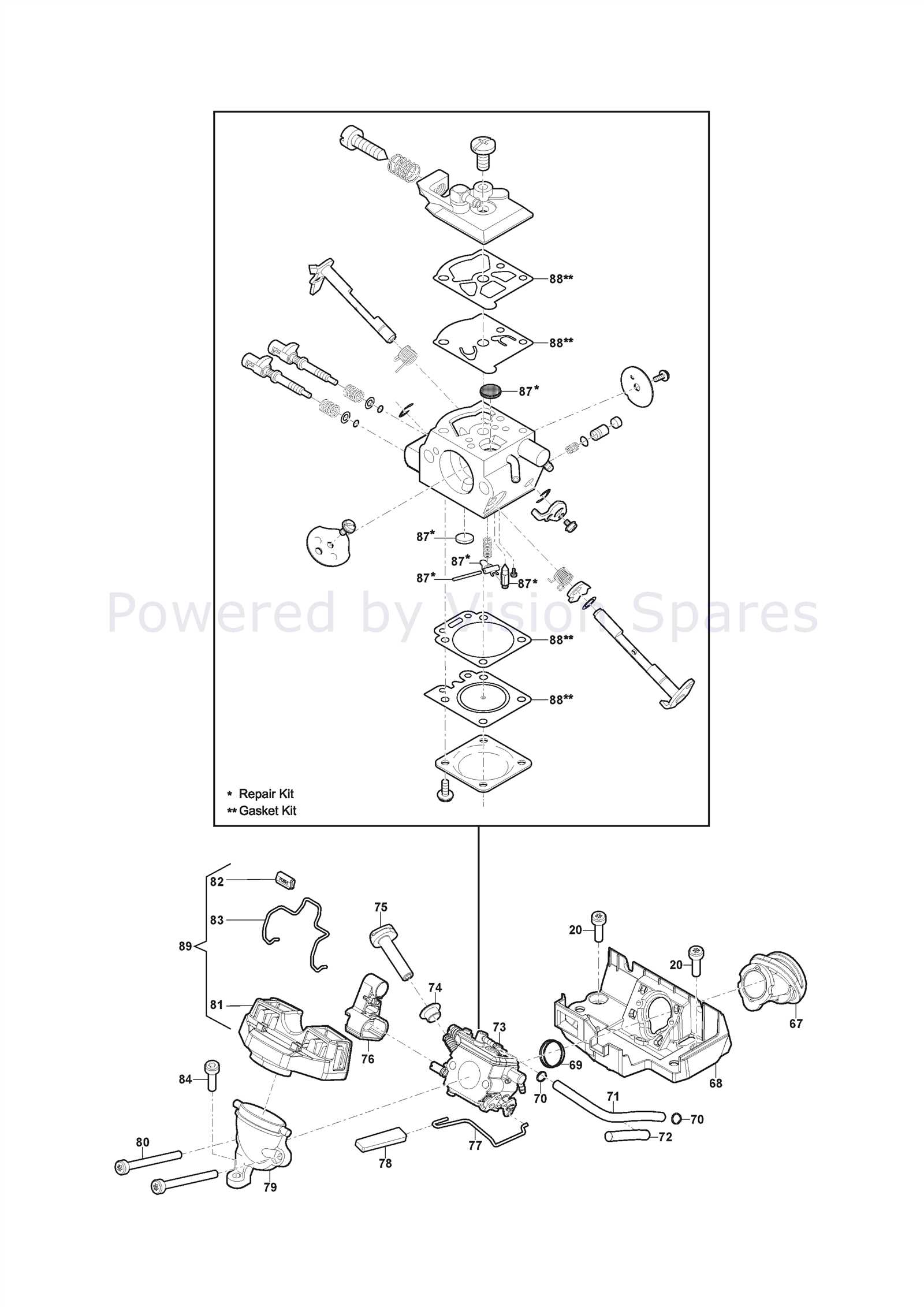
How to Disassemble a Carburetor
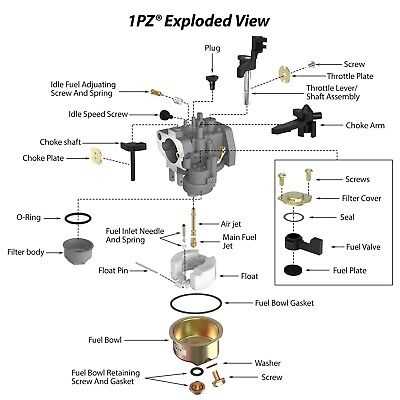
Disassembling the fuel mixing device is an essential task for maintenance and repair. Understanding the internal components and their arrangement can help ensure proper functionality and performance. This process allows for thorough cleaning and inspection of all critical elements, ultimately extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Before beginning, gather all necessary tools, including a screwdriver, pliers, and cleaning supplies. Start by ensuring that the engine is off and cool to avoid accidents. Disconnect any fuel lines and remove the assembly from its housing carefully.
