In the world of construction and maintenance, effective elevation systems play a crucial role in ensuring safety and efficiency. These essential frameworks provide support and access to various heights, facilitating work in diverse environments. A comprehensive grasp of the individual components that comprise these systems is vital for proper assembly and usage.
By examining the various elements involved, one can appreciate how each piece contributes to the overall integrity and functionality of the setup. This exploration not only enhances operational understanding but also underscores the importance of using quality materials and adhering to safety standards. Knowing the distinct functions of each element empowers users to optimize their use and improve worksite safety.
Furthermore, recognizing how these components interact with one another aids in troubleshooting and maintenance. A well-structured approach to assembly and disassembly can significantly reduce risks and increase productivity. Emphasizing the significance of these frameworks in the construction industry reveals their impact on project success and worker safety.
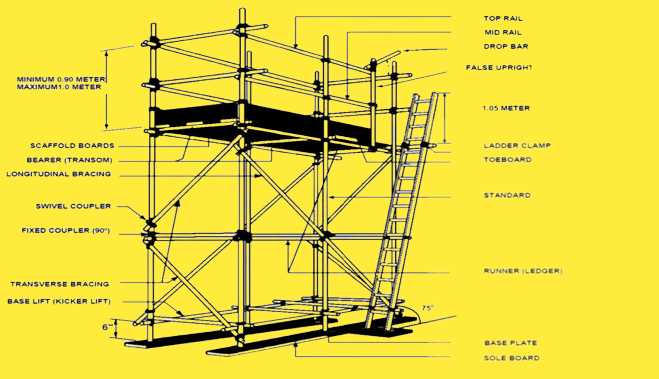
Understanding Scaffold Components
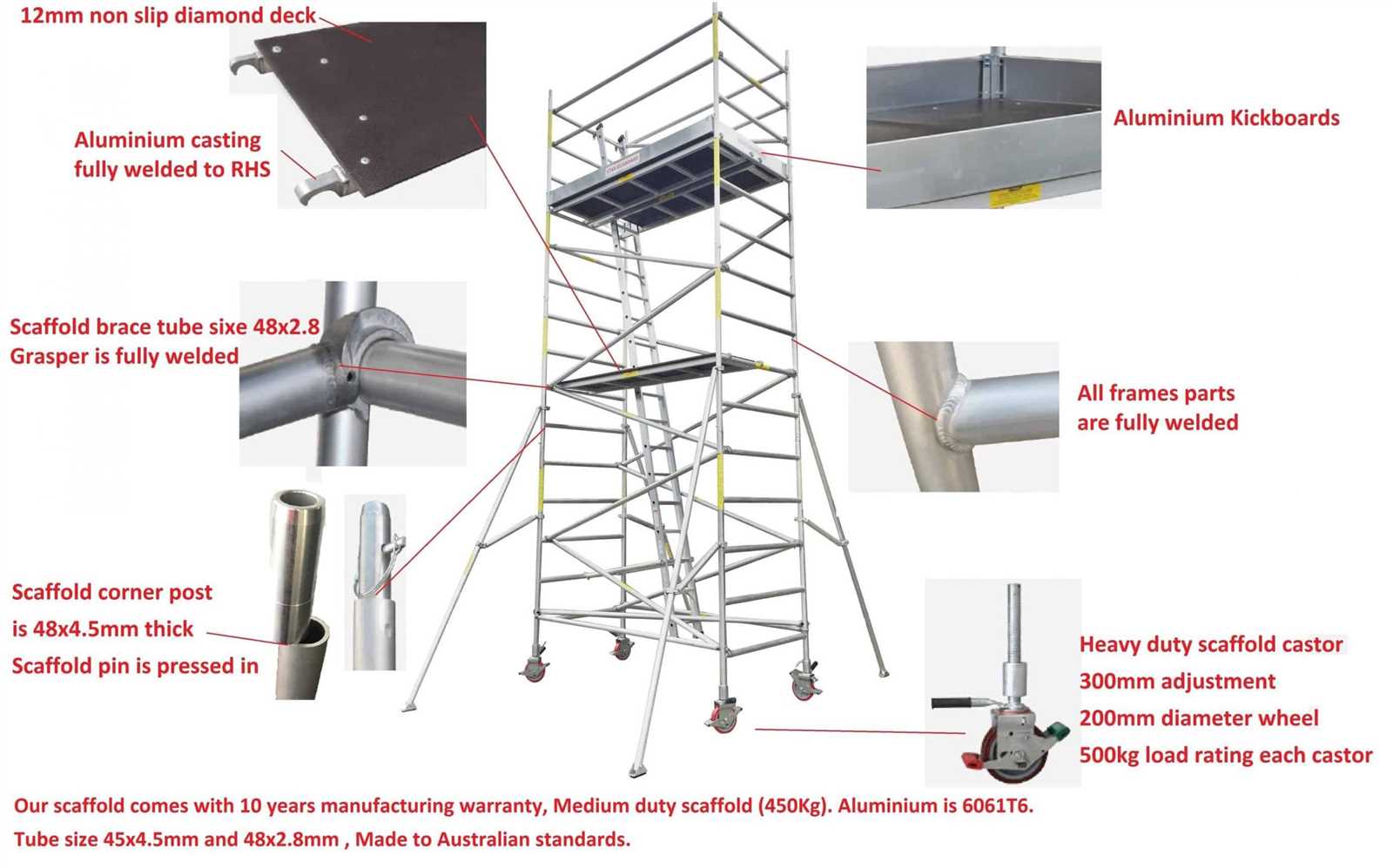
In the realm of construction, certain structures play a vital role in ensuring safety and efficiency. These essential elements provide support and access during various phases of building projects. A clear comprehension of these elements is crucial for both workers and project managers alike.
