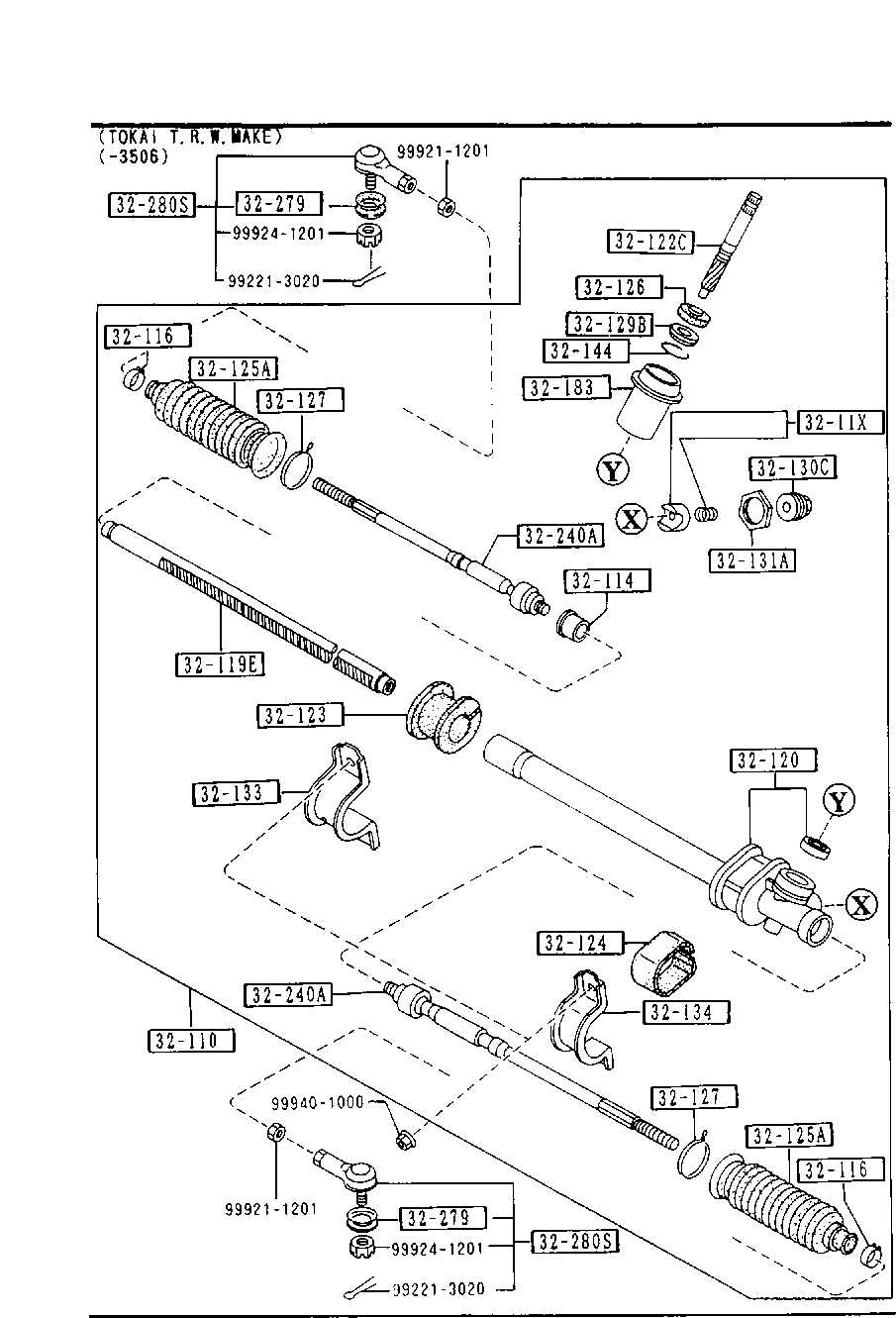
The intricate assembly responsible for directing a vehicle involves various elements working in unison. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth navigation and precise handling. A thorough grasp of these constituents is essential for effective maintenance and repair, enabling vehicle owners to enhance performance and safety on the road.
Recognizing how these individual elements interact can illuminate their significance within the overall system. This knowledge aids in diagnosing issues and understanding the functionality of the steering system. A comprehensive overview of these components can provide valuable insights for both enthusiasts and professionals alike.
