
In the realm of visual representation, certain structures serve to encapsulate various elements under a single, cohesive theme. These frameworks allow for the organization of diverse ideas, providing clarity and enhancing understanding. Each segment within this overarching construct plays a vital role in illustrating relationships and hierarchies among the concepts being conveyed.
The essence of such a visualization lies in its ability to offer a comprehensive view while maintaining a degree of flexibility. Each section contributes uniquely, allowing for both detailed exploration and an overarching perspective. This adaptability makes it an invaluable tool for both educators and communicators, facilitating the dissemination of knowledge in an engaging manner.
As we delve deeper into the specifics, it becomes evident that the interplay between the various elements fosters a richer narrative. Understanding how these individual components interact and support one another is crucial for effectively utilizing this method of representation. By examining these relationships, one can gain insights that extend beyond the mere surface of the concepts at hand.
Understanding the Umbrella Diagram
The concept at hand serves as a visual tool designed to organize complex information in a structured manner. It facilitates the categorization of ideas, allowing for a clearer understanding of various components and their relationships.
In this framework, several key elements come into play:
- Central Theme: This is the main focus around which everything revolves, providing a foundation for further exploration.
- Subcategories: These are derived from the central theme, helping to break down the information into manageable sections.
- Connections: Illustrating how different ideas relate to one another is crucial for understanding the overall structure.
Utilizing this model has numerous benefits:
- Enhances clarity by visually representing information.
- Encourages deeper engagement with the material.
- Facilitates easier retention of complex concepts.
Overall, this visual representation can transform how we perceive and interact with information, making it a valuable tool for learning and communication.
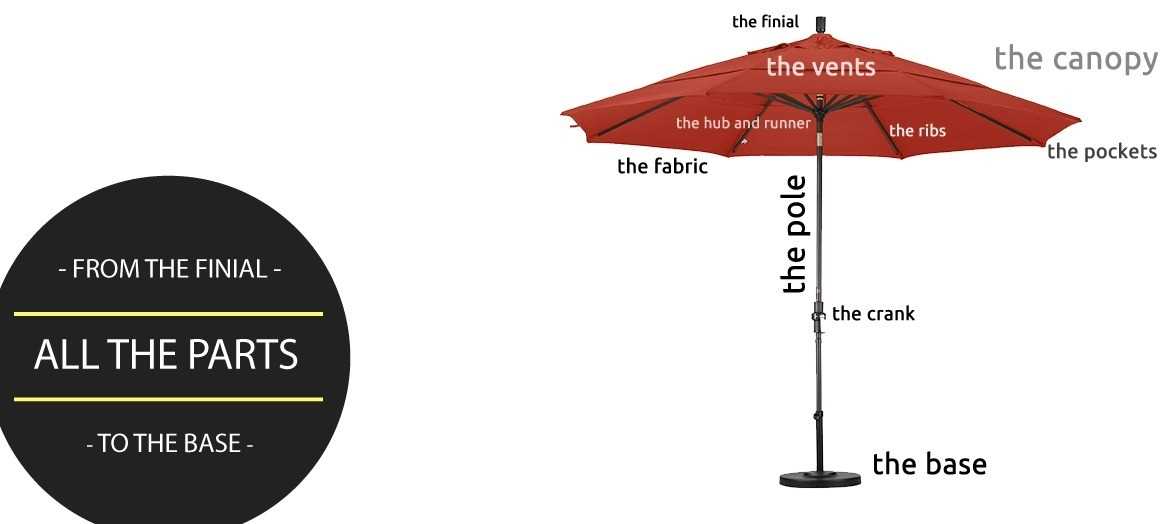
Key Components of the Diagram
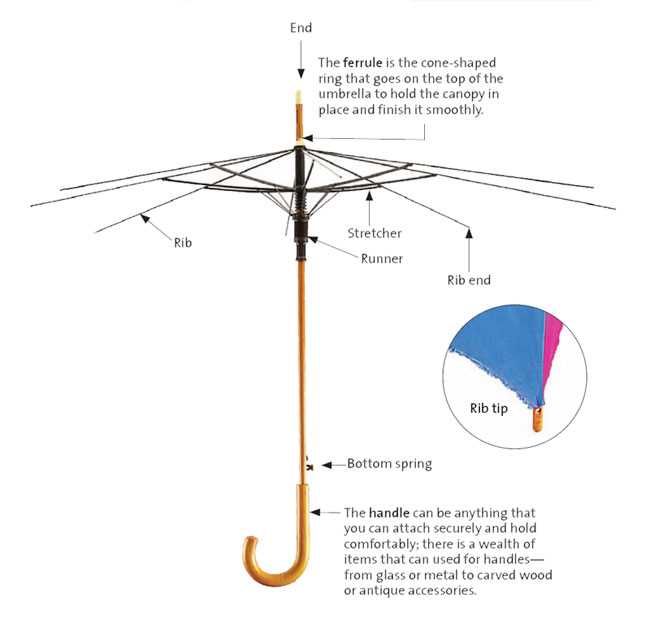
Understanding the essential elements of a visual representation is crucial for effective communication and clarity. These fundamental units work together to convey complex information in a structured and comprehensible manner. Each element plays a vital role in enhancing the overall functionality and interpretability of the visual tool.