Key components are designed to serve specific purposes, facilitating a seamless workflow. Below are some of the main elements commonly found in such systems:
- Base Plates: These serve as the foundation, distributing weight and stabilizing the entire structure.
- Standards: Vertical supports that provide the necessary height and strength.
- Ledgers: Horizontal beams that connect the vertical supports, creating a secure framework.
- Braces: Diagonal supports that enhance stability and prevent swaying.
- Decking: Platforms that create working surfaces, allowing for safe movement and operations.
Understanding the functionality and arrangement of these components is essential for maintaining safety standards and ensuring effective use. Proper assembly and maintenance can significantly impact the success of any project, highlighting the importance of training and awareness among all personnel involved.
To sum up, recognizing these fundamental elements enables a clearer perspective on construction safety and efficiency, laying the groundwork for successful project completion.
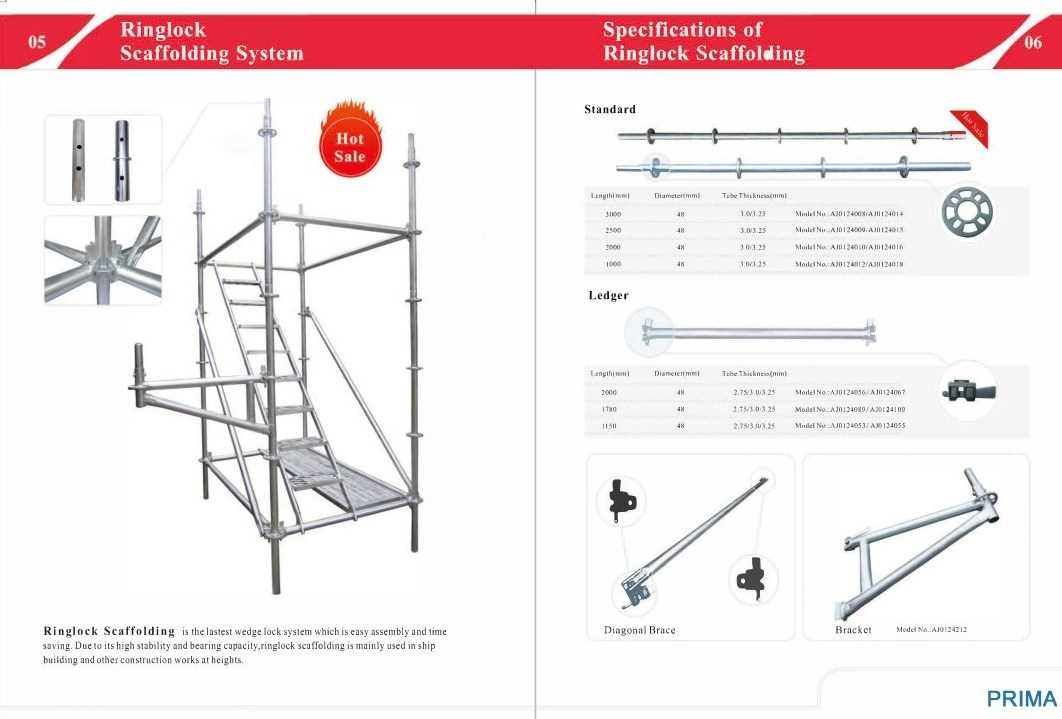
Types of Scaffolding Systems
In the realm of construction and maintenance, various temporary structures are employed to support workers and materials at elevated heights. These systems play a crucial role in ensuring safety and efficiency during projects, and they come in several forms, each designed to meet specific needs and conditions. Understanding the distinct categories of these frameworks can greatly enhance project planning and execution.
Frame Systems
One of the most commonly used structures is the frame system, which consists of vertical frames connected by horizontal braces. This configuration provides a stable and versatile platform, allowing for quick assembly and disassembly. Ideal for a wide range of projects, from residential buildings to large commercial sites, frame systems offer flexibility in height and load capacity.
