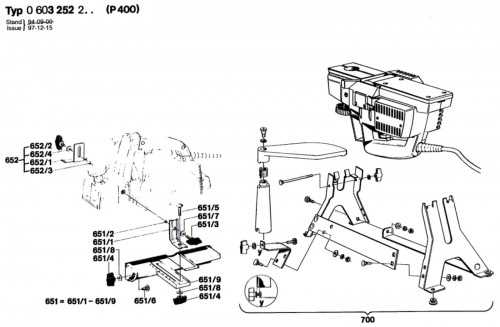
Understanding the internal structure and key elements of a professional sprayer is essential for its maintenance and optimal performance. Each individual element contributes to the efficient operation of the device, ensuring smooth application and reducing the chances of malfunction.
In this section, we will delve into the essential components that make up this powerful spraying machine. By breaking down its core elements, you can better grasp the role each part plays in delivering consistent results, from fluid movement to precision control.
Whether you’re performing routine upkeep or troubleshooting, having a clear view of how everything fits together will make your task much simpler. Let’s take a closer look at the individual pieces that enable the system to function seamlessly.
Comprehensive Breakdown of Titan 640 Components
Understanding the detailed structure of this advanced sprayer model is crucial for optimal maintenance and performance. Each element is designed to ensure reliability and efficiency during operation. Familiarizing yourself with the core components allows for easier troubleshooting and proper care, ensuring longevity and top-notch performance.
Pump Assembly: This section is responsible for delivering consistent pressure and flow. Regular inspection of its seals and valves can help prevent leakage and maintain consistent operation.
Control Unit: The control mechanism provides precise adjustments during application. Keeping this part well-calibrated enhances the overall functionality of the equipment.
Spray Gun: The applicator ensures even distribution of the material. Maintenance of its nozzles and trigger system is essential for achieving a smooth and uniform spray pattern.
Motor System: The power source drives the entire system, ensuring efficient performance. Regular checks for overheating or unusual noises are key to extending its lifespan.
Key Internal Mechanisms and Their Functions
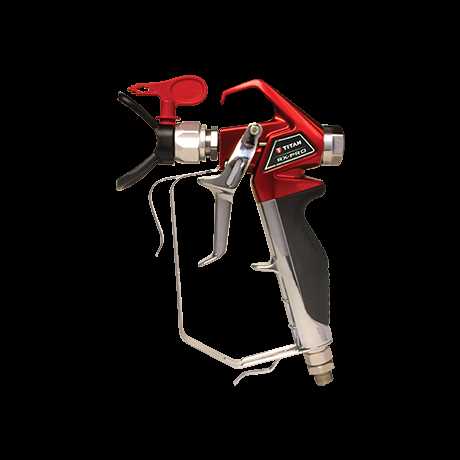

The internal structure of modern spray equipment relies on the harmonious interaction of several essential components. These mechanisms work together to ensure smooth operation, optimal performance, and longevity of the system. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintaining and troubleshooting the device.
Pump System
The pump is a central component that drives the fluid through the machine. It builds the necessary pressure to atomize the liquid, allowing for a consistent and even distribution. Proper maintenance of the pump is vital to avoid pressure drops or irregular flow.
Pressure Control Valve
This valve is responsible for regulating the pressure within the system. By adjusting the pressure levels, the operator can ensure that the fluid is delivered at the correct intensity, ensuring the desired application result. A malfunctioning valve can lead to overspray or uneven coverage.
External Parts Layout for Easy Maintenance
When it comes to efficient upkeep, the arrangement of external components plays a critical role in simplifying the process. A well-organized exterior layout allows users to access key elements quickly, reducing the time needed for routine checks and adjustments. This structure not only promotes easy upkeep but also ensures smooth operation by minimizing the potential for errors during handling.
Clear Access to Key Components
Positioning essential components in accessible areas makes regular servicing straightforward. By focusing on a design that keeps critical elements within easy reach, it reduces the need for dismantling other parts during maintenance, leading to faster and more efficient repairs.
Minimizing Downtime Through Smart Design
An intelligent exterior setup ensures that maintenance tasks can be performed swiftly, minimizing downtime. This layout helps operators identify areas requiring attention and allows for swift interventions, ensuring the equipment remains operational for longer periods without unnecessary interruptions.
