Understanding the arrangement and functionality of various mechanical elements is crucial for maintaining and enhancing vehicle performance. In this guide, we delve into the key structural features of a popular off-road machine, exploring the relationship between individual units that work together to ensure smooth and reliable operation. Each section provides detailed insights into the essential mechanisms that drive this vehicle’s power and agility, helping enthusiasts and mechanics alike understand its inner workings.
The analysis will cover the major sections of the machine, offering a clear view of how specific units connect and interact with one another. Whether you’re interested in how the propulsion system functions or how suspension mechanisms are designed to handle rough terrain, this guide offers an in-depth look at each vital component. By understanding these connections, you’ll be better equipped to perform maintenance, repairs, or upgrades, ensuring the vehicle performs at its peak.
Understanding the Components of an Apollo Dirt Bike

Recognizing the various elements that make up a two-wheeled off-road machine is essential for maintaining performance and ensuring safety. Each element plays a vital role in the smooth operation of the vehicle, from propulsion to handling. A thorough understanding of these elements can significantly extend the lifespan of your vehicle while also enhancing your riding experience.
The core of the machine lies in its mechanical assembly, which is designed to withstand the challenges of rugged terrain. The power source, responsible for driving the wheels, must work in harmony with other systems such as suspension, braking, and transmission to provide a reliable and efficient ride.
The framework and supportive structures are equally critical, ensuring that all mechanical components are securely in place and that the vehicle can handle the stresses of uneven surfaces. Adjustments and proper care of each section of the vehicle contribute to both rider comfort and control, making it essential to familiarize yourself with every part.
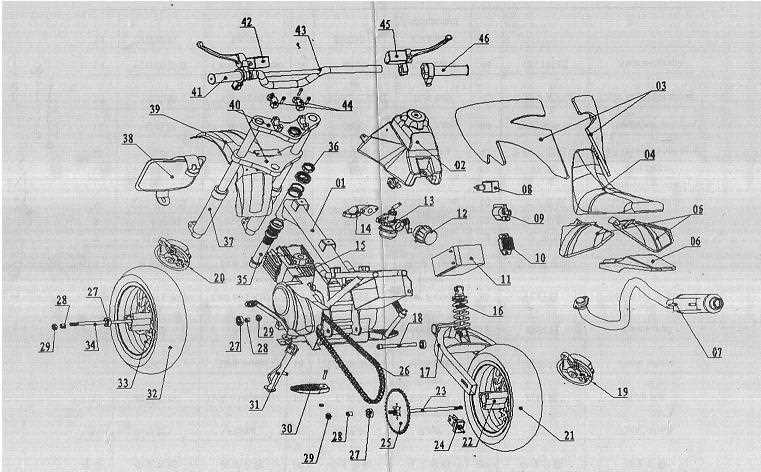
Frame and Chassis Overview
The foundation of any two-wheeled vehicle lies in its structural integrity, which directly impacts overall performance and handling. The metal framework and supportive structure create a solid base, ensuring stability and providing support for various components.
Structural Components
The main framework consists of multiple interconnected sections that work together to form a strong, lightweight construction. These sections are designed to absorb shocks, distribute weight evenly, and maintain the balance of the vehicle during operation.
- Main Frame: Serves as the backbone, connecting all major components and ensuring rigidity.
- Subframe: A secondary structure supporting the rear section, often detachable for easier repairs.
- Swingarm: Attaches to the rear suspension, allowing for controlled movement and shock absorption.
Chassis Functionality
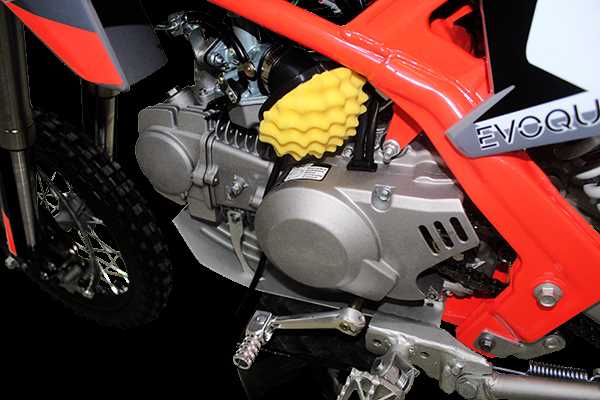
Designed for durability and precision, the vehicle’s chassis must balance flexibility and strength. The materials used are lightweight yet tough, ensuring the frame withstands regular stress and impacts.
