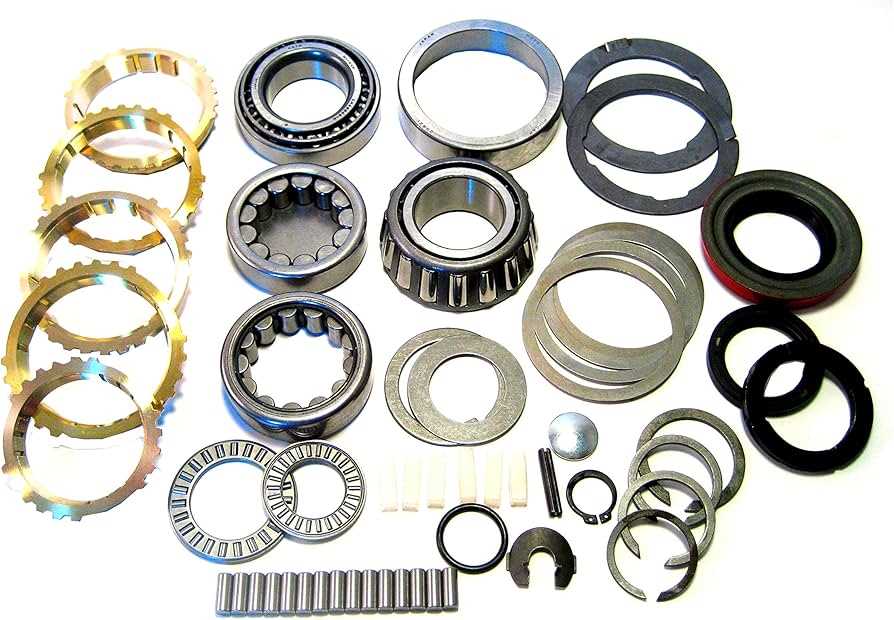

In every mechanical system designed to transfer motion and power, various interconnected elements play a crucial role in ensuring efficient performance. These systems rely on precise coordination to regulate the speed, torque, and direction of movement. The interaction between these components determines the overall functionality, reliability, and longevity of the mechanism. A comprehensive understanding of each part’s role is essential for diagnosing issues and optimizing performance.
At the heart of such mechanisms are the intricate structures that manage rotational forces. These elements work together in harmony, transmitting energy from one section to another, each component designed for a specific function. Some parts are responsible for modifying rotational speed, while others are involved in altering the force applied or changing the direction of movement. Knowing the roles of these key components allows for better maintenance and efficient operation of complex systems.
When studying the arrangement and function of these essential elements, it becomes clear that even small adjustments can lead to significant improvements in system efficiency and durability. Proper care and understanding of each unit’s contribution ensure the entire system operates smoothly over time.
Understanding Transmission Diagrams
Understanding the structure and operation of a vehicle’s mechanical system is essential for diagnosing issues and improving overall performance. This visual representation of how power flows through various components can significantly aid in grasping the relationships between gears, shafts, and other crucial elements. These charts provide insight into the interaction of different components, allowing for a clearer understanding of how energy is transferred from the engine to the wheels.
By examining these illustrations, one can better appreciate how different configurations of gears and mechanisms contribute to achieving the desired speed and torque. Whether it’s the manual or automatic system, these visuals help in understanding the complex processes at play when shifting or selecting gears, offering a detailed look into the intricacies of the vehicle’s functioning.
In addition, these technical visuals are valuable tools for both enthusiasts and professionals, enabling quick identification of key elements and making troubleshooting more efficient. A clear and accurate representation helps in understanding how minor adjustments can have a significant impact on overall performance.
Key Components of Transmission Systems
Understanding the essential elements that drive a vehicle’s movement is crucial for both performance and durability. These core components work in unison to transmit energy from the engine to the wheels, enabling efficient power transfer and optimal operation under various conditions. Each element plays a specific role in ensuring that power is distributed seamlessly, allowing the vehicle to accelerate, decelerate, and maintain stability.
Gearbox: The gearbox is a crucial unit responsible for adjusting the torque and speed generated by the engine. It allows the driver to control the vehicle’s speed and power output by shifting between different gear ratios, enhancing fuel efficiency and overall driving experience.
Clutch: The clutch is a device that momentarily disconnects the engine from the wheels, enabling smooth gear changes without damaging the system. This component is vital for transitioning between gears smoothly and controlling the vehicle’s acceleration.