Critical Components of the Spray System
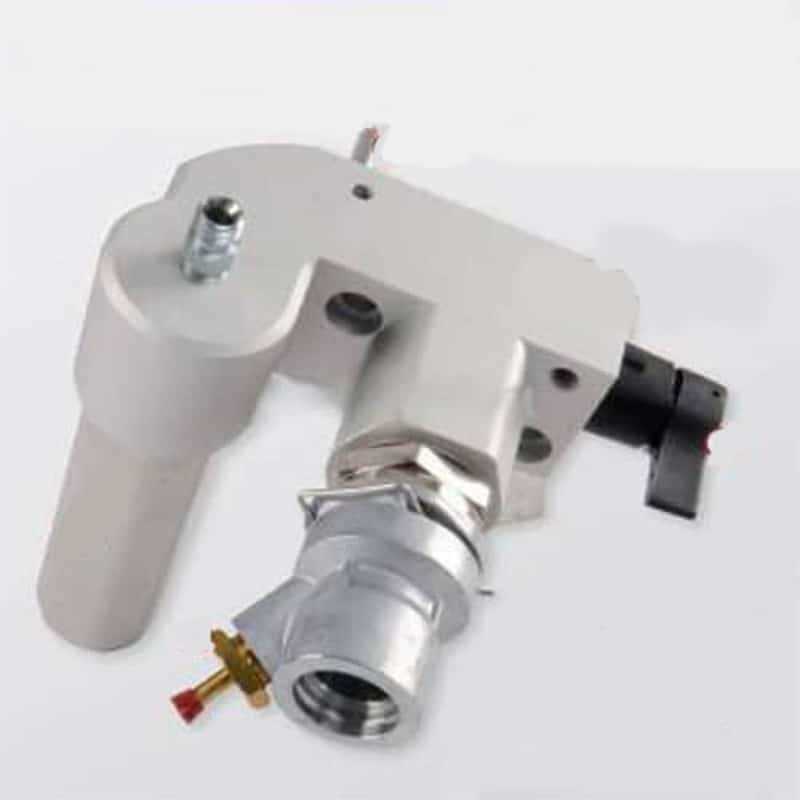

The functionality of a spray system relies on several interconnected elements that work together to deliver efficient coating application. These essential parts ensure that the fluid is consistently pressurized, filtered, and delivered smoothly, allowing for optimal performance in various industrial and residential projects.
Fluid Management Components
- Pump Assembly – The heart of the system, responsible for generating the necessary pressure to move the liquid through the system.
- Filters – Critical in preventing debris from entering the system, these maintain clean operation and extend the lifespan of the unit.
- Pressure Regulators – Ensure the correct level of pressure is maintained throughout the application process.
Application Mechanism
- Spray Gun – The tool used to control the release of fluid,
Common Replacement Parts and Their Roles
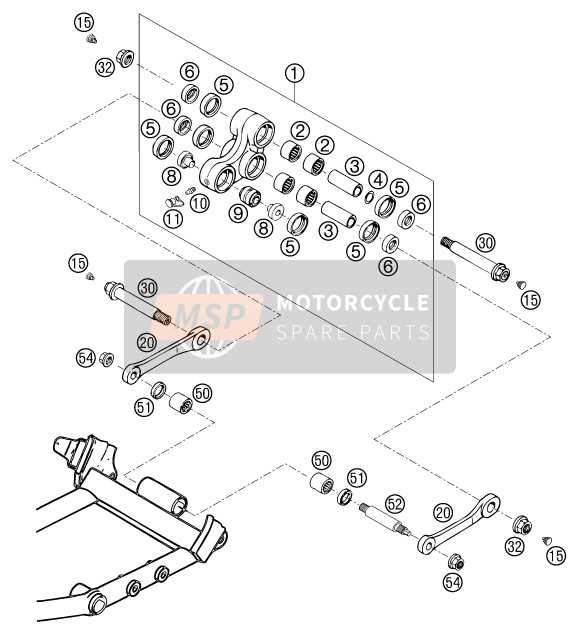
In various spray systems, certain components frequently require replacement due to wear and tear. These elements are essential for maintaining the overall performance and longevity of the equipment, ensuring smooth operation over time. Knowing which components to replace can significantly extend the lifespan of the machinery.
Pumps are vital in creating the necessary pressure to ensure the even distribution of materials. Over time, they can wear out and need replacement to maintain consistent performance.
