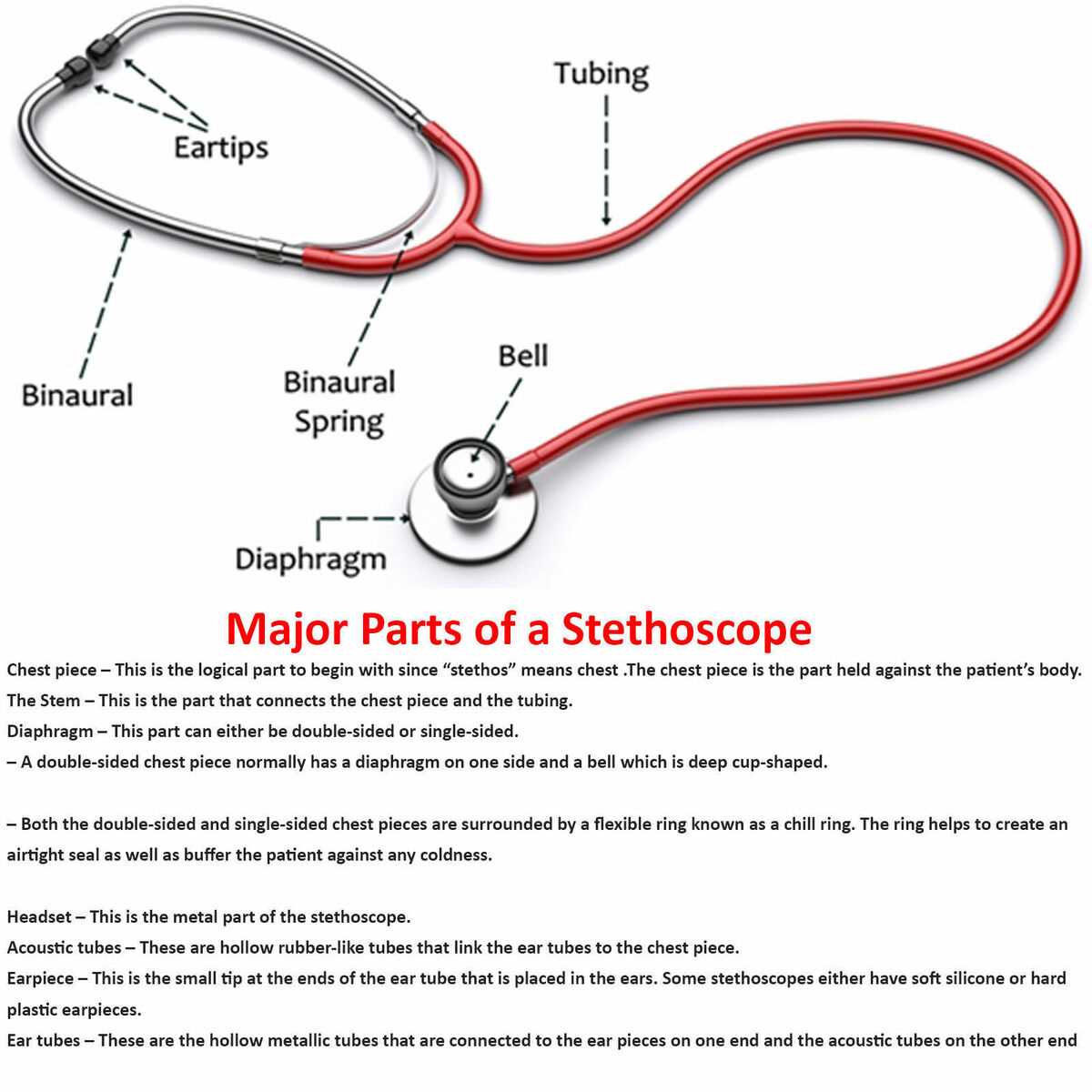
In the realm of healthcare, certain tools stand out for their vital role in patient assessment. Among these, a specialized instrument facilitates the examination of internal bodily sounds, providing healthcare professionals with essential insights into a patient’s condition. This section delves into the intricate design of this essential equipment, exploring the various elements that contribute to its functionality.