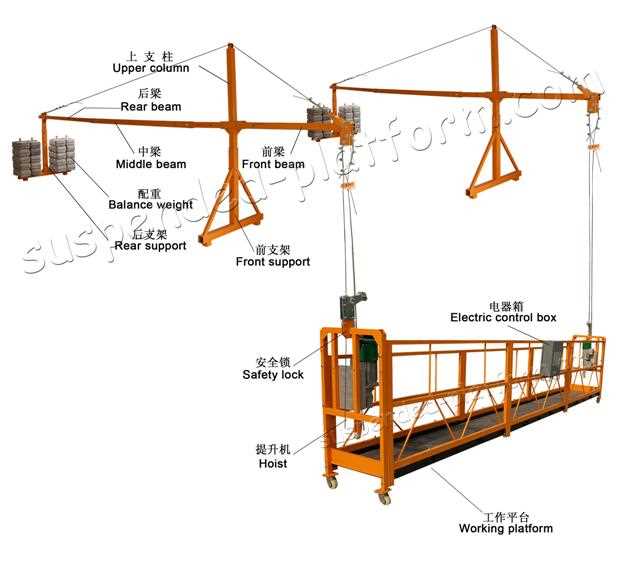
Suspended Structures
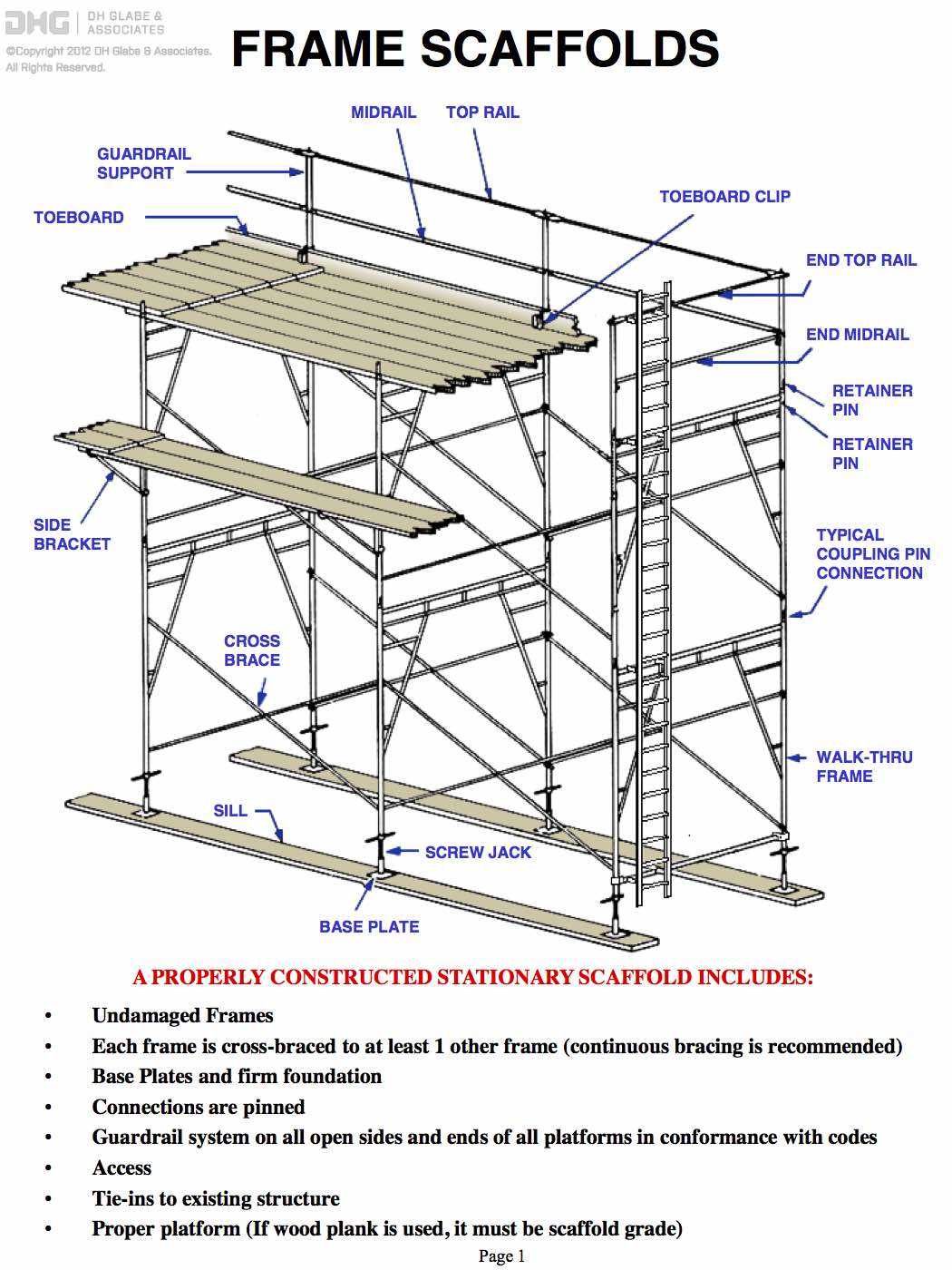
Another notable type is the suspended structure, which is typically used in situations where ground access is limited. These systems are hung from overhead support beams, allowing for work to be done on high-rise buildings or bridges. They provide workers with the necessary access while minimizing the footprint on the ground level, making them an excellent choice for urban environments.