By familiarizing oneself with the structure and operation of these key elements, individuals can make informed decisions regarding repairs and upgrades. This understanding not only promotes longevity but also contributes to a more enjoyable driving experience. A detailed exploration of these components can reveal the sophistication of automotive engineering.
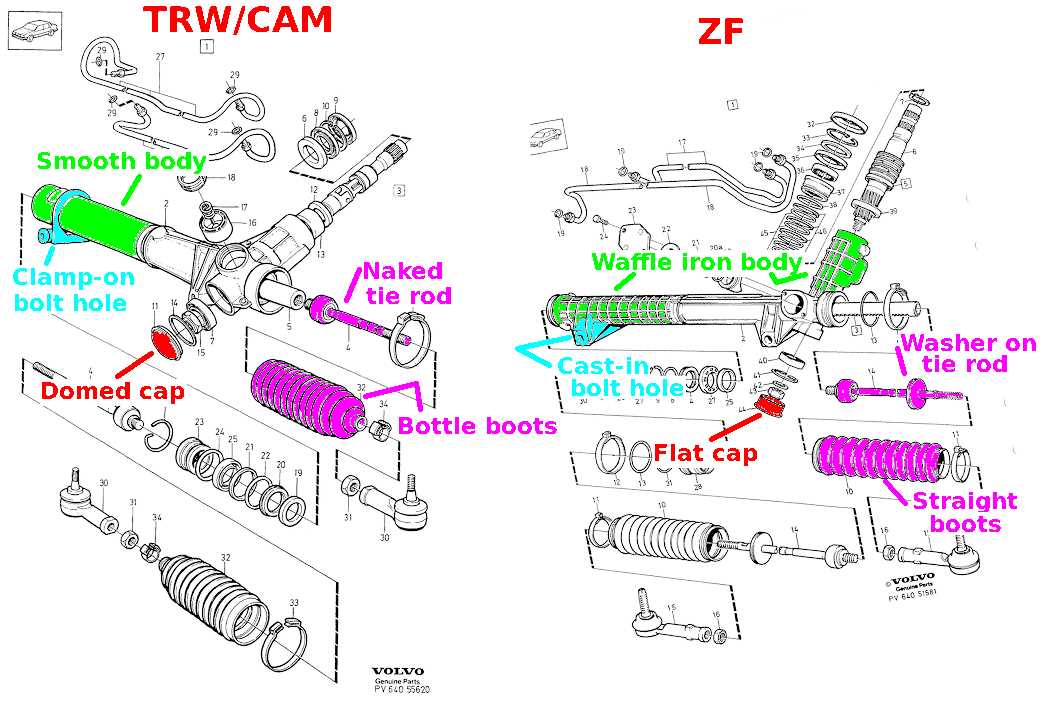
This section aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of a vital component in automotive systems. It covers the functionality, importance, and design elements of these critical assemblies that ensure precise vehicle control and safety.
These assemblies are designed to translate the driver’s input into directional movement, playing a crucial role in the overall driving experience. The construction of such systems involves various elements, each contributing to its effectiveness and reliability.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Housing | The outer casing that protects internal components. |
| Sector Shaft | Connects the input from the driver to the mechanism that turns the wheels. |
| Input Shaft | Transfers motion from the steering wheel to the assembly. |
| Gear Assembly | Contains gears that amplify the driver’s input for enhanced control. |
| Piston | Assists in the movement and stability of the steering mechanism. |
Key Components of Steering Mechanism
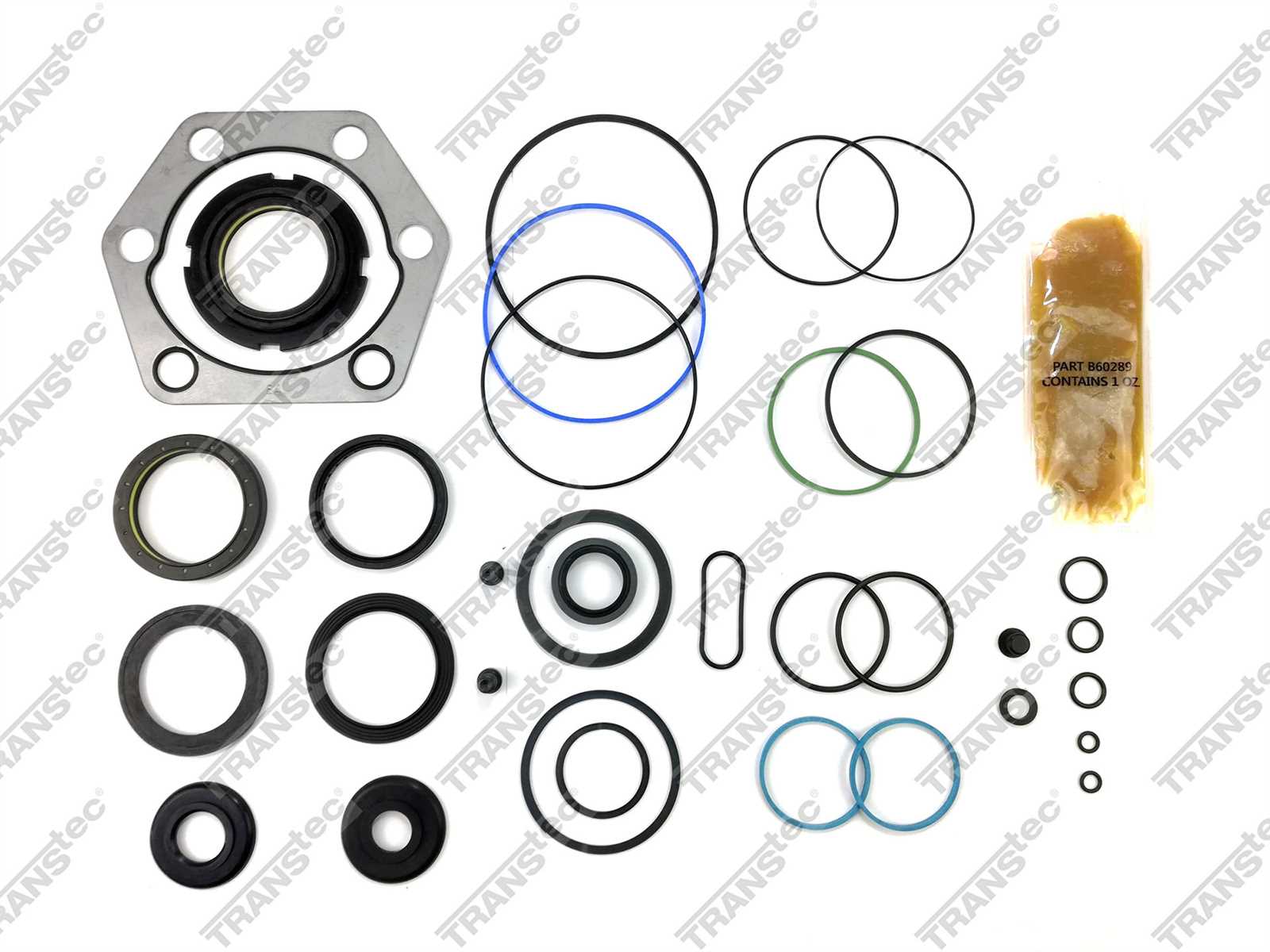

The functionality of a vehicle’s directional control system relies on several essential elements. Understanding these components is vital for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring safe operation.
- Column: The central shaft that transmits the driver’s input to the mechanism.
- Gear Assembly: A set of gears that translates the rotational movement from the column into linear motion.
- Control Linkage: Connects the gear assembly to the wheels, allowing for directional changes.
- Power Assist Unit: A hydraulic or electric component that reduces the effort needed to turn the wheels.
- Knuckles: Pivot points that allow the wheels to turn while maintaining stability.
Each of these elements plays a crucial role in achieving precise maneuverability, contributing to the overall driving experience.
Functionality of Each Steering Part

This section delves into the various components involved in the directional control system of a vehicle, highlighting their roles and interconnections.
- Control Mechanism: This element is responsible for transmitting driver input, allowing for precise maneuvering of the vehicle.
- Connecting Links: These links facilitate the transfer of motion from the control mechanism to the wheels, ensuring a seamless response to driver commands.
- Sector Gear: This component converts the rotational motion from the control mechanism into linear motion, allowing for effective wheel movement.
