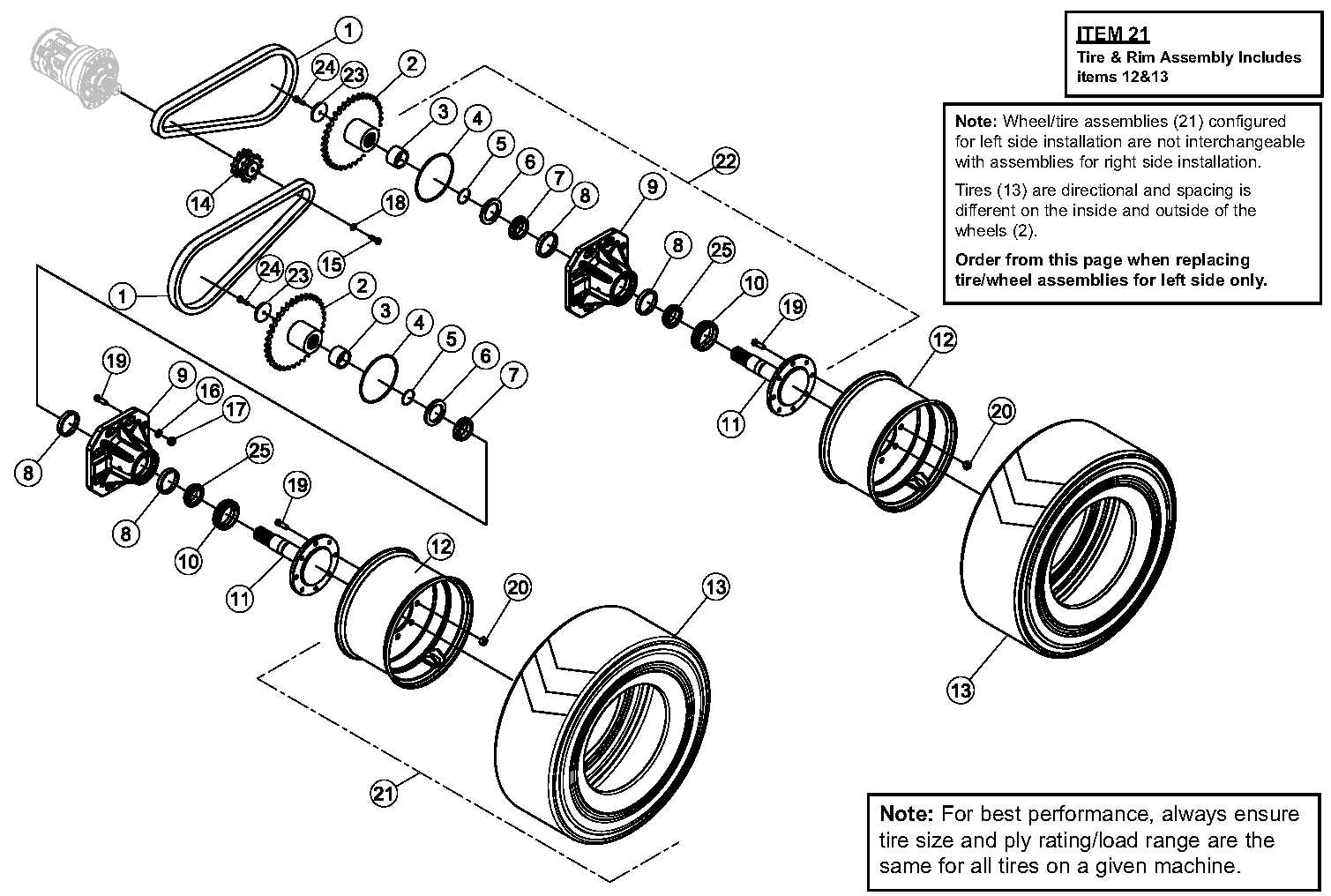
When working with heavy machinery, it is essential to have a clear understanding of how various elements are connected and function together. Recognizing the structure and key elements of the equipment allows for better maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring that the machine operates efficiently and safely.
In this section, we will explore the organization of crucial elements within a compact loader. By examining the layout and connections, users can gain insights into the operational aspects and identify potential issues more effectively. This knowledge is vital for those involved in routine checks and repairs, as it aids in optimizing the equipment’s lifespan and performance.
We will take a closer look at the configuration of different mechanical and hydraulic systems, focusing on their role in the overall functionality of the machine. Whether for repair or general upkeep, a comprehensive understanding of these systems ensures smooth operation and minimizes downtime.
Understanding the Structure of Compact Track Loader
Exploring the structure of this compact machine reveals a well-coordinated design that ensures efficiency in various types of terrain. The core layout emphasizes balance, stability, and versatility, making it a powerful tool for multiple construction tasks.
Core Components Overview
- Chassis Framework: The foundation is designed to distribute weight evenly, offering durability and optimal ground contact.
- Hydraulic System: This feature controls the movement of the machine’s arms, enhancing precision and responsiveness during operation.