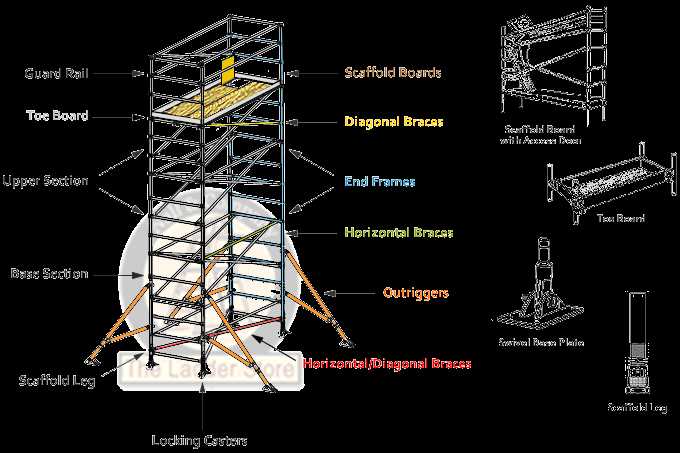
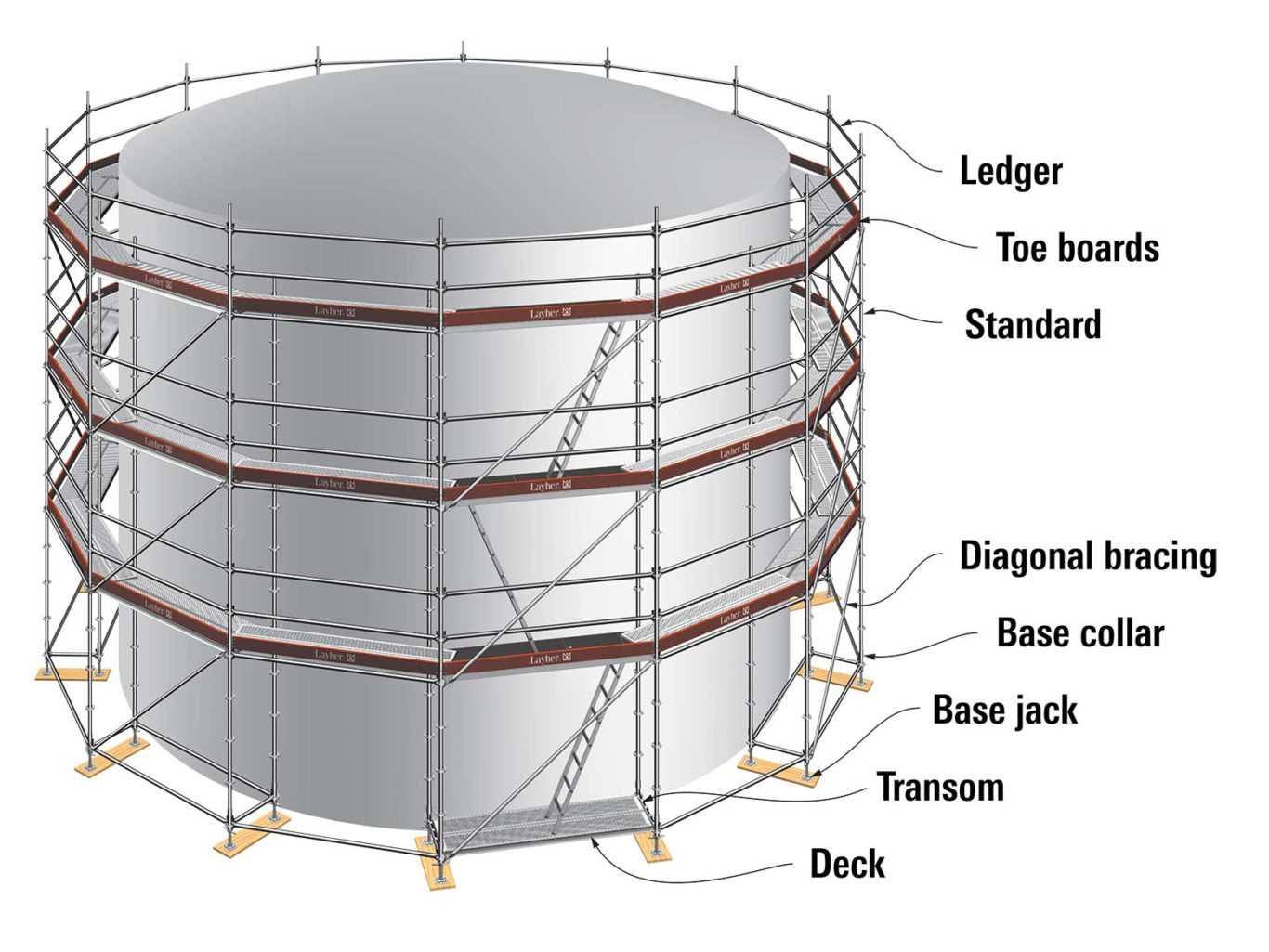
Key Elements of Scaffold Structures
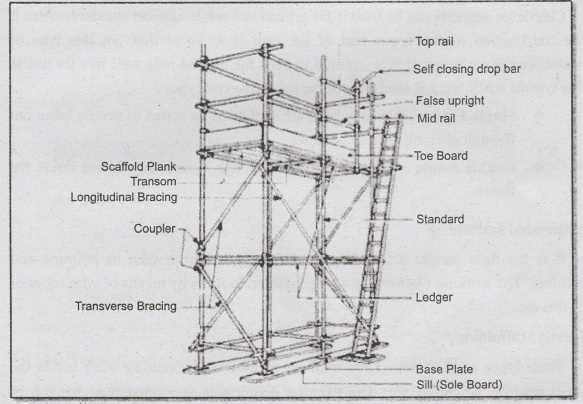
Understanding the fundamental components of temporary support frameworks is essential for ensuring safety and efficiency in construction projects. Each element plays a crucial role in providing stability and accessibility, allowing workers to perform tasks at various heights with confidence.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Standards | Vertical tubes that provide the primary support and determine the height of the structure. |
| Ledgers | Horizontal tubes that connect vertical standards, providing stability and a platform for other elements. |
| Braces | Diagonal supports that enhance the rigidity of the framework, preventing swaying and movement. |
| Platforms | Surfaces made of boards or metal that create the working area for personnel and equipment. |
| Couplers | Connectors used to join different components together securely, ensuring structural integrity. |
Each of these elements must be carefully selected and installed to meet safety standards and project requirements. A well-designed assembly not only supports the workforce but also enhances productivity on site.
