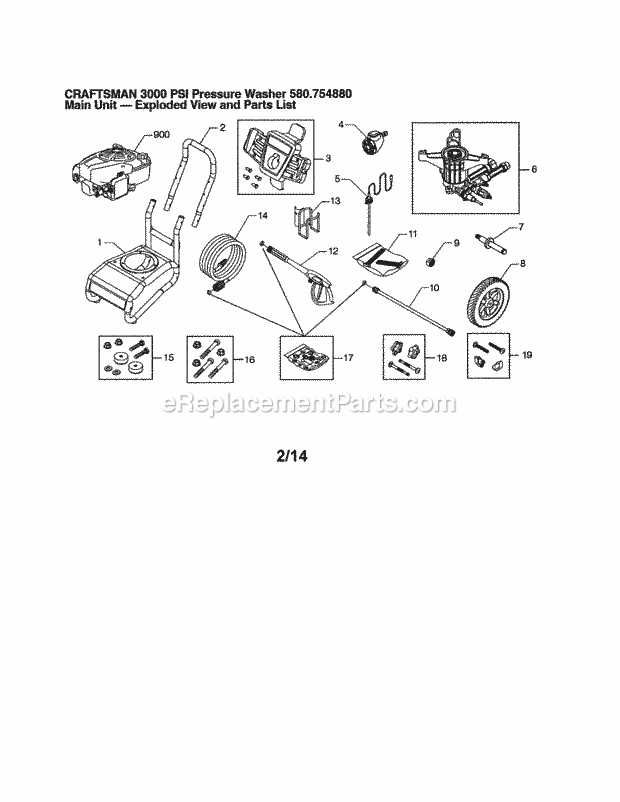
25° to
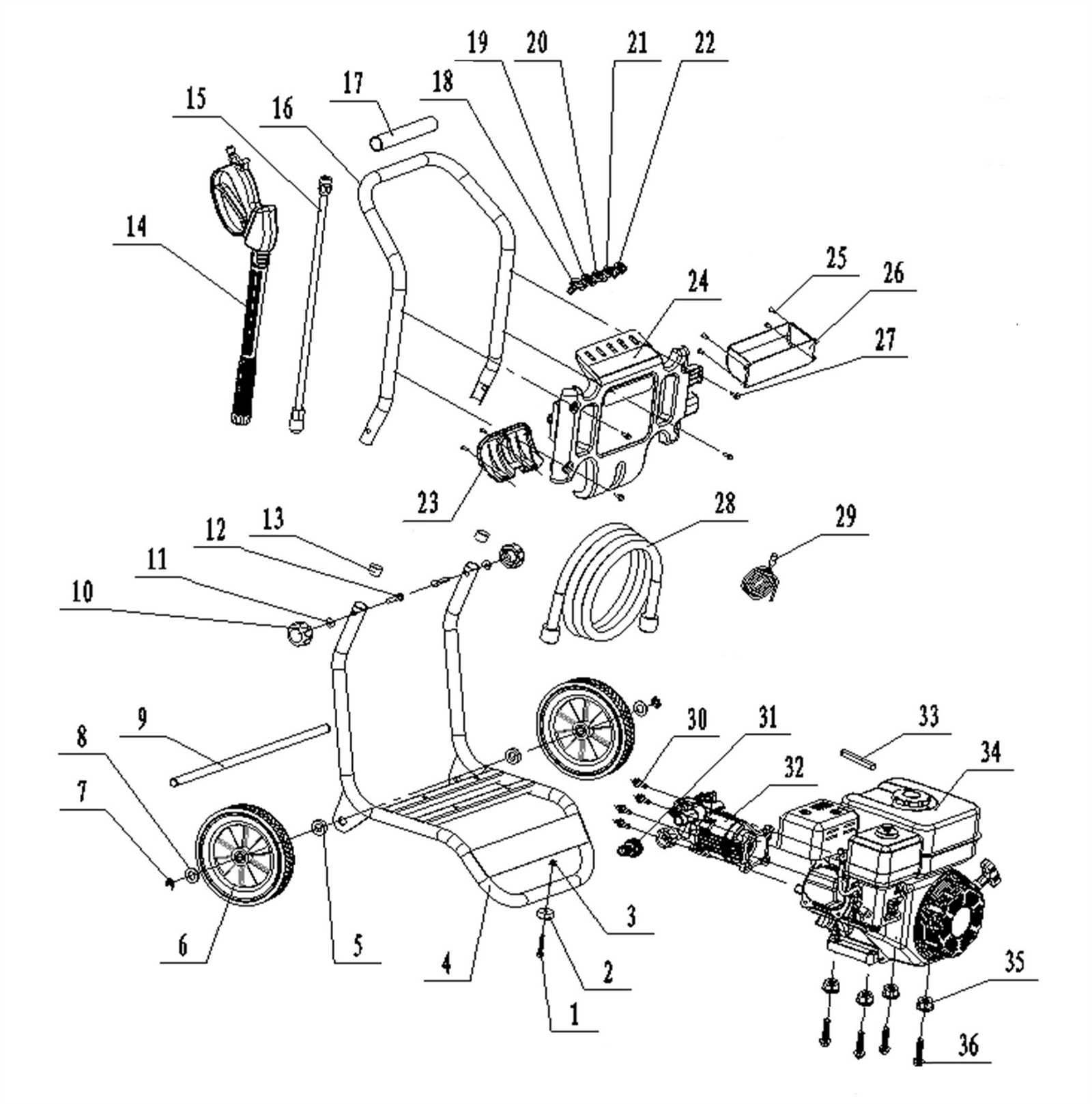
Understanding the Pump Mechanism
The heart of the system responsible for creating the necessary force to clean effectively is the pump. This essential component transforms energy into motion, driving water through the machine and enabling the required flow for various cleaning tasks. The functionality of this part is key to the overall efficiency of the system, ensuring steady operation under different conditions.
How the Mechanism Works
The core function relies on a series of pistons or plungers that move in a rhythmic motion. These create suction, drawing in the fluid, and then apply pressure to expel it at high velocity. The speed and precision of these internal movements define how well the cleaning system performs, making it a critical aspect to maintain and understand.
Key Elements to Consider
In the pump, several vital elements work together. These include valves that control the intake and release of water, seals that prevent leaks, and bearings that support the movement. Each of these plays a role in ensuring smooth operation, and regular upkeep is essential to prolong the lifespan of the mechanism.
Role of the Water Inlet and Outlet

