Creating a cozy atmosphere in a living space often involves the integration of innovative heating solutions. This particular system not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also offers practicality in maintaining warmth during colder months. By exploring the essential elements that contribute to its functionality, one can appreciate the sophisticated design and engineering behind this comforting fixture.
Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring efficiency and safety while providing the desired ambiance. From the mechanisms that facilitate combustion to the components that manage heat distribution, a comprehensive understanding reveals how these intricacies come together harmoniously. The synergy between these various segments exemplifies modern advancements in home heating technology.
Delving into the layout allows for a deeper insight into how each component interacts, forming a cohesive unit. Recognizing these elements empowers users to make informed choices about installation, maintenance, and operation, ultimately enhancing their experience. Embracing this knowledge not only enriches one’s appreciation but also ensures optimal performance in creating a warm and inviting environment.
Understanding Gas Fireplace Components
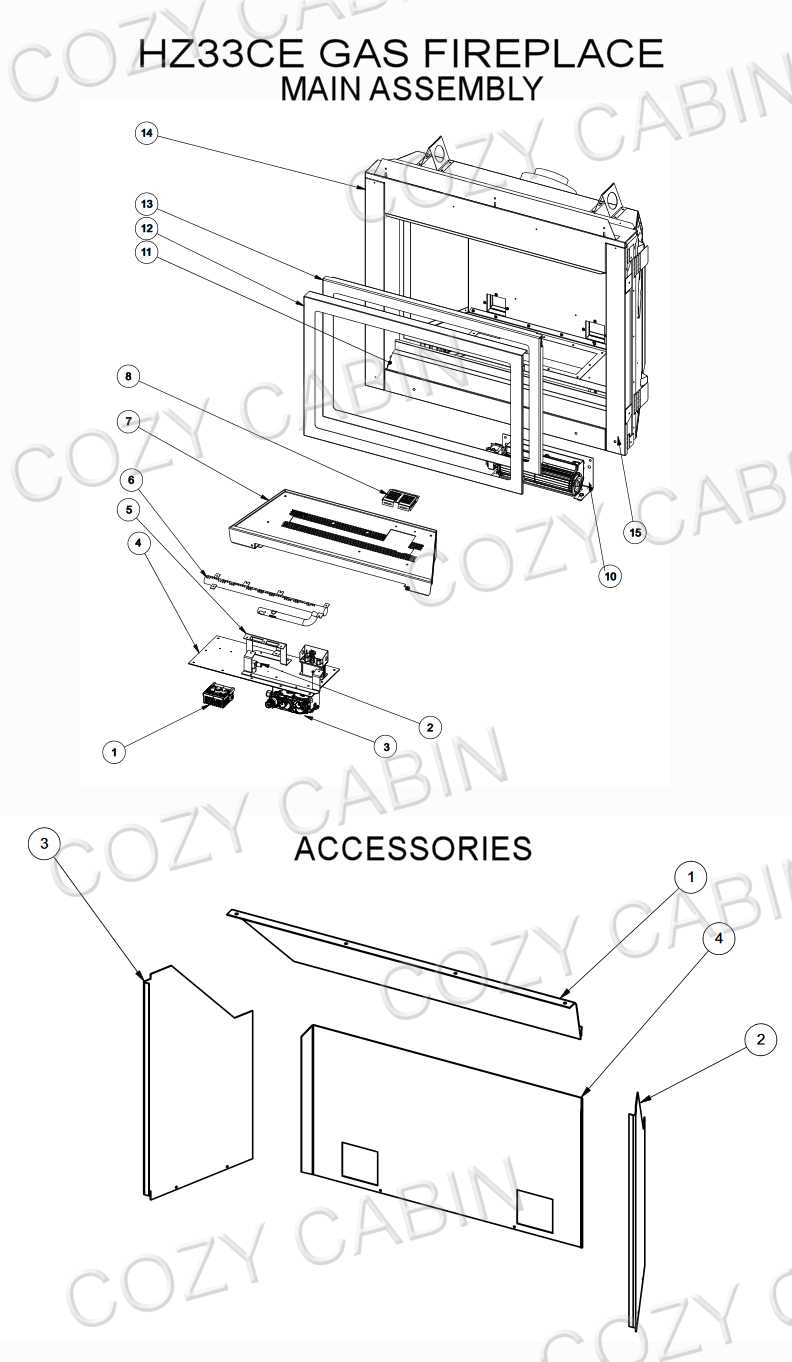
Creating a warm and inviting atmosphere requires an understanding of the essential elements that contribute to the efficient operation of your heating appliance. Each component plays a critical role in ensuring safety, functionality, and overall performance. A comprehensive grasp of these elements will help in maintenance and troubleshooting, allowing for a more enjoyable experience.