- Track System: A robust track system allows for smooth movement over rough surfaces, improving the machine’s ability to handle various worksite conditions.
Mechanical Operation Features
- Control Mechanisms:
Main Components of the Compact Loader
The core systems of this versatile machine are designed to ensure smooth operation across various environments. Its robust structure integrates multiple essential parts that contribute to overall efficiency, durability, and performance. Each section works in harmony to deliver consistent power and control.
Engine and Powertrain
The heart of this loader is its engine, providing reliable horsepower for heavy-duty tasks. Connected to the powertrain, it efficiently transmits energy to the wheels or tracks, ensuring optimal movement and torque in challenging terrains.
Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system controls various attachments and enhances operational flexibility. This setup allows for seamless movement of arms, buckets, or other tools, delivering precise control for various tasks, from digging to lifting.
Hydraulic System Overview

The hydraulic system plays a crucial role in powering various components within a machine, providing the force necessary for its smooth and efficient operation. By utilizing fluid dynamics, this system enables the transfer of energy, driving essential functions and ensuring reliable performance under varying conditions.
Key Components
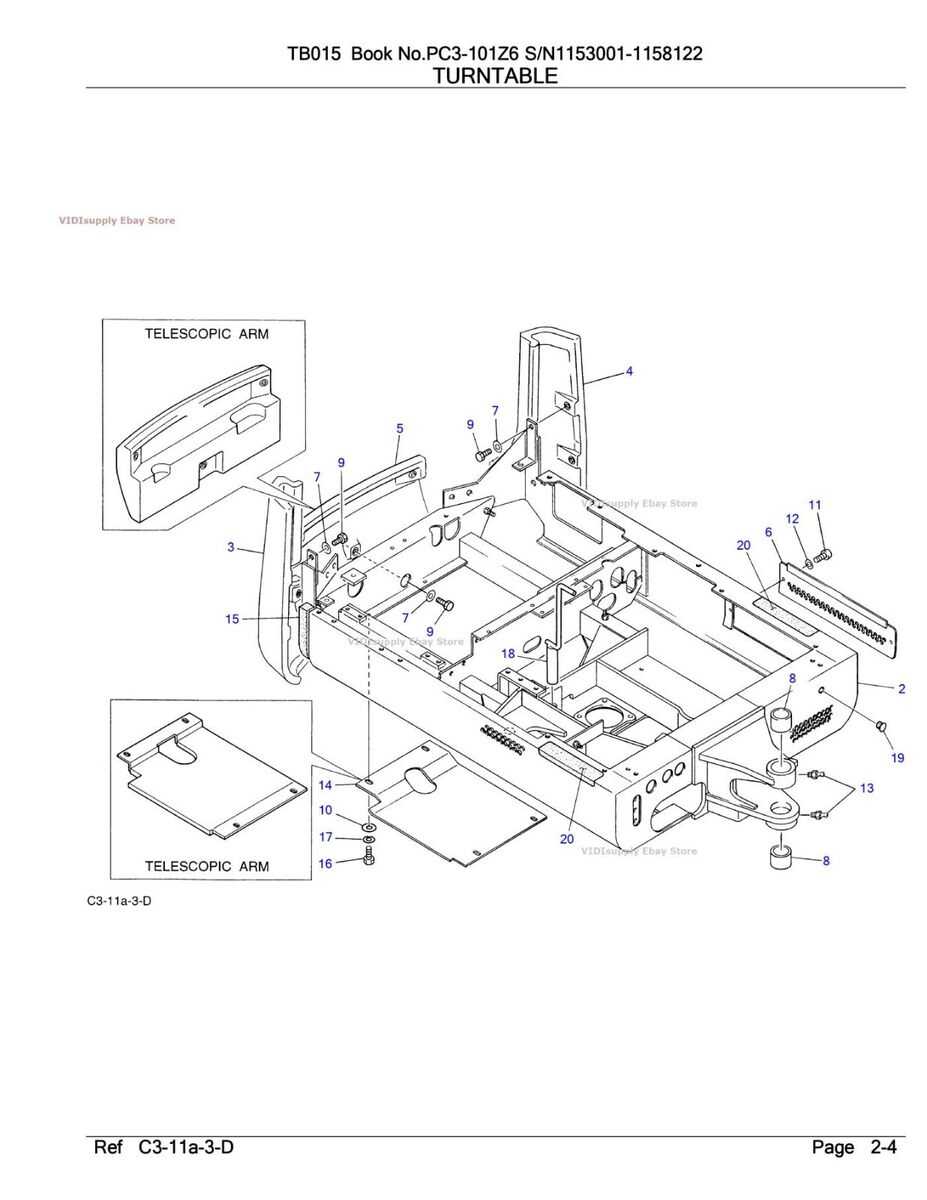
The hydraulic system is composed of several main elements that work together to deliver precise control and power. These include pumps, valves, and cylinders, each responsible for handling different aspects of the machine’s movement and pressure regulation.
Fluid Flow and Pressure Control
At the core of the system is fluid management, where pressure is carefully regulated to match the demands of the task at hand. Valves adjust the flow of hydraulic fluid, ensuring optimal pressure levels, while pumps maintain a steady supply to all moving parts.