The mechanism of this acoustic device is not only a marvel of engineering but also a testament to the advancements in medical technology. Each segment is meticulously crafted to serve a specific purpose, ensuring optimal performance during examinations. By comprehending these elements, one can appreciate how they collectively enhance the efficacy of diagnostic procedures.
Furthermore, understanding the anatomy of this instrument is crucial for aspiring medical practitioners and seasoned professionals alike. A clear grasp of how each component interacts enables improved usage and maintenance, ultimately leading to more accurate assessments and better patient care. As we explore this topic, we will highlight the significance of each section, enriching your knowledge and appreciation of this indispensable tool in modern medicine.
Understanding the Stethoscope Components
Exploring the various elements that come together in this essential medical instrument reveals the intricate design that enables healthcare professionals to perform their duties effectively. Each component plays a crucial role in facilitating accurate diagnostics, ensuring that the device functions harmoniously to capture vital sounds from the body.
Main Features
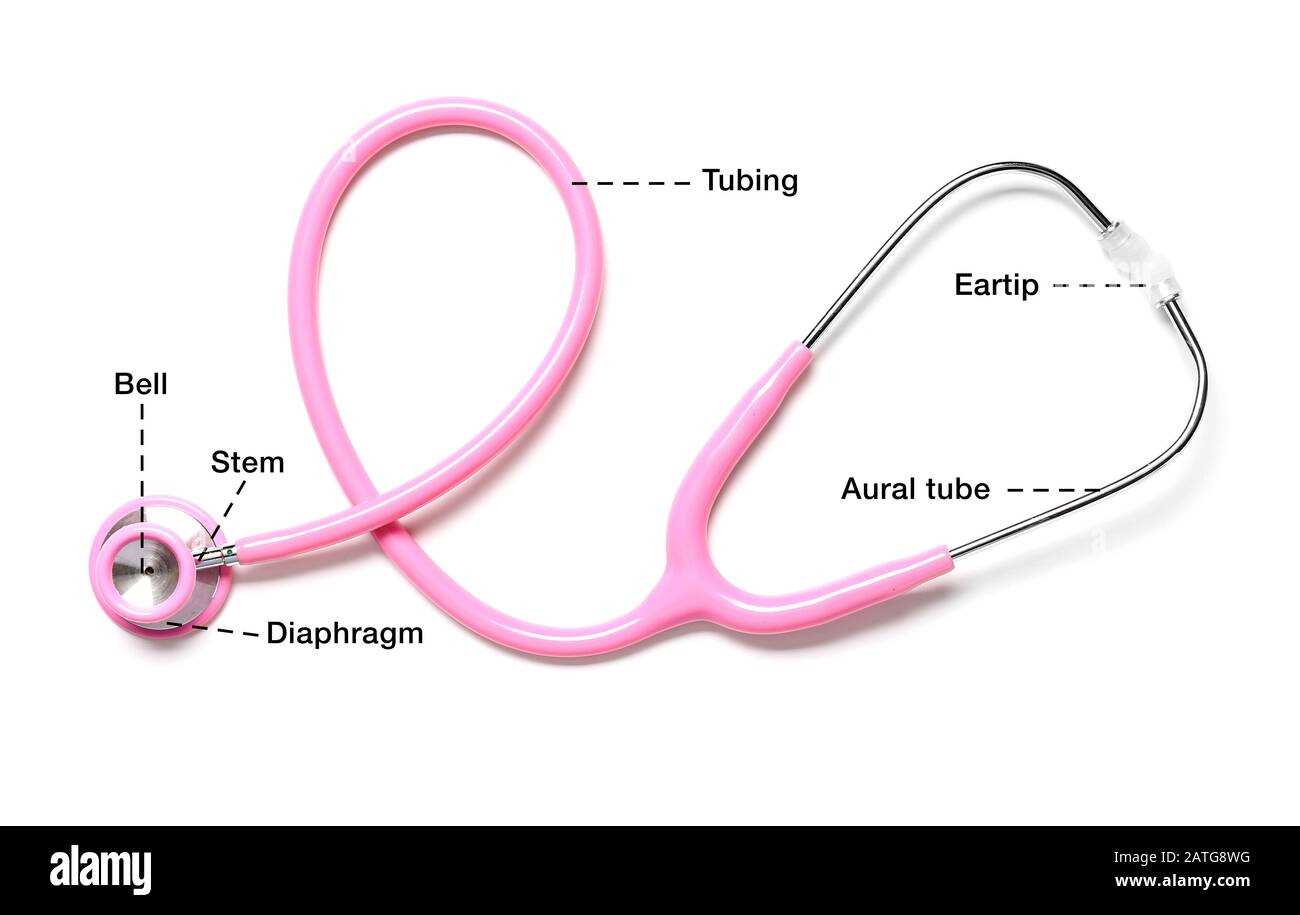
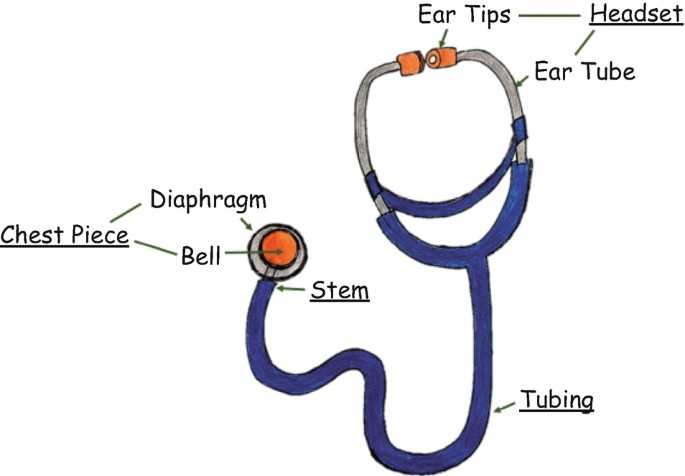
