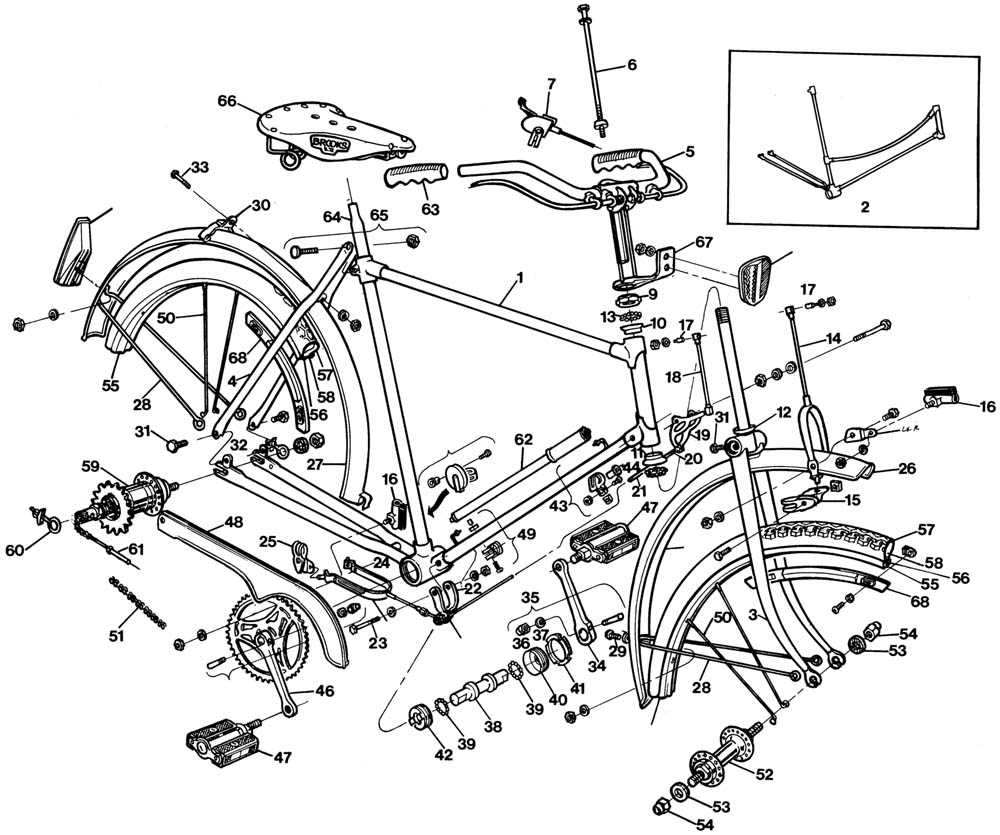
In the world of two-wheeled transportation, the ability to halt safely and efficiently is paramount. This section delves into the crucial elements that contribute to the overall effectiveness of stopping systems. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring rider safety and vehicle performance, providing insights into how they function in unison.
From the mechanisms that engage to the materials used in construction, the intricacies of these systems are essential for every enthusiast and professional alike. A comprehensive grasp of these components not only enhances maintenance practices but also empowers riders to make informed decisions about upgrades and repairs.
By exploring these fundamental elements, readers will gain a clearer understanding of how each piece contributes to the reliability and responsiveness of the entire stopping mechanism. Knowledge in this area can lead to safer journeys and an enriched riding experience.
Understanding the various components involved in stopping a two-wheeled vehicle is essential for both safety and performance. This section will explore the fundamental mechanisms that facilitate the deceleration of these vehicles, highlighting their roles and interactions within the overall system. By examining these elements, riders can gain insight into how to maintain and enhance their stopping efficiency.
Core Elements of the Stopping System
The stopping system consists of several key components that work together to bring the vehicle to a halt. Each part has a specific function that contributes to the overall performance:
- Levers: Used to activate the stopping mechanism, providing the necessary force.
- Cables: Transmit the force from the levers to the stopping mechanisms, ensuring timely response.
- Calipers: Grip the wheels to create friction, slowing down the rotation.