Key Elements and Their Functions
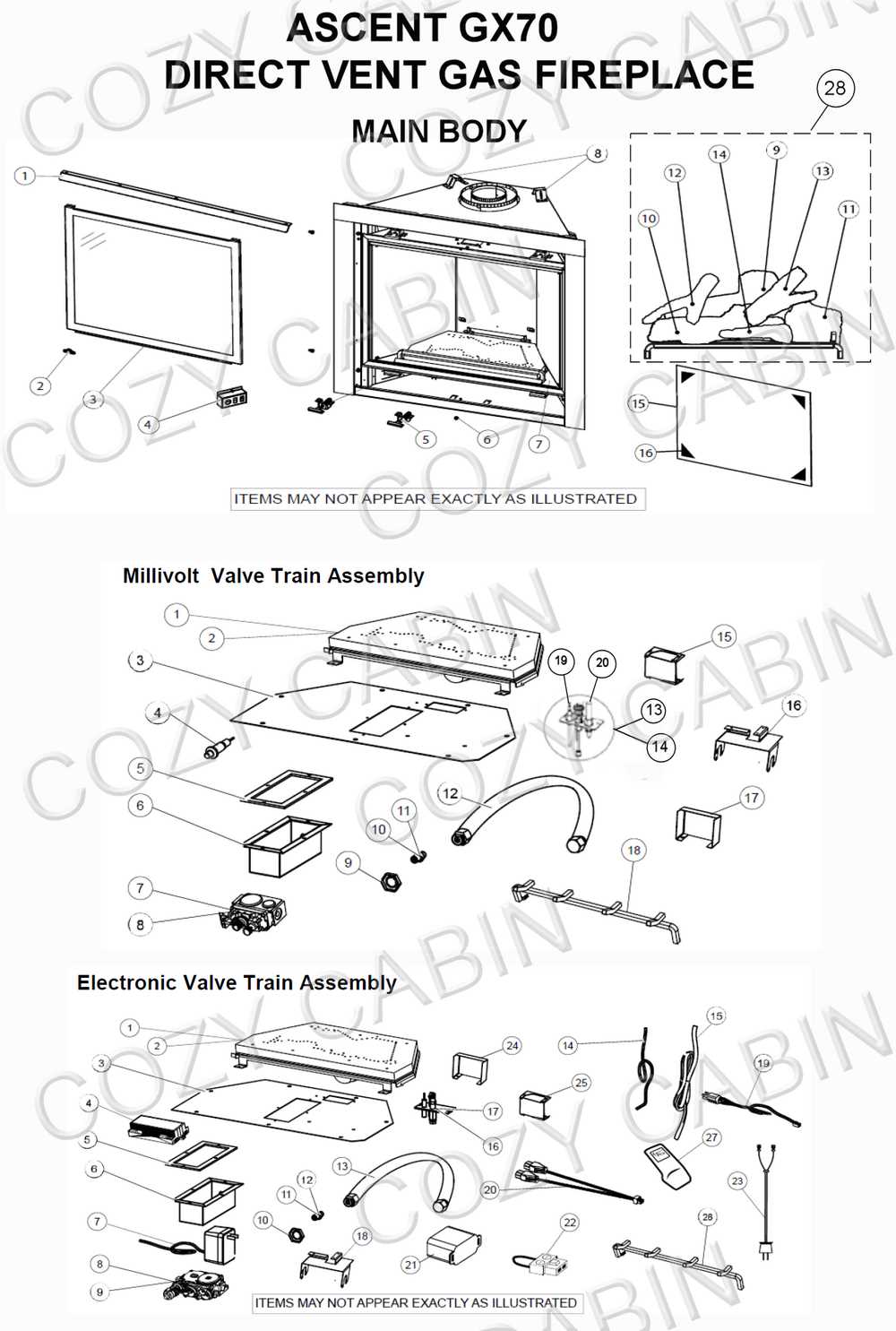
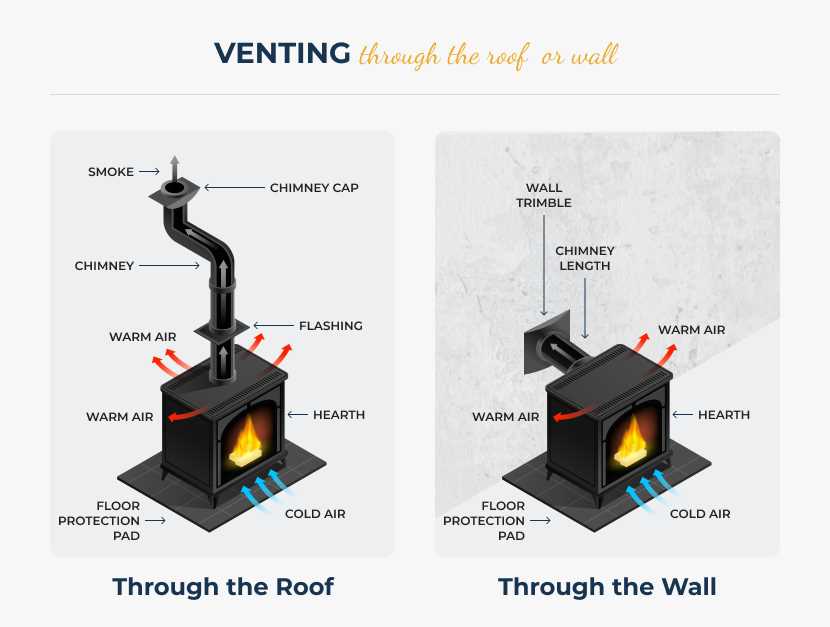
Among the fundamental elements, the ignition system initiates the combustion process, ensuring a reliable start. The burner distributes fuel evenly, facilitating a consistent flame. Additionally, the venting mechanism ensures that byproducts of combustion are safely expelled, maintaining air quality within the space. Each of these components must work in harmony to deliver both warmth and safety.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations