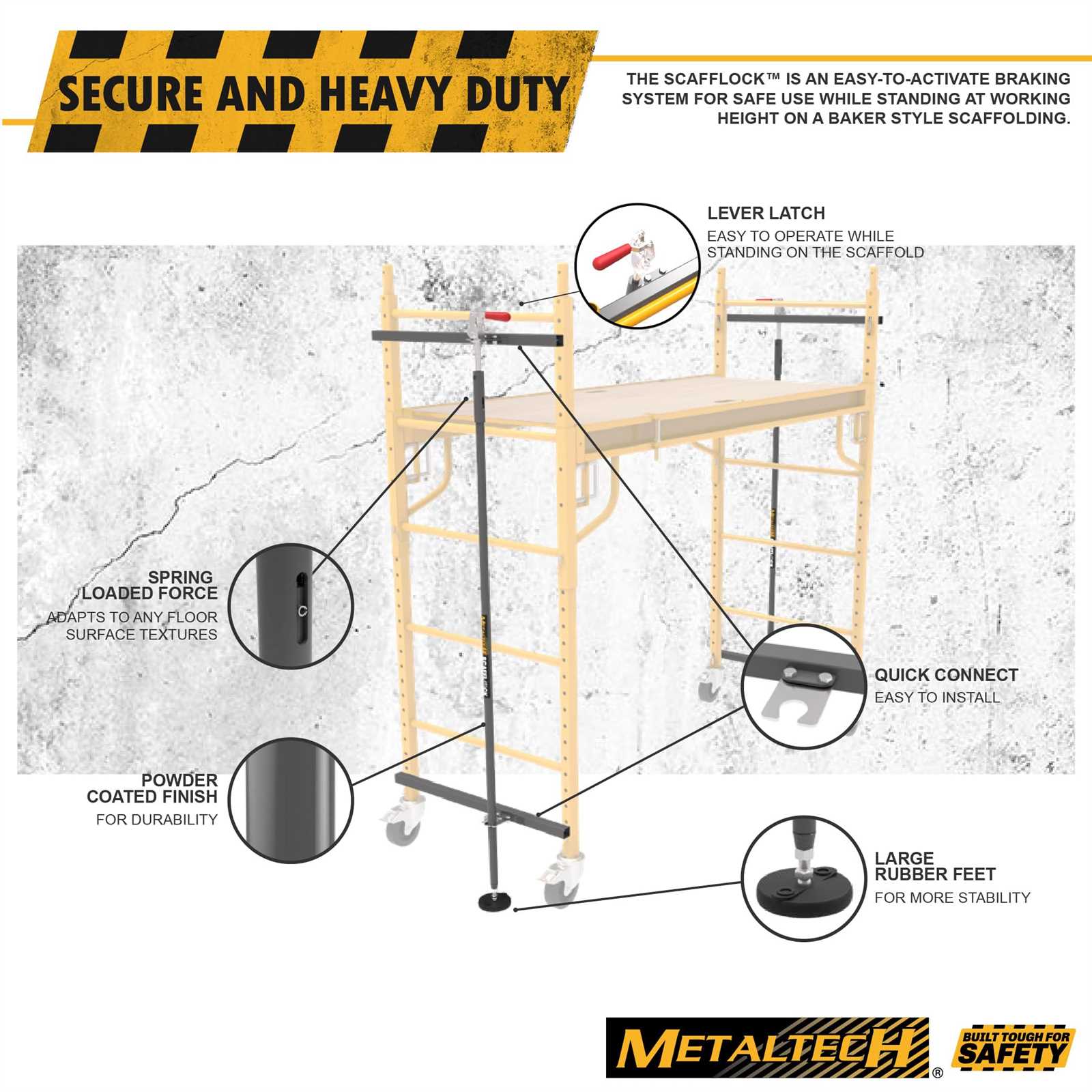
Safety Features in Scaffold Design
Ensuring the protection of workers at heights requires a thoughtful approach to structural design. Incorporating safety elements not only enhances stability but also significantly reduces the risk of accidents. Understanding these features is crucial for creating a secure working environment.
Several critical aspects contribute to the overall safety of elevated structures. These components work together to prevent falls and ensure durability, addressing both worker safety and structural integrity.
| Safety Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Guardrails | Installed around elevated surfaces to prevent accidental falls. |
| Toe Boards | Placed at the edge of platforms to stop tools and materials from falling. |
| Stable Base | Ensures even weight distribution and prevents tipping. |
| Load Capacity | Designed to support a specified weight limit to avoid structural failure. |
| Inspection Checklists | Regular evaluations to ensure all elements are in good condition and compliant. |
By emphasizing these safety features, designers and contractors can significantly mitigate hazards associated with working at heights, promoting a culture of safety in the construction industry.