- Rotors: Attached to the wheels, they work in conjunction with the calipers to create stopping power.
- Pads: Provide the friction needed against the rotors, playing a crucial role in effective deceleration.
Interactions and Maintenance
Proper maintenance of these components ensures optimal performance and safety. Regular inspections and timely replacements can significantly impact the reliability of the stopping system. Consider the following best practices:
- Check the integrity of levers and cables for any signs of wear.
- Inspect calipers and pads for even wear and adequate thickness.
- Ensure rotors are clean and free from debris to maintain friction.
- Adjust cable tension as needed to ensure responsive activation.
Components of Bicycle Stopping Systems
The mechanism responsible for halting the motion of a two-wheeled vehicle is vital for safety and control. This system is comprised of several elements that work together to ensure efficient and effective deceleration. Understanding these components helps in maintaining performance and enhancing overall riding experience.
Main Elements
- Levers: These devices allow the rider to initiate the stopping process by applying force.
- Cables: Essential for transmitting the rider’s input from the lever to the stopping mechanism.
- Calipers: These components grip the wheels, providing the necessary friction to slow down or stop movement.
- Pads: Often made from materials that provide high friction, these elements make contact with the wheels to create resistance.
- Rotors: Present in some systems, they work in conjunction with pads to enhance stopping power.
Additional Components
- Master Cylinder: In hydraulic systems, this unit converts the lever force into hydraulic pressure.
- Reservoir: Stores fluid in hydraulic systems, ensuring the system operates smoothly.
- Brake Fluid: Essential in hydraulic systems for transmitting force from the lever to the calipers.
- Mounting Brackets: These secure the various components in place, ensuring stability during operation.
Types of Brake Systems Explained
Understanding the various systems that halt motion is essential for anyone interested in two-wheeled vehicles. Different mechanisms offer distinct advantages and are designed to meet diverse riding conditions and preferences. This section delves into the primary types of stopping systems available, highlighting their unique features and functions.
Mechanical Systems rely on cables and levers to apply force to the stopping mechanism. These systems are straightforward and easy to maintain, making them popular for casual riders. They provide reliable performance but may require regular adjustments to ensure optimal effectiveness.
Hydraulic Systems, on the other hand, utilize fluid pressure to operate the stopping mechanism. This technology allows for smoother and more powerful stopping action, particularly under heavy loads or in challenging conditions. While these systems may be more complex and require professional servicing, they often deliver superior performance and modulation.
Disc Mechanisms are becoming increasingly common due to their effectiveness in various environments. Positioned near the wheel, they offer consistent performance regardless of weather conditions. Their design allows for efficient heat dissipation, preventing fade during extended use.
In contrast, Rim Systems engage the outer edge of the wheel. While they can be lightweight and effective, their performance can diminish in wet conditions. However, advancements in materials and design have improved their reliability significantly.
Each type of system has its unique characteristics, catering to different riding styles and preferences. Evaluating these options allows riders to select the most suitable mechanism for their needs, ensuring a safer and more enjoyable experience.
Key Parts of Disc Brakes
Understanding the essential components of a disc stopping mechanism is crucial for both maintenance and enhancement of performance. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring effective deceleration, providing reliability and safety during operation. This section will explore the main constituents that work together to achieve optimal functionality.