The function of water entry and exit points is fundamental to ensuring the optimal flow of water through the entire cleaning system. These connections manage the input of water from a supply source and its output after it has cycled through the internal components. Understanding how these channels work is crucial for maintaining the overall performance of the equipment.
Water Inlet Function
- Receives water from an external supply, typically a hose.
- Filters out debris and contaminants to prevent blockages.
- Regulates the water pressure as it enters the internal system.
Water Outlet Mechanism
- Allows the processed water to exit after it has been used within the system.
- Connected to an adjustable nozzle for directing the water flow.
- Ensures proper discharge to avoid build-up and maintain consistent pressure.
Functionality of Detergent Injection Systems
The detergent injection system plays a crucial role in enhancing the cleaning capability of equipment by allowing the mixing of cleaning solutions with water. This mechanism is designed to improve the efficiency of removing dirt, grime, and stains from surfaces, making the cleaning process more effective and less time-consuming.
Key Components and Operation
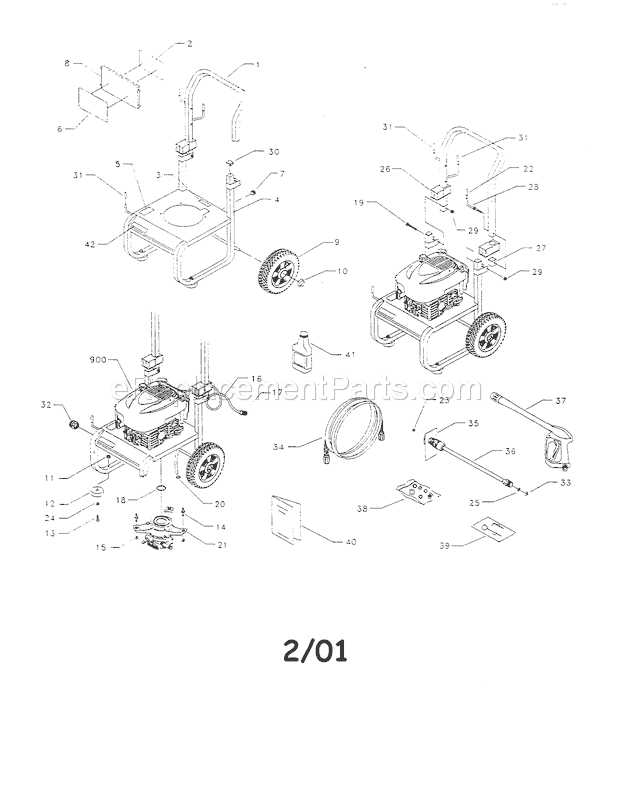
- Mixing Valve: Controls the flow of cleaning solutions, allowing a precise blend with the water stream.
