In this segment, we delve into the intricate network of components that collectively ensure the efficient operation and distribution of heated water within a typical residential setting. Our journey through this labyrinthine arrangement unveils the essential elements that orchestrate the seamless transition from cold to comforting warmth, transforming raw potential into practical utility.
Firstly, we scrutinize the core components responsible for initiating and regulating the flow of thermal energy, tracing their path from initial ignition to controlled dispersion. These pivotal mechanisms, often concealed within the confines of utility spaces, work harmoniously to uphold the equilibrium between supply and demand, fostering a harmonious balance of functionality.
Further along, our exploration extends to the peripheral devices whose roles, though less conspicuous, are equally indispensable in ensuring the reliability and safety of the entire apparatus. Through a nuanced examination of these supporting actors, we illuminate their intricate interplay with the primary drivers of thermal management, elucidating the holistic framework that sustains the promise of consistent performance.
Understanding Water Heater Components
This section aims to explore the essential elements that contribute to the functioning of a thermal storage unit. Each component plays a critical role in ensuring efficiency and performance, ultimately affecting the user experience and energy consumption.
Key Elements
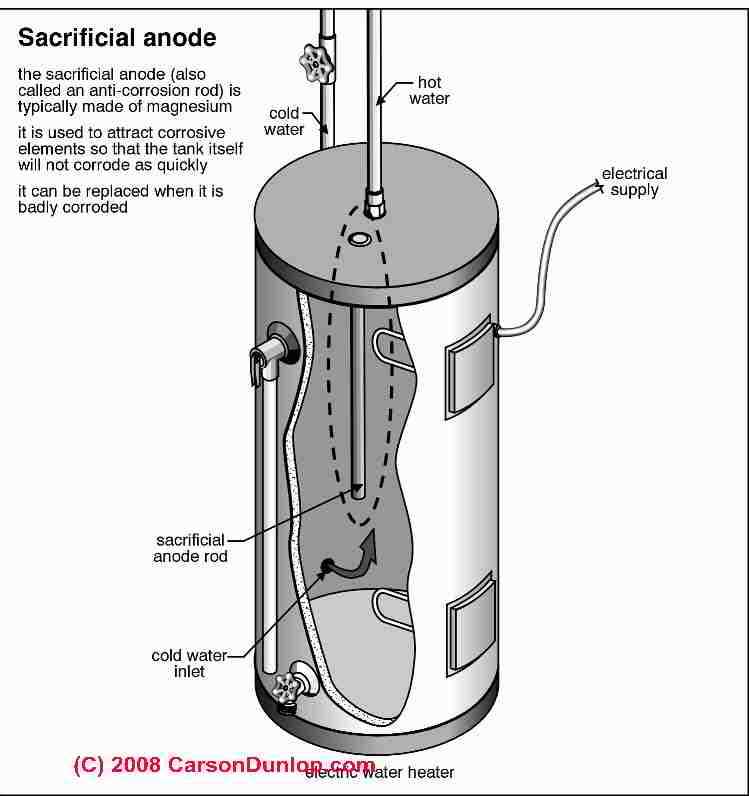
- Tank: The main reservoir where liquid is stored and heated.
- Thermostat: A device that regulates the temperature of the stored liquid.
- Heating Element: The source of heat, often electric or gas-powered.
- Vent: A pathway for gases to escape, crucial for safety.
Supporting Components
- Anode Rod: Prevents corrosion within the tank.
- Pressure Relief Valve: Ensures safety by releasing excess pressure.
- Insulation: Reduces heat loss, improving energy efficiency.
- Pipes and Fittings: Connect various components, facilitating the flow of liquid.
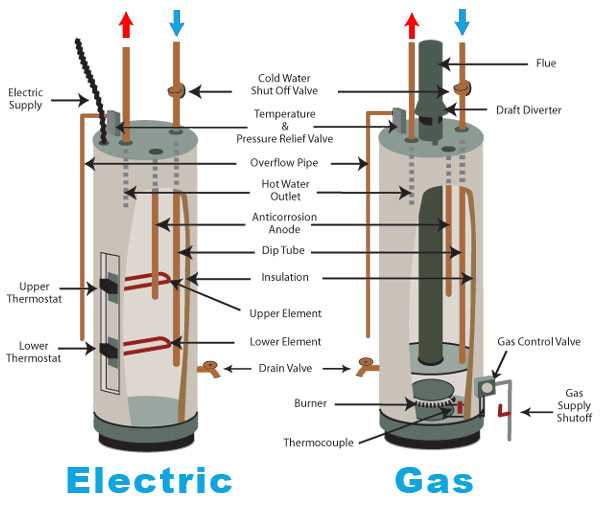
Key Elements of a Water Heater
Understanding the fundamental components of a heating system is essential for effective maintenance and efficient operation. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring that the system functions optimally and meets user needs.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermostat | Regulates the temperature to maintain desired warmth. |
| Tank | Stores heated liquid for distribution. |
| Heating Element | Generates heat to warm the stored liquid. |
| Drain Valve | Facilitates the removal of sediment and maintenance. |
| Insulation | Reduces heat loss and enhances efficiency. |
Types of Water Heating Systems
In modern households, various methods exist for generating and maintaining thermal energy for domestic use. These approaches differ in efficiency, design, and the source of energy utilized, catering to diverse needs and preferences.
