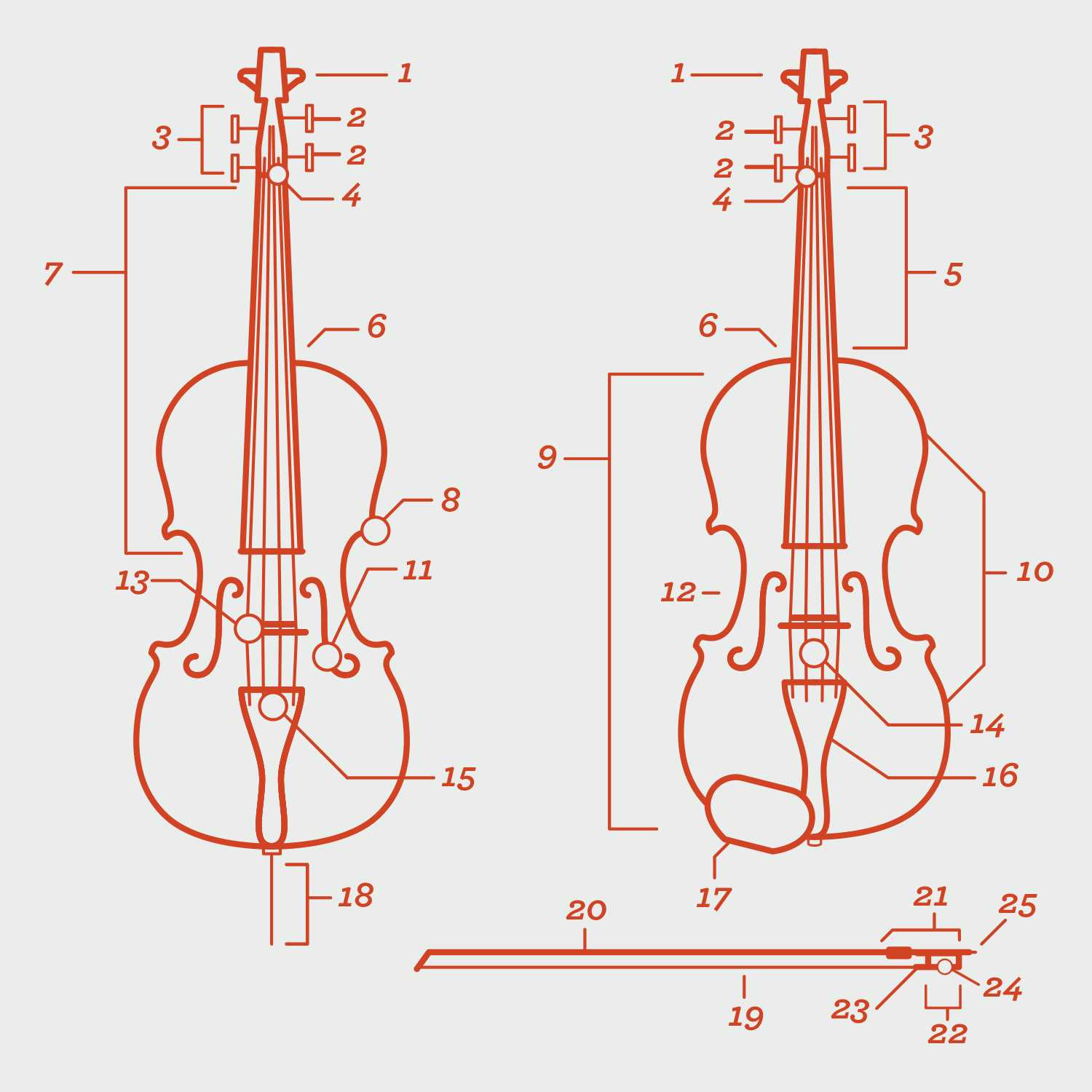
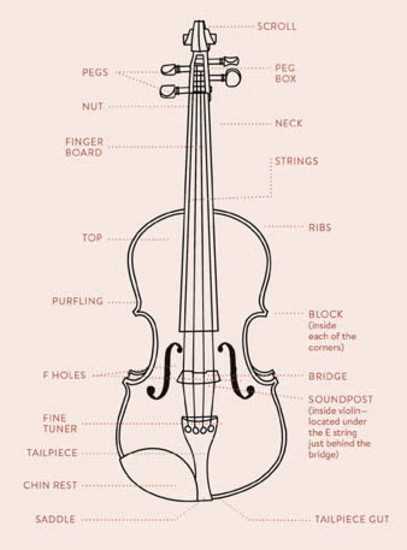
Exploring the intricacies of a string instrument reveals a world of craftsmanship and artistry. Each element contributes to the overall sound and playability, making it essential for musicians to familiarize themselves with these crucial features. This knowledge enhances not only performance but also appreciation for the instrument’s construction.
From the curved body to the finely tuned strings, the ensemble of features plays a significant role in producing harmonious melodies. Recognizing the function of each section empowers players to make informed choices during maintenance and setup. As one delves deeper into the anatomy, the relationship between form and function becomes increasingly apparent.
Understanding these aspects can greatly enhance both learning and teaching experiences. Whether you’re a seasoned performer or a budding enthusiast, grasping the significance of these individual components fosters a greater connection to the music created. This exploration serves as a foundation for deeper engagement with the instrument, enriching your musical journey.
