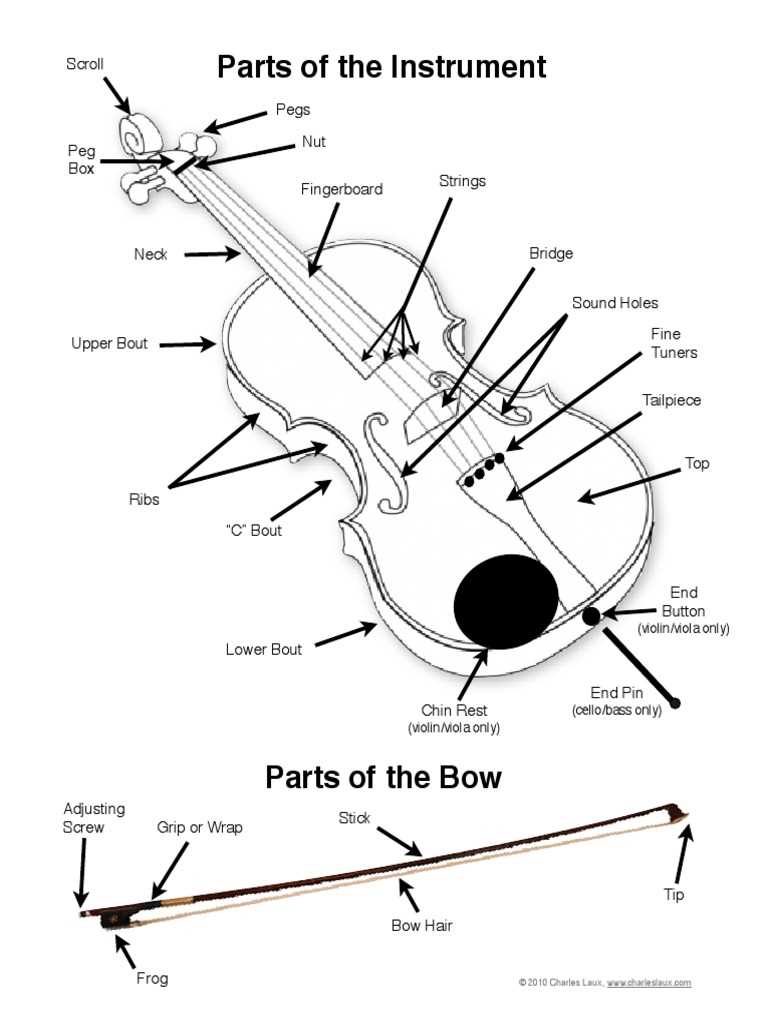
Understanding the structure of a stringed instrument reveals how each element contributes to its sound production and playability. Every section plays a crucial role in shaping the experience of both musician and listener. From the frame to the strings, each part is meticulously designed to produce harmonious tones when played with precision.
Various segments of the instrument work together to create its distinctive voice. Musicians should be familiar with these essential features to maintain and enhance their performance. Whether one is a beginner or a seasoned player, knowing these aspects is fundamental to achieving the desired resonance and tonal quality.
In this guide, we will explore the essential aspects that define this sophisticated musical tool. By identifying each element, players will gain a deeper appreciation for the craftsmanship involved in producing the melodious sounds that are cherished worldwide.