Core Elements
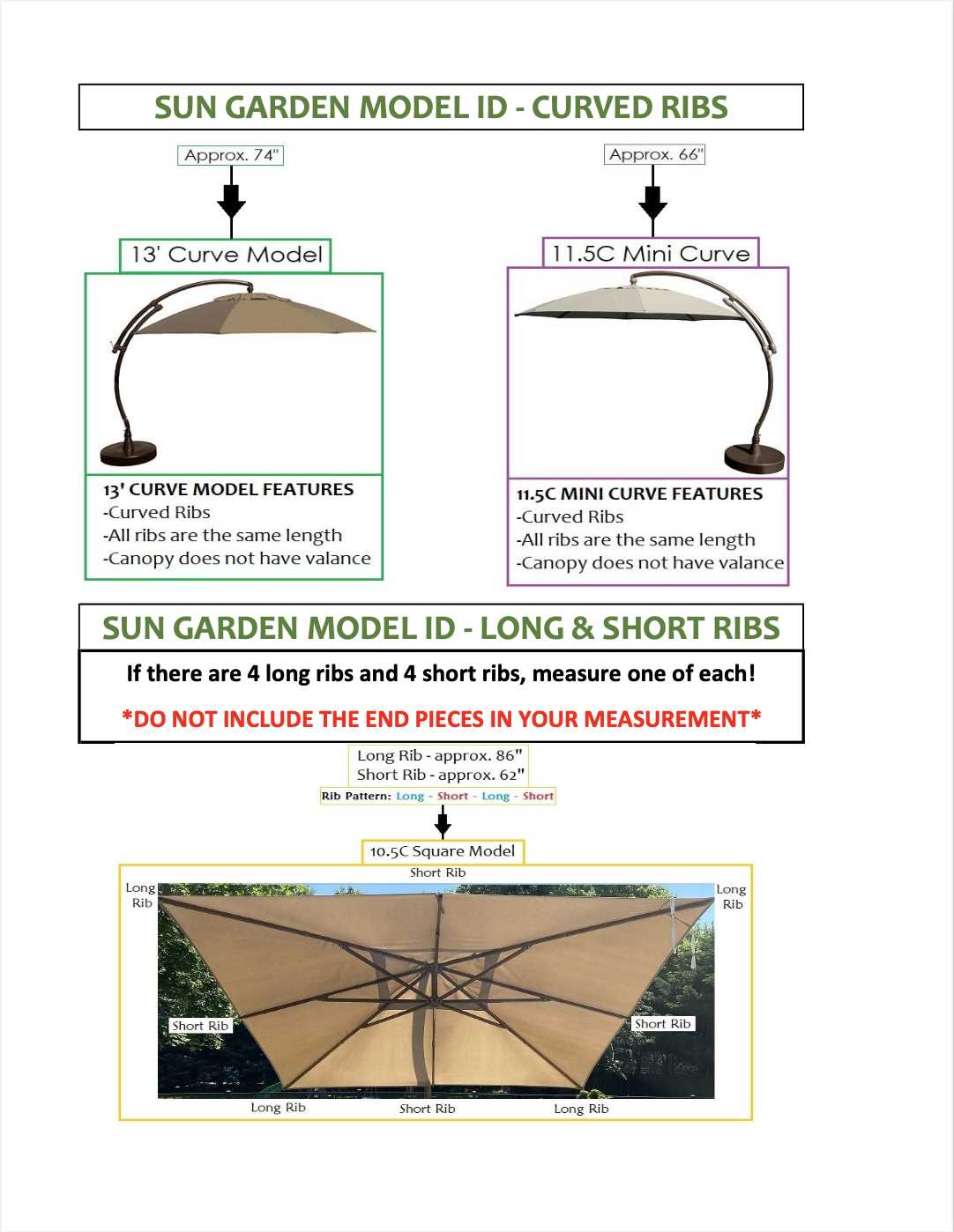
The core components serve as the backbone of the visualization. They include the main categories that encapsulate the primary themes or concepts. By organizing these central themes, the representation provides a clear framework, allowing the audience to easily navigate through the information presented. The relationships among these categories can significantly influence the viewer’s understanding.