- Pinion Shaft: The pinion shaft serves as a vital link between the control mechanism and the sector gear, enabling efficient motion transfer.
- Power Assist Unit: This unit enhances the driver’s input, providing additional force to ease the effort required for steering, especially at lower speeds.
- Mounting Bracket: This part secures the entire assembly, ensuring stability and alignment during operation.
Understanding the functionality of each component is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring safety on the road.
Common Issues with Steering Boxes
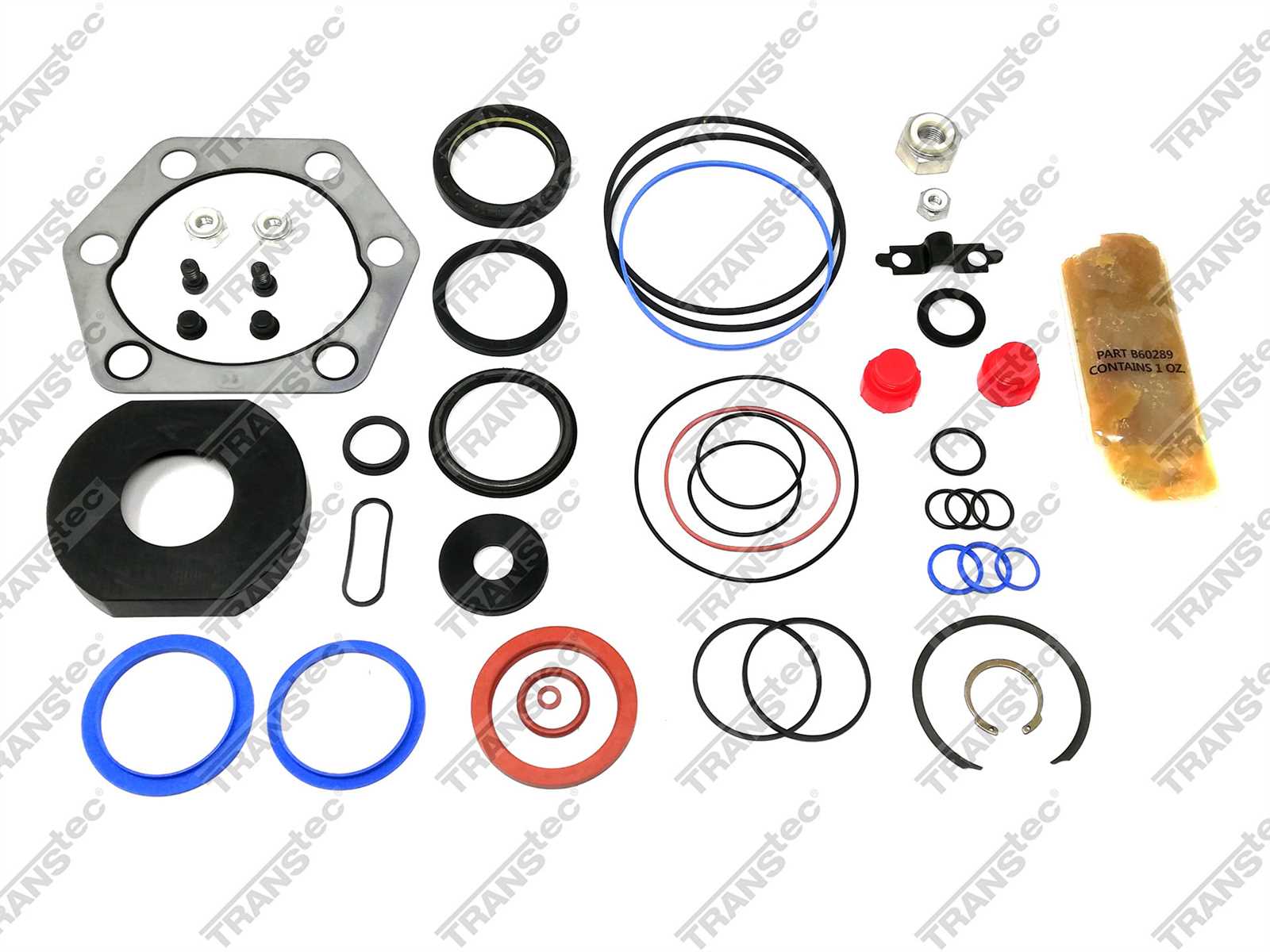

Mechanisms designed for directional control in vehicles often encounter various challenges that can impact their functionality. Understanding these common problems can aid in maintaining optimal performance and safety.