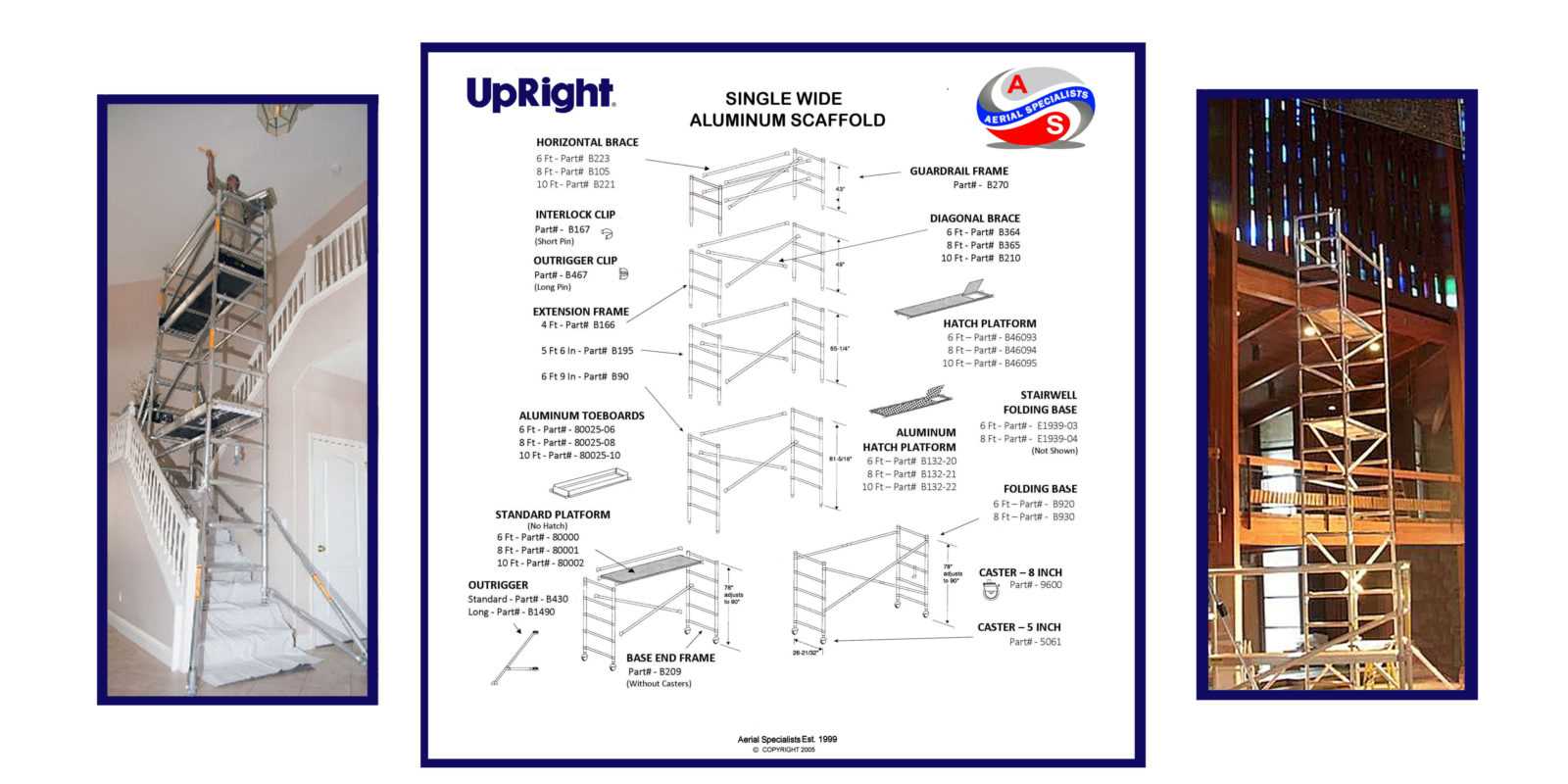
Benefits of Using Scaffolding
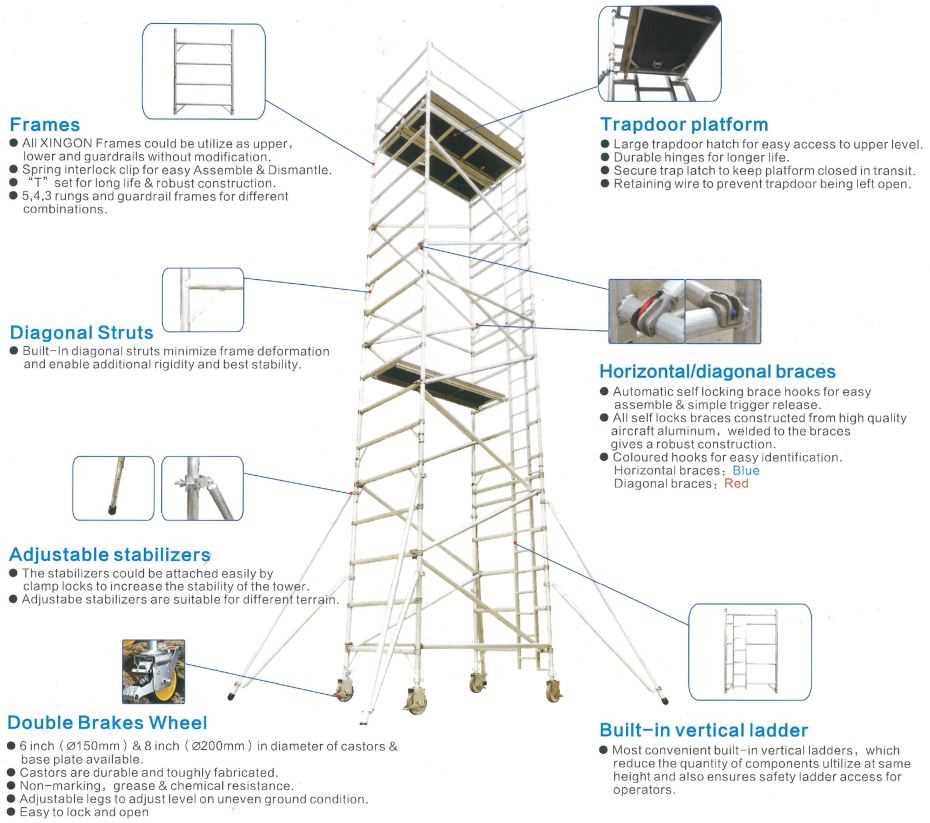
The implementation of temporary structures in construction and maintenance offers numerous advantages that enhance safety, efficiency, and accessibility on job sites. These frameworks serve as vital support systems, allowing workers to perform tasks at various heights with greater ease and security.
Enhanced Safety
One of the primary benefits is the significant improvement in safety for workers. By providing stable and reliable platforms, these structures reduce the risk of falls and injuries. Properly constructed frameworks ensure that employees can focus on their tasks without the constant concern of unstable footing, thereby fostering a safer working environment.