Essential Components Overview
The primary components that constitute a disc stopping mechanism include the rotor, caliper, and pads. Each of these elements interacts with one another to facilitate smooth and efficient stopping action. Below is a table summarizing their key features and functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Rotor | Provides a surface for the pads to grip, allowing the mechanism to slow down or stop. |
| Caliper | Houses the pads and applies pressure to them against the rotor when engaged. |
| Pads | Friction materials that create resistance against the rotor, leading to deceleration. |
Importance of Maintenance
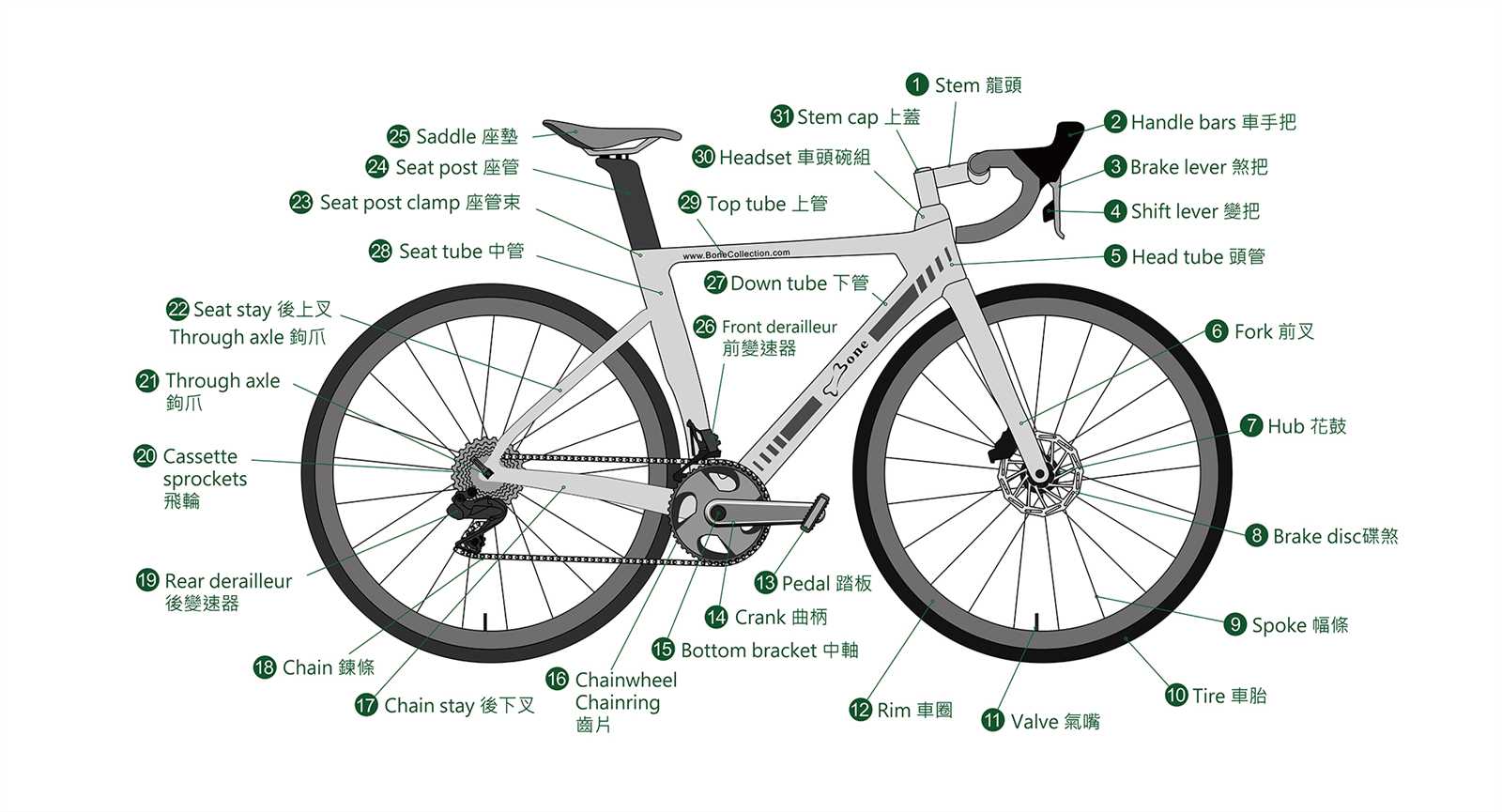
Regular inspection and care of these key elements are essential for ensuring longevity and efficiency. Neglecting any component can lead to reduced performance, increased wear, and potential safety hazards. Proper maintenance practices will enhance the overall functionality of the disc stopping system.
