The fundamental components of a vehicle’s safety mechanism play a crucial role in ensuring passenger protection during travel. These intricate systems are designed to minimize the risk of injury in the event of sudden stops or collisions, highlighting the importance of each individual element working in harmony.
By exploring the various sections and functions of this protective apparatus, one can appreciate how each component contributes to overall safety. From the locking mechanisms to the tensioning devices, every part is engineered to enhance security and reliability.
In this discussion, we will delve into the key elements that comprise this essential system. Understanding these components not only sheds light on their operational significance but also emphasizes the ultimate goal of safeguarding occupants within the vehicle.
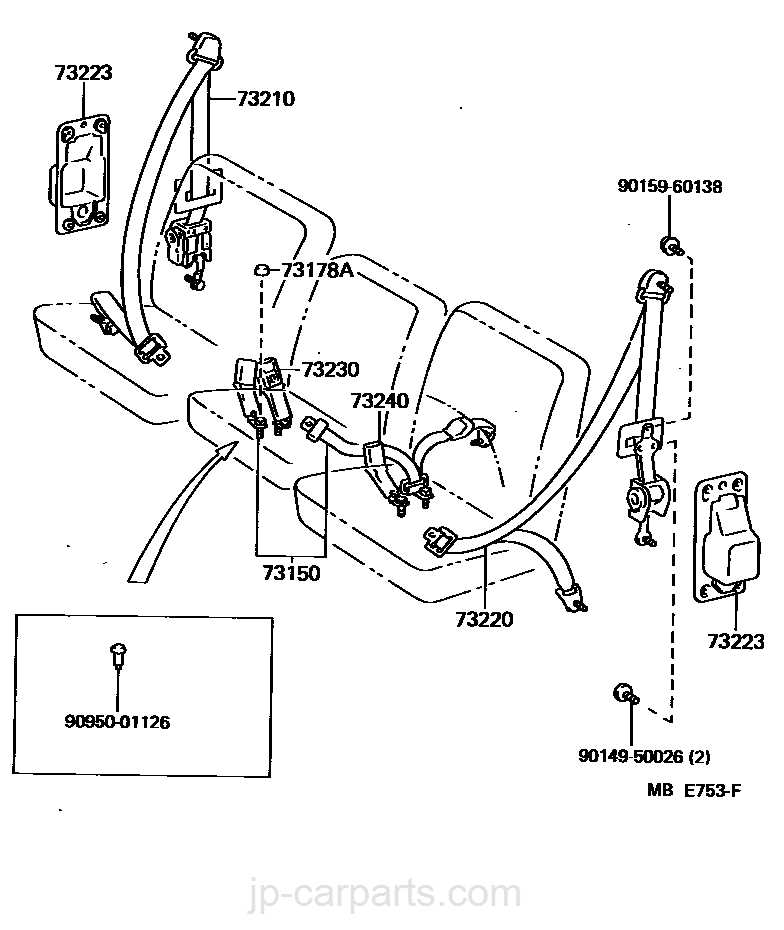
Understanding Seat Belt Components
In the realm of automotive safety, the essential elements that contribute to restraint systems play a crucial role in protecting occupants during travel. This section delves into the various components that work together to ensure reliability and effectiveness in the event of a collision.
Key Elements of Restraint Systems
- Webbing: The primary material that forms the main structure, designed for strength and durability.
- Reel Mechanism: This component manages the extension and retraction of the webbing, allowing for comfort and safety.
- Anchor Points: Fixed locations that secure the system to the vehicle, ensuring stability.
- Retractor: A crucial element that locks the webbing in place during sudden stops or impacts.
- Load Limiter: A feature that reduces the force exerted on occupants during a crash, enhancing safety.
Additional Considerations
- Regular maintenance is essential for the longevity and reliability of these systems.
- Understanding the interaction between components can aid in improving overall safety measures.
- Innovations in technology continue to enhance the functionality and effectiveness of restraint systems.
How Seat Belts Work Mechanically
The mechanics of occupant restraint systems are designed to enhance safety during sudden stops or collisions. These systems utilize a combination of materials and mechanisms to secure individuals in place, minimizing movement and reducing the risk of injury.
