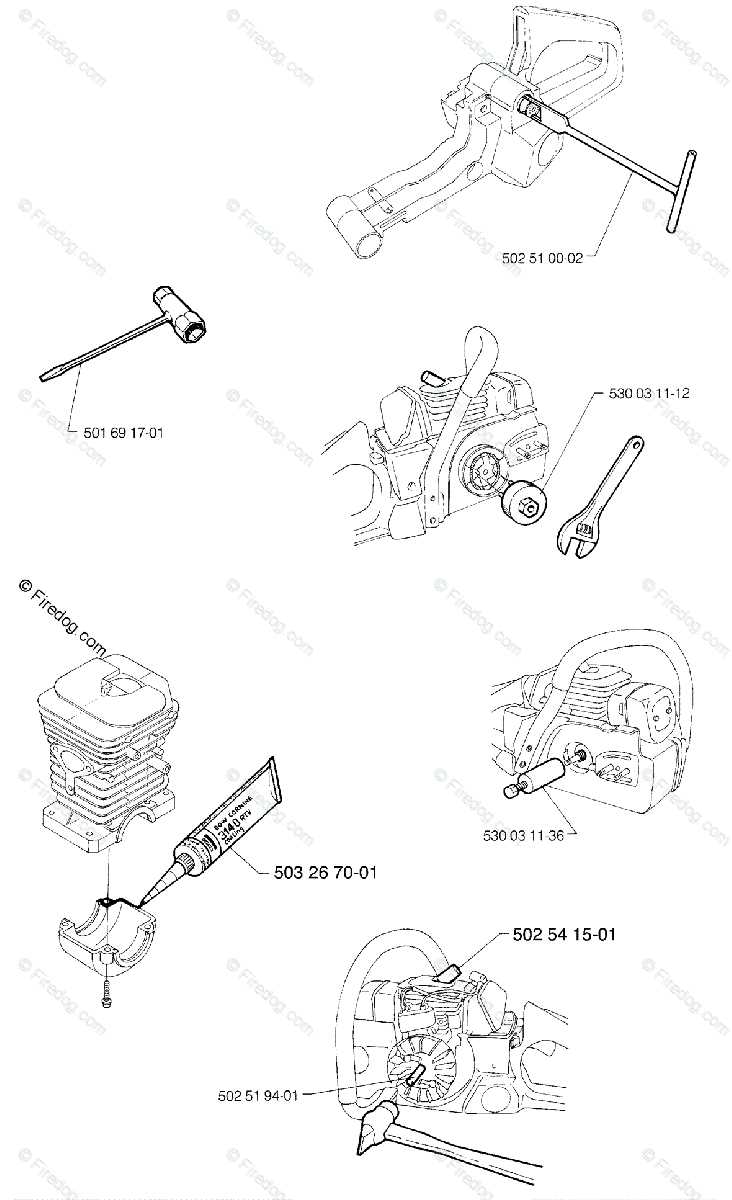
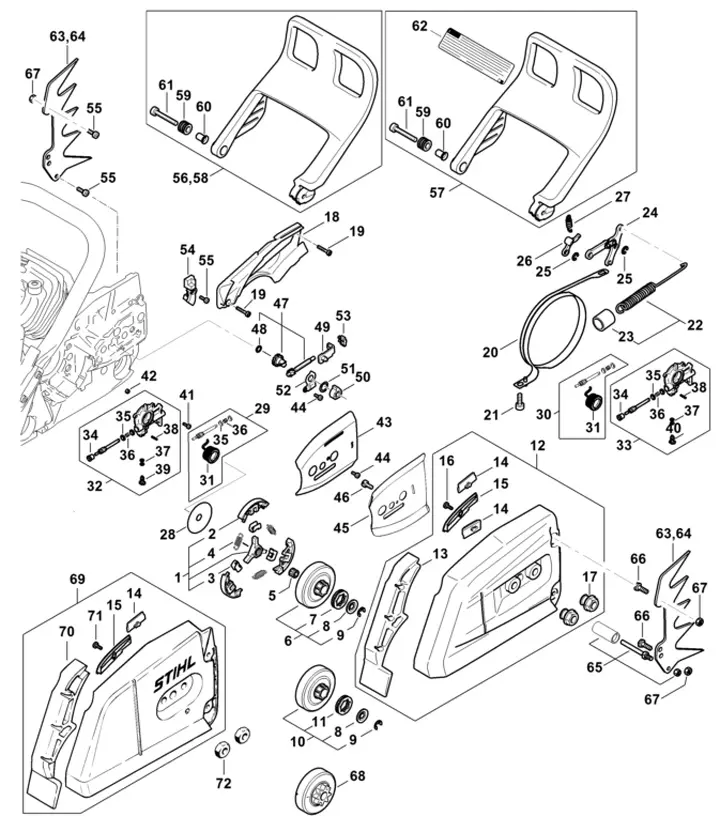
The intricate machinery of a powerful cutting tool encompasses a variety of essential elements, each contributing to its efficient operation. These components work in harmony, enabling the device to perform demanding tasks with precision and ease. A comprehensive overview of these features reveals their significance in enhancing functionality and user experience.