Next, pay attention to the fasteners securing the various elements together. Use the appropriate screwdriver to remove screws and detach the different sections. Be mindful of any springs or small components that may be under tension; these can easily be lost if not handled carefully.
Once the main body is disassembled, clean each component thoroughly with suitable solvents. Inspect for wear or damage, as this can affect the overall efficiency of the mechanism. After cleaning, reassemble the unit in the reverse order of disassembly, ensuring all parts fit snugly and securely.
Key Parts of a Carburetor
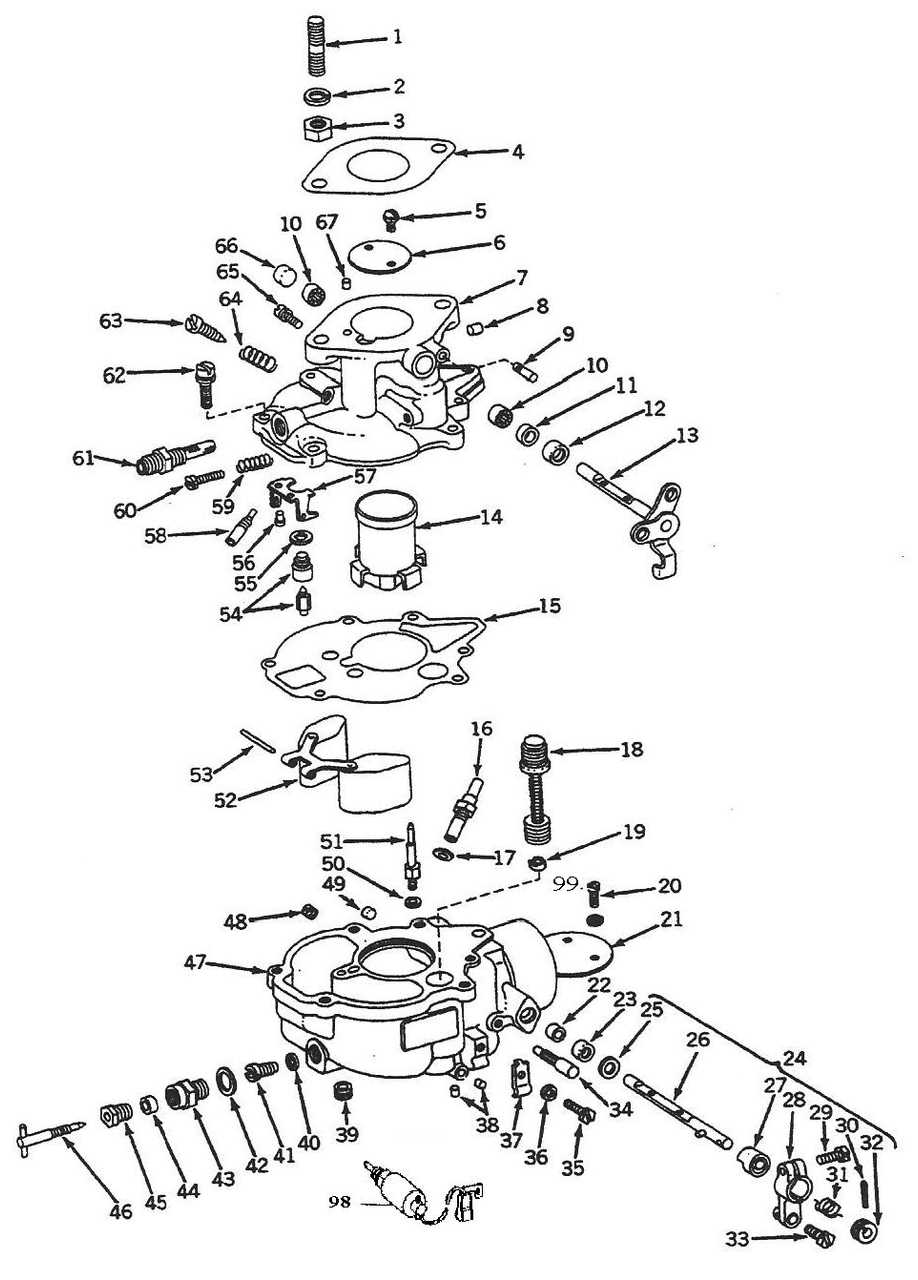
This section highlights the essential components that contribute to the functionality of the fuel delivery system in small engines. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Fuel Delivery Mechanism
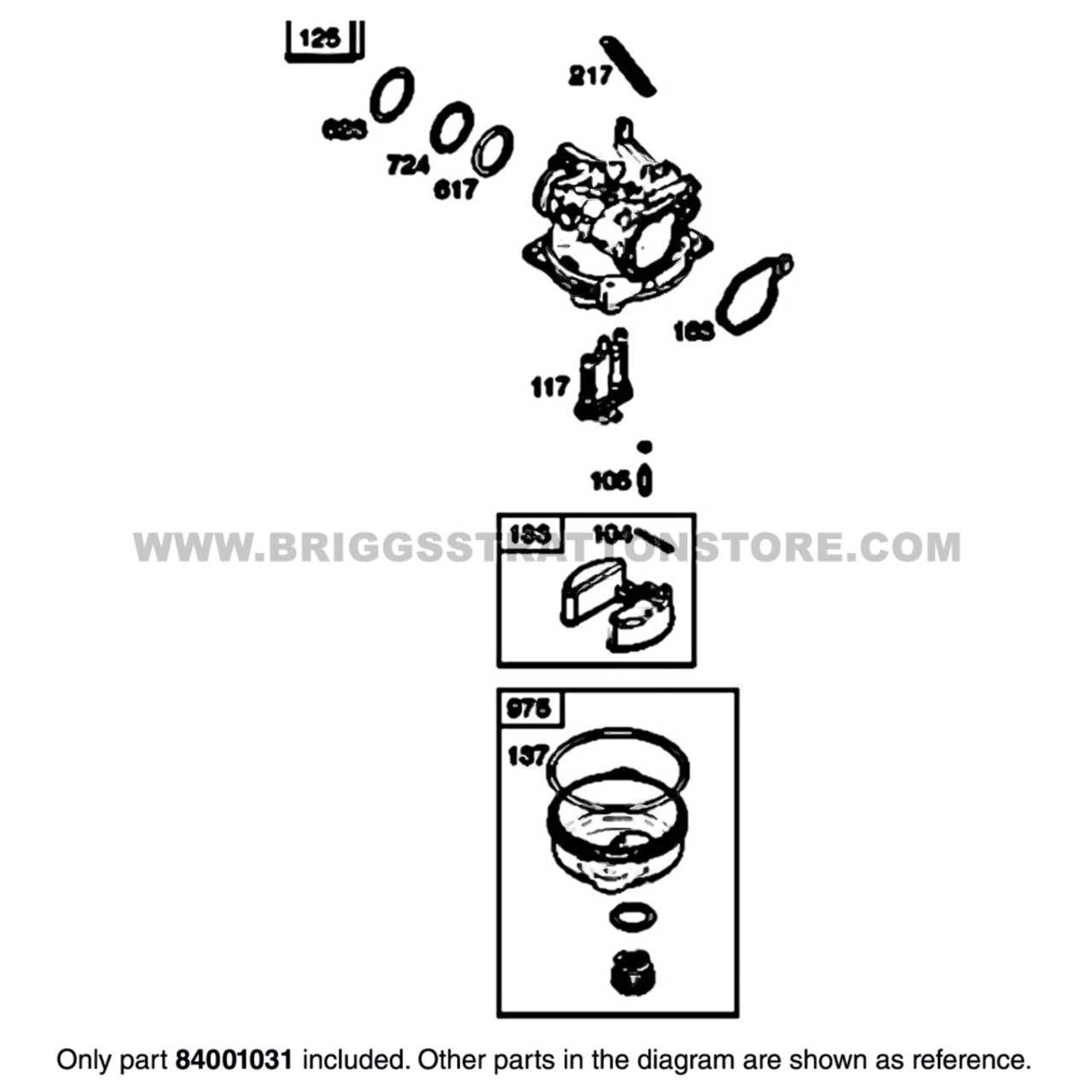
The fuel delivery mechanism is responsible for supplying the appropriate amount of liquid to the combustion chamber. It ensures that the mixture of air and fuel is balanced, which is vital for optimal performance.
Air Intake System