Supporting Features
In addition to the core elements, supporting features enrich the overall message. These include annotations, color schemes, and connecting lines that guide the viewer’s eye and emphasize relationships. Annotations can offer additional insights, while a well-chosen color palette enhances visual appeal and aids in differentiating between various aspects. Together, these supporting elements create a cohesive and engaging visual experience.
Types of Umbrella Diagrams
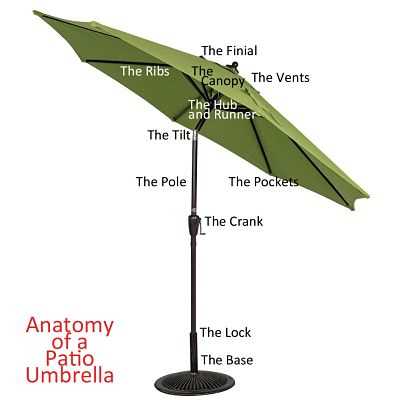
Various models serve distinct purposes, each tailored to visualize complex information effectively. Understanding these different variations can enhance clarity and communication in presenting interconnected concepts.
Conceptual Models are designed to illustrate overarching themes, allowing viewers to grasp the primary ideas at a glance. They focus on high-level insights rather than intricate details.
Structural Models emphasize the relationships and hierarchies among components. These representations are particularly useful for showcasing how individual elements contribute to the overall framework.
Process Models outline sequential steps or phases, guiding audiences through a series of actions or developments. They are essential for illustrating workflows or project timelines.
Analytical Models focus on breaking down data into manageable sections, enabling a deeper dive into specific areas while still connecting to the broader context.
By exploring these diverse forms, one can effectively tailor their visual communication to suit various audiences and objectives, ensuring the ultimate understanding of complex ideas.
Applications in Various Fields
The versatile framework for organizing concepts has found its place in numerous domains, proving its utility in enhancing understanding and communication. This structured approach allows for a clearer representation of complex relationships, facilitating better decision-making and strategic planning.
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Education | Used for curriculum design and illustrating course connections. |
| Business | Helps in project management and visualizing organizational structures. |
| Healthcare | Assists in mapping patient care pathways and treatment options. |
| Technology | Aids in software development by showcasing system architectures. |
| Research | Facilitates the organization of literature reviews and study frameworks. |
This method not only simplifies information but also enhances collaborative efforts across various sectors, leading to innovative solutions and improved outcomes.