In any advanced mechanical system, recognizing how each element interacts is crucial. From the engine that drives the entire apparatus to the blades that execute the cutting action, understanding these relationships helps users appreciate the craftsmanship involved. Furthermore, knowing the roles of various components can aid in maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring longevity and reliability.
This exploration delves into the specific features of this powerful implement, shedding light on their design and purpose. By examining these integral sections, we can gain insights into how they collectively enhance performance and safety, making the tool an indispensable ally for both professionals and hobbyists alike.
Understanding Chainsaw Components

To effectively operate and maintain a powerful cutting tool, it is essential to comprehend the various elements that contribute to its functionality. Each segment plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and safety during use, facilitating a deeper connection between the user and the equipment.
Core Elements
The main constituents include the engine, guide bar, and cutting chain, each working in harmony to achieve efficient cutting. The engine serves as the powerhouse, generating the necessary force, while the guide bar provides stability and direction. The cutting chain, equipped with sharp teeth, performs the actual slicing, demonstrating the ultimate synergy of design and engineering.
Supportive Features
Additional components, such as the fuel system and safety mechanisms, enhance the tool’s usability. The fuel system ensures a steady supply of energy, while features like the brake and throttle control help manage speed and prevent accidents. Understanding these supportive elements is vital for achieving proficiency and maximizing safety during operation.
Key Parts of a Chainsaw Explained
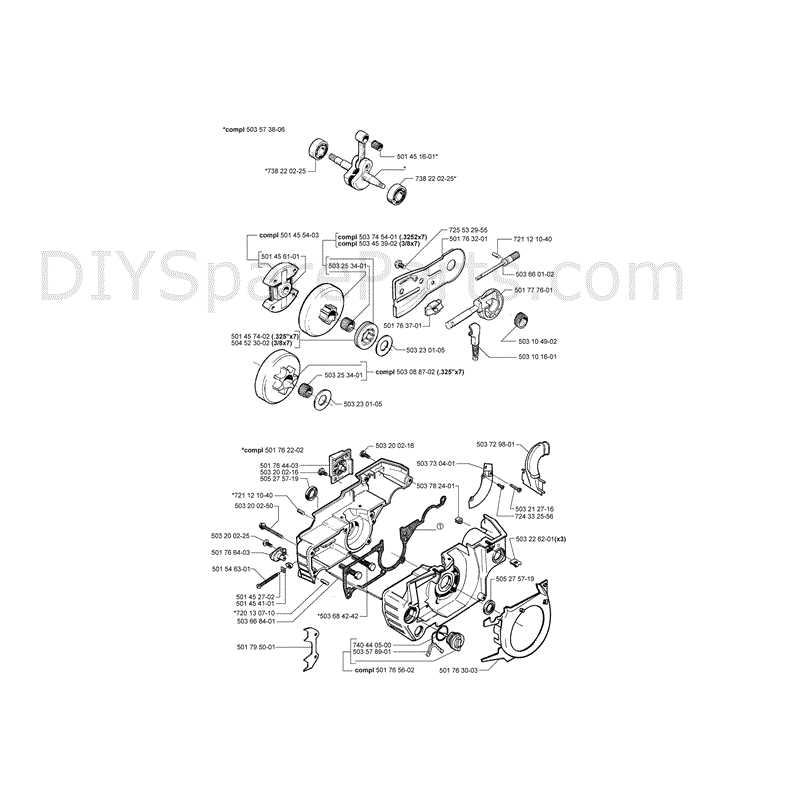
Understanding the essential components of this powerful tool is crucial for optimal performance and maintenance. Each element plays a significant role in ensuring efficiency, safety, and ease of use. Here, we delve into the fundamental elements that contribute to its operation.
Engine and Fuel System
The heart of the machine is the engine, which converts fuel into mechanical energy. A reliable fuel system ensures a steady supply of energy, enabling the tool to function smoothly. Regular checks on the fuel lines and filters are vital for preventing blockages and ensuring longevity.