This section delves into the roles and significance of various components found in a string instrument, illustrating how they contribute to the overall sound and playability. Understanding these functions enhances appreciation for the craftsmanship and design behind this musical creation.
Key Components and Their Roles
Each element serves a unique purpose, affecting both sound quality and performance. Below is a summary of essential elements and their respective functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Body | The main structure that resonates sound, amplifying the vibrations produced by the strings. |
| Strings | Produce musical notes when vibrated; their tension and material affect pitch and tone. |
| Bridge | Supports the strings and transmits vibrations to the body, crucial for sound projection. |
| Fingerboard | Allows players to press the strings at specific points, altering pitch and producing melodies. |
| F-Holes | Facilitate sound emission; their shape and placement enhance acoustic properties. |
Impact on Sound Quality
The interplay between these elements directly influences the instrument’s tonal quality and responsiveness. Mastery of their usage can lead to remarkable auditory experiences, showcasing the skill of the musician.
Overview of the Body Structure
The construction of a string instrument encompasses various components that contribute to its overall functionality and sound production. Understanding the arrangement and characteristics of these elements is crucial for both players and enthusiasts. This section delves into the essential features that define the body, focusing on how each segment plays a role in enhancing acoustics and playability.
At the heart of this structure lies the main body, which is pivotal for resonance and tonal quality. The top plate serves as a fundamental element, crafted to vibrate and project sound effectively. Beneath it, the back plate complements the design, aiding in sound reflection and contributing to the instrument’s richness. The sides connect these two surfaces, forming a cohesive unit that enhances durability while maintaining a light weight.
Additionally, the sound hole is strategically positioned to allow sound waves to escape, further enriching the tonal palette. This design feature not only influences acoustics but also adds aesthetic appeal. Understanding these components provides insights into how craftsmanship and engineering converge to create a captivating musical experience.
Strings and Their Importance
The significance of the components responsible for producing sound cannot be overstated. They serve as the fundamental medium through which musical expression is conveyed, directly influencing the overall tone and character of the instrument.
These elements are crafted from various materials, each contributing unique qualities to the sound produced. The choice of material, along with the tension and thickness of these components, plays a crucial role in determining the instrument’s tonal range and responsiveness.
| Material | Characteristics | Impact on Sound |
|---|---|---|
| Gut | Warm, rich tone | Preferred for classical music |
| Synthetic | Durable, consistent | Versatile for various genres |
| Steel | Bright, clear sound | Excellent projection and volume |
Ultimately, understanding the role and qualities of these components enhances the appreciation of the instrument’s artistry and the skill of the musician.
Bow Features and Uses
The bow is an essential tool in string performance, enabling musicians to produce sound with elegance and precision. This implement consists of various elements that contribute to its functionality, ensuring that players can express a wide range of emotions and techniques through their art.
Structure and Materials

Typically crafted from materials like wood, horsehair, and sometimes synthetic fibers, the construction of a bow significantly influences its performance. The balance and weight distribution are crucial for comfort and control, allowing the artist to execute various strokes with ease. A well-made bow can enhance the tonal quality of the instrument, making it a vital consideration for any performer.
Techniques and Applications
Bow techniques are diverse, encompassing methods such as legato, staccato, and spiccato. Each approach requires different handling and pressure adjustments, showcasing the versatility of this implement. Musicians can adapt their style based on the genre and desired expression, making the bow not just a tool, but an extension of the artist’s voice.
Maintenance of Violin Parts
Proper upkeep of string instrument components is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Regular attention ensures that the elements function harmoniously, enhancing the overall sound quality. This section explores essential care practices to maintain the integrity and aesthetics of your cherished instrument.
Regular Cleaning
Cleaning is a fundamental aspect of maintenance. Dust and rosin residue can accumulate over time, impacting both the appearance and sound. Use a soft cloth to gently wipe the surface after each use, focusing on avoiding scratches. For deeper cleaning, consider specialized products that do not harm the finish.
Periodic Inspections
Conducting inspections at regular intervals is vital. Examine the tension and alignment of the strings, and check for any signs of wear or damage. It is also beneficial to evaluate the bridge and sound post positioning to ensure optimal resonance. Address any issues promptly to prevent further complications.
Common Issues and Solutions
Every string instrument can face a variety of challenges that impact its performance and sound quality. Understanding these common concerns and their respective remedies can significantly enhance the playing experience.
- String Buzz: This issue often arises due to improper setup or worn-out strings. To resolve this, ensure the strings are correctly positioned and consider replacing them if they are old.
- Poor Sound Quality: If the tone is dull or unclear, it may be due to insufficient bowing technique or dirty strings. Regular cleaning of the strings and practicing proper bowing can improve the sound.
- Difficulty in Tuning: Instruments can sometimes resist tuning, leading to frustration. This can often be fixed by ensuring the pegs are correctly lubricated and turning smoothly.
- Intonation Issues: If notes sound off-pitch, the instrument may require adjustments. Consulting a professional for fine-tuning the bridge and nut can help achieve better accuracy.
- Physical Discomfort: Players may experience discomfort while playing. Proper posture and hand positioning are crucial, so consider taking lessons to refine your technique.
By recognizing these common issues and implementing effective solutions, musicians can maintain their instruments in optimal condition and enjoy a more rewarding playing experience.