Essential Elements of Rim Brakes
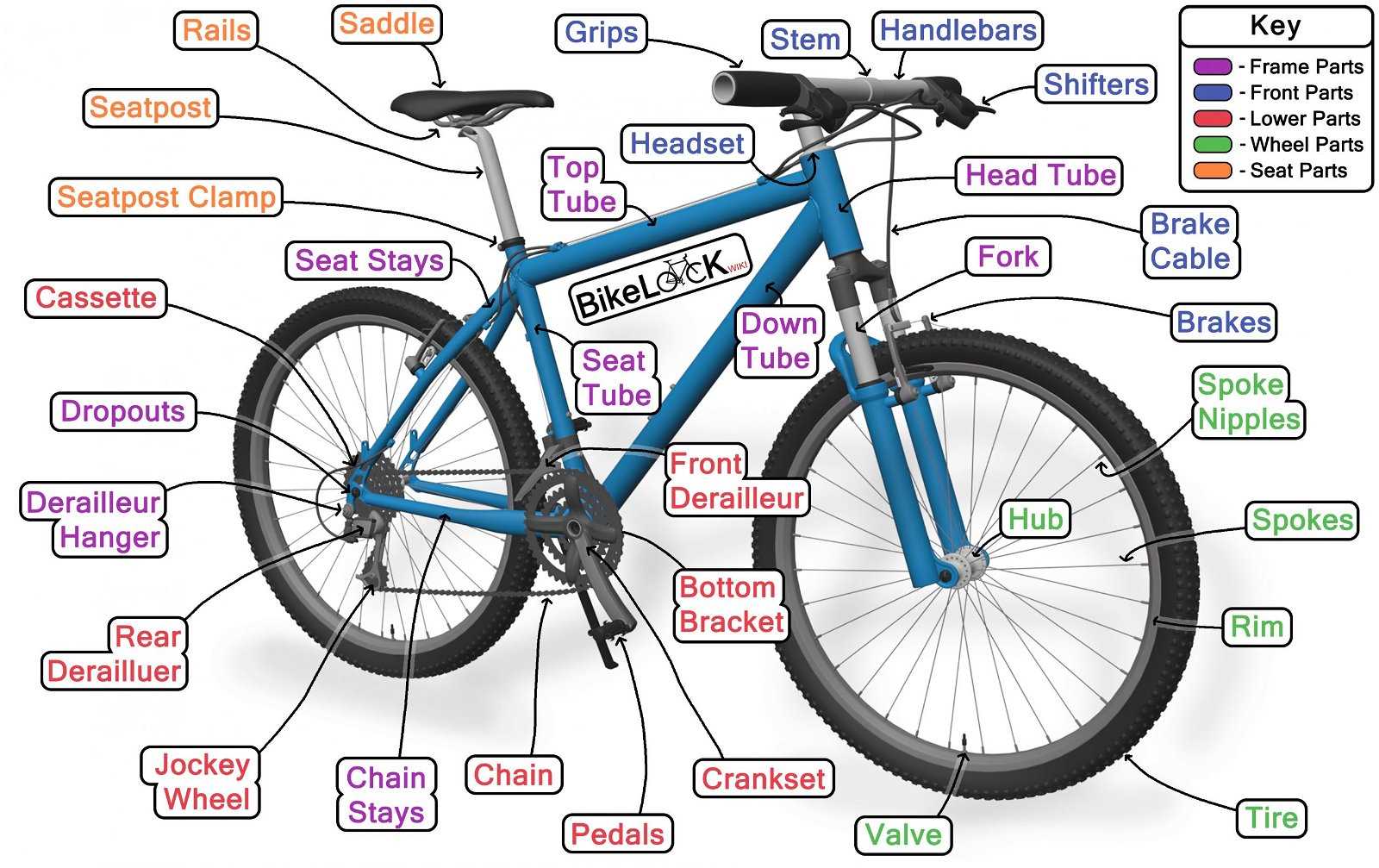
The effectiveness of a stopping system relies on several crucial components that work in harmony to ensure smooth and reliable deceleration. Understanding these fundamental elements is essential for maintenance and performance optimization.