Increased Efficiency
Additionally, the use of temporary support systems can greatly boost productivity. Workers are able to reach elevated areas more quickly and effectively, streamlining the construction process. With easy access to tools and materials, teams can complete projects in a timely manner, leading to better overall project management and cost-effectiveness.
In summary, the strategic use of temporary structures not only enhances safety but also promotes greater efficiency, making them an essential component in modern construction practices.
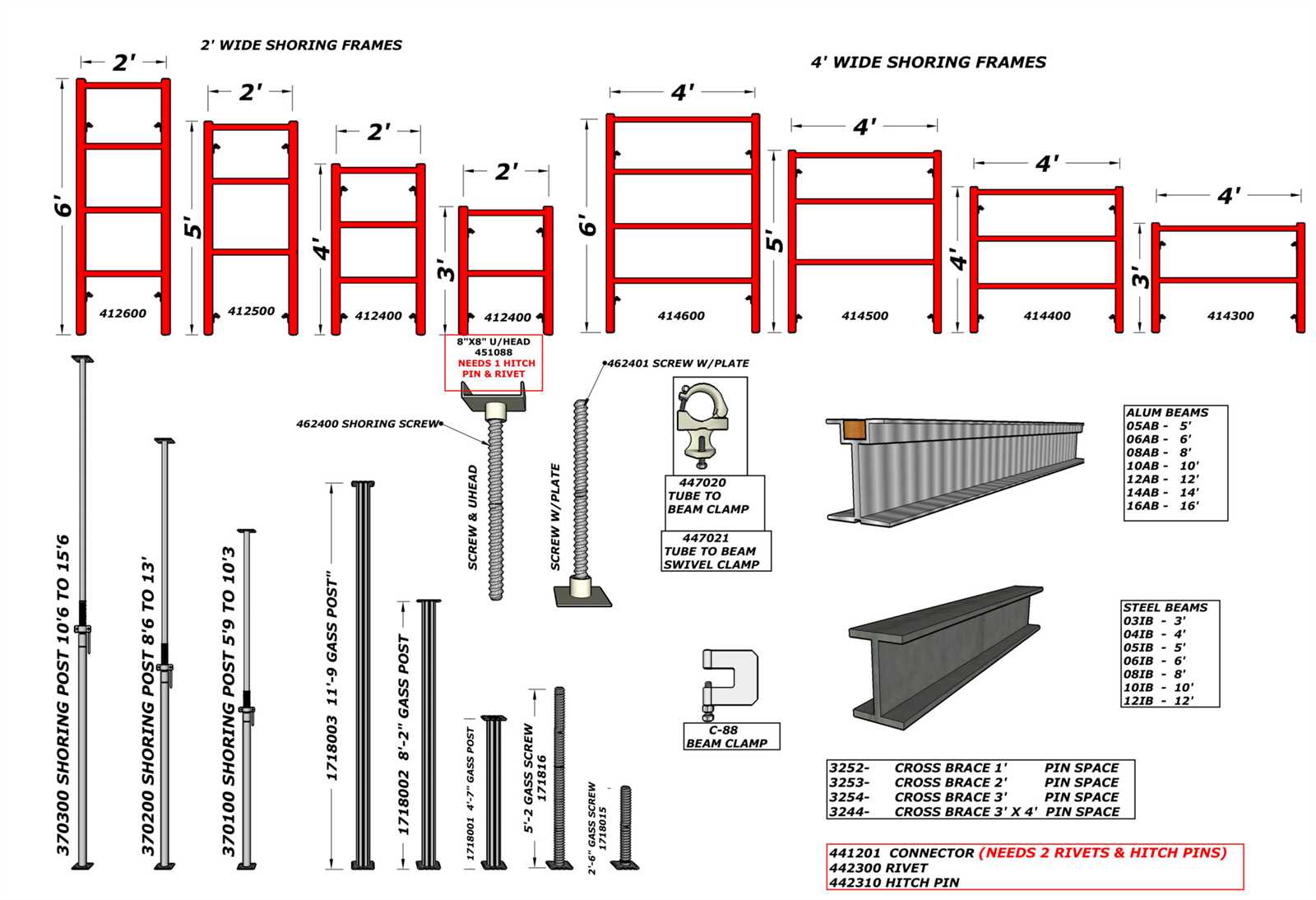
Common Materials for Scaffold Construction
In the realm of construction and maintenance, the choice of materials plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and structural integrity. Various components are utilized, each selected for their unique properties and suitability for specific tasks. Understanding the different types of materials can help in making informed decisions for any project.
Metal Options
Metal is one of the most prevalent choices due to its strength and durability. Aluminum is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and easy to assemble, making it ideal for various applications. Steel, on the other hand, offers exceptional strength and stability, often preferred for heavy-duty requirements. Both materials provide excellent load-bearing capacities, ensuring reliability in demanding environments.
Wood and Composite Materials
Wood is another traditional option, valued for its accessibility and cost-effectiveness. While it may not offer the same strength as metal, properly treated timber can be a viable choice for lighter applications. Composite materials, combining wood fibers with plastic, are gaining popularity for their resistance to moisture and decay, presenting an innovative alternative in construction settings.