- Fluid Leaks: One of the most prevalent issues is the leakage of hydraulic fluid, which can lead to reduced efficiency and potential failure of the mechanism.
- Worn Components: Over time, internal parts may wear out due to friction and stress, causing misalignment and impaired operation.
- Unusual Noises: Grinding, whining, or clunking sounds during operation can indicate underlying mechanical problems that require immediate attention.
- Reduced Responsiveness: A noticeable delay or lack of responsiveness when turning can signify issues with internal mechanisms or fluid levels.
- Excessive Play: Increased play in the control mechanism may result from worn bushings or joints, affecting the precision of directional changes.
Addressing these concerns promptly can prevent more severe complications and enhance the longevity of the directional control system.
Maintenance Tips for Steering Systems
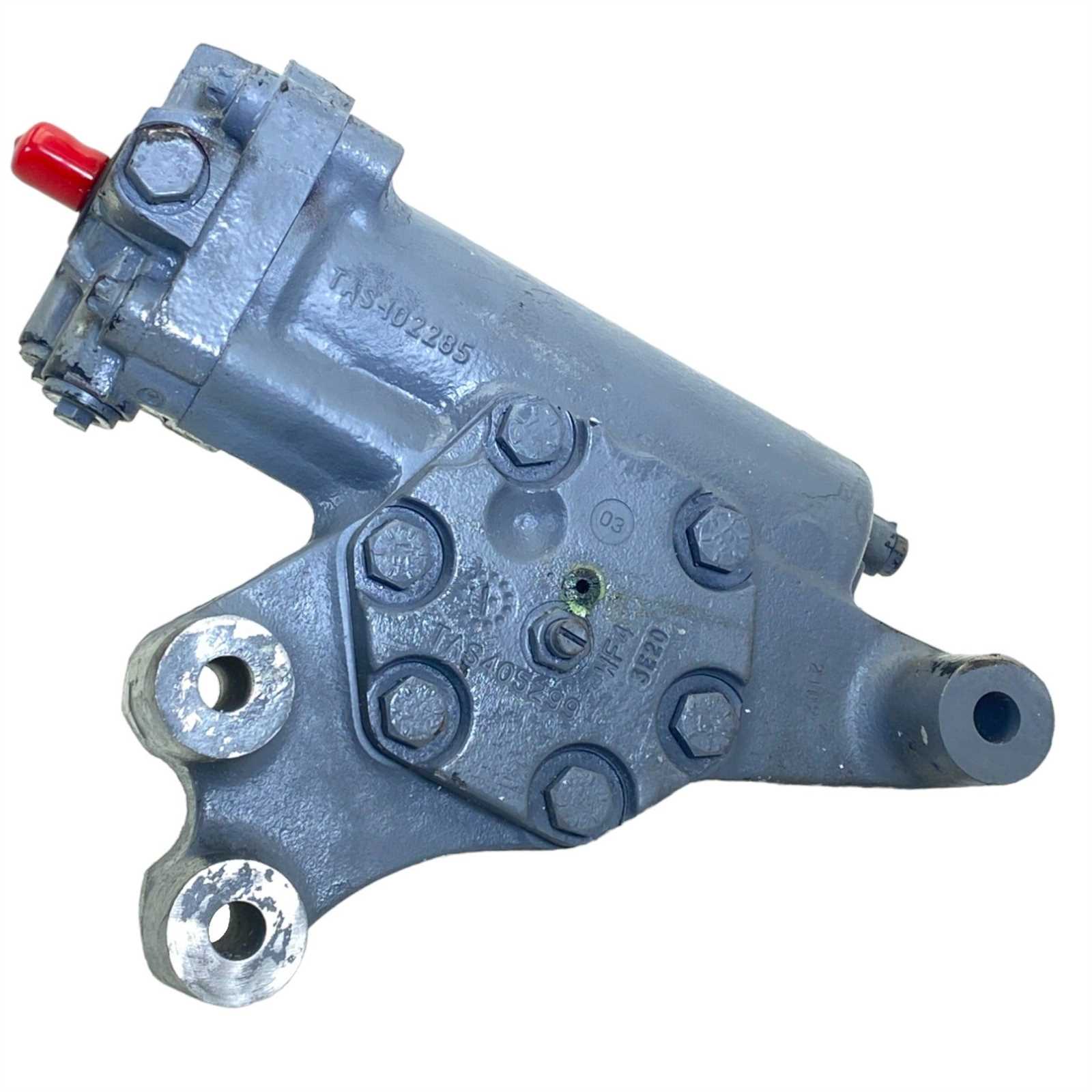

Proper upkeep of guidance mechanisms is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Regular attention to these components can prevent costly repairs and enhance safety on the road. Below are some key recommendations to maintain these critical systems.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct frequent evaluations to identify any signs of wear or damage. Look for leaks, cracks, or unusual noises.