How to Create Your Diagram
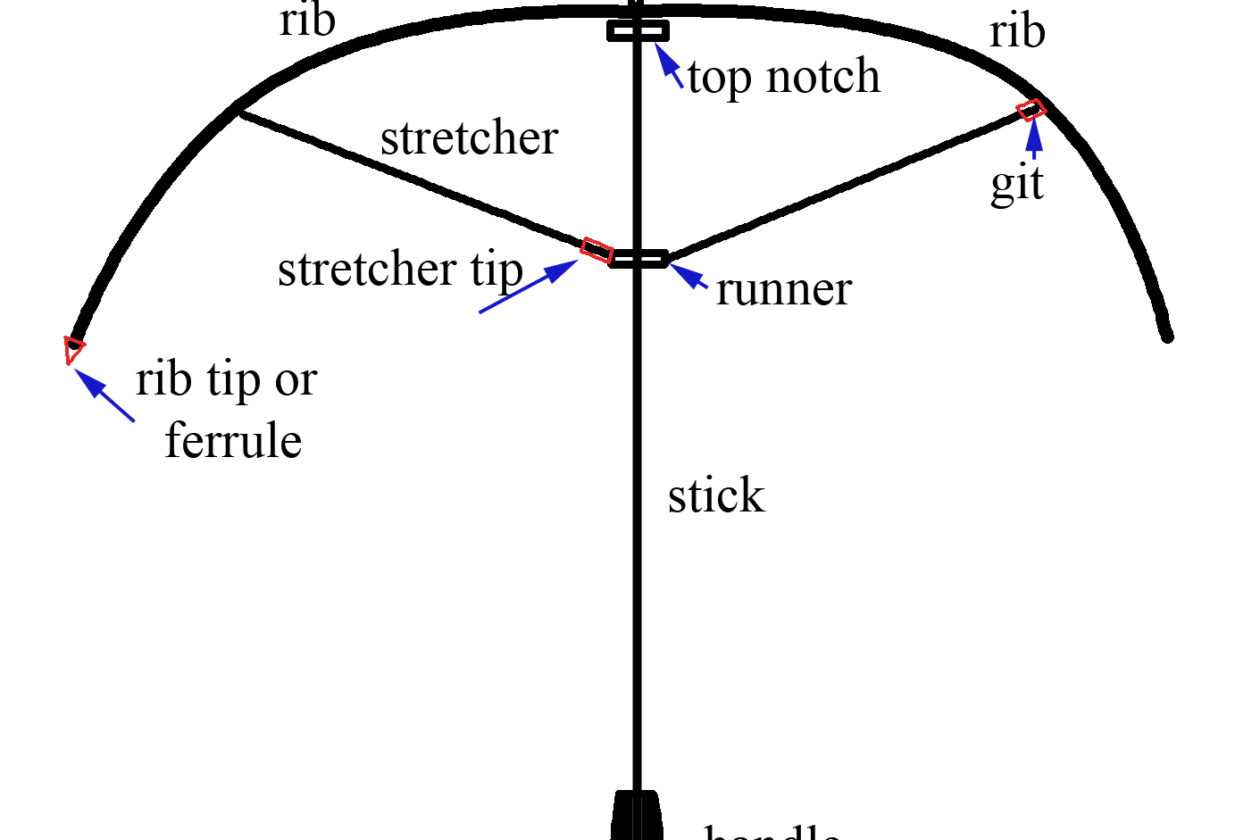
Crafting a visual representation requires thoughtful planning and organization. It’s essential to understand the components that will effectively convey your message and structure the information logically.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Identify the central concept you wish to illustrate. |
| 2 | Gather relevant ideas or themes that connect to the main topic. |
| 3 | Organize these ideas into categories to establish a clear hierarchy. |
| 4 | Choose a suitable layout that enhances comprehension. |
| 5 | Add visual elements to support your information, such as lines or shapes. |
Benefits of Using Umbrella Diagrams

Utilizing a visual framework to organize information provides numerous advantages in both clarity and communication. By creating a structured representation, one can easily convey complex ideas, making them more digestible for various audiences.
Enhanced Clarity: A visual structure allows individuals to quickly grasp relationships and hierarchies within information. This simplification leads to better understanding and retention of concepts.
Effective Communication: When presenting ideas, visuals can bridge gaps in understanding. They facilitate discussions and ensure that everyone is on the same page, reducing the likelihood of misinterpretation.
Strategic Planning: Employing such representations enables teams to identify connections and gaps in their strategies. This holistic view aids in decision-making and prioritization of tasks.
Collaboration: Visual tools promote teamwork, as they encourage group input and foster a collaborative environment. This collective approach can lead to more innovative solutions.