Hoses play a crucial role in transporting fluids. Their durability can diminish with extended use, leading to leaks or reduced pressure, making them a common replacement item.
Valves are responsible for controlling the flow and pressure. Replacing worn-out valves helps prevent malfunctions and ensures precise control during operation.
Filters prevent debris from entering critical components, safeguarding the system from damage. Regularly replacing clogged or damaged filters helps maintain peak efficiency.
Proper maintenance and timely
How the Pump Assembly Is Structured
The structure of a pump assembly is crucial for its efficient operation. It typically consists of several interconnected components that work harmoniously to facilitate fluid movement. Each part plays a specific role in the overall functionality, ensuring that the system operates smoothly and effectively.
The primary component is the housing, which encases the internal mechanisms and provides structural integrity. Within the housing, you will find the impeller, which is responsible for drawing in and expelling the fluid. The volute surrounds the impeller, guiding the fluid towards the outlet while converting kinetic energy into pressure. Additionally, a set of seals and bushings are integrated to prevent leaks and reduce friction, ensuring longevity and reliability in operation.
Furthermore, the assembly includes a motor that powers the impeller, creating the necessary force to move the fluid. The alignment of these components is vital; any misalignment can lead to reduced performance or mechanical failure. Proper maintenance and understanding of the assembly’s structure contribute to optimal functioning and durability.
Understanding the Hose Connections and Fittings
Effective management of fluid flow relies heavily on the proper configuration of hoses and their corresponding attachments. This section explores the various components involved, emphasizing the significance of each element in ensuring a seamless operation.
Types of Connections: There are several types of connections used to join hoses, each designed for specific applications. These include quick-disconnect fittings, threaded joints, and clamp-style connectors. Each type offers distinct advantages in terms of ease of use and reliability.
Material Considerations: The choice of materials for both hoses and fittings is crucial. Durable materials such as reinforced rubber or high-grade plastics are commonly used to withstand pressure and resist wear. Selecting the right materials can significantly enhance the longevity of the system.
Maintenance Tips: Regular inspection of hose connections is vital for preventing leaks and ensuring optimal performance. Checking for wear and tear, tightening fittings, and replacing damaged components are essential practices that can extend the life of the entire assembly.
Conclusion: Understanding the various hose connections and fittings is essential for maintaining an efficient and effective fluid transfer system. Proper selection and maintenance of these components contribute to overall performance and reliability.
Electrical Parts Overview and Wiring Guide
This section provides a comprehensive examination of the electronic components and their interconnections, focusing on functionality and the importance of proper wiring. Understanding these elements is essential for ensuring optimal performance and safety in the system.
Key Components and Functions
Various electronic components play critical roles in the overall operation of the unit. Each element must be carefully integrated to achieve desired outcomes. Below is a brief overview of essential components:
Component Description Function Relay An electromechanical switch. Controls high-power devices using low-power signals. Fuse A safety device that protects circuits. Prevents overloads by breaking the circuit. Connector A device for joining electrical circuits. Facilitates reliable connections between wires. Voltage Regulator A component that maintains consistent voltage levels. Ensures stable operation of sensitive electronics. Wiring Techniques
Proper wiring techniques are crucial for ensuring reliability and safety in electronic systems. Following best practices can prevent issues such as shorts or signal loss. Here are some recommended methods:
- Use appropriate gauge wires for the current load.
- Ensure all connections are secure and free of corrosion.
- Route wires away from heat sources to avoid damage.
Important Seals and O-rings in Titan 640
In mechanical systems, seals and O-rings play a crucial role in maintaining functionality and efficiency. These components are designed to prevent fluid leakage, ensuring the integrity of systems under various pressure conditions. Understanding the significance of these elements helps in proper maintenance and repair practices.
Types of Seals and Their Functions
Different types of seals serve specific purposes, ranging from preventing leaks to protecting internal components from contaminants. Their material composition and design influence their performance in various operating environments.
Seal Type Function Material Dynamic Seals Prevent leakage during movement Rubber, PTFE Static Seals Seal non-moving components Rubber, Silicone O-rings Seal joints under compression Nitrile, EPDM Maintenance Considerations
Regular inspection of seals and O-rings is essential to prevent unexpected failures. Signs of wear or damage can lead to significant system malfunctions. Timely replacement and proper lubrication are key factors in extending the lifespan of these components.