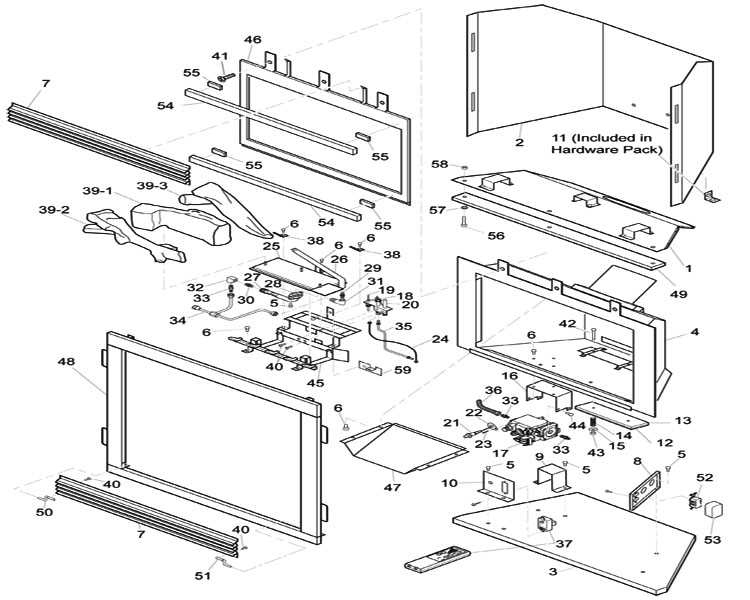
Regular inspections of these crucial components are necessary to ensure optimal performance. Cleaning the ignition and burner areas prevents buildup that could hinder function. Moreover, checking the venting system for blockages is essential for safety, as it protects against harmful emissions. Understanding these elements and their maintenance needs will enhance both longevity and efficiency.
