Understanding the intricate layout of equipment assemblies can be invaluable when aiming to maintain or restore machinery to peak condition. This guide provides insights into the organization of various internal elements, detailing each section’s role and connections. With clear visual references, navigating complex setups becomes a straightforward task, even for those new to the process.
Each section within this reference highlights essential components, giving a clear picture of how individual elements interact within the larger assembly. Whether you’re tackling a repair or simply exploring the equipment’s structure, this overview is designed to make identifying and working with each piece easier and more efficient.
Finally, this resource serves as both a learning tool and a practical guide for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. By breaking down each segment, this guide aims to foster a deeper understanding of how various sections function and how they can be best utilized, helping to extend the longevity and performance of your machinery.
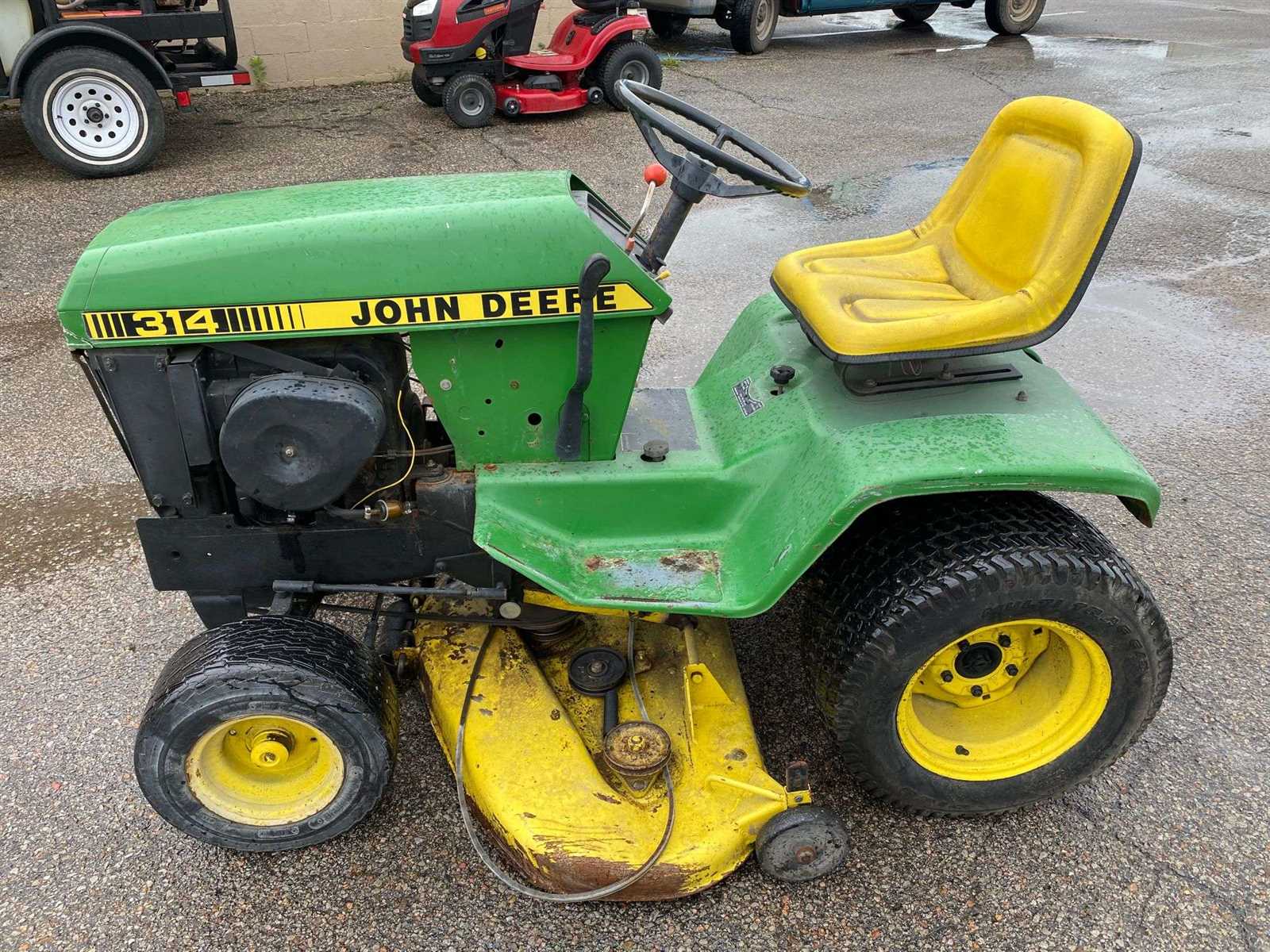
Essential Components of John Deere 314

Understanding the primary elements of this machine allows for smoother operation, efficient maintenance, and enhanced performance. Each part plays a specific role, ensuring that the equipment works seamlessly for various tasks. Below is an outline of the core components that make this machinery highly functional and durable.