Essential Components of a Cello
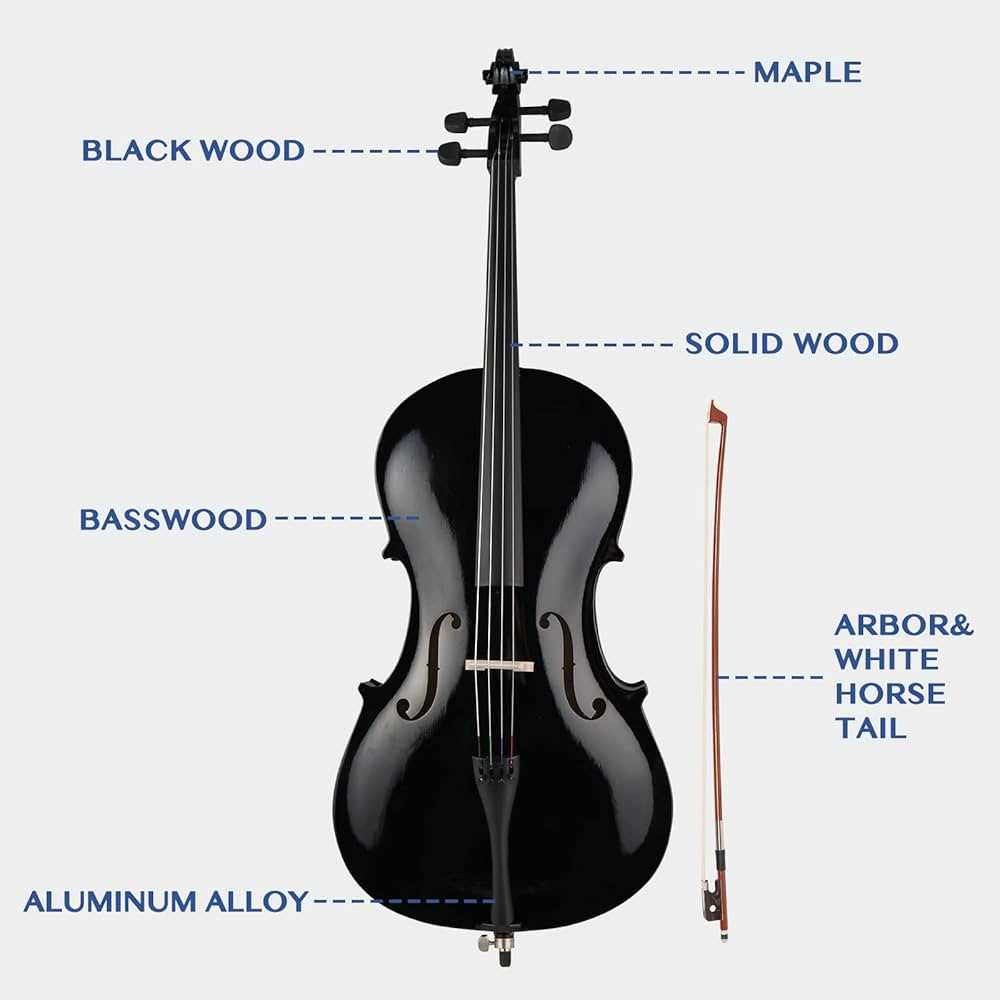
The structure of this stringed instrument is a complex yet elegant combination of various elements, all working together to create its distinct tone and resonance. Each piece contributes to the overall sound, ensuring smooth playability and a rich acoustic experience. The craftsmanship behind its construction is vital for achieving both aesthetic beauty and technical precision.
Key Elements of the Frame
The main body is composed of several integral parts that provide both support and resonance. These components are meticulously crafted to enhance the depth and warmth of the sound. Strong wooden materials are commonly used to achieve a balance between durability and acoustic quality.
Vital Acoustic Elements
Critical components are essential for fine-tuning and sound projection. These elements control the vibrations, ensuring that the instrument produces clear and harmonious tones. Proper adjustment and maintenance of these parts are crucial for maintaining consistent performance over time.
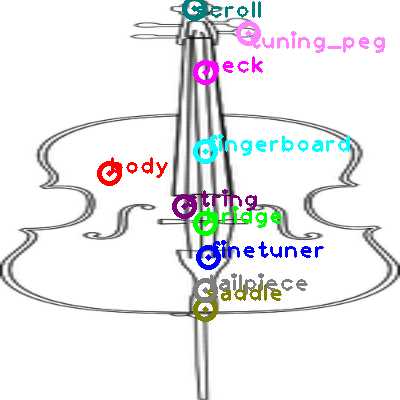
Exploring the Cello’s Body Structure
The anatomy of this classical string instrument is both intricate and purposeful. Each component plays a critical role in shaping its resonance and tonal quality. With a rich history behind its development, understanding its construction offers insight into how sound is produced and amplified, creating the deep, warm tones that define its unique character.
Main Framework
The primary structure of the instrument is designed to support both tension and vibration. The robust frame, typically crafted from fine wood, acts as a resonating chamber that amplifies the strings’ vibrations. Every detail in the woodwork contributes to the overall harmony and balance of sound.
Acoustic Resonance
The shape and materials used in construction are integral to its ability to project sound. The curved contours allow for sound waves to travel freely, while the internal bracing ensures that the vibrations are distributed evenly. This combination of form and function results in a rich, full-bodied sound that has made the instrument a favorite in orchestras and solo performances alike.
Understanding the Role of the Bridge
The bridge plays a crucial role in creating sound by acting as an intermediary between the strings and the body of the instrument. Its precise placement and shape directly influence how vibrations are transmitted, which affects the resonance and tonal quality. Without this component, achieving the desired sound would be nearly impossible.
How Sound Travels Through It
When a bow pulls across the strings, the vibrations are sent through the bridge. This element transfers those vibrations into the body, allowing the entire structure to amplify and project the sound. The more efficiently it does this, the richer and more resonant the tones become.