- Fluid Checks: Ensure that hydraulic fluid levels are within the recommended range. Replace fluids as necessary to maintain effectiveness.
- Alignment Services: Schedule routine alignment checks to ensure that all components function harmoniously, preventing uneven tire wear.
- Component Cleaning: Keep all elements free from dirt and debris. This will help avoid contamination that can impair function.
- Professional Maintenance: Engage qualified technicians for thorough inspections and repairs. They can provide insights that might not be visible during casual checks.
By adhering to these maintenance practices, vehicle owners can significantly enhance the performance and safety of their guidance systems, ensuring a smoother driving experience.
Identifying Parts in Diagrams
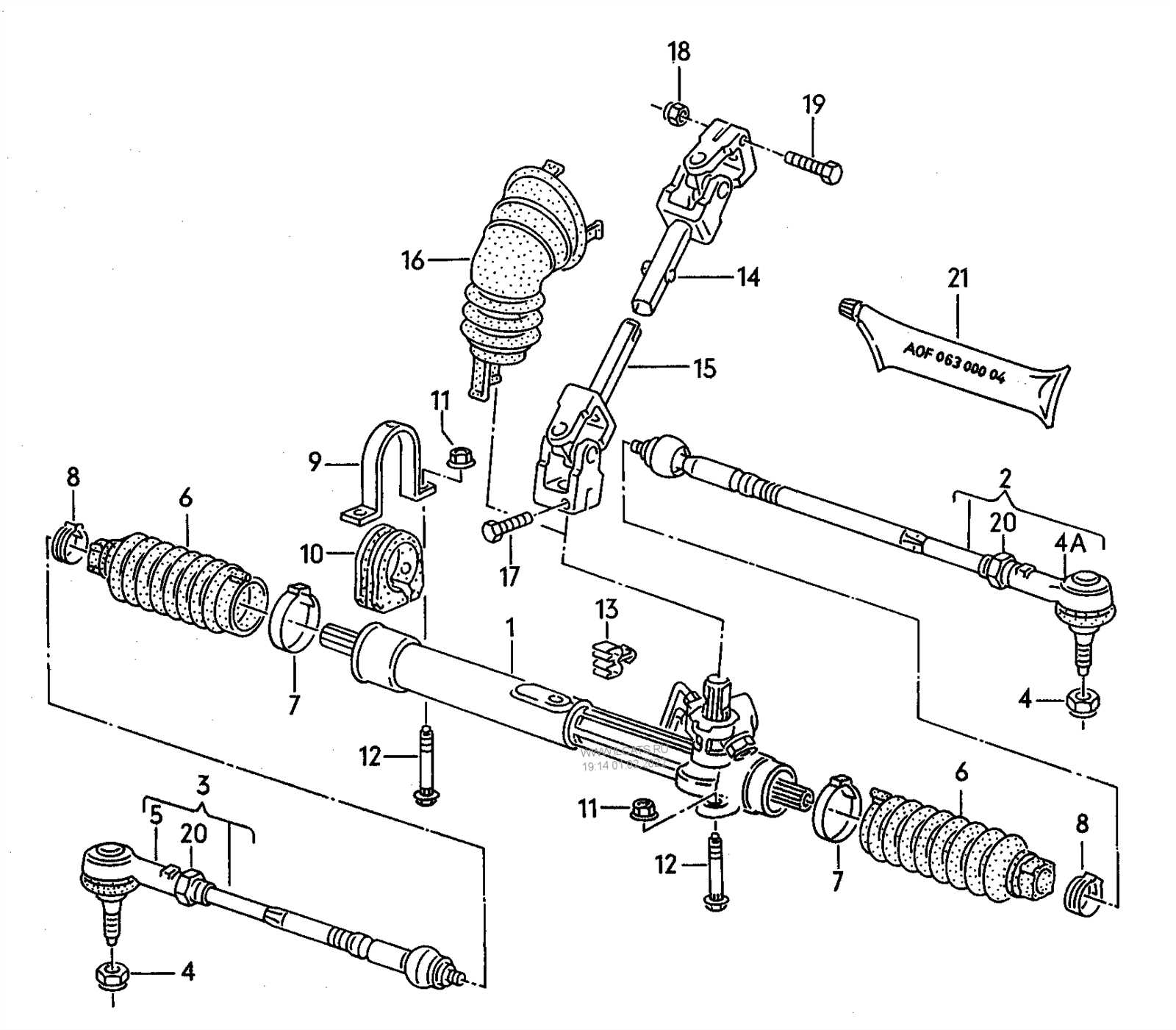
Understanding the components represented in technical illustrations is crucial for effective maintenance and repair. Recognizing these elements allows individuals to navigate complex schematics with ease and ensures that each piece functions harmoniously within the assembly.
Key Components to Recognize

- Connectors: Often represented as circles or blocks, these elements facilitate connections between different sections.
- Control Elements: Typically shown as levers or knobs, these components allow for the manipulation of the system.
- Housing: Illustrated as outlines or shaded areas, this defines the structure that contains the inner workings.
Common Symbols Used

- Lines: Indicate pathways for movement or flow.
- Arrows: Show direction or operation flow, providing clarity on how components interact.
- Labels: Textual descriptions that help identify specific functions or characteristics of the parts.
Comparative Analysis of Steering Models

This section presents a detailed examination of various designs used in vehicle guidance systems. By exploring different frameworks, we aim to highlight their unique features, advantages, and limitations, ultimately providing a comprehensive understanding of how these mechanisms operate within modern vehicles.
Key Features of Different Designs
- Design A: Characterized by a compact structure, it offers enhanced responsiveness and precision.
- Design B: Known for its durability, this model withstands high stress, making it ideal for off-road applications.
- Design C: Features advanced technology that provides greater control and feedback to the driver.