Cutting Mechanism
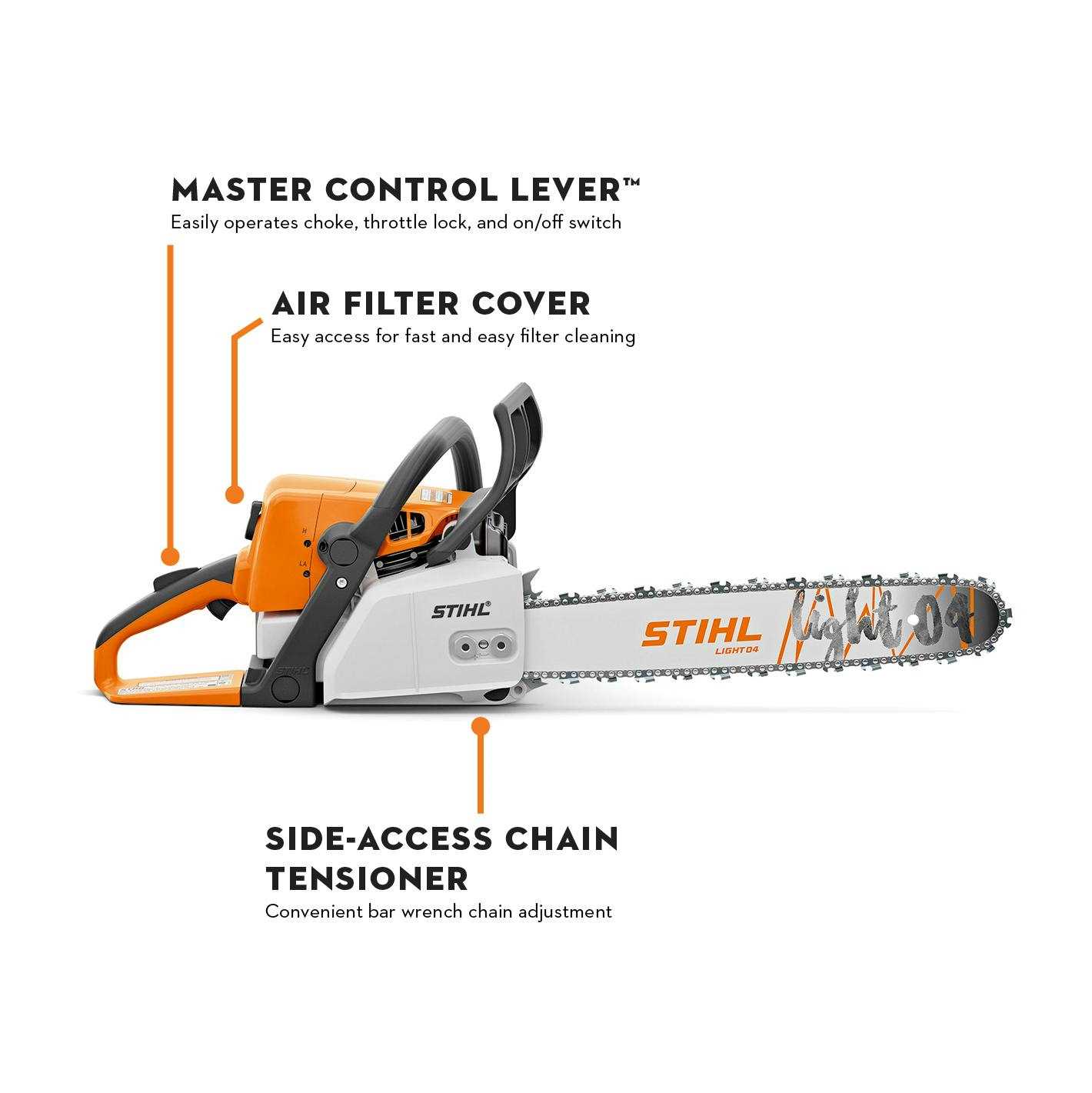
At the forefront of its design is the cutting mechanism, consisting of a guide bar and chain. The guide bar provides stability, while the chain features sharp teeth that slice through wood. Maintaining the sharpness and tension of the chain is essential for achieving clean cuts and enhancing safety during operation.