Key Components
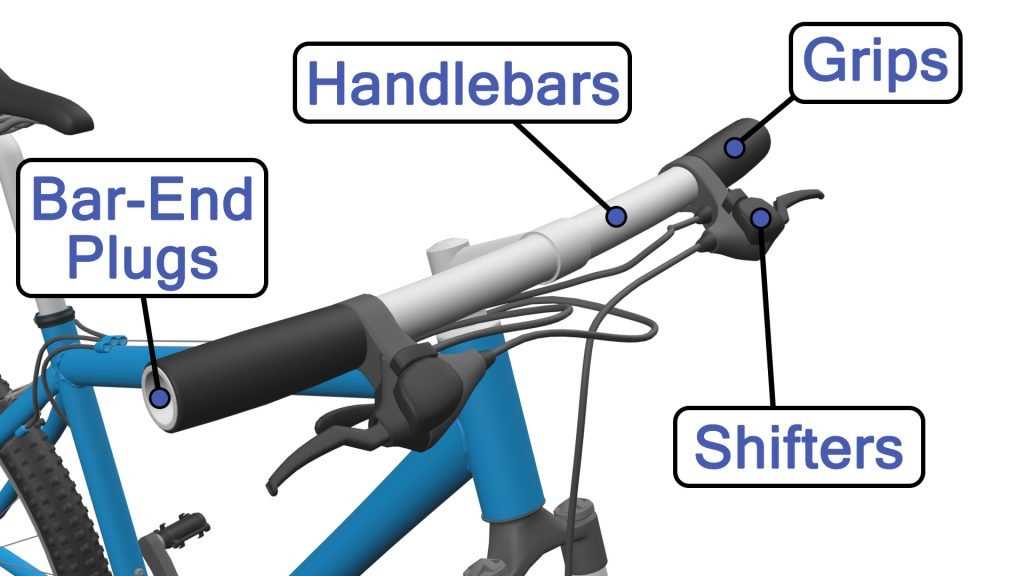
At the heart of this system lies a robust framework that includes a pair of friction materials, which press against the wheel’s outer surface. This interaction generates the necessary force to reduce speed. Additionally, the connection mechanism, often a lever or cable, facilitates the engagement of these materials, allowing the rider to control the intensity of the deceleration.
Maintenance and Care
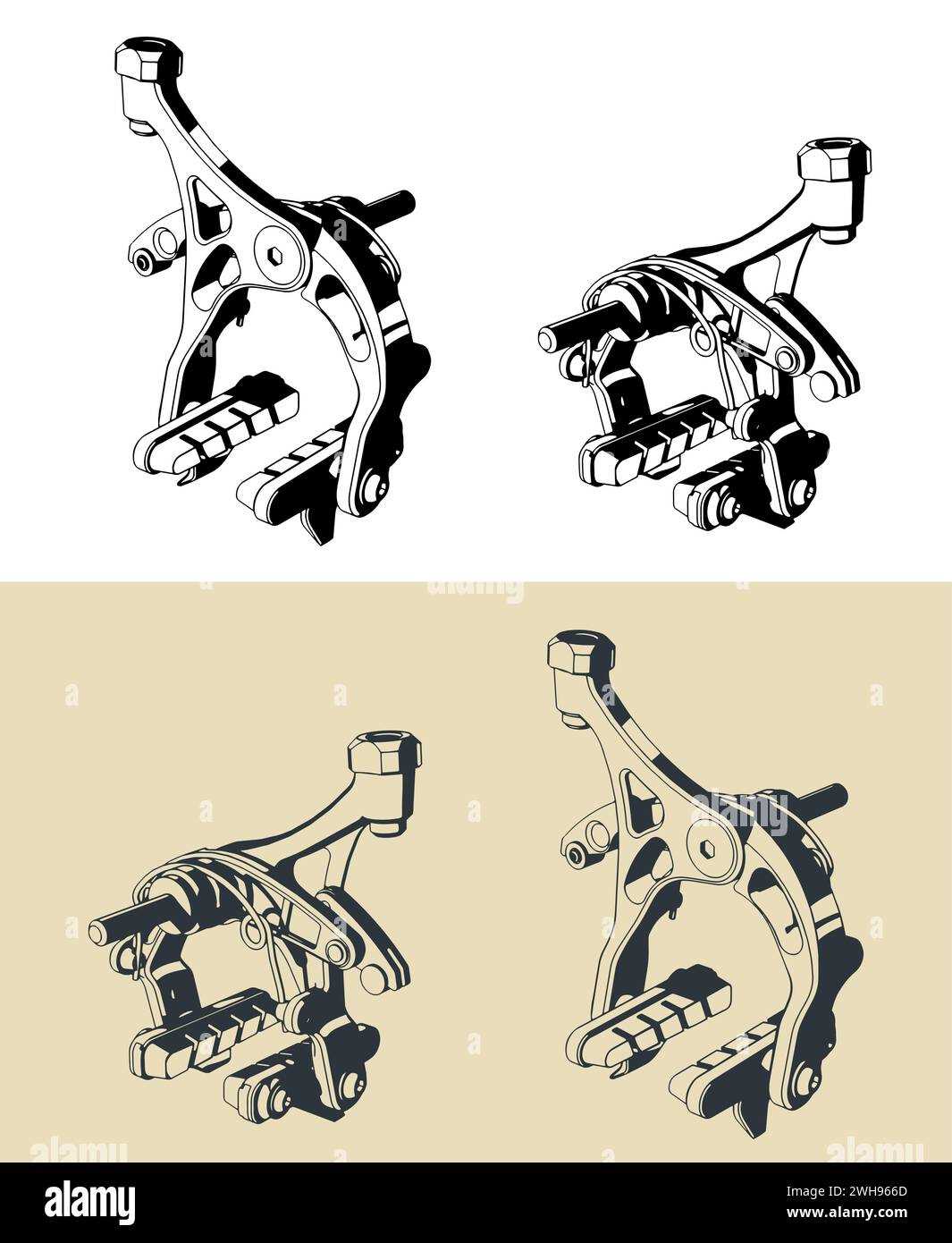
Regular inspection and upkeep of these components are vital for safety and performance. Ensuring that the friction materials are free from debris and wear can significantly enhance the overall effectiveness. Moreover, checking the alignment and tension of the connecting mechanism is crucial to achieving optimal responsiveness during operation.
Functions of Brake Cables and Levers
The components responsible for controlling the stopping mechanism of a two-wheeled vehicle play a vital role in ensuring safety and responsiveness. These elements work in harmony to transmit force from the handlebar to the stopping mechanism, allowing for precise control during operation. Understanding their functions is essential for maintaining optimal performance and rider confidence.
Role of Cables
Cables serve as the conduits for force transfer, linking the lever at the handlebar to the stopping mechanism located at the wheel. When the lever is engaged, the cable tightens, applying pressure to the stopping mechanism. This action initiates the process of slowing down or halting the movement of the vehicle. High-quality cables are crucial for smooth operation, as they minimize friction and ensure responsive action.
Function of Levers