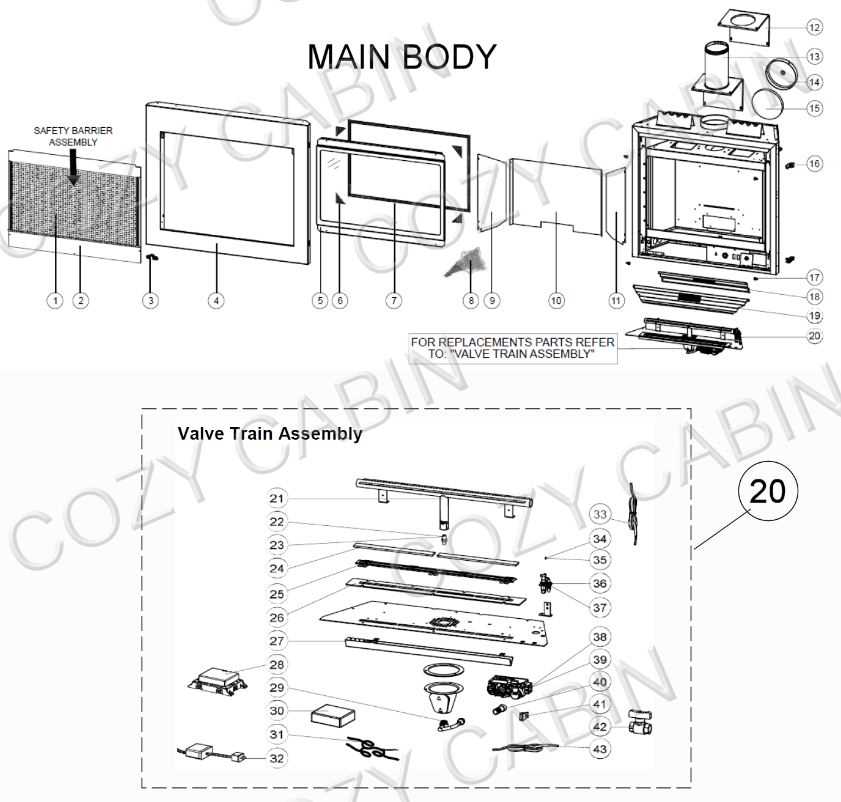
Function of the Burner Assembly
The burner assembly serves a crucial role in the overall operation of a heating appliance. It is designed to facilitate the combustion process, ensuring efficient fuel utilization while producing warmth. This component acts as the primary source of heat, converting energy into a form that can be effectively radiated into the surrounding environment.
Central to its functionality is the even distribution of flames, which is essential for consistent heating. The assembly regulates the flow of fuel and air, optimizing the combustion process to achieve a clean and efficient flame. Additionally, it incorporates safety mechanisms to prevent unwanted leaks or malfunctions, safeguarding users and property.
Moreover, the burner assembly’s design allows for various flame settings, enabling users to adjust the intensity of heat output according to their needs. This flexibility contributes to both comfort and energy efficiency, making it an indispensable element in modern heating solutions.
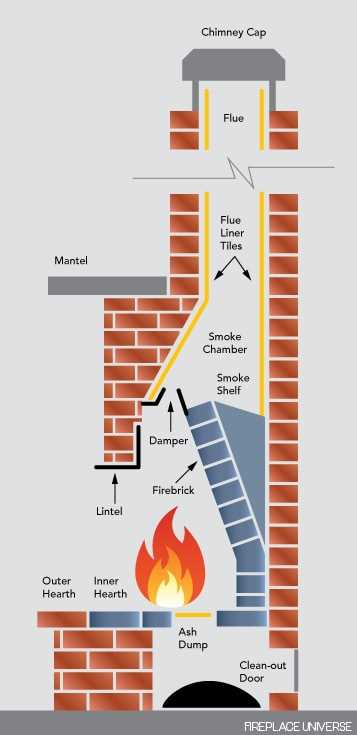
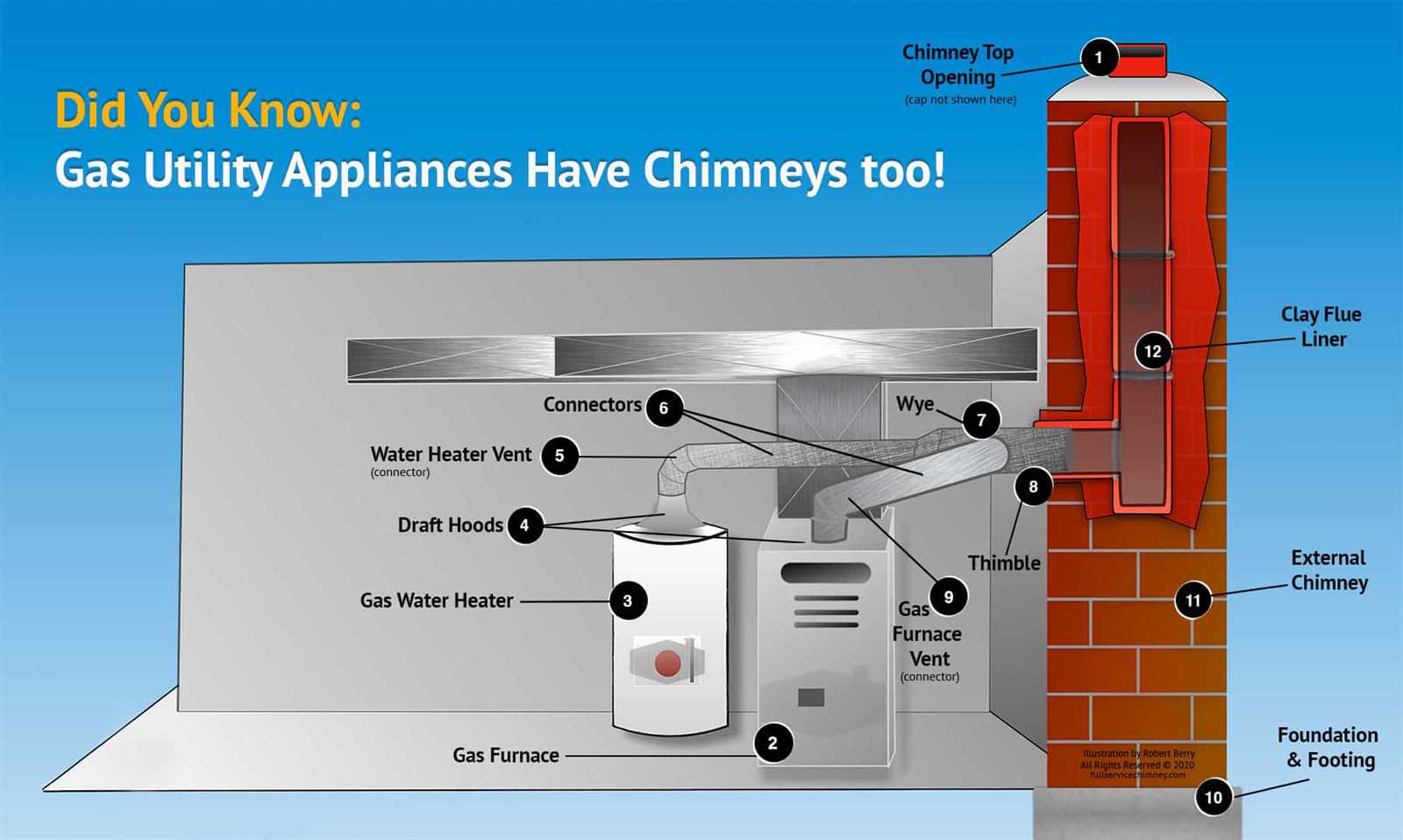
Importance of the Venting System
The venting mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring safe and efficient operation. It facilitates the proper expulsion of combustion byproducts, safeguarding indoor air quality and promoting overall functionality.
Safety Considerations

A well-designed venting system prevents the accumulation of harmful gases, reducing health risks for occupants. Proper ventilation is essential to ensure that toxic substances are efficiently removed from the living space.
Efficiency and Performance

An effective exhaust pathway enhances performance by optimizing airflow, allowing for better heat distribution and reducing energy consumption. This ultimately leads to a more economical and reliable heating solution.