Advantages and Limitations

- Design A:
- Advantages: Lightweight, quick response.
- Limitations: May lack durability in extreme conditions.
- Design B:
- Advantages: Robust, reliable under various conditions.
- Limitations: Heavier, which can affect fuel efficiency.
- Design C:
- Advantages: High precision, excellent driver feedback.
- Limitations: More complex and potentially costlier to repair.
Upgrading and Replacing Components

Enhancing the functionality of your vehicle’s control system often involves upgrading or replacing specific components. This process can lead to improved handling, responsiveness, and overall driving experience. Whether you’re looking to enhance performance or replace worn-out parts, understanding the options available is crucial.
When considering upgrades, it is essential to assess the compatibility of new components with your existing setup. Replacements should focus on high-quality alternatives that offer durability and efficiency. Below is a table outlining various components that can be upgraded or replaced, along with their potential benefits.
| Component | Potential Upgrade | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Control Arm | Adjustable Control Arms | Improved alignment and handling |
| Bushing | Polyurethane Bushings | Enhanced stability and durability |
| Linkage | Heavy-Duty Linkage | Increased strength and reliability |
| Hydraulic System | Performance Hydraulic System | Better response and feedback |
Resources for Further Learning

For those interested in deepening their knowledge about automotive mechanisms and components, various educational materials are available. Exploring different types of literature, online platforms, and workshops can enhance understanding and practical skills in this field.
Below is a table summarizing some valuable resources:
| Resource Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Books | Automotive Engineering Textbook | A comprehensive guide covering various automotive systems and their functions. |
| Online Courses | Coursera – Automotive Basics | Offers foundational knowledge about vehicle mechanics and components. |
| Workshops | Local Mechanic Classes | Hands-on learning experiences with industry professionals to gain practical insights. |
| Forums | Automotive Enthusiasts Forum | A community platform for discussing various topics related to vehicle mechanics. |