- Support for engine and suspension components.
- Maintains the balance and alignment of the vehicle.
- Ensures optimal handling through rugged terrains and sharp turns.
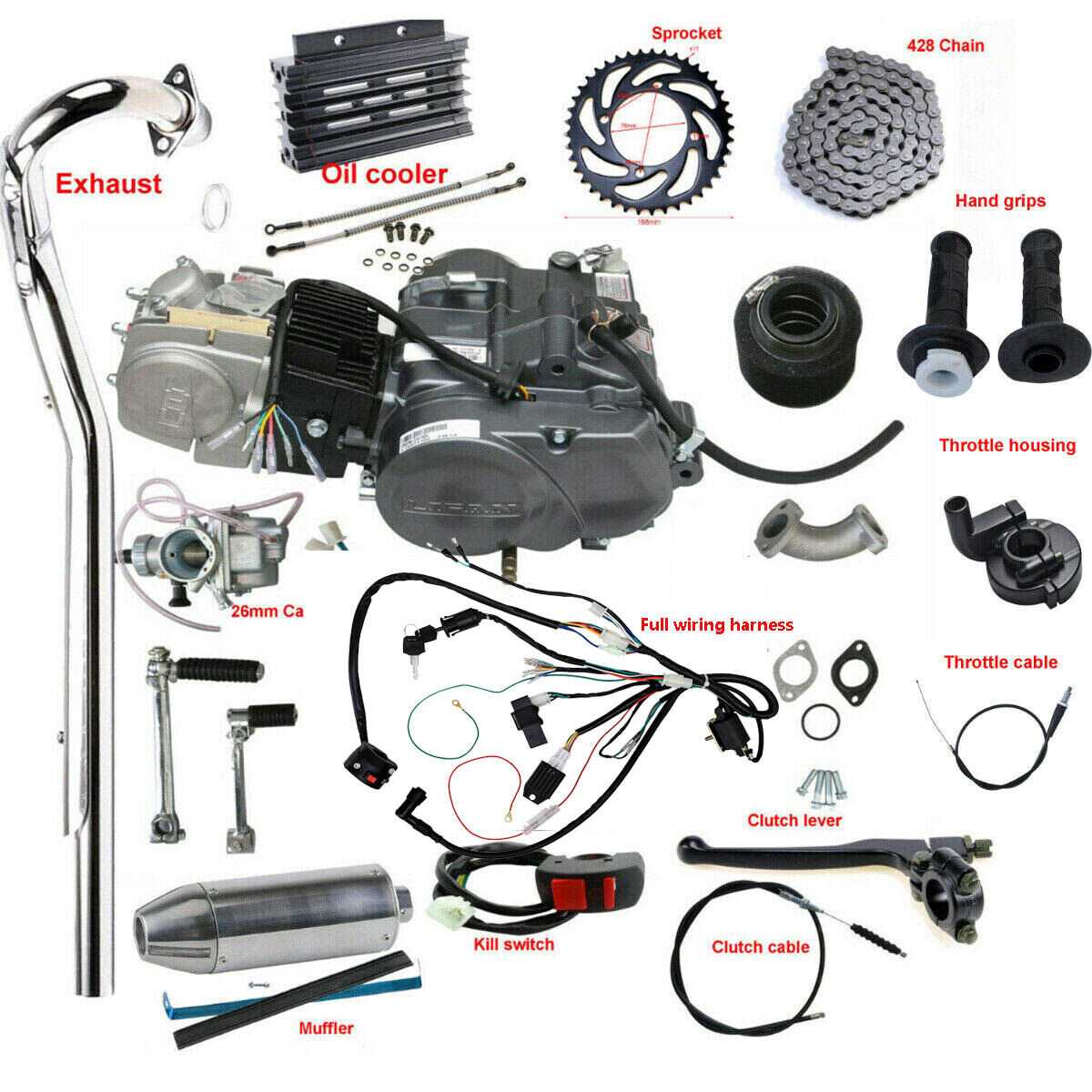
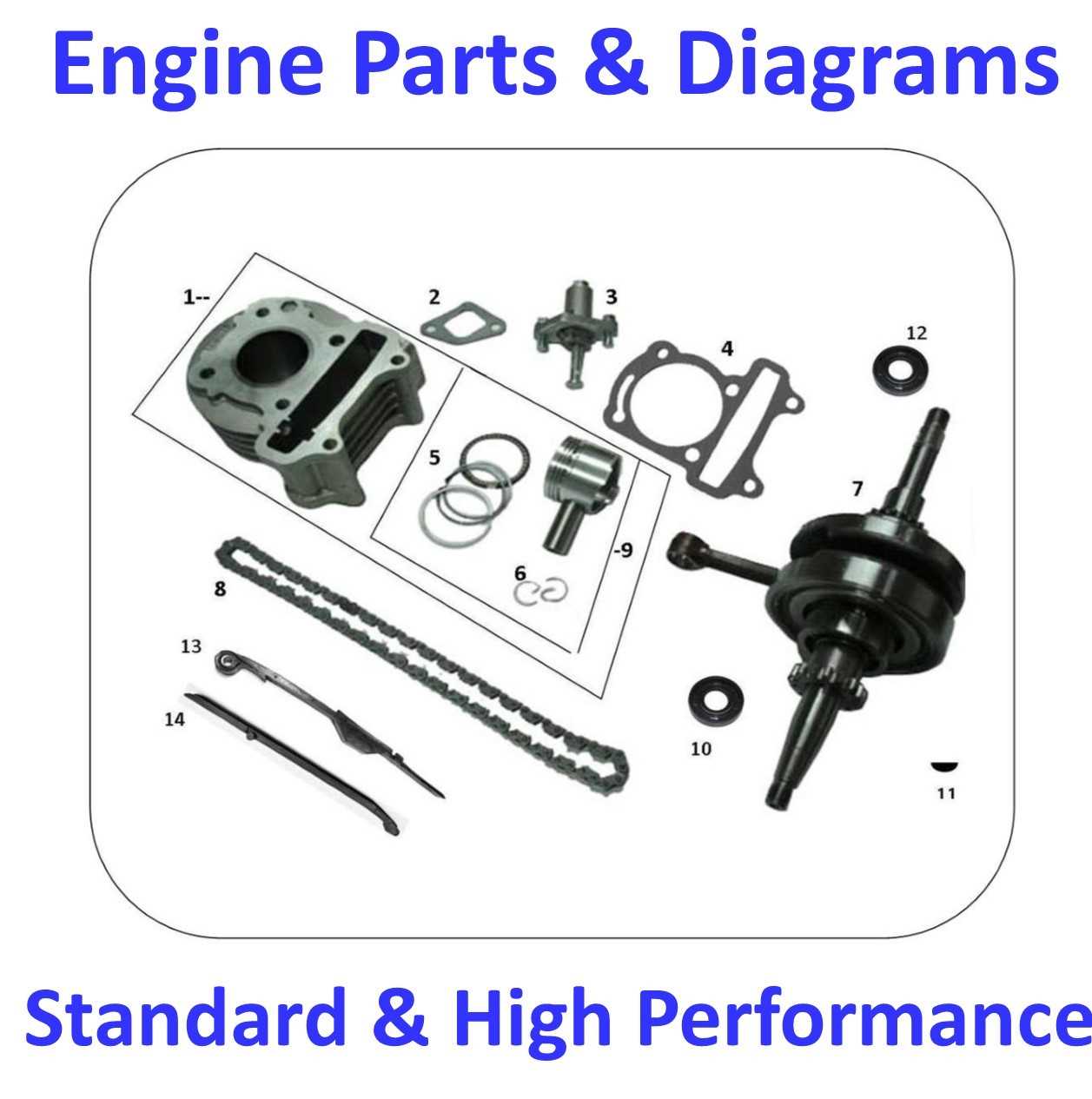
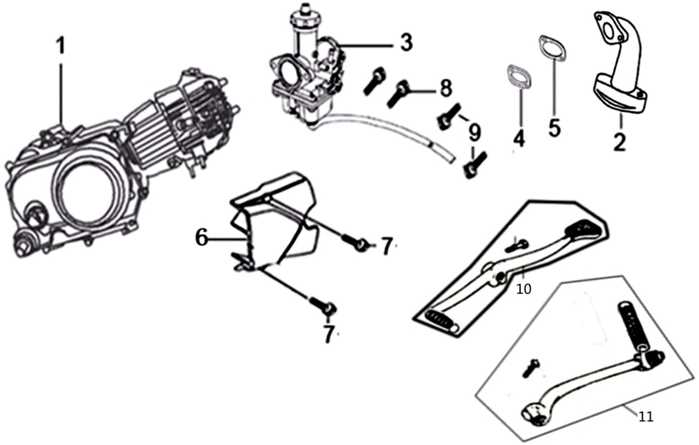
Engine Configuration and Key Parts

The engine is the core component of any off-road machine, designed to convert energy into motion. Understanding how this essential mechanism is structured and identifying its key elements is crucial for efficient maintenance and performance improvements. The internal design varies, but all engines share fundamental components that work together to deliver power.
