
Understanding how intricate systems come together is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. When looking into the internal composition of equipment, having a clear view of the interconnected elements can significantly simplify repairs and upgrades.
A well-structured layout of the core mechanisms allows for easy identification of each element’s purpose. It offers a roadmap to understand how individual modules interact within the system, ensuring smooth operations and precise handling of potential issues.
By examining technical breakdowns of assemblies, users gain insight into operational dynamics and can make informed decisions when handling replacements, improvements, or routine upkeep. This kind of clarity ensures efficiency while reducing guesswork.
Overview of Subzero Component Structure
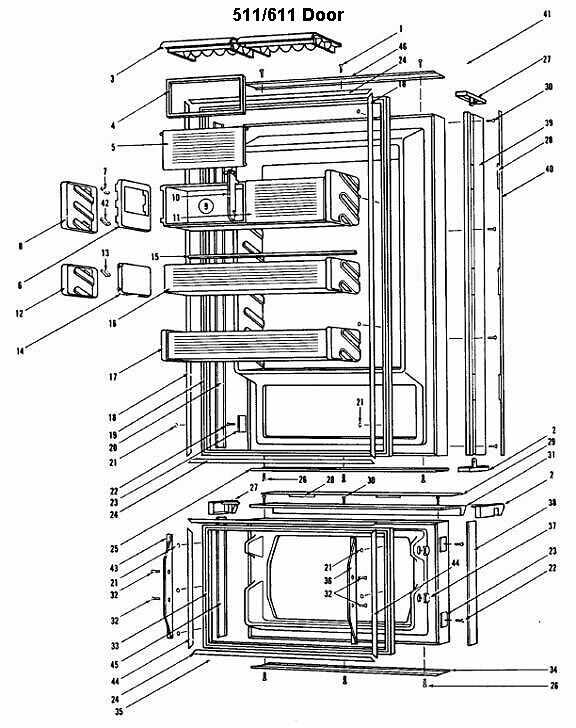
This section provides a detailed look into the internal framework and how individual elements are organized to ensure optimal functionality. Each component plays a specific role in the overall system, contributing to its performance, reliability, and longevity.
The structure consists of interconnected modules, with critical units positioned to maximize efficiency. The arrangement supports smooth operation, allowing seamless interaction between mechanical and electronic systems. Proper alignment of these elements is essential to maintaining peak performance under various conditions.
Design principles focus on durability and modularity, ensuring that individual sections can be easily accessed or replaced without disrupting the entire system. Thoughtful engineering minimizes complexity, promoting ease of maintenance and consistent operation over extended periods.
How to Identify Key Elements
Recognizing the essential components of a system helps ensure efficient maintenance and troubleshooting. By understanding how individual elements contribute to the overall functionality, it becomes easier to pinpoint potential issues or areas that need attention.
Analyze Structural Components
Start by examining the system’s main framework and physical sections. Look for distinguishing features such as fasteners, connectors, and mechanical joints. These elements often indicate how the assembly is held together and which sections can be disassembled for inspection or replacement.
Check for Functional Indicators
Observe key operational elements like control modules, wiring, and sensors. Pay attention to markings or serial identifiers that suggest specific roles or functions. Such details make it easier to distinguish between critical and auxiliary components, guiding more effective repairs or adjustments.
Exploring the Interior Layout
The internal arrangement of cooling equipment is designed to balance functionality and accessibility. Every component inside serves a specific purpose, contributing to seamless performance and ease of maintenance. This section provides an overview of how different elements are positioned and interconnected, ensuring optimal operation.
Key Structural Elements
The layout is divided into distinct sections, each dedicated to a particular function. Shelving and storage compartments are configured to maximize available space while ensuring proper air circulation. Cooling systems, including fans and ventilation pathways, are strategically located to maintain even temperature distribution.
Accessibility and Maintenance

Accessibility is prioritized by arranging key elements within reach for regular cleaning or adjustments. Maintenance areas are clearly defined, allowing quick identification of areas requiring attention. Flexible panel designs and modular components further enhance convenience, minimizing downtime during repairs.
Common Issues Related to Specific Parts
Identifying and resolving recurring technical problems often requires focusing on individual components within a system. Over time, certain elements tend to experience predictable challenges due to wear, improper handling, or environmental factors.