Drive Shaft: The drive shaft transmits rotational force from the gearbox to the wheels, ensuring that power generated by the engine is effectively converted into movement. It plays an essential role in maintaining the vehicle’s momentum and smooth motion.
Differential: The differential allows for differences in the rotational speeds of the wheels, especially when turning. It ensures that power is distributed evenly to both wheels, preventing slipping or loss of traction during turns.
Torque Converter: Commonly found in automatic systems, the torque converter acts as a fluid coupling that transfers power from the engine to the gearbox. It helps smooth out gear shifts and enhances acceleration by allowing the engine to keep running while the vehicle is stationary.
Each of these components contributes to a finely tuned system, which ensures the efficient delivery of power and control, providing the driver with the necessary responsiveness and comfort. Proper understanding and maintenance of these elements are key to ensuring long-lasting performance and safety.
Functions of Gears in Transmissions
Gears play a crucial role in the mechanism of power transfer, enabling efficiency and control in movement. Their design allows for the modification of speed and torque, making them essential components in various machines and vehicles.
Speed Regulation
One of the primary functions of gears is to adjust the speed of rotation. By changing the gear ratio, they can either increase speed for rapid movement or decrease it for greater control and stability.
Torque Enhancement
Gears also serve to amplify torque, allowing engines to perform effectively under various loads. This enhancement is vital for tasks requiring substantial force, such as hauling heavy objects or climbing steep inclines.
Importance of Clutch Mechanisms
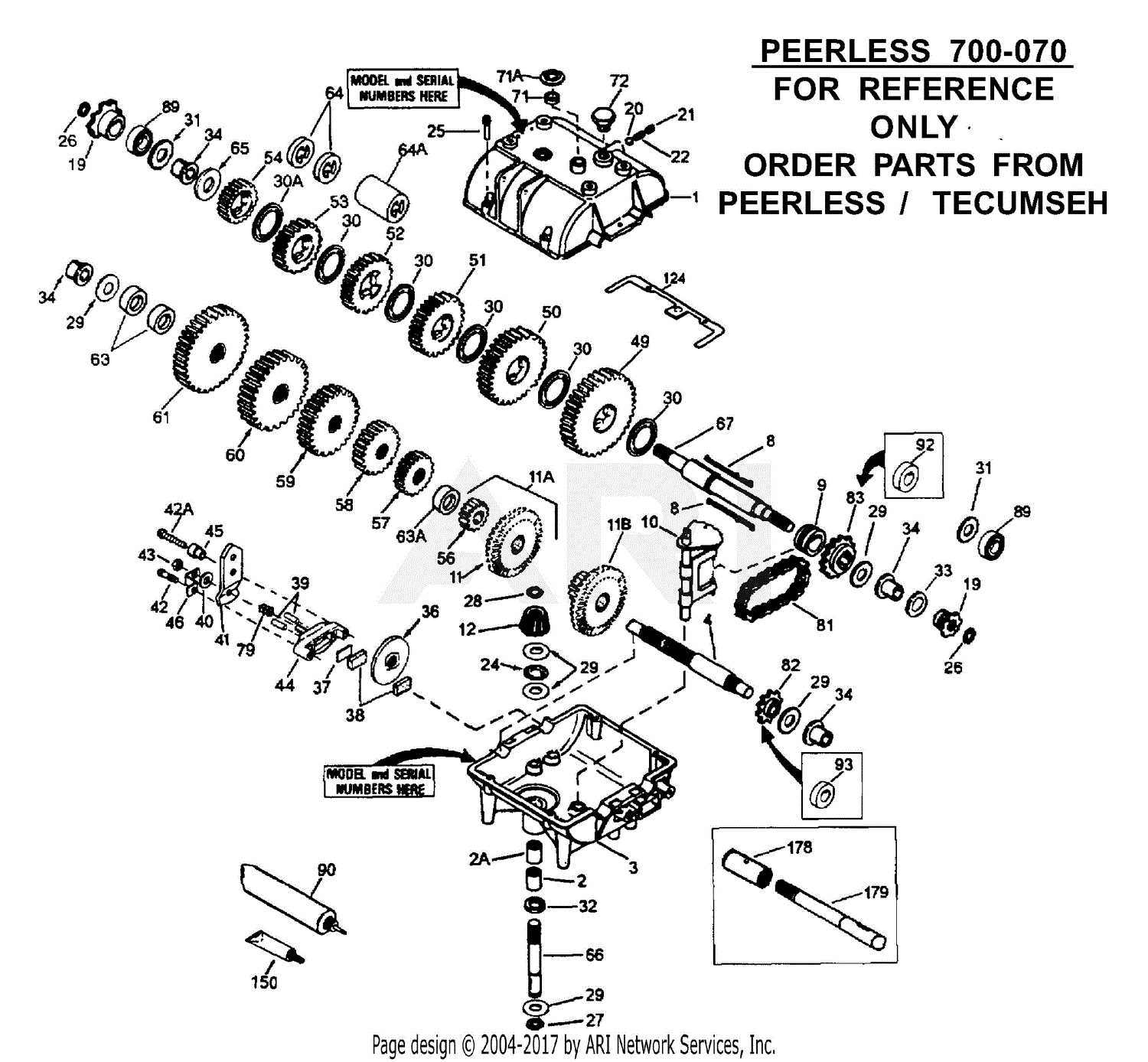
Clutch mechanisms are critical components in the smooth operation of any vehicle, ensuring that the power from the engine is transferred effectively to the wheels. These systems allow for seamless engagement and disengagement between the engine and the drive system, facilitating a smooth start, change of gears, and stopping without stalling. Without proper clutch functionality, the vehicle would struggle to operate efficiently, leading to poor performance and potential damage to other key systems.
Role in Power Transfer
The clutch serves as an intermediary that controls the connection between the engine’s output and the drivetrain. By engaging and disengaging, it provides the driver with control over the vehicle’s movement, enabling acceleration, deceleration, and smooth gear transitions. This function is essential for maintaining optimal engine efficiency, ensuring that the vehicle can accelerate or decelerate as needed without causing undue strain on the engine or gearbox.
Impact on Driving Experience