Main Components Overview

Every engine consists of several vital elements responsible for its operation. These include the combustion area, which ignites the fuel mixture, and the mechanical systems that translate this energy into movement. Other important areas involve systems for fuel delivery, cooling, and exhaust handling.
Detailed Breakdown

| Component | Description | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
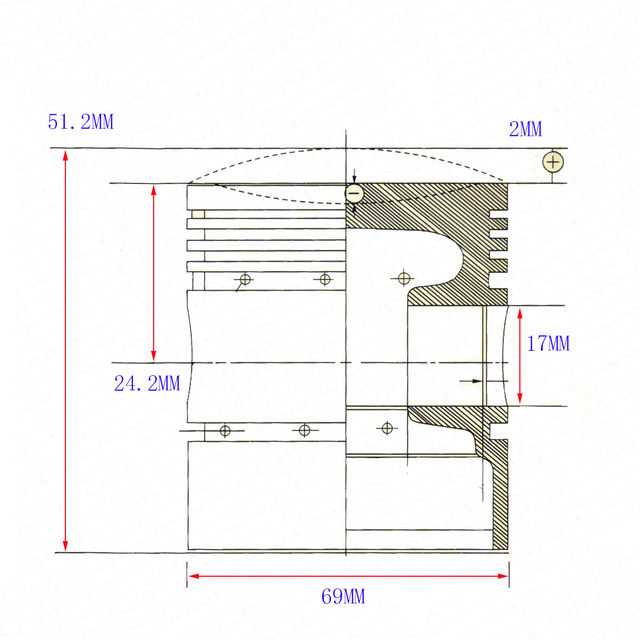
| Piston | Responsible for converting energy from combustion into mechanical motion. | |||||||||||
| Crankshaft | Rotates to transfer power from the piston to the drivetrain. | |||||||||||
| Cylinder | Forms the chamber where the combustion process occurs. | |||||||||||
| Camshaft | Controls the opening and closing of the engine’s valves. | |||||||||||
| Carburetor | Mixes air and fuel for combustion in precise ratios. | |||||||||||
| Cooling System |
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | Stores the fuel until needed by the engine. |
| Fuel Lines | Transport fuel from the tank to the engine components. |
| Fuel Filter | Removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine. |
| Fuel Pump | Moves fuel through the lines under pressure. |
| Carburetor | Mixes fuel with air to create a combustible mixture for the engine. |
Connections and Flow

The connections between these components ensure a seamless flow of fuel. The fuel pump draws liquid from the tank and sends it through the filter, which cleanses it of contaminants. Subsequently, the purified fuel travels through the lines to the carburetor, where it is mixed with air in the correct ratio for combustion. Proper understanding of these connections is vital for diagnosing and resolving fuel delivery issues.
Electrical Wiring and Battery Diagram

This section provides an overview of the electrical system, highlighting the essential components and their interconnections. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring safe operation.
The electrical layout typically includes various elements that contribute to the overall functionality:
- Power source: The battery provides the necessary energy for starting and running the engine.
- Wiring harness: This is a collection of wires that connect different electrical components, facilitating communication and power distribution.
- Switches: These devices control the flow of electricity to various systems, such as lights and ignition.
- Fuses: Protect the electrical system by breaking the circuit in case of overloads.
- Connectors: Allow for easy assembly and disassembly of the wiring system, ensuring secure connections between components.
To effectively troubleshoot and modify the electrical setup, it is important to refer to a schematic representation that details the connections and specifications of each component. This can assist in identifying issues and implementing upgrades.