Regulations and Standards for Scaffolds
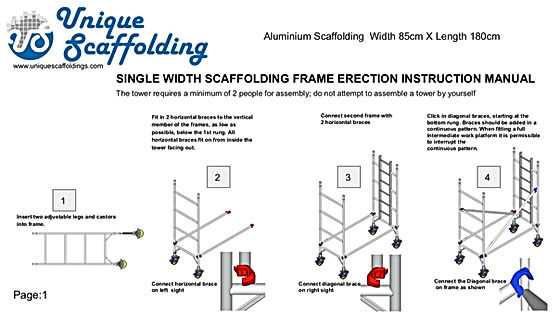
The construction industry is governed by a framework of regulations and standards designed to ensure safety and reliability in temporary structures. These guidelines are essential for minimizing risks associated with elevated work environments, providing specifications for design, use, and maintenance to protect workers and the public.
Key organizations and governmental bodies set forth these regulations, which vary by region but generally focus on structural integrity, load capacity, and worker safety training. Compliance with these standards is crucial for reducing accidents and ensuring that temporary supports function as intended.
| Organization | Standard | Overview |
|---|---|---|
| OSHA | 29 CFR 1926.451 | Regulations for safety practices and performance criteria. |
| ANSI | ANSI A10.8 | Standards for design and use of temporary structures. |
| BSI | BS 5973 | Guidelines for the erection and dismantling of temporary systems. |
| AS/NZS | AS/NZS 1576 | Standards for materials, design, and performance in Australasia. |
Adherence to these regulations not only promotes safety but also enhances the overall efficiency of construction projects. Workers trained in compliance standards are better equipped to recognize hazards, operate safely, and contribute to a culture of safety on job sites.
Maintenance Tips for Scaffold Parts
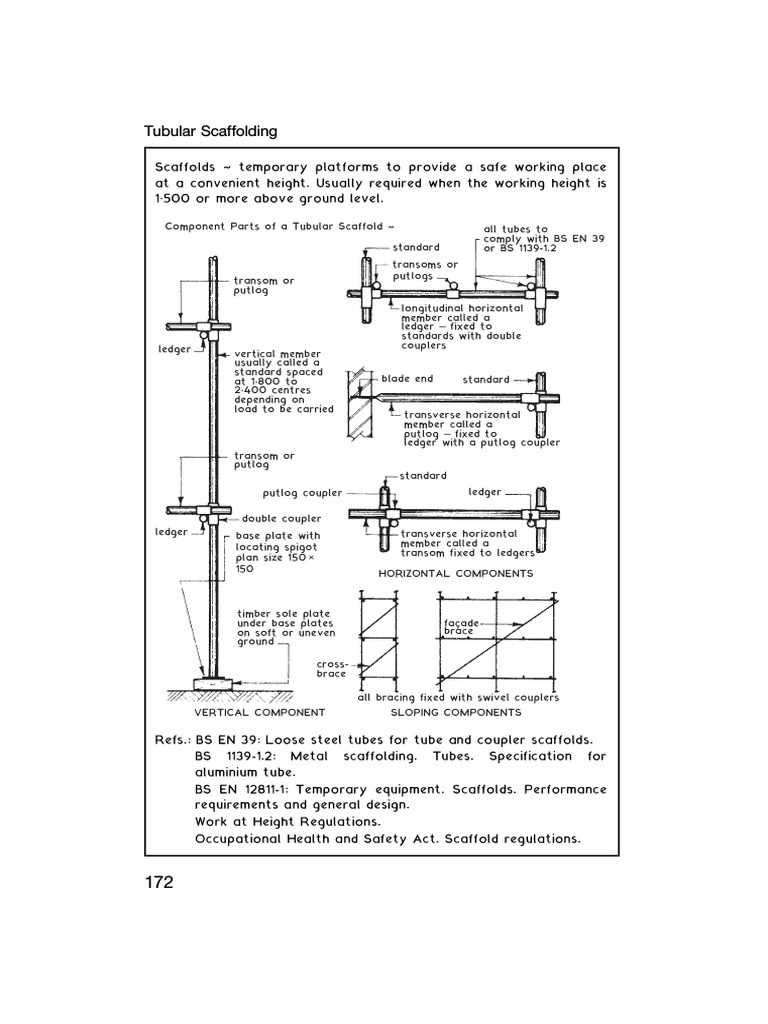
Regular upkeep is essential to ensure the longevity and safety of your elevated work structures. By following specific guidelines, you can maintain their functionality and prevent potential hazards. Here are some practical tips to keep in mind.
Routine Inspections
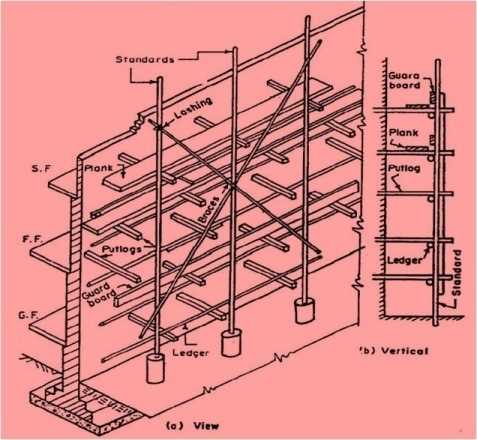
- Conduct visual checks before each use to identify any visible damage or wear.
- Look for rust, dents, or cracks that may compromise stability.
- Ensure that all connections are secure and components are properly aligned.
Cleaning and Maintenance
- Regularly clean all surfaces to remove dirt, debris, and any corrosive materials.
- Lubricate moving parts to ensure smooth operation and prevent friction-related damage.
- Store components in a dry place to minimize the risk of rust and deterioration.
By adhering to these maintenance strategies, you can extend the life of your equipment and enhance safety for all users. Regular attention to these details will pay off in improved performance and reliability.