The primary features include the chest piece, which houses the diaphragm and bell, designed to amplify different frequencies of sound. The tubing connects the chest piece to the earpieces, allowing for clear transmission of sound while minimizing external noise interference.
The earpieces are designed for comfort and a secure fit, ensuring that the user can listen intently without distractions. Understanding how each element contributes to the overall functionality enhances the appreciation for this vital tool in patient care.
Key Parts of a Stethoscope
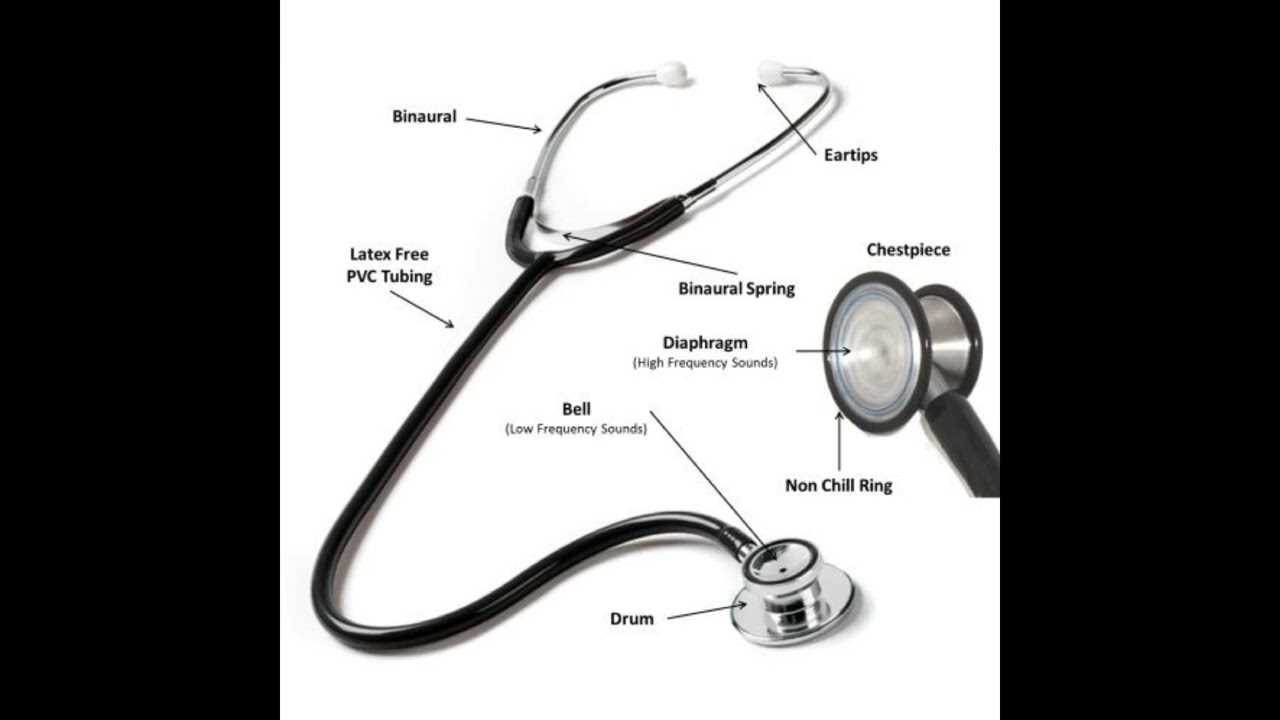
Understanding the essential components of this medical instrument is crucial for effective use and optimal performance. Each element plays a significant role in sound transmission and clarity, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions based on their assessments.
Major Components
- Chest Piece: The section that comes in contact with the patient’s body, designed to capture heartbeats and other sounds.
- Diaphragm: A flat surface that amplifies high-frequency sounds.
- Bell: A concave area used for low-frequency sounds, such as certain heartbeats.
Additional Features
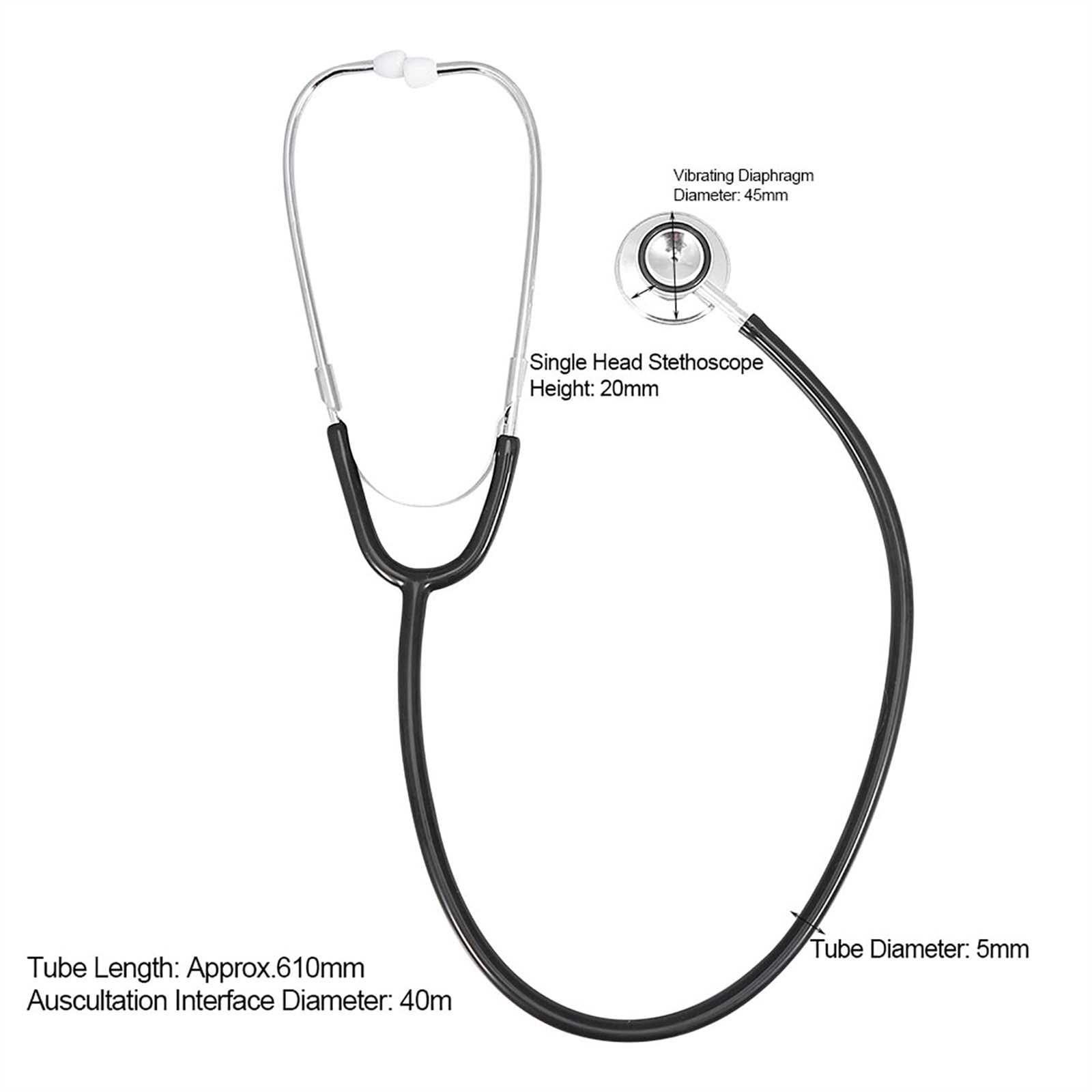
- Tubing: Connects the chest piece to the listening end, transmitting sound waves.
- Earpieces: Comfortable fittings that allow for sound isolation and clarity when listening.
Functionality of Each Component