Time Efficiency: Organizing thoughts visually can save time in both brainstorming sessions and project management. Stakeholders can quickly identify critical elements and focus their efforts accordingly.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
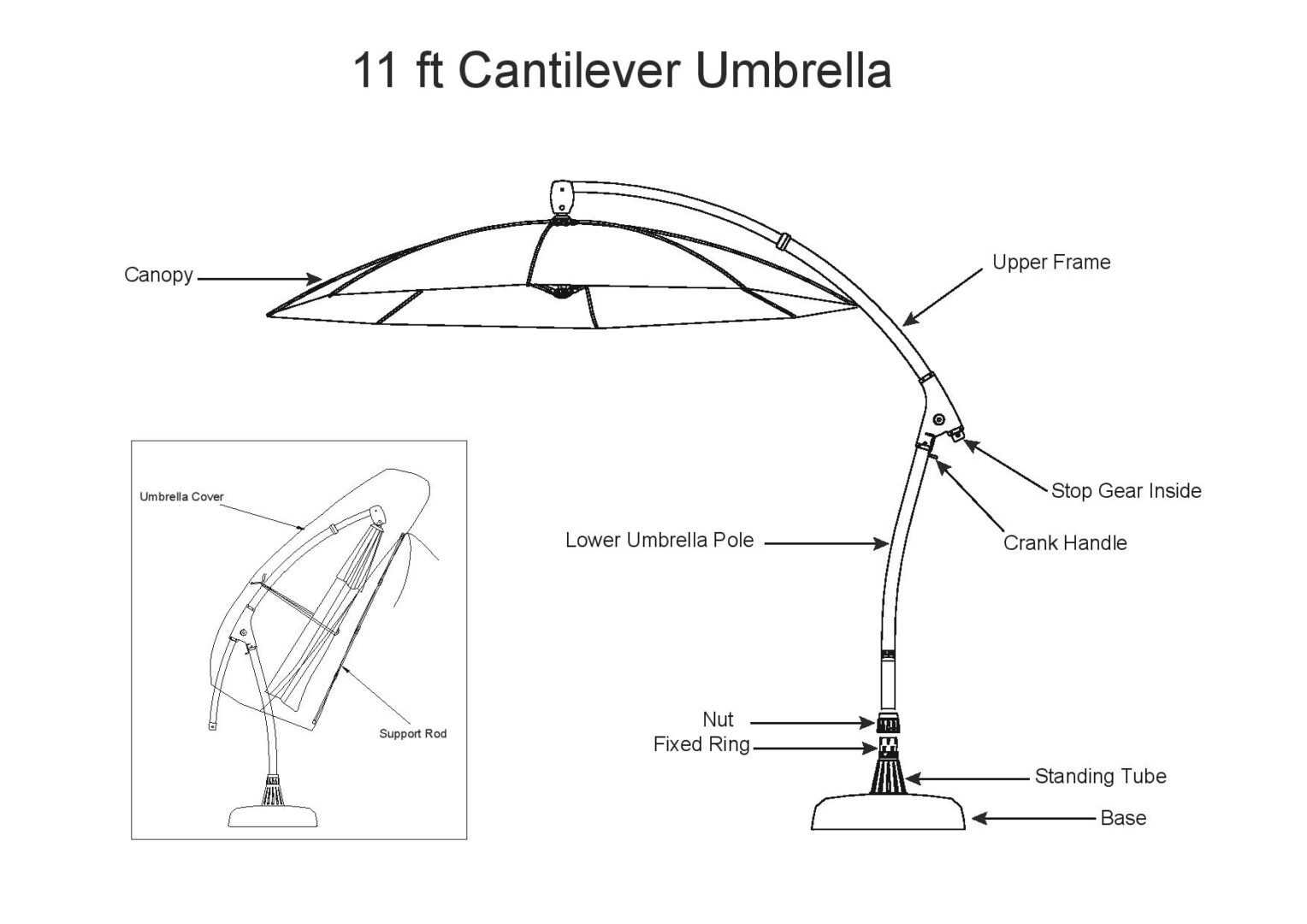
In the pursuit of effective visual representations, several pitfalls can undermine clarity and purpose. Recognizing these errors can enhance communication and improve understanding.
- Overcomplicating the Structure: Adding unnecessary elements can confuse the audience.
- Poor Labeling: Failing to use clear and concise labels leads to ambiguity.
- Lack of Consistency: Inconsistent styles can distract and detract from the main message.
- Ignoring Audience Needs: Not considering the target audience may result in misinterpretation.
- Neglecting Hierarchical Order: Without a clear hierarchy, relationships between ideas can become obscured.
Avoiding these common missteps ensures that your visual tools effectively convey the intended message.