Key Components
Understanding the main elements involved in these safety devices reveals how they function together to provide protection.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Webbing | Acts as the primary restraining element, distributing force across a larger area. |
| Retractor | Automatically pulls excess webbing to maintain tension and release when needed. |
| Anchor Points | Securely attach the system to the vehicle, providing stability and support. |
Operational Mechanism
When a force is applied, the device locks into place, preventing further movement. This mechanical action is crucial for maintaining the safety of passengers during unexpected incidents.
Key Functions of Each Part
This section explores the essential roles played by various components involved in passenger restraint systems. Understanding these functions is crucial for appreciating how they contribute to overall safety during travel.
Primary Components and Their Roles
- Webbing: Provides the main support by distributing force during an impact.
- Retractor: Ensures the webbing is snug and automatically adjusts during sudden stops.
- Anchor Points: Securely attach the system to the vehicle frame, maintaining integrity.
- Buckle: Allows users to fasten and release the system easily while ensuring a secure fit.
Additional Elements and Their Contributions
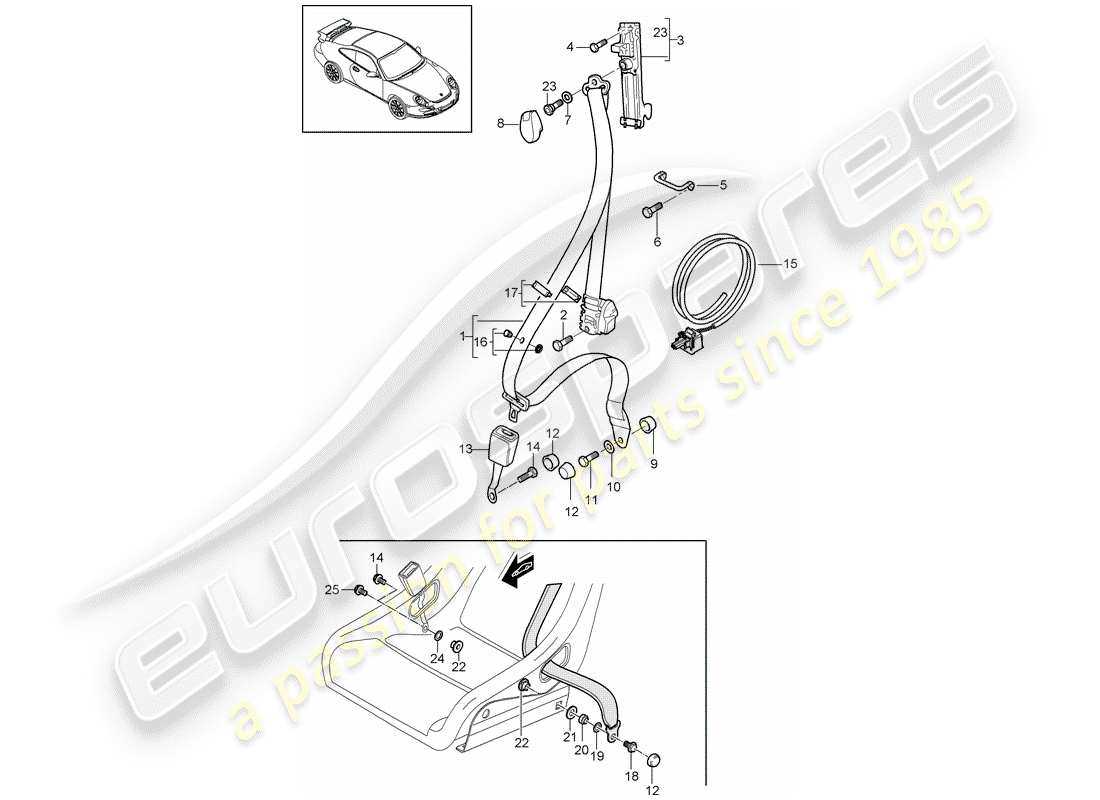
- Pre-tensioners: Tighten the webbing instantly upon collision, minimizing slack.
- Load Limiters: Control the force exerted on the occupant to reduce injury risk.