Understanding the roles of various elements in this medical instrument is crucial for effective usage. Each component plays a vital role in enhancing the overall performance and accuracy of the device, allowing healthcare professionals to assess and monitor patients efficiently.
The main components include:
- Chest Piece: This is the primary interface with the patient, designed to detect sounds within the body.
- Diaphragm: A flat surface that amplifies high-frequency sounds, facilitating the detection of specific bodily functions.
- Bell: A smaller, cupped section that captures low-frequency sounds, useful for identifying certain heartbeats and vascular noises.
- Tubing: This flexible conduit transmits sound from the chest piece to the listener’s ears, ensuring clarity and reducing background noise.
- Earpieces: Designed for comfort and fit, these allow the practitioner to listen without distraction, creating a proper seal for sound transmission.
In summary, each element contributes uniquely to the instrument’s effectiveness, enabling healthcare providers to perform accurate examinations and make informed decisions about patient care.
Types of Stethoscope Designs
Various designs of this medical instrument cater to the diverse needs of healthcare professionals, offering unique features and functionalities. Each configuration is tailored to specific environments and specialties, enhancing the ability to assess patient conditions effectively.
One common style is the classic model, characterized by its dual-headed design, allowing practitioners to easily switch between high-frequency and low-frequency sounds. This versatility makes it a popular choice among general practitioners and specialists alike.
Another prevalent type is the lightweight variant, designed for portability and ease of use. This model is ideal for professionals who require mobility without compromising on performance, making it a favored option in emergency situations.
For pediatric care, specialized models are available that feature smaller diaphragms and softer materials, ensuring comfort for younger patients while maintaining acoustic quality. These instruments are designed to cater specifically to the needs of children.
Digital variants have also emerged, integrating advanced technology to enhance sound amplification and recording capabilities. These innovative designs offer healthcare providers tools to capture and analyze data more effectively, representing a significant advancement in clinical assessment.
Overall, the variety of designs available allows practitioners to choose an instrument that best fits their specific requirements, ensuring optimal performance and patient care across different medical settings.