Tips for Effective Communication
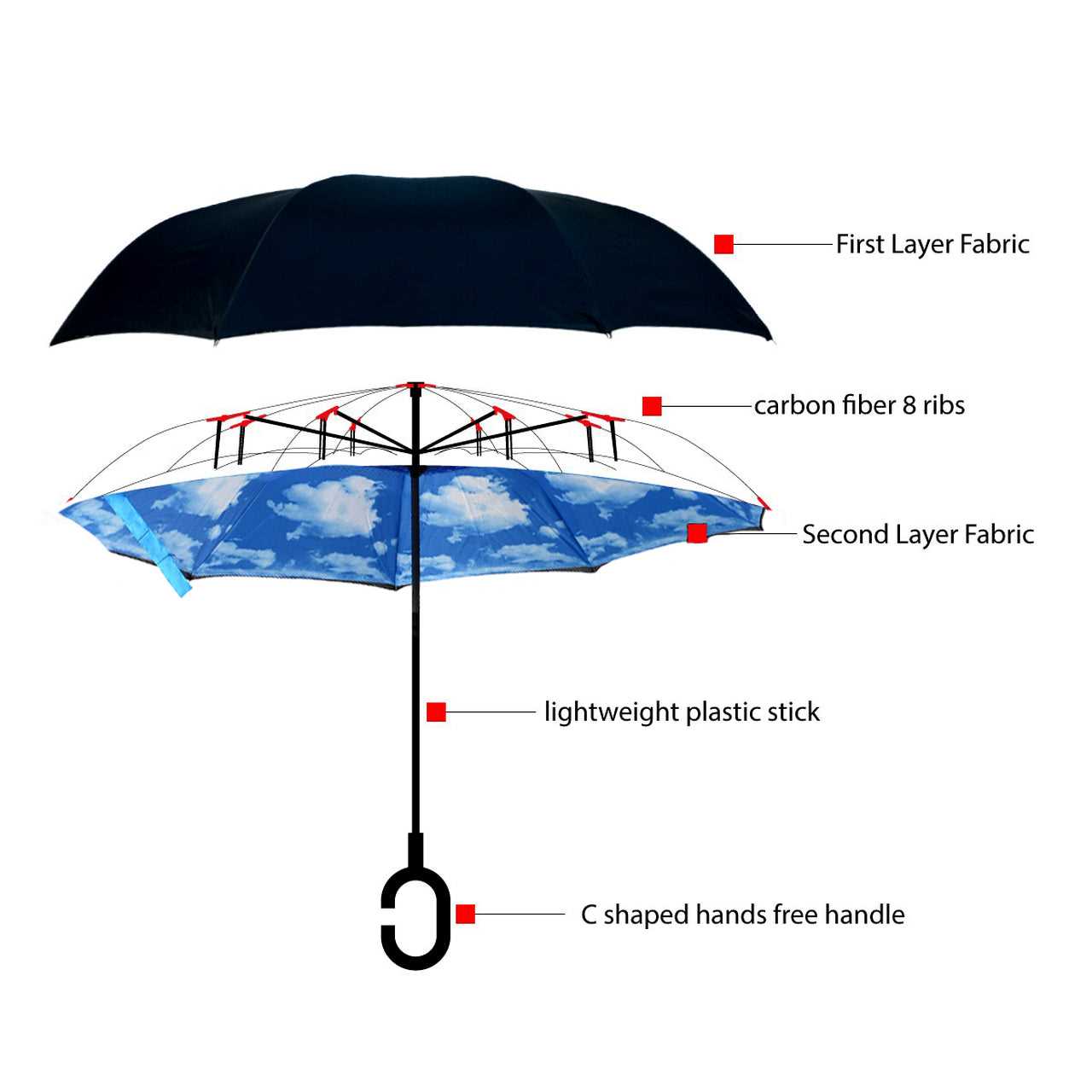
Clear and impactful exchange of ideas is essential for successful interactions in both personal and professional contexts. Mastering the art of conveying thoughts involves understanding not just the words spoken, but also the underlying emotions and intentions. Here are some valuable strategies to enhance your communicative abilities.
Active Listening

One of the cornerstones of effective interaction is the practice of truly listening. Active listening goes beyond hearing words; it involves engaging with the speaker, providing feedback, and demonstrating understanding. This fosters a more open dialogue and builds trust.