Impact on Sound Quality
The design and material used for the bridge can have a significant effect on sound. A well-crafted bridge ensures that all frequencies are balanced, enabling the performer to express a wide range of dynamics and nuances. Proper maintenance and setup are key to preserving its functionality over time.
The Function of the Cello’s Fingerboard
The elongated surface where the player places their fingers plays a crucial role in determining pitch and sound. This component allows for precise control over intonation and tonal variation by adjusting finger positions along its length. The structure and smoothness of this element directly influence how easily the musician can glide between notes, enabling fluid transitions during performance.
By providing a stable foundation for finger placement, it contributes significantly to the instrument’s overall playability. Its design ensures that notes resonate cleanly, allowing the musician to achieve the desired expression and dynamics through subtle shifts in pressure and position.
Strings and Their Impact on Sound
Vibrating strings play a fundamental role in shaping the character of musical tones. Their material, thickness, and tension significantly influence the depth and warmth of the sound, as well as its brightness and clarity. The resonance produced by the strings forms the basis of the instrument’s voice, creating a wide range of tonal colors.
Material and Resonance
Strings are crafted from various materials, each contributing distinct sonic qualities. For instance, steel produces a bright, focused tone, while synthetic or gut strings offer a softer, richer sound. The resonance depends not only on the material but also on how the vibrations interact with the body of the instrument, enhancing specific frequencies.
Tension and Pitch Stability
The tension of the strings determines not just pitch, but also how stable and consistent the notes remain during performance. Higher tension results in a more stable pitch and a brighter sound, whereas lower tension tends to provide more flexibility and a warmer tone, though it may sacrifice some stability.
How the Cello’s Tailpiece Works
The tailpiece plays a crucial role in sound production, ensuring proper string tension and balance. It connects the lower end of the strings to the body, acting as a stabilizer for the entire instrument. Without this component, achieving the right tonal balance and tuning precision would be impossible.
Maintaining String Tension
By holding the strings securely in place, the tailpiece allows them to maintain the tension needed for optimal resonance. The way it is constructed and positioned affects how efficiently vibrations travel through the strings and into the body, influencing the overall sound.
Fine-Tuning Adjustments
Often equipped with fine-tuners, the tailpiece allows for precise tuning adjustments. These small devices give players control over the tension of individual strings, making it easier to achieve the perfect pitch without significant manual adjustments at the pegs.
The Bow and Its Interaction with the Instrument
The bow plays a crucial role in producing sound, working in harmony with the strings to create a variety of tones. Its movement across the strings brings out the unique qualities of the instrument, allowing for expressive, dynamic playing. Understanding how the bow influences sound opens up new possibilities for musical interpretation.
Structure of the Bow
The design of the bow significantly affects how it interacts with the strings. From its carefully crafted stick to the horsehair that draws across the strings, each part has a function that contributes to sound production. The bow’s flexibility, weight, and balance all play a role in how easily it can create different dynamics and tonal qualities.
Techniques and Sound Creation
- Legato: Smooth, connected strokes create a flowing, uninterrupted sound.
- Spiccato: Short, bouncing strokes offer a more percussive, lively sound.
- Pizzicato: While the bow is not used, its absence allows for plucking, offering a contrasting texture.
Mastering these techniques allows for a wide range of expression, giving the musician control over
Cello Pegs and Tuning Mechanisms
One of the key aspects of adjusting string tension involves small but essential components that allow precise control. These elements are used to fine-tune pitch and maintain stability while playing. Their function is vital for achieving the correct sound, as they offer both flexibility and accuracy in string tension management.
How Pegs Work
Pegs are responsible for adjusting the tension of each string. They are typically made from durable materials and are designed to fit tightly in the instrument’s head. Turning them either increases or decreases the tension, affecting the pitch.
- Made from hardwood for durability
- Ensure stability during tuning
- Must be turned carefully to avoid damage
Fine Tuners
These smaller mechanisms provide more detailed control over tuning. Often found on certain strings, they allow slight adjustments without needing to turn the larger pegs. Fine tuners are especially useful for players seeking quick corrections during a performance.
- Offer precise tuning adjustments
- Typically
Importance of the Endpin in Playability
The adjustable rod beneath the instrument greatly affects the overall ease of performance. It provides stability and positioning, allowing musicians to maintain control and comfort during long sessions. Its role in supporting the instrument directly impacts sound projection and technique, enabling players to express themselves more freely.
Durability and material quality of this component are essential. A well-constructed support rod not only ensures better playability but also prevents strain on the musician’s body, improving posture and reducing fatigue. These factors contribute significantly to a more enjoyable and effective musical experience.