- Engine Assembly: The powerhouse of the machine, responsible for delivering energy to drive all its essential functions. It includes multiple smaller parts that work together to ensure consistent output and efficiency.
- Transmission System: This part controls the flow of power from the engine to the wheels, allowing for smooth movement and handling. It includes gears and linkages essential for managing different speeds and terrains.
- Hydraulic Mechanism: A vital system for operating attachments and additional tools. The hydraulic assembly provides the necessary force to raise, lower, and adjust equipment with precision and ease.
- Cooling Unit: Essential for regulating engine temperature, preventing overheating during prolonged use. This system helps maintain optimal conditions within the machine, prolonging its lifespan.
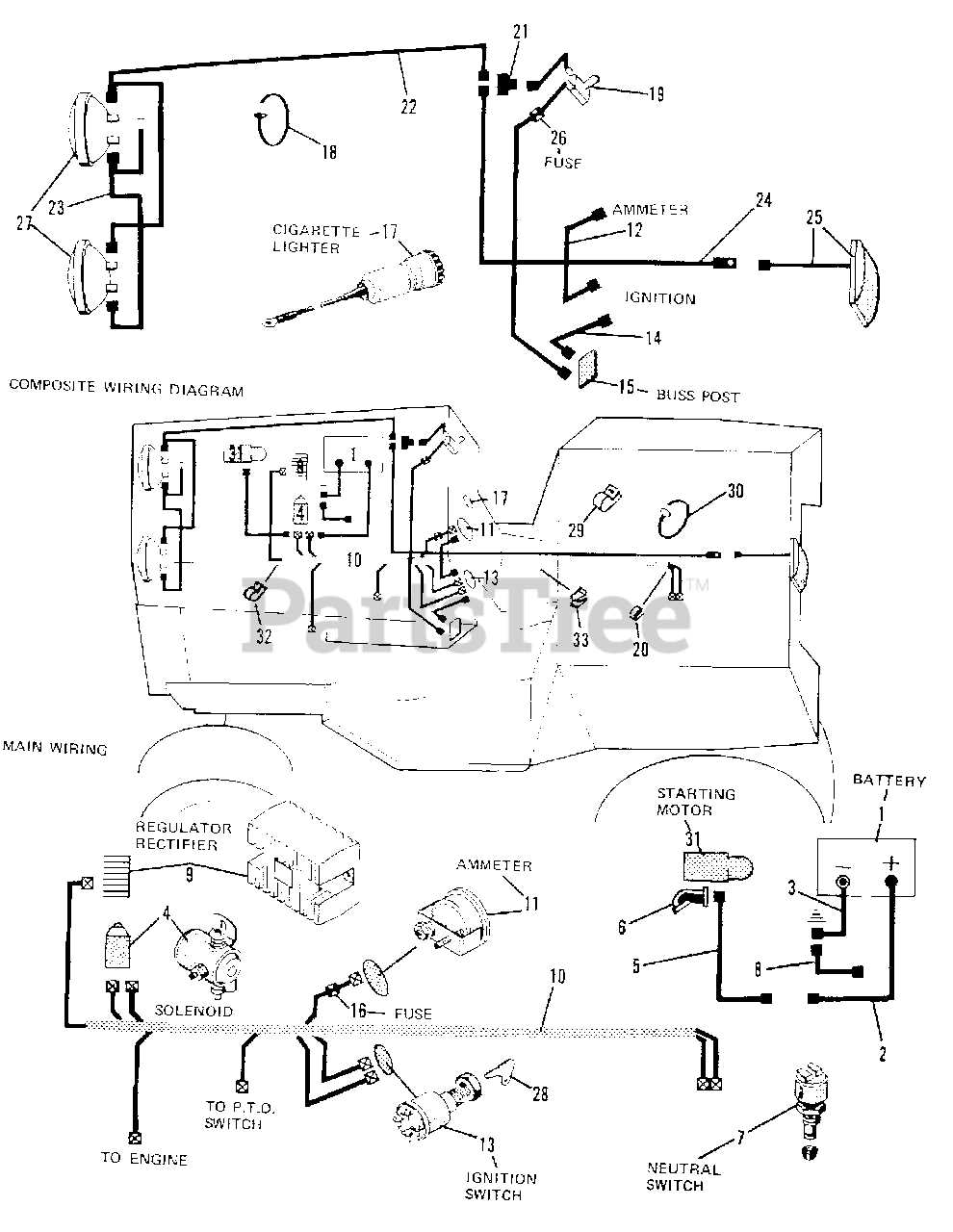
- Electrical Components: The wiring and controls are essential for proper functionality, from ignition to lighting. Reliable electrical parts ensure safety and operational accuracy.