- Indicator Lights: Signal the status of the system, ensuring it is engaged correctly.
Importance of Seat Belt Maintenance
Proper upkeep of restraint systems in vehicles is crucial for ensuring passenger safety. Regular inspection and care can significantly reduce the risk of injury during an accident, enhancing the overall effectiveness of these protective devices.
Neglecting maintenance can lead to wear and tear, which may compromise functionality. Components may fray or become less reliable over time, making it essential to monitor their condition. Here are some key reasons why regular checks are vital:
| Reason | Description |
|---|---|
| Injury Prevention | Well-maintained systems significantly reduce the likelihood of serious injuries in collisions. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adhering to maintenance guidelines ensures compliance with safety regulations. |
| Longevity | Routine care prolongs the lifespan of protective mechanisms, saving costs over time. |
| Resale Value | Vehicles with documented maintenance records are often more valuable in the resale market. |
Investing time in regular inspections and upkeep not only protects occupants but also contributes to overall road safety. Ensuring these devices are in top condition can save lives and prevent injuries.
Common Seat Belt Issues Explained
Ensuring the functionality of occupant restraint systems is vital for safety in vehicles. Various problems can arise, leading to concerns about effectiveness and reliability. Understanding these common issues can help drivers maintain their systems properly.
- Fraying or Damage: Over time, the fabric can wear down due to friction or exposure to elements. This can compromise safety.
- Stuck Mechanism: Sometimes, the retraction mechanism can jam, preventing the system from extending or retracting smoothly.
- Latch Malfunctions: Difficulty in securing or releasing the locking mechanism may indicate a need for inspection or replacement.
- Noise During Operation: Unusual sounds when pulling or releasing may suggest internal issues requiring attention.
- Improper Installation: Systems not correctly installed may not function as intended, posing a risk during use.
Regular checks and maintenance can help identify these issues early. Addressing problems promptly ensures that the safety measures in vehicles remain effective and reliable.
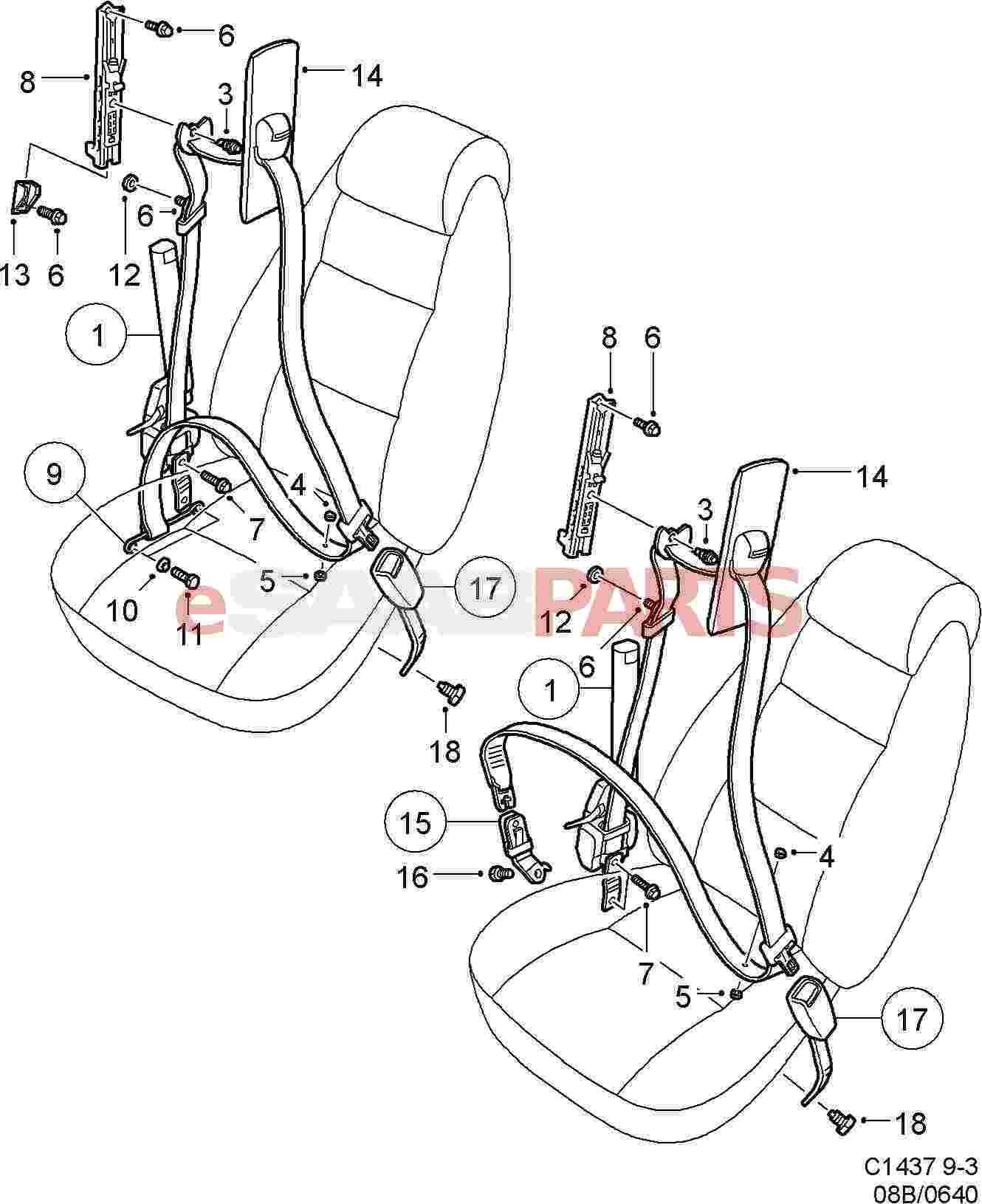
Visual Guide to Seat Belt Diagrams
This section aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the components involved in a safety restraint system. By exploring various illustrations and descriptions, readers can gain insights into how these crucial mechanisms function and contribute to passenger safety.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Webbing | The fabric that forms the main harness, designed to absorb force during a collision. |