Common Types
- Storage Systems
- Tankless Systems
- Heat Pump Systems
- Solar Systems
- Indirect Systems
Energy Sources
- Electricity
- Natural Gas
- Propane
- Solar Power
- Geothermal Energy
Understanding these variations enables homeowners to select the most suitable option based on their specific requirements and energy efficiency goals.
How a Water Heater Works
This section explores the fundamental principles behind a common household device that provides essential comfort. Understanding its operation reveals the intricacies of heating and storing liquid efficiently.
At the core of this device is a mechanism that utilizes energy to elevate the temperature of the liquid. Typically, energy sources may include electricity or gas, which activate a heating element or burner. This process transforms the initial cold state into a desired warm condition.
Once heated, the liquid is retained in an insulated tank, ensuring minimal heat loss. A thermostat regulates the temperature, providing a balance between energy consumption and user comfort. When the desired level is reached, the system maintains it until the demand increases.
Upon demand, the warm liquid is drawn from the tank, with fresh, cold liquid entering to replace it. This continuous cycle ensures that users have immediate access to heated liquid as needed, demonstrating the efficiency of this essential appliance.
Common Issues and Repairs
Understanding frequent challenges and their solutions is essential for maintaining optimal performance of your heating appliance. Many users encounter similar problems that can often be resolved with basic troubleshooting techniques. This section highlights typical malfunctions and the recommended corrective measures to ensure a reliable operation.
Temperature Fluctuations
Inconsistent heating can lead to discomfort and inefficiency. This issue may stem from faulty thermostats or sediment buildup inside the tank. Regularly checking and replacing the thermostat or flushing the system to remove deposits can significantly improve performance.
Leaking Units
Leakage is a common concern that may indicate damaged seals or corrosion. Identifying the source of the leak is crucial. If the issue arises from a loose connection, tightening it might suffice. However, severe corrosion may require part replacements or professional assistance to prevent further damage.
Choosing the Right Model
Making an informed decision when selecting an appropriate system can significantly enhance comfort and efficiency. Various factors influence this choice, from functionality to energy source.
- Assess your needs: Consider the size of your household and daily usage.
- Energy efficiency: Look for models with high energy ratings to reduce costs.
- Installation type: Determine whether you prefer a tank or tankless option.
- Maintenance requirements: Evaluate how much upkeep each model necessitates.
Ultimately, understanding these aspects will help you navigate the selection process effectively.
Energy Efficiency in Water Heaters
Enhancing the effectiveness of thermal devices is crucial in today’s world, where resource conservation and cost savings are paramount. Efficient systems not only reduce energy consumption but also minimize environmental impact, contributing to a more sustainable future.
One of the primary aspects influencing effectiveness is the technology utilized within these systems. Modern advancements have led to the development of units that operate on innovative principles, allowing for significant energy savings compared to traditional models.
Additionally, regular maintenance plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance. By keeping components in good condition and addressing any issues promptly, users can maintain high efficiency levels throughout the lifespan of their devices.
Furthermore, selecting the appropriate size for a household’s requirements is essential. Oversized systems can lead to unnecessary energy usage, while undersized units may struggle to meet demand, causing inefficiencies.
Investing in energy-efficient models often yields long-term financial benefits. While the initial costs may be higher, the reduced utility bills can offset this expense over time, making such choices economically sensible.
Ultimately, understanding and prioritizing efficiency when choosing and maintaining thermal appliances can lead to substantial savings and a positive impact on the environment.
Safety Features in Water Heating
Ensuring secure operation is crucial in systems designed for thermal management. Various mechanisms are integrated to prevent hazards, enhance performance, and protect users from potential dangers. These features play a vital role in promoting efficiency while minimizing risks associated with overheating and pressure buildup.
One of the primary components is the thermostat, which regulates temperature and prevents excessive heat accumulation. Additionally, pressure relief valves are essential for releasing built-up pressure, thus averting potential explosions. Insulation materials further contribute to safety by reducing the risk of burns and enhancing energy efficiency.
Regular maintenance checks are also recommended to ensure all safety features function properly. By understanding these critical aspects, users can maximize safety and reliability in thermal systems, ultimately leading to a more secure and efficient environment.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Regular care and attention can significantly extend the lifespan of your heating system, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Implementing simple practices can prevent costly repairs and improve reliability.
Routine Inspections
- Check for any signs of leaks or corrosion.
- Inspect the connections and wiring for wear.
- Monitor the overall functionality on a regular basis.
Cleaning and Servicing
- Flush the tank periodically to remove sediment buildup.
- Clean the exterior to maintain airflow and prevent overheating.
- Schedule professional servicing at least once a year.