Seals and Gaskets: Frequent wear and degradation can lead to air leaks, reducing system efficiency. Inspecting for cracks or hardening is crucial to maintain optimal performance.
Cooling Units: Blockages or insufficient maintenance may result in temperature inconsistencies. Regular cleaning and proper airflow ensure consistent operation.
Electrical Modules: Loose connections or short circuits often occur over time. Routine inspections help detect faulty wiring or connectors before critical failures happen.
Doors and Hinges: Misalignment or excessive wear on moving parts may cause improper sealing, leading to energy loss. Adjustments or timely lubrication can prevent these issues.
Maintenance Tips for Long-Term Use

Ensuring the durability and efficient performance of complex systems requires consistent upkeep. Regular attention to key components helps prevent wear and tear, while extending the system’s overall lifespan. Proactive care not only minimizes unexpected breakdowns but also ensures smooth operation in demanding environments.
Routine Cleaning and Inspection
- Perform periodic inspections to identify early signs of malfunction or corrosion.
- Clean surfaces and internal sections to avoid dirt buildup that could affect functionality.
- Use appropriate cleaning agents compatible with the materials to prevent damage.
Component Replacement Strategy
- Follow manufacturer-recommended intervals for replacing essential elements.
- Keep spare
Where to Find Replacement Components
Locating suitable components for your refrigeration unit is essential for maintaining optimal performance and longevity. Whether you’re addressing a malfunction or simply upgrading, knowing where to source these items can save both time and effort.
Authorized Retailers
One of the most reliable avenues for obtaining replacement items is through authorized retailers. These establishments often provide:
- Genuine components that ensure compatibility.
- Expert advice on installation and maintenance.
- Warranties on parts purchased.
Online Marketplaces
The internet offers a plethora of options for acquiring components. Popular online marketplaces include:
- eCommerce websites that specialize in appliance parts.
- Auctions and second-hand platforms for used components.
- Manufacturer websites that may offer direct sales.
When purchasing online, it’s advisable to verify the credibility of the seller and check reviews to ensure a positive buying experience.
Understanding Wiring and Connectivity
Comprehending the intricacies of electrical connections is essential for maintaining and troubleshooting various appliances. A clear grasp of how components interconnect can significantly enhance efficiency and reliability in operation. This section delves into the fundamental concepts surrounding wiring systems and their significance in ensuring optimal performance.
Wiring systems can often seem complex, but breaking them down into manageable parts can simplify the understanding process. Each connection serves a specific purpose, contributing to the overall functionality of the appliance. By familiarizing oneself with the basic components and their interrelationships, one can better navigate any potential issues that may arise.
Component Function Power Source Provides the necessary energy for operation. Wires Facilitate the transfer of electricity between components. Connectors Join different wires or components to create a complete circuit. Grounding Prevents electrical shock and ensures safety by directing excess current away. By understanding these elements and their roles, individuals can approach appliance maintenance with greater confidence and expertise. This knowledge not only aids in identifying issues more effectively but also empowers users to make informed decisions regarding repairs and upgrades.
Signs of Wear in Mechanical Parts
Mechanical components are subject to various forms of degradation over time due to continuous use and environmental factors. Recognizing the indicators of deterioration is essential for maintaining optimal performance and preventing costly failures. By observing certain characteristics, one can determine the state of these elements and take appropriate actions to ensure their longevity.
Visual Inspection: One of the simplest methods to identify wear is through visual examination. Look for scratches, dents, or discoloration that may suggest excessive friction or contact with other surfaces. Such imperfections can indicate that a component is nearing the end of its operational life.
Unusual Noises: Noises that are out of the ordinary, such as grinding or squeaking, can be signs of worn-down parts. These sounds often result from inadequate lubrication or improper alignment, leading to increased friction and eventual failure if not addressed.
Performance Degradation: A noticeable decrease in efficiency or effectiveness can also signal wear. For instance, if a mechanical system operates slower than usual or struggles to perform its intended function, it may be time to inspect the relevant components for signs of damage.
Heat Generation: Excessive heat is another critical indicator. If certain elements are running hotter than normal, it could suggest that they are experiencing increased friction due to wear. Regular monitoring of temperature can help in identifying potential issues before they escalate.
Physical Play: Any unexpected movement or play in components can indicate that they have loosened or worn out. This can lead to instability and further damage if not remedied. Ensuring tight connections and monitoring for any shifts can help in early detection.