Functionality of the Chainsaw Mechanism
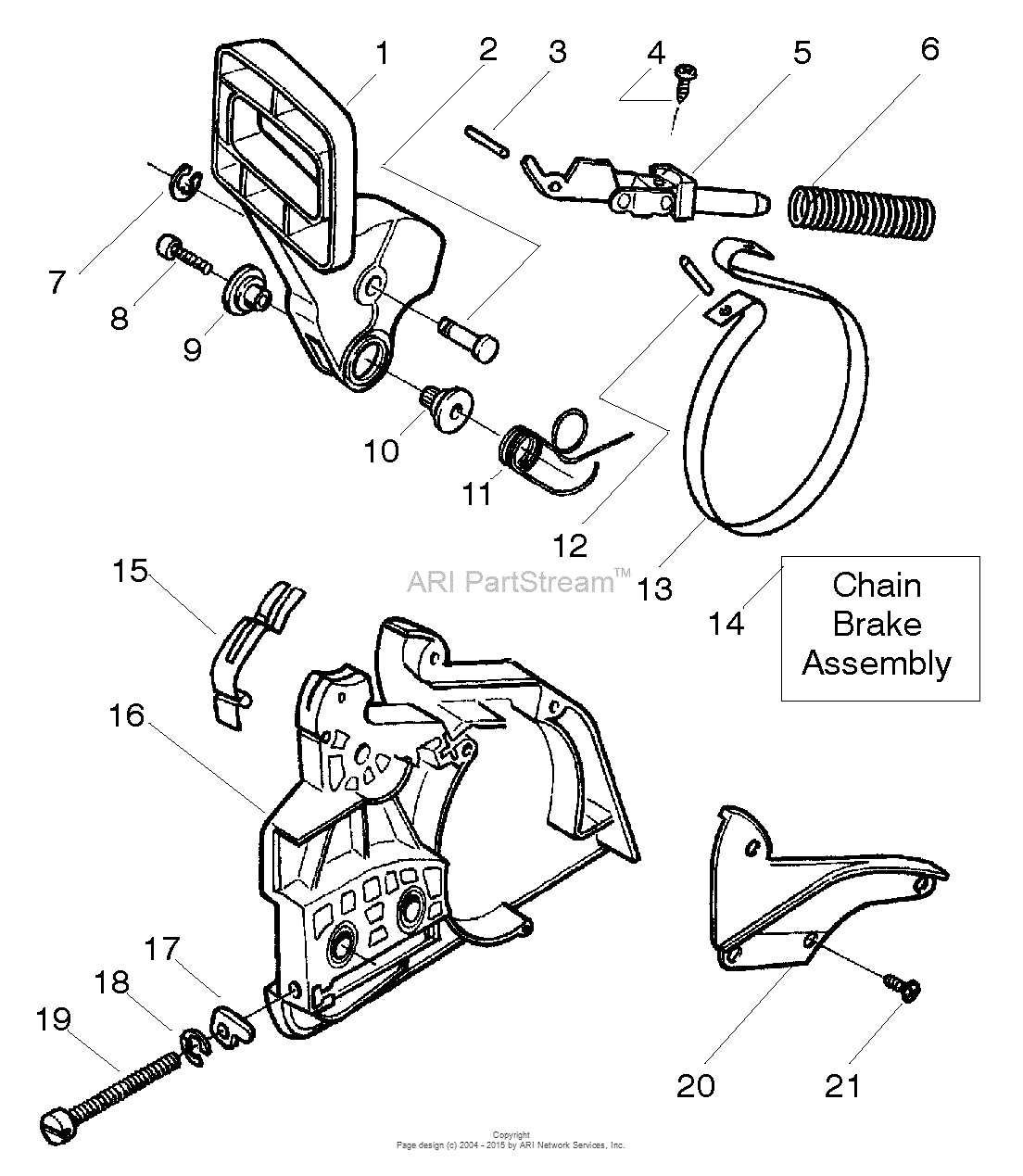
This section explores the intricate workings of a powerful cutting tool, highlighting the interrelated components that contribute to its efficiency. Understanding how these elements function together is crucial for grasping the overall performance and capabilities of this machine.
The operation of this tool relies on a series of coordinated actions that allow for effective cutting through various materials. Here are the key mechanisms involved:
- Power Source: The engine generates the necessary energy, converting fuel into mechanical power.
- Drive Mechanism: This element transfers the power from the engine to the rotating component, enabling it to move at high speeds.
- Cutting Element: Designed with sharp teeth, this part engages the material, creating a clean cut.
- Chain Tensioning System: This mechanism ensures that the cutting element remains taut, optimizing performance and safety.
- Safety Features: Integrated systems prevent accidental activation and provide protection to the operator during use.