In addition to mechanical efficiency, the clutch plays a significant role in the overall driving experience. A well-designed system allows for precise control over the vehicle, contributing to smoother rides and less wear on the components. Drivers rely on the clutch to provide responsive feedback when shifting, and its performance directly influences how easily the vehicle can be operated in various driving conditions, from city streets to highways.
| Clutch Type | Function | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Single Plate Clutch | Simple engagement and disengagement of the engine and drive system | Used in most manual vehicles |
| Multi-Plate Clutch | Enhanced power handling, ideal for high-performance vehicles | Compact design with increased torque capacity |
| Hydraulic Clutch | Uses hydraulic fluid for smoother operation and reduced effort | Offers easier pedal control |
Types of Transmission Fluids Explained
Fluids that facilitate smooth shifting and optimal performance of the drivetrain are crucial for the longevity and functionality of any vehicle. These liquids serve as lubricants, coolants, and cleaning agents, helping to ensure that all moving components work together seamlessly. Selecting the right type of fluid is essential for maintaining the efficiency and reliability of the system that transfers power from the engine to the wheels.
There are several kinds of fluids used in various systems, each tailored to specific mechanical needs. The most common include automatic fluid, manual fluid, and synthetic fluid. Each type offers unique characteristics that influence shifting ease, temperature control, and protection against wear and tear.
Automatic fluid is designed for vehicles with automatic gearboxes. It has a unique formulation that ensures smooth gear changes and assists with temperature regulation. This fluid is often red or pink, making it easy to identify in the event of a leak.
Manual fluid is thicker and provides a greater level of friction needed for manual shifting systems. This type is typically more resistant to breakdown and provides better lubrication for gear synchronizers.
Synthetic fluid is a modern alternative that offers enhanced performance and longevity compared to traditional fluids. It is specially engineered to withstand extreme temperatures and offers superior protection against wear, oxidation, and sludge buildup.
Choosing the right fluid is essential not only for ensuring efficient operation but also for extending the lifespan of the mechanical system. Each type of fluid has been formulated to meet specific requirements, so it’s important to refer to the vehicle’s manufacturer recommendations to ensure compatibility.
Role of Bearings in Gear Systems
Bearings play a crucial role in the smooth functioning and efficiency of mechanical assemblies involving gears. They act as the supporting elements that facilitate rotation, minimize friction, and help maintain the alignment of rotating components. By reducing wear and tear on gear mechanisms, bearings ensure a longer operational lifespan and enhance overall system performance.