Non-Verbal Cues
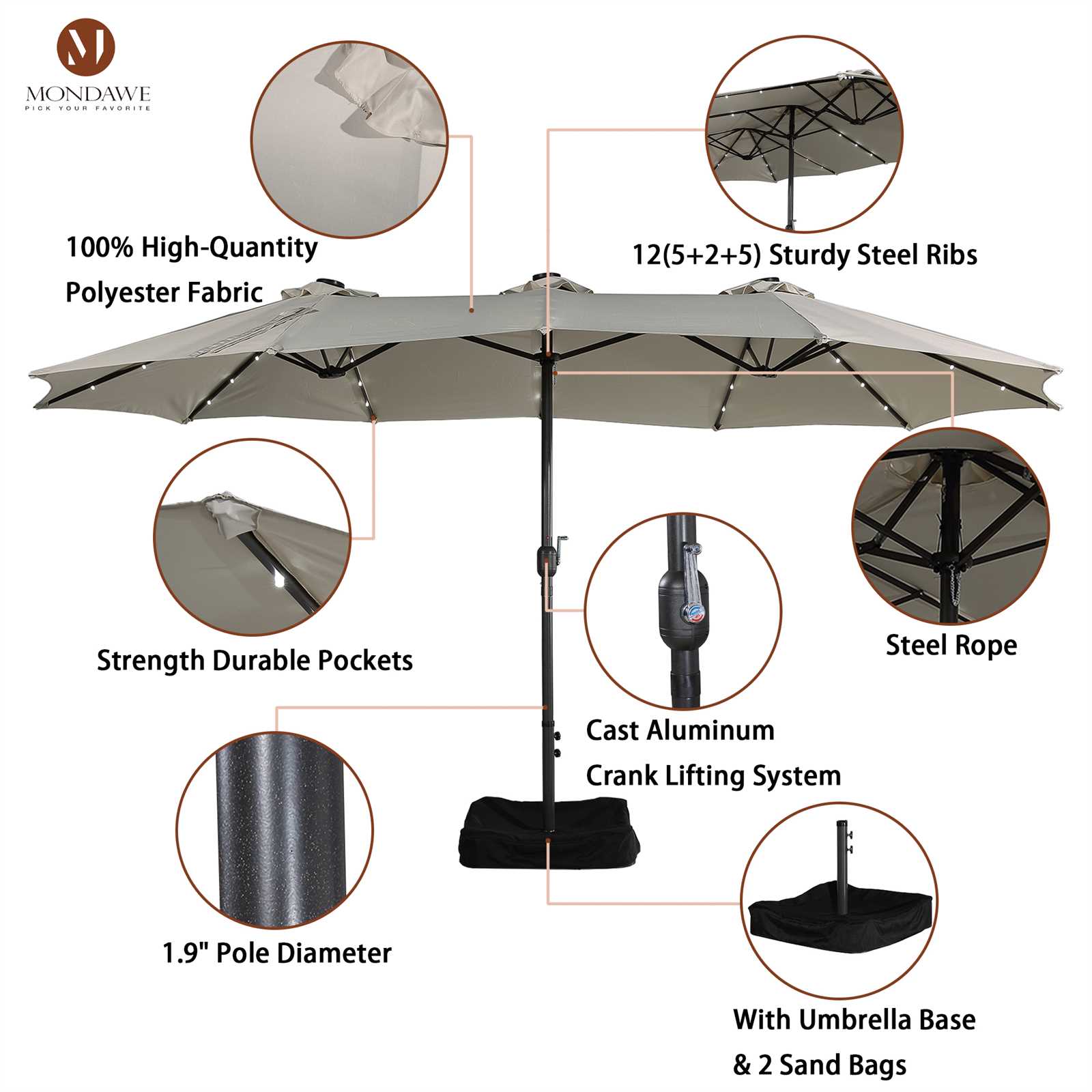
Body language, facial expressions, and eye contact play a crucial role in how messages are received. Being mindful of these non-verbal signals can greatly enhance the clarity of your communication. Consistency between verbal and non-verbal messages helps to prevent misunderstandings.
