
Understanding how different elements of cooling systems function together is crucial for maintaining efficient climate control. This guide delves into the key mechanisms and features that ensure optimal temperature regulation in residential and commercial environments.
In modern cooling units, each component plays a specific role in maintaining a comfortable atmosphere. From the core systems responsible for heat exchange to the additional features enhancing user experience, knowing their functions helps in troubleshooting and improving performance.
Explore how these integral parts work together to create a seamless and efficient solution for cooling and comfort.
Understanding Mini Split Air Conditioner Components
Comprehending the various elements involved in this cooling system helps users maintain and optimize its performance. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring proper function, efficiency, and durability. A closer look at these components reveals their distinct purposes and how they work together to provide effective climate control.
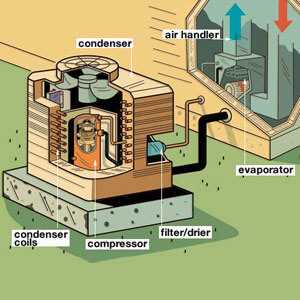
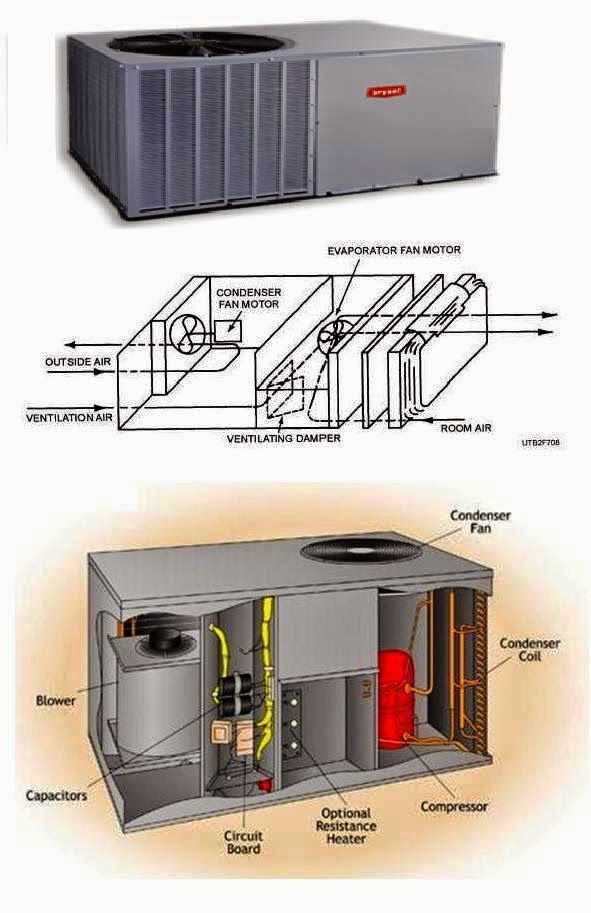
- Compressor: The heart of the system, responsible for circulating the refrigerant through the system by increasing its pressure.
- Evaporator: The section where the refrigerant absorbs heat from the indoor environment, transforming it into vapor.
- Condenser: Located in the external unit, it expels the absorbed heat outside by turning the refrigerant back into a liquid state.
- Expansion Valve: This device regulates the refrigerant flow into the evaporator, ensuring the proper amount is used for cooling.
- Fans: Positioned in both the internal and external units, they move air over the evaporator and condenser to support the heat exchange process.
Key Internal Parts of a Mini Split System
Understanding the primary components within this cooling solution is essential for optimal performance. Each element works in harmony to maintain temperature control, ensuring energy efficiency and comfort. These components are strategically designed to regulate and distribute cooling effectively, providing users with a seamless experience.
Compressor
The compressor acts as the system’s heart, circulating refrigerant and maintaining the necessary pressure levels for effective heat exchange. It drives the cooling cycle, converting low-pressure gas into high-pressure gas, enabling the absorption and release of heat.
Evaporator Coil

The evaporator coil is responsible for absorbing heat from the surrounding environment. As refrigerant passes through this component, it changes from liquid to gas, removing warmth from the air and contributing to the cooling process. This transformation is crucial for regulating the temperature.
The Role of the Compressor in Cooling
The compressor plays a fundamental part in the cooling process, ensuring the system can efficiently regulate temperatures. By compressing and circulating refrigerant, it creates the necessary conditions for heat exchange and effective temperature control within a space. This component is crucial for maintaining a consistent and comfortable environment.
How Compression Works
In the cooling cycle, the compressor is responsible for increasing the pressure of the refrigerant, turning it into a high-temperature, high-pressure gas. This process helps move the refrigerant through the system, enabling it to release heat outside and absorb warmth from the interior, facilitating the overall cooling process.
Compressor Types and Efficiency
There are several types of compressors, each designed to suit different efficiency needs. Common varieties include rotary, scroll, and reciprocating compressors. The choice of compressor impacts not only energy consumption but also the durability and performance of the entire cooling system.
Compressor Type Advantages Disadvantages Rotary Compact, reliable Limited power for larger systems Scroll High efficiency, low noise How the Evaporator Coil Functions
The evaporator coil is a crucial component in the cooling system, responsible for absorbing heat from the surrounding environment. It operates through a cycle where a refrigerant passes through the coil, enabling efficient thermal exchange. This process is essential for maintaining a comfortable temperature in indoor spaces.
Heat Absorption Process