Levers are the interface between the rider and the stopping mechanism, providing the necessary leverage to engage the stopping system. When the rider pulls the lever, it creates a mechanical advantage that multiplies the force applied. This design allows for easier engagement of the stopping mechanism, making it accessible even under varying conditions, such as when descending hills or navigating through traffic. Proper adjustment and maintenance of the lever ensure effective communication between the rider and the stopping system.
Importance of Brake Pads and Shoes
Components designed for friction play a crucial role in the overall safety and functionality of a vehicle. Their primary function is to create the necessary resistance for effective stopping power. The efficiency of these elements significantly influences the overall performance and reliability during operation.
High-quality friction materials ensure consistent contact with the surface, which is vital for maintaining control and stability. As these elements wear down over time, their effectiveness diminishes, leading to potential safety hazards. Regular inspection and timely replacement are essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent unexpected failures.
The choice of appropriate materials can also enhance the lifespan of other related components, minimizing maintenance costs. Therefore, understanding the significance of these friction elements is essential for anyone concerned with safe and reliable transportation.
How Brake Calipers Operate

Understanding the functionality of stopping mechanisms is essential for ensuring safety and performance. These components play a crucial role in the deceleration of a vehicle, utilizing hydraulic force to apply pressure effectively. The interaction between various elements leads to a significant reduction in speed, providing control and stability.