Materials Used in Stethoscope Parts
The construction of medical listening devices involves a diverse array of materials, each selected for its unique properties that enhance performance, durability, and comfort. Understanding these materials is crucial for appreciating how these instruments function effectively in clinical settings.
| Component | Material | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Chest Piece | Stainless Steel | Provides durability and an optimal acoustic environment for sound transmission. |
| Diaphragm | Polycarbonate | Ensures clear sound amplification while being lightweight and resistant to wear. |
| Tubing | PVC or Rubber | Offers flexibility and noise reduction, allowing for comfortable handling and effective sound transmission. |
| Earpieces | Soft Silicone | Enhances comfort and creates a secure fit, reducing external noise interference. |
| Spring | Metal Alloy | Ensures structural integrity and maintains tension for adjustable earpieces. |
Common Issues with Stethoscope Components
Various elements of medical listening devices can encounter specific challenges that affect their performance. Understanding these common issues is essential for ensuring accuracy and reliability during use. Regular maintenance and awareness of potential problems can enhance the longevity and functionality of these essential tools.
Wear and Tear
Frequent usage can lead to deterioration in materials, resulting in compromised sound quality. Components such as tubes and diaphragms are particularly susceptible to wear, necessitating timely replacement to maintain optimal functionality.
Improper Cleaning
Neglecting proper sanitation can lead to buildup of debris, which may obstruct sound transmission. Regular cleaning is crucial for preserving the integrity of the device and ensuring accurate readings during examinations.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Proper care and routine maintenance are essential for ensuring that medical instruments remain reliable and effective over time. By following specific practices, users can enhance the durability and performance of their equipment, leading to more accurate assessments and prolonged usage.
Regularly inspect the device for any signs of wear or damage. Clean it after each use with appropriate solutions to prevent buildup of contaminants. Store it in a protective case to avoid unnecessary stress and exposure to harmful environments. Avoid excessive pressure or bending, especially on flexible components.
Ensure that the device is calibrated correctly and serviced periodically by a professional. Keeping track of usage patterns can also help identify when maintenance is needed. By being proactive, you can ensure that your equipment remains in optimal condition for years to come.
Upgrades and Accessories for Stethoscopes
Enhancing your listening instrument can significantly improve its performance and usability. Various upgrades and accessories are available to tailor your experience, ensuring optimal functionality and comfort. From new earpieces to specialized bells, these additions can elevate the overall effectiveness of your diagnostic tool.
Common Accessories
There are several popular enhancements that practitioners often consider to improve their auditory experience:
| Accessory | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Comfort Earpieces | Provide a better fit and reduce fatigue during long examinations. |
| Replacement Diaphragms | Ensure accurate sound transmission and clarity. |
| Carrying Cases | Protect the instrument from damage while providing convenient storage. |
| Custom Engravings | Add a personal touch, making your instrument easily identifiable. |
Upgrading Options
When considering enhancements, think about features that align with your specific needs:
| Upgrade | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Dual-Head Design | Allows for versatile listening modes for different situations. |
| High-Fidelity Tubing | Improves sound quality and reduces ambient noise interference. |
| Specialty Bells | Facilitate detection of specific conditions through targeted auscultation. |
Choosing the Right Stethoscope Model
When it comes to selecting an appropriate acoustic device for medical practice, several factors come into play that can significantly affect performance and user experience. The right model can enhance diagnostic capabilities and improve the interaction between healthcare providers and patients. Understanding the features and specifications of various models is essential in making an informed decision.
Firstly, consider the intended use of the device. Different environments, such as hospitals, clinics, or private practices, may require unique functionalities. For example, a model designed for cardiology may emphasize superior sound quality and frequency response, while a general-purpose option may suffice for routine examinations.
Additionally, think about the design and comfort of the device. Healthcare professionals often use these instruments for extended periods, so ergonomics play a crucial role. A lightweight model with soft ear tips and adjustable tubing can minimize discomfort during long shifts.
Furthermore, it’s important to evaluate the materials used in construction. High-quality instruments are often made from durable materials that withstand daily use, ensuring longevity. Models with flexible tubing and stainless steel components tend to offer better resilience.
Finally, budget considerations should not be overlooked. While high-end devices may offer advanced features, there are also reliable, cost-effective options available. Balancing performance with price will help in selecting a model that meets both clinical needs and financial constraints.