Each component contributes to the overall functionality, making the machine a robust tool for various ta
Overview of Engine Assembly
The engine assembly comprises several interconnected components working together to deliver optimal performance. Each element, from the core structure to the smallest fastener, plays a crucial role in ensuring the system’s durability, efficiency, and smooth operation. Understanding the layout and function of each part can aid in maintenance and troubleshooting, as well as in ensuring long-term reliability.
Main Components of the Engine
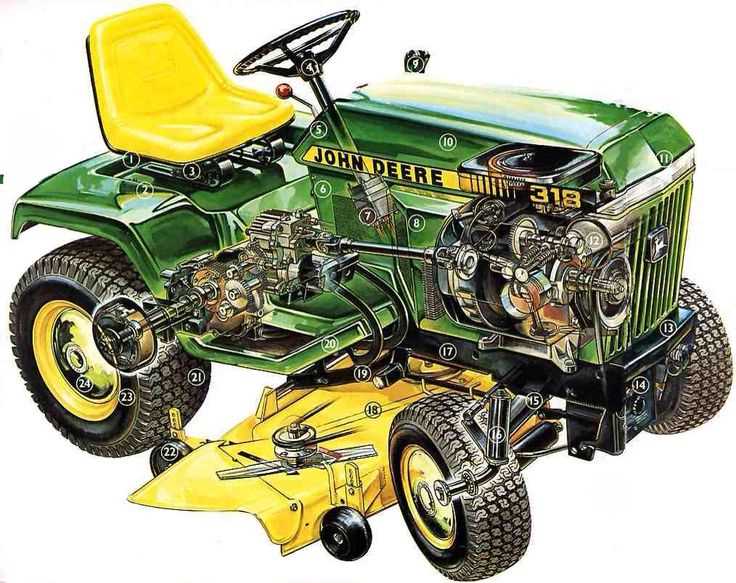

This assembly includes primary elements responsible for power generation and efficiency. Key components include the cylinder block, crankshaft, pistons, and camshaft, each contributing to different stages of the combustion process. Proper alignment and calibration of these parts are essential to maintain consistent performance and avoid issues related to wear and overheating.
Auxiliary Components and Connectors
In addition to the main structure, several auxiliary systems support and regulate the engine’s function. These include the fuel injection system, cooling system, and exhaust system, all essential for maintaining balance and stability within the engine’s operation. Connectors and fasteners within these systems require regular inspection to ensure seamless integration and reliability.
| Component | Function | Maintenance Tips | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cylinder Block | Houses the cylinders, enabling compression and combustion. | Regularly inspect for cracks or wear. |
| Component | Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steering Wheel | Allows the operator to control the direction by turning it to transmit force through the mechanism. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Steering Column | Connects the wheel to other internal parts, facilitating the transfer of motion. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Linkage | Consists of rods and levers that guide the wheels based on the wheel’s rotation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydraulic Cylinder | Provides additional power to the system, making it easier to turn the wheels, especially under heavy loads. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Steering Knuckles | Attached to the front wheels, enabling them to pivot in response to directional changes. |
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Hydraulic Pump | Generates flow by converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, moving fluid through the system. |
| Hydraulic Cylinder | Transforms hydraulic energy back into mechanical energy, enabling linear motion for various attachments. |
| Control Valve | Regulates fluid flow and pressure, directing the movement of the hydraulic actuators based on operator input. |
| Reservoir | Stores hydraulic fluid, providing a supply for the pump and allowing for the expansion of fluid as it heats up. |
| Filters | Remove contaminants from the hydraulic fluid to protect components and maintain system efficiency. |
Conclusion
A thorough comprehension of the hydraulic system’s components and their respective functions is vital for optimal performance and reliability. Regular inspection and maintenance of these elements contribute significantly to the longevity of the equipment and enhance overall productivity in agricultural operations.