Component Engine and Powertrain Elements
The components responsible for the operation of the engine and power delivery system form a crucial aspect of heavy machinery. These elements ensure smooth operation, transferring energy effectively from the engine to the wheels or tracks. A well-maintained system enhances the machine’s performance, ensuring that all tasks are carried out with optimal efficiency.
Engine Structure: The heart of the machine, the engine converts fuel into mechanical energy. Its design focuses on durability and reliability, supporting long hours of work under various conditions. Regular checks and upkeep are essential to maintain its optimal functioning.
Transmission and Drive Systems: The transmission system channels power from the engine to the operational components. It consists of gears and linkages that control the speed and direction of movement. Smooth transitions between gears are vital to prevent wear and ensure longevity.
Cooling and Lubrication Systems: The cooling mechanism prevents overheating during extended use, while the lubrication system ensures that
Cabin and Control Layout

The operator’s area is designed to maximize comfort and efficiency, ensuring all necessary controls are within easy reach. The layout is intuitive, allowing for seamless operation of the machine without distraction. Each feature is thoughtfully placed to support a smooth and productive workflow.
Seat and Comfort: The seating area provides ample space, offering ergonomic support for long hours of use. The positioning of the seat can be adjusted, ensuring a tailored fit for operators of different heights and preferences.
Control Access: The main control levers and switches are strategically arranged to minimize movement, reducing operator fatigue and enhancing precision. Visibility of all essential functions is clear from the seated position, making it easier to monitor and adjust performance as needed.
Display and Monitoring: The control panel features a user-friendly interface with all critical indicators in full view, ensuring the operator stays informed of the machine’s status at all times. This setup supports optimal decision-making and rapid response to
Undercarriage Parts and Functions
The undercarriage system is essential for the overall performance and stability of construction machinery. This section will explore various components that contribute to the mobility and durability of these machines, as well as their respective roles in ensuring efficient operation.
Key Components of the Undercarriage
- Tracks: The continuous bands provide traction and support, allowing the vehicle to navigate different terrains.
- Rollers: These cylindrical elements help in distributing weight and ensuring smooth movement over surfaces.
- Sprockets: These toothed wheels engage with the tracks, facilitating movement and maintaining tension.
- Idlers: Located at the front and rear, these components guide the track and help in maintaining proper alignment.
- Suspension System: This system absorbs shocks and vibrations, enhancing comfort and stability during operation.
Functions and Importance
- Mobility: The undercarriage design directly affects the machine’s ability to traverse various surfaces.
- Weight Distribution: Properly designed components ensure that weight is evenly spread, reducing wear and tear.
- Stability: A robust undercarriage contributes to the overall balance of the equipment, minimizing the risk of tipping.
- Durability: Quality materials used in the construction of undercarriage components enhance longevity and reduce maintenance needs.
Cooling and Ventilation System Breakdown
The cooling and ventilation system is a crucial component that ensures optimal performance and longevity of machinery. Proper airflow and temperature regulation are essential for maintaining efficient operation and preventing overheating. Understanding the different elements of this system can help in effective troubleshooting and maintenance.
Key Components of the System
- Radiator: Responsible for dissipating heat generated by the engine.
- Cooling Fan: Helps circulate air through the radiator to enhance cooling efficiency.
- Thermostat: Regulates the flow of coolant based on temperature readings.
- Hoses: Transmit coolant between the engine and radiator.
Common Issues and Solutions
- Overheating: Check for blockages in the radiator or malfunctioning thermostat.
- Insufficient Airflow: Inspect the fan for proper operation and clear any debris obstructing airflow.
- Coolant Leaks: Examine hoses for cracks or loose connections that may cause fluid loss.
Electrical System and Wiring Details
The electrical framework of the machinery is crucial for its operational efficiency and safety. Understanding the various components and their interconnections can aid in troubleshooting and maintenance. This section provides insights into the essential wiring arrangements and electrical components used in the system.
Component Description Function Battery Stores electrical energy for startup and operation. Supplies power to the electrical system. Fuse Protective device that interrupts electrical flow. Prevents overload and potential damage. Starter Motor Initiates engine operation. Transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. Alternator Generates electricity while the engine runs. Charges the battery and powers electrical systems. Wiring Harness Network of wires connecting components. Facilitates communication between electrical parts. Maintenance Tips for Key Components
Ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of vital machinery elements is essential for efficient operation. Regular upkeep not only enhances functionality but also helps prevent costly repairs. This section will explore essential maintenance practices that can be applied to various significant components.
Component Maintenance Tip Hydraulic System Regularly check fluid levels and replace filters to maintain optimal pressure and prevent contamination. Engine Perform oil changes as recommended and inspect air filters frequently to ensure proper airflow and function. Tracks Keep tracks clean and inspect for wear and tear; adjust tension as needed to prolong life. Electrical Components Examine wiring for frays and secure connections; ensure battery terminals are clean and free of corrosion. Cooling System Check coolant levels regularly and clean radiators to prevent overheating and maintain efficiency.