As the refrigerant flows through the evaporator coil, it undergoes a phase change from a liquid to a gas. During this transition, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the surrounding air, cooling the area effectively. The ability of the coil to facilitate this transfer is what makes it a key element in the cooling mechanism.
Maintaining Efficiency
To ensure proper performance, the coil must remain clean and free from debris. A well-maintained evaporator coil allows the refrigerant to function efficiently, which directly impacts the overall cooling system’s effectiveness. Neglecting the coil can lead to reduced efficiency and higher energy consumption.
Condensing Unit and Its Importance
The condensing unit plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of any cooling system. It is responsible for the efficient transfer of heat, ensuring the proper circulation of refrigerant within the system. By managing temperature and pressure, it helps maintain an optimal cooling environment, which is vital for the performance and longevity of the entire system.
Main Functions of the Condensing Unit
- Heat Dissipation: The unit releases heat absorbed by the refrigerant, lowering its temperature for further cooling cycles.
- Pressure Regulation: It controls the pressure levels within the system, ensuring that the refrigerant is in the right state for each stage of operation.
- Energy Efficiency: By effectively managing heat exchange, the condensing unit contributes to the overall energy efficiency of the system.
Components of the Condensing Unit

- Compressor: The driving force that circulates refrigerant throughout the system, compressing it for efficient heat release.
- Explaining the Expansion Valve’s Purpose
The expansion valve plays a vital role in regulating the flow of refrigerant through a cooling system. It controls the amount of liquid that enters the evaporator, helping maintain efficiency and proper functioning. By adjusting pressure and flow, it ensures the refrigerant evaporates effectively, which is essential for heat exchange and the overall cooling process.
How the Valve Works
The expansion valve works by reducing the pressure of the liquid refrigerant before it enters the evaporator coil. This pressure drop causes the refrigerant to expand, transforming it into a mixture of liquid and gas. The valve adjusts the flow based on the cooling system’s needs, ensuring that the evaporator coil gets the right amount of refrigerant for optimal performance.
Key Benefits
By regulating refrigerant flow, the expansion valve ensures the system operates efficiently, preventing overcooling or undercooling. It also helps avoid system stress by controlling refrigerant flow, reducing energy consumption, and preventing possible damage due to improper pressure levels.
Function Benefit Pressure Regulation Prevents excessive or insufficient refrigerant flow Flow Control Optimizes refrigerant flow for better cooling efficiency Energy Efficiency Helps reduce energy consumption by maintaining balanced pressure Refrigerant Lines: Connecting the System

In any cooling setup, the efficient flow of refrigerant is crucial for proper operation. These lines play a pivotal role in transporting the refrigerant between the various components, ensuring the system runs smoothly. Proper installation and maintenance of these lines are essential for maximizing energy efficiency and ensuring long-term performance.
Types of Refrigerant Lines
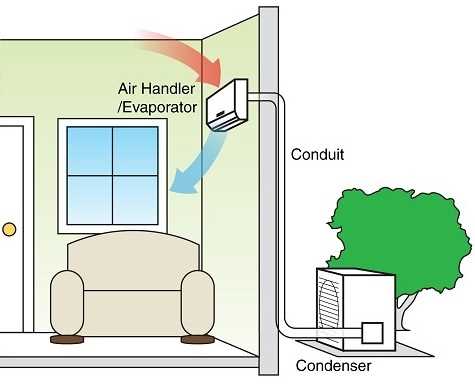
- Liquid Line: This line carries refrigerant in liquid form from the evaporator to the condenser.
- Suction Line: It transports the low-pressure, gaseous refrigerant back from the evaporator to the compressor.
- Discharge Line: The high-pressure refrigerant moves from the compressor to the condenser through this line.
Installation Tips
- Ensure proper insulation around the lines to prevent energy loss and frost formation.
- Use the correct diameter for the lines to maintain refrigerant pressure and flow.
- Check for leaks before final installation to avoid system inefficiencies.
- Ensure all connections are tight to prevent refrigerant loss over time.
The Impact of Air Filters on Efficiency
Efficient operation of cooling systems relies heavily on the cleanliness and functionality of certain components. Among these, filters play a crucial role in ensuring that the system operates at its peak potential. By trapping dust, debris, and pollutants, they not only improve the quality of the environment but also contribute to the overall performance of the unit. When filters are neglected, the system faces increased strain, leading to higher energy consumption and potential mechanical failures.
How Clean Filters Enhance System Performance
When filters are free from obstructions, airflow is maximized, allowing the unit to work efficiently without overloading the motor. This leads to reduced energy usage, longer operational lifespans, and improved cooling effectiveness. Regular maintenance, including cleaning or replacing the filters, ensures that the system can operate with minimal energy waste, thus promoting a cost-effective and sustainable solution.
Consequences of Clogged Filters
Clogged filters restrict airflow, forcing the system to work harder. As a result, the compressor may overheat, and energy consumption increases significantly. In the long run, this not only raises operational costs but also accelerates wear and tear on the system, potentially leading to expensive repairs or replacements. Maintaining clean filters is essential for maintaining optimal performance and extending the life of the system.
Thermostats and Controls: Managing Temperature
Effective temperature regulation is crucial for maintaining comfort and energy efficiency in indoor environments. The core elements responsible for controlling the internal climate are the temperature sensors and control systems, which work together to ensure the desired settings are consistently met.
At the heart of this process are the thermostats and associated controls, which monitor and adjust the system’s performance. By sensing room temperature and responding to changes, they help in managing the system’s operation and preventing energy wastage.
- Thermostat Functionality: These devices detect room temperature and communicate with the system to adjust heating or cooling functions accordingly.
- Control Systems: The control systems can vary in complexity, from simple manual dials to advanced digital interfaces with smart features.
- Efficiency Considerations: Properly calibrated thermostats ensure the system operates only when necessary, preventing unnecessary energy consumption.
Thermostats often feature adjustable settings, allowing users to fine-tune the temperature according to their preferences. Some models even include programmable features, enabling users to set specific schedules for when the system should operate.
In more advanced systems, integration with home automation platforms allows for remote adjustments and optimization of climate control, providing added convenience and efficiency.