In gear systems, bearings are responsible for supporting the shafts and other rotating elements, thereby allowing them to turn smoothly without excessive resistance. This smooth motion is essential for the accurate transmission of force and motion between the gears. Additionally, the load distribution provided by bearings prevents excessive stress on individual gear teeth, reducing the risk of failure or premature wear.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduce Friction | Bearings minimize friction between rotating parts, which helps to reduce energy losses and heat generation. |
| Support Alignment | They maintain the correct alignment of shafts and other rotating components to ensure smooth operation. |
| Load Distribution | Bearings help distribute loads evenly across the system, reducing stress and wear on individual gear teeth. |
| Extend Lifespan | By reducing friction and minimizing wear, bearings contribute to the durability and longevity of the entire gear system. |
Common Issues in Transmission Parts
Mechanical systems often face a variety of challenges that can impact their overall performance and longevity. Understanding these common issues is essential for effective maintenance and repair. Below are some frequent problems that can arise within these crucial components.
- Fluid Leaks: Loss of hydraulic fluid can lead to inadequate pressure and functionality.
- Overheating: Excessive heat can cause wear and tear, leading to component failure.
- Noise and Vibration: Unusual sounds can indicate misalignment or wear of internal mechanisms.
- Slipping: Inability to maintain proper engagement can result in reduced efficiency and power transfer.
Regular inspection and timely intervention can help mitigate these issues. It’s crucial to keep an eye on performance indicators and address any irregularities promptly.
- Monitor fluid levels regularly.
- Inspect for visible leaks or discoloration.
- Check for unusual noises during operation.
- Ensure that all components are properly aligned.
By being proactive, one can ensure the smooth operation of these vital mechanisms and extend their lifespan.
Maintenance Tips for Transmission Longevity
Regular upkeep of the vehicle’s drive system is crucial for ensuring smooth performance and extending its lifespan. Proper maintenance minimizes wear and tear, reduces the risk of costly repairs, and keeps the vehicle operating efficiently. By staying on top of routine checks and addressing potential issues early, you can avoid major breakdowns and ensure the vehicle runs optimally for years.
Key Maintenance Practices
To maintain the health of your vehicle’s drivetrain, it is essential to follow specific guidelines. Regular fluid checks, timely replacements, and careful monitoring of operational conditions can make a significant difference. Below are the key elements of a maintenance schedule:
| Task | Frequency | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Level Check | Every 30,000 miles | Ensures proper lubrication, reducing friction and wear |
| Fluid Replacement | Every 60,000 miles | Prevents contamination and degradation of lubricants |
| Inspection for Leaks | Every 6 months | Prevents loss of fluid and potential damage to seals and components |
| Drive Belts and Chains Check | Annually | Ensures proper tension and alignment, preventing slippage and excessive wear |
Additional Tips for Optimal Function
Aside from regular checks, driving habits also play a role in the lifespan of the vehicle’s powertrain. Avoiding sudden acceleration or hard braking, as well as giving the vehicle time to warm up before heavy use, can significantly reduce unnecessary stress on the system. Keeping an eye on unusual noises or performance changes will help catch any issues early, allowing for prompt attention before they escalate.
Future Trends in Transmission Technology
The evolution of vehicle propulsion systems is set to redefine mobility. Innovations are paving the way for enhanced efficiency, sustainability, and user experience, addressing the demands of modern society.
Key Innovations on the Horizon
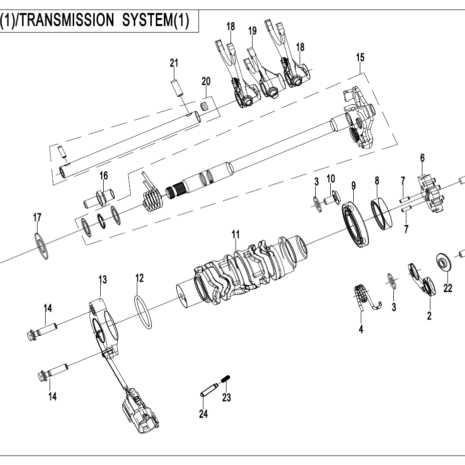
- Electrification: The rise of electric drivetrains is transforming traditional models.
- Smart Systems: Integration of AI for real-time performance optimization.
- Lightweight Materials: Use of advanced composites to reduce weight and increase efficiency.
Sustainability and Efficiency
- Hybrid Technologies: Combining different energy sources to minimize environmental impact.
- Recycling Initiatives: Focus on materials recovery to promote circular economy practices.
- Alternative Fuels: Research into hydrogen and biofuels to further reduce carbon footprints.