- Detergent Tank: Holds the cleaning solution, typically a liquid detergent, which is drawn into the system as needed.
- Siphoning Mechanism: Uses pressure differences to pull the detergent into the water stream without the need for a pump.
Advantages of Using a Detergent System
- Improves the cleaning power by breaking down tough stains and grease more effectively.
- Reduces water consumption as the combination of detergent and water requires less time and effort.
- Offers flexibility by allowing users to adjust the detergent concentration based on the cleaning task.
Exploring the Hose Connections
The connections between the main unit and the water supply play a crucial role in ensuring optimal functionality. Properly securing and managing these linkages can significantly impact overall performance and longevity. Understanding the various types of attachments and how they interact is essential for smooth operation.
Understanding the Water Inlet
The water inlet is the primary point where the external source connects to the equipment. Ensuring a tight fit is key to preventing leaks and maintaining consistent flow. Look for secure seals and appropriate hose fittings to support uninterrupted water delivery.
High-Flow Outlet Considerations
The outlet, designed for high-flow water ejection, requires compatible hoses that can handle strong water pressure. Reinforced materials and secure locking mechanisms are recommended to avoid disconnection during use. Inspect the outlet regularly to ensure there are no blockages or wear that might impede performance.
Importance of the Pressure Regulator
The pressure regulator plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance and efficiency in various cleaning equipment. By controlling the flow and intensity of the fluid, it ensures that tasks are executed effectively without causing damage to surfaces or the machinery itself. This component is essential for achieving consistent results, particularly when dealing with diverse cleaning tasks that require different levels of force.
Proper regulation of fluid pressure not only enhances the cleaning capabilities but also contributes to the longevity of the device. By preventing excessive pressure buildup, the regulator protects vital components from wear and tear, reducing the likelihood of costly repairs or replacements. Additionally, it aids in conserving resources, making the cleaning process more economical and environmentally friendly.
Overall, understanding the significance of this component can lead to better maintenance practices and improved performance in cleaning applications, ensuring that users achieve the best possible outcomes while prolonging the life of their equipment.
Maintaining the Engine for Optimal Performance
To ensure the longevity and efficiency of your motorized equipment, regular upkeep is crucial. This involves various tasks aimed at keeping the engine running smoothly and effectively. By adhering to a consistent maintenance routine, you can prevent potential issues, enhance performance, and extend the lifespan of your machinery.
Key Maintenance Tasks
Performing essential maintenance tasks will help optimize engine performance. Below are some critical activities to include in your routine:
| Maintenance Task |
Frequency |
Description |
| Oil Change |
Every 50 hours of use |
Replacing old oil with fresh lubricant to ensure proper engine function. |
| Air Filter Inspection |
Every 25 hours of use |
Checking and cleaning the air filter to ensure adequate airflow. |
| Spark Plug Replacement |
Every season or as needed |
Replacing worn or dirty spark plugs to maintain ignition efficiency. |
| Fuel System Cleaning |
Annually |
Using fuel additives or manual cleaning to remove deposits from the fuel system. |
| Fuel Filter Change |
Every 100 hours of use |
Replacing the fuel filter to prevent contaminants from entering the engine. |
Best Practices for Maintenance
Incorporating best practices into your maintenance routine will enhance performance and reliability. Always use high-quality fluids and replacement components, and consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific recommendations. Keeping a detailed log of maintenance activities will also help track usage and identify patterns that may require attention.
|