| Latch | A fastening mechanism that secures the harness in place, ensuring stability. |
| Retractor | A device that retracts the webbing, keeping it taut and ready for use. |
| Anchor Points | Fixed locations where the harness is attached to the vehicle, providing support. |
Safety Standards for Seat Belts
The effectiveness of restraint systems in vehicles is crucial for ensuring passenger protection during collisions. Various regulations and guidelines govern the design, manufacturing, and performance of these safety features, aiming to minimize injuries and fatalities on the road. Adherence to these standards is essential for manufacturers to guarantee that their products provide optimal safety in diverse driving conditions.
Key Regulatory Bodies
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
- European Committee for Standardization (CEN)
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
Essential Standards and Testing Procedures
- Crash Testing: Systems must undergo rigorous crash simulations to evaluate their effectiveness in protecting occupants.
- Durability Testing: Materials and mechanisms are tested for resistance to wear, fatigue, and environmental factors.
- Performance Metrics: Standards dictate acceptable limits for forces experienced by occupants during an impact.
Compliance with these regulations not only enhances safety but also builds consumer trust in automotive products. As technology evolves, continuous updates to safety standards are vital for adapting to new challenges in vehicle design and road safety.
Upgrades and Innovations in Seat Belt Design
Recent advancements in restraint system technology have significantly improved occupant safety and comfort in vehicles. Innovations in materials, mechanisms, and smart features have redefined how these systems protect passengers during collisions, while also enhancing user experience. The focus on reducing injuries and improving functionality reflects a commitment to ongoing development in automotive safety engineering.
Advanced Materials and Design
The introduction of high-strength synthetic fabrics and lightweight composites has revolutionized the structure of restraint systems. These materials not only offer increased durability but also contribute to weight reduction, leading to improved fuel efficiency in modern vehicles. Enhanced cushioning technology has also been integrated, providing better shock absorption during impact.
Smart Technology Integration
With the rise of smart vehicle technology, restraint systems are now equipped with sensors and automatic adjustments. These innovations allow for real-time monitoring of passenger positioning and provide alerts if a passenger is not securely restrained. Furthermore, adaptive mechanisms can modify tension based on collision severity, optimizing protection for each individual.