The air intake system plays a significant role in regulating airflow into the engine. By controlling the volume and velocity of the incoming air, it aids in creating the right mixture with the fuel, ultimately affecting the engine’s efficiency and power output.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Proper upkeep is essential for extending the lifespan of your equipment. Regular attention can prevent wear and tear, ensuring optimal performance over time. Implementing a consistent maintenance routine not only enhances functionality but also saves on repair costs in the long run.
Cleanliness is key. Regularly remove debris and buildup from components to maintain airflow and efficiency. Using a soft brush or cloth can help eliminate dirt without damaging sensitive areas.
Check and replace filters periodically. Air and fuel filters play a vital role in keeping the engine running smoothly. Clogged filters can lead to reduced performance, so replacing them at regular intervals is advisable.
Inspect for leaks. Regularly check for any signs of fluid leaks, as these can indicate underlying issues. Addressing leaks promptly can prevent further damage and maintain the integrity of the system.
Store properly during off-seasons. When not in use, ensure the equipment is stored in a dry, sheltered location. Draining fuel and cleaning components before storage can prevent corrosion and buildup.
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance schedules and procedures. Adhering to these recommendations will ensure that the equipment remains in peak condition, maximizing its lifespan and performance.
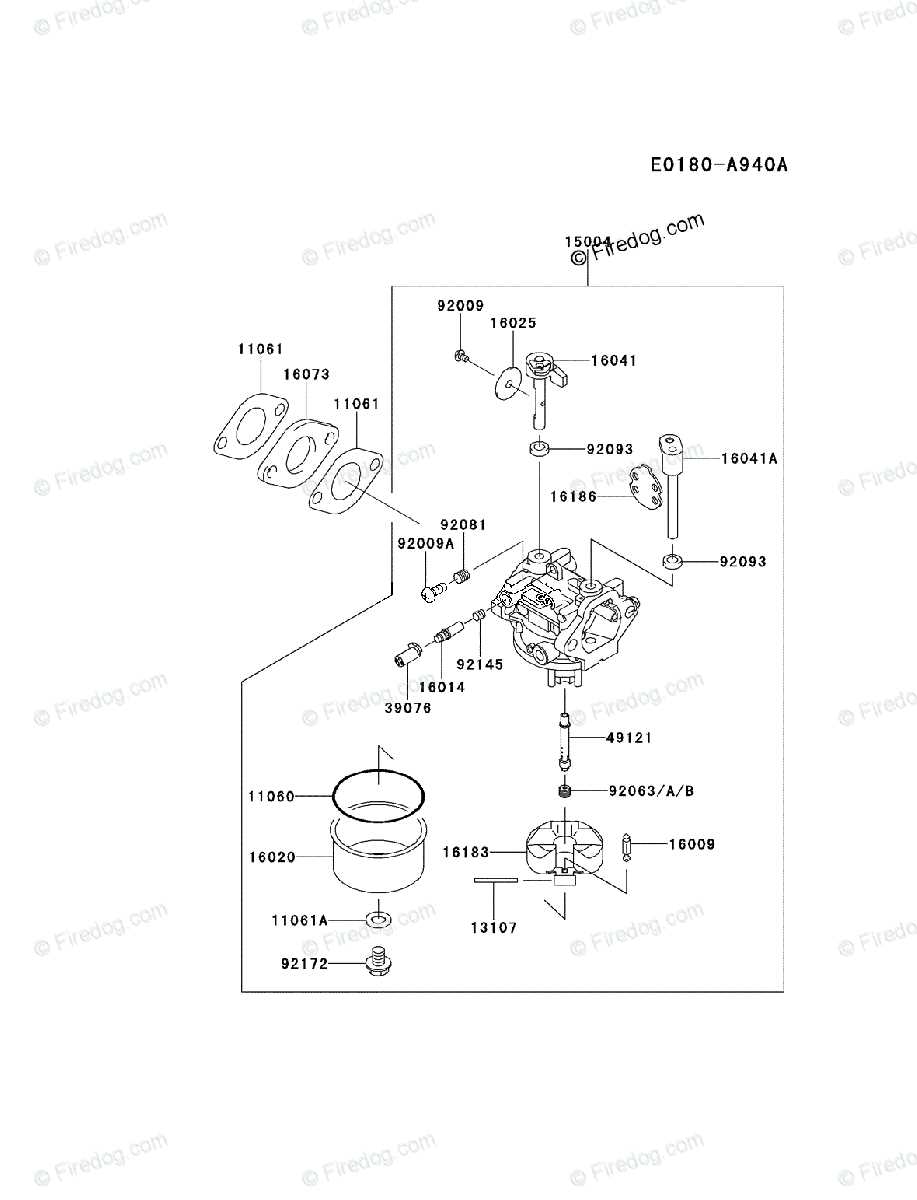
Identifying Carburetor Models
Understanding various engine fuel systems is essential for effective maintenance and repairs. Recognizing different designs can streamline troubleshooting and replacement processes. This section will guide you through the key features and identification methods for various fuel systems, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your equipment.
| Model Type | Identification Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Type A | Single diaphragm, compact design, typically with a metal housing | Small engines, including handheld tools |
| Type B | Dual diaphragm, larger size, often with plastic components | Medium to large engines, including some garden equipment |
| Type C | Variable venturi, adjustable jets, more complex design | High-performance engines, often found in commercial machinery |
Safety Precautions During Repairs
Ensuring personal safety is paramount when undertaking maintenance tasks on equipment. Adhering to proper precautions not only protects the individual performing the repairs but also extends the lifespan of the machinery. Familiarizing oneself with safety guidelines is essential for a successful and incident-free experience.
Before beginning any repair work, it is crucial to gather the necessary tools and protective gear. This includes gloves, goggles, and appropriate clothing to prevent injuries from sharp components or harmful substances. Additionally, it is vital to ensure the equipment is turned off and disconnected from any power sources.
| Precaution | Description |
|---|---|
| Use Protective Gear | Always wear gloves and goggles to shield against injuries and irritants. |
| Disconnect Power Source | Make sure the machine is powered off and unplugged to avoid accidental starts. |
| Work in a Well-Ventilated Area | Ensure good airflow to prevent inhaling harmful fumes during repairs. |
| Organize Tools and Parts | Keep your workspace tidy to reduce the risk of accidents and misplacing items. |
| Follow Manufacturer Instructions | Refer to the manual for specific guidelines and recommendations for safe repairs. |