At the core of this mechanism lies the caliper, which houses a pair of essential components:
- Pistons: These elements are responsible for exerting pressure on the friction material, allowing for effective contact with the rotating surface.
- Friction Material: This component creates the necessary resistance, converting kinetic energy into heat, thereby slowing down the motion.
The operation process involves several key steps:
- When the operator engages the stopping system, hydraulic fluid is directed into the caliper.
- This fluid pressurizes the pistons, forcing them outward.
- The pistons push the friction material against the spinning surface, creating friction.
- This friction generates heat and reduces the rotational speed of the wheel.
- Once the stopping system is disengaged, the pistons retract, allowing the friction material to separate from the surface.
Regular maintenance of these mechanisms is vital to ensure optimal performance and safety. Inspections should focus on:
- Checking for fluid leaks
- Assessing the condition of the friction material
- Ensuring proper alignment of the caliper
Maintenance Tips for Brake Systems
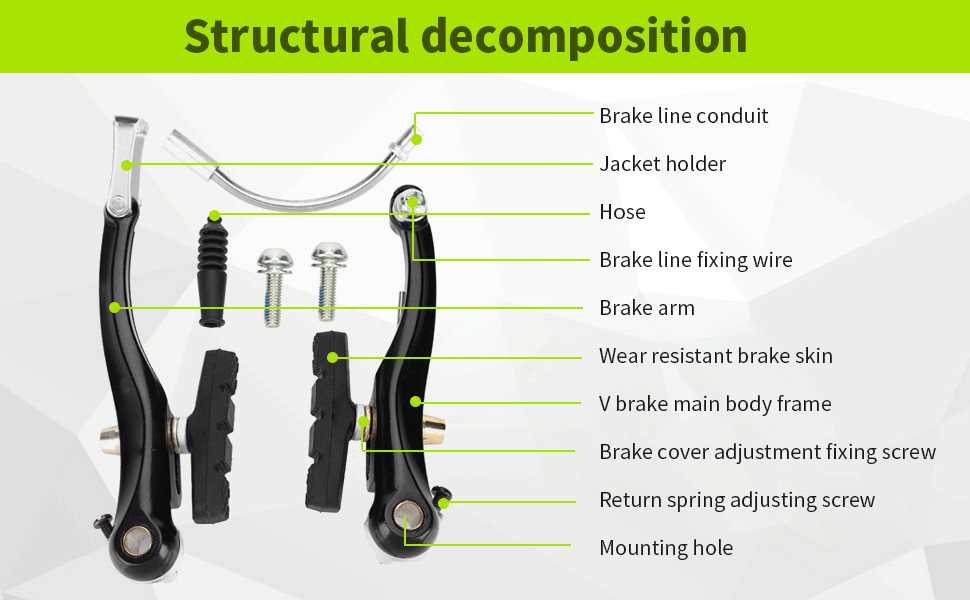
Ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of the stopping mechanism is essential for any vehicle. Regular upkeep not only enhances safety but also improves overall handling. Here are some vital suggestions to maintain these crucial components effectively.
Regular Inspection: Conduct frequent assessments of the entire assembly to identify signs of wear and tear. Look for any unusual noises or changes in responsiveness that may indicate potential issues.
Clean Components: Keep all elements free from dirt and debris. Using a soft cloth or brush, gently clean the surfaces to prevent contamination that could lead to diminished functionality.
Lubricate Moving Parts: Ensure that all moving elements are adequately lubricated to facilitate smooth operation. Use a suitable lubricant that does not attract dust or dirt.
Monitor Performance: Pay attention to how the system performs during operation. If there is a noticeable decrease in effectiveness, investigate the underlying causes immediately.
Replace Worn Components: Do not hesitate to replace any parts that show significant signs of wear. Timely replacements can prevent more serious issues and ensure reliable performance.
Seek Professional Help: If you are unsure about any maintenance procedure, consult a professional technician. Expert advice can save you time and resources while ensuring optimal safety.