Each of these components plays a vital role in the overall functionality, ensuring that the tool operates smoothly and efficiently. Understanding this synergy allows users to appreciate the engineering behind it and enhances their operational skills.
Safety Features in Chainsaw Design
When it comes to power tools designed for cutting, prioritizing user safety is paramount. Advanced engineering and thoughtful design have led to the incorporation of various protective mechanisms aimed at minimizing risks during operation. These features not only enhance user confidence but also promote safer working environments.
Automatic Chain Brake
One of the most critical innovations in tool safety is the automatic chain brake. This mechanism activates instantly upon sudden movements, effectively halting the chain’s rotation. By reducing the likelihood of kickback incidents, this feature significantly protects the operator from potential injuries, making it an essential component in modern models.
Ergonomic Handles and Grip
Another key aspect of safety is the design of the handles and grip areas. Ergonomic shapes not only facilitate comfortable handling but also allow for better control during operation. Non-slip materials enhance grip stability, ensuring that the user maintains a secure hold even in challenging conditions. This thoughtful approach helps prevent accidental slips, further enhancing overall safety.
Maintenance Tips for Chainsaw Longevity
Proper upkeep is essential for ensuring the durability and performance of your cutting tool. By following a few straightforward practices, you can significantly enhance its lifespan and efficiency.
- Regularly clean the exterior to prevent debris buildup.
- Check and tighten all fasteners to maintain structural integrity.
- Sharpen the cutting chain frequently to ensure smooth operation.
- Inspect the guide bar for wear and replace if necessary.
- Store in a dry place to avoid rust and corrosion.
Incorporating these practices into your routine will help maintain optimal functionality and extend the life of your equipment.
Common Chainsaw Troubleshooting Issues
When working with power tools, encountering operational challenges is not uncommon. Understanding the frequent issues that may arise can help users quickly identify and resolve problems, ensuring efficient performance and safety during use.
Engine Performance Problems
A common dilemma involves difficulties in starting the engine. This may result from fuel issues, such as stale gasoline or improper mixing of oil and gas. Additionally, a clogged air filter can restrict airflow, leading to poor combustion. Regular maintenance of the fuel system and filter can prevent these issues and enhance overall performance.
Cutting Efficiency Issues
Another frequent challenge is diminished cutting effectiveness. This can be attributed to a dull chain, which requires sharpening or replacement. Furthermore, improper tension can lead to inefficient cutting, making it essential to regularly check and adjust the chain tension. Maintaining the cutting equipment not only improves performance but also extends the lifespan of the tool.
Comparing Gas and Electric Chainsaws
When it comes to cutting tools, the choice between fuel-powered and electric models often sparks debate among enthusiasts and professionals alike. Each type brings its own set of advantages and drawbacks, making the decision largely dependent on the user’s specific needs and preferences. Understanding these differences can help in selecting the right tool for various tasks.
Performance and Power
Fuel-powered models generally offer higher power output, enabling them to tackle larger and more demanding tasks with ease. They are ideal for heavy-duty applications, such as felling trees or cutting through thick logs. On the other hand, electric versions provide sufficient power for lighter tasks and are often favored for their quiet operation and lower maintenance requirements. Users seeking mobility and ease of use might find electric models particularly appealing.
Convenience and Environment
In terms of convenience, electric options typically win out due to their lightweight nature and the absence of fuel-related hassles. Users can simply plug in and start working without worrying about refueling or emissions. Conversely, fuel-powered versions may require more upkeep but offer extended runtime, making them suitable for larger jobs away from power sources. Ultimately, the choice hinges on the balance between performance demands and personal comfort.
Innovations in Chainsaw Technology
Recent advancements in cutting equipment technology have transformed the landscape of outdoor work and forestry. These innovations enhance efficiency, safety, and user experience, catering to both professionals and hobbyists alike. The integration of modern materials, improved ergonomics, and smart features are at the forefront of this evolution.
Enhanced Performance
One of the most significant breakthroughs is the development of high-efficiency engines and battery systems. These power sources not only increase cutting speed but also reduce emissions and noise levels, making outdoor tasks more environmentally friendly and less disruptive. Battery-operated models are particularly popular, providing users with the freedom to operate without the constraints of fuel lines and cords.
Smart Technology Integration
Another exciting trend is the incorporation of smart technology into cutting devices. Features such as automatic tensioning systems, built-in diagnostics, and connectivity with mobile applications allow users to monitor performance and receive maintenance alerts. These advancements not only improve usability but also prolong the lifespan of the equipment, ensuring that users can work efficiently without frequent interruptions.