Front and Rear Axle Assembly
The axle assembly plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and stability of machinery, providing support and enabling efficient movement. This section delves into the essential components and their interconnections, highlighting the importance of a well-structured assembly for optimal performance.
Components of the Axle Assembly
The assembly consists of several integral elements, including the axle housing, differential, and various gears. Each component is designed to withstand heavy loads and ensure smooth operation under varying conditions. The quality and alignment of these parts are vital for maintaining balance and control.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
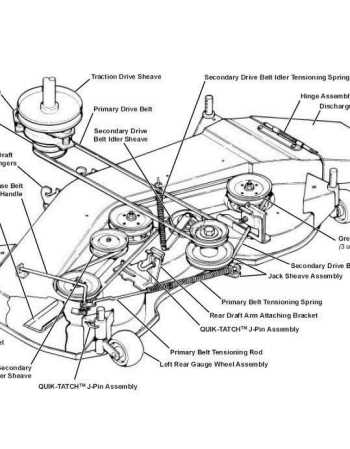
Regular inspection and maintenance of the axle assembly are essential to prevent wear and tear. Signs of issues may include unusual noises or vibrations during operation. Addressing these problems promptly can enhance longevity and efficiency, ensuring the machinery operates at its best.
Common Maintenance Parts and Replacements
Regular upkeep is essential for optimal performance and longevity of machinery. Understanding which components require periodic attention can greatly enhance efficiency and reliability. Below are some frequently needed replacements that contribute to smooth operation.
| Component | Description | Frequency of Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Filters | These components trap contaminants from fluids, ensuring clean operation. | Every 50-100 hours of operation |
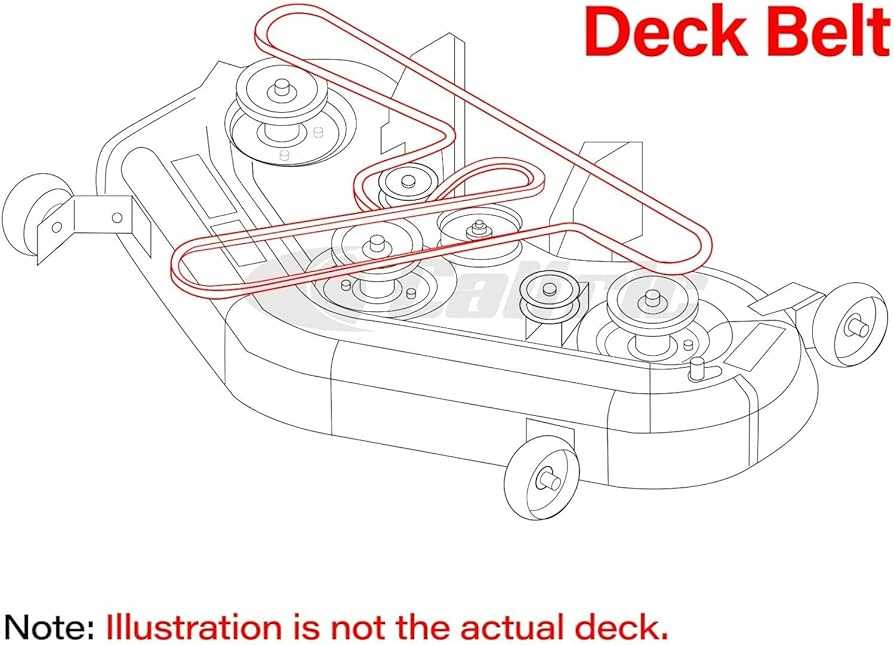
| Belts | Used for transferring power between different parts, they are vital for functionality. | Check every 100 hours, replace as needed |
| Blades | Essential for cutting and maintaining optimal grass height. | Every 25-50 hours, or when dull |
| Battery | Provides the necessary power for starting and running electrical components. | Replace every 2-3 years |
| Lubricants | Used to minimize friction between moving parts, enhancing performance. | Check levels regularly, apply as necessary |