Role of the Control Valve
The control valve is a critical component that ensures the proper functioning of a heating appliance. It regulates the flow of fuel, maintaining a safe and efficient operation while allowing the user to adjust the intensity of the flame. This mechanism plays a vital role in balancing performance and safety.
Functionality and Operation
Primarily, the control valve manages the release of fuel, enabling it to ignite and sustain combustion. By responding to user inputs, it can increase or decrease the flow, thus altering the heat output. The precision of this device is essential, as it not only affects the comfort level but also contributes to energy efficiency.
Safety Mechanisms
In addition to regulating fuel flow, the control valve is equipped with safety features that prevent malfunctions. These mechanisms can shut off the fuel supply in the event of a fault, thereby minimizing the risk of hazards. The reliability of the control valve is paramount, ensuring peace of mind for users during operation.
Heat Exchanger Mechanism Explained
The heat exchanger serves a vital function in transferring thermal energy from one medium to another without allowing them to mix. This process maximizes efficiency by ensuring that warmth generated is effectively utilized while minimizing energy loss. Understanding how this mechanism operates can provide insights into optimal heating practices.
Operational Principles
At its core, the heat exchanger relies on the principles of conduction and convection. Hot air or gases pass through a series of tubes or fins, transferring their heat to a surrounding fluid, such as air or water, which then circulates to warm a space. This setup enables a continuous flow, allowing for consistent temperature regulation and comfort.
Benefits of Efficient Design
An effective heat exchanger design enhances