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Be Clear | Avoid jargon and ambiguous language to ensure your message is easily understood. |
| Ask Questions | Encourage clarification and discussion to deepen understanding and engagement. |
| Practice Empathy | Consider the feelings and perspectives of others to foster a more supportive environment. |
Future Trends in Diagram Design
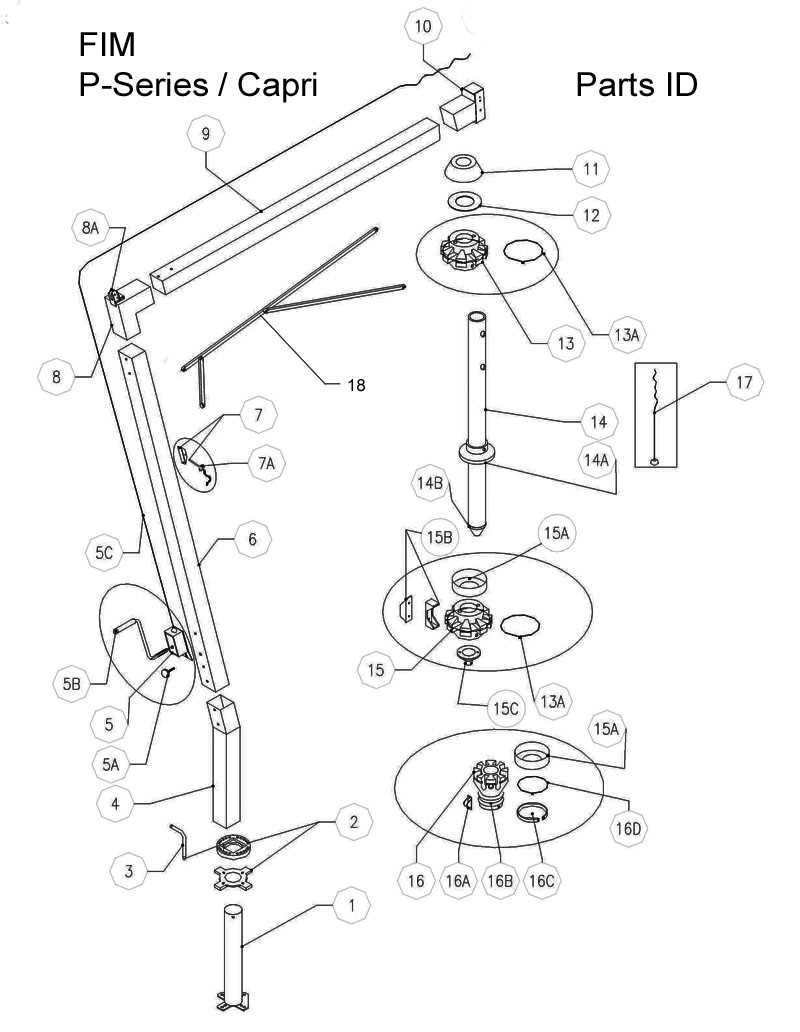
The evolution of visual representations is paving the way for innovative approaches that enhance clarity and engagement. As technology advances, new methodologies are emerging, allowing creators to communicate complex information more effectively.
Integration of Interactive Elements
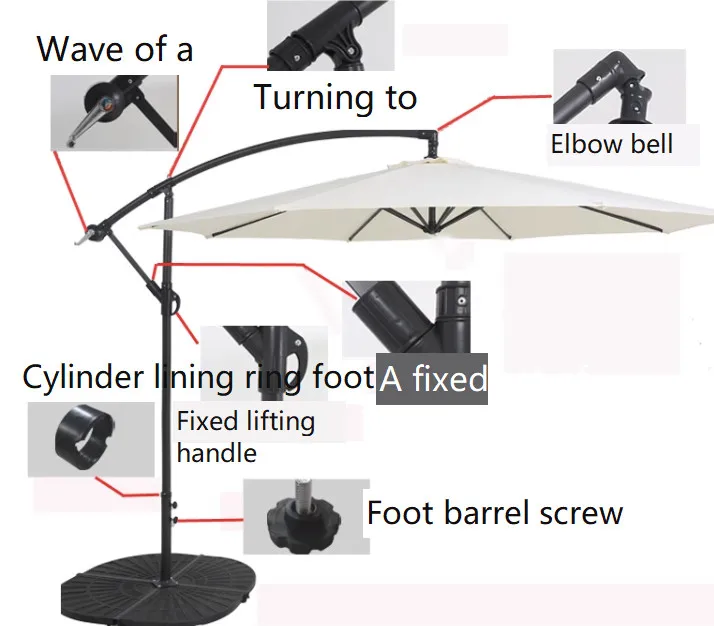
Interactivity is becoming a crucial feature in visual constructs. This trend includes:
- Clickable components for deeper exploration
- Dynamic data visualization that updates in real-time
- User-driven navigation for personalized experiences
Emphasis on Aesthetics and User Experience

Aesthetics play a significant role in how audiences perceive information. Future designs will focus on:
- Minimalistic styles that prioritize essential content
- Use of vibrant colors and gradients to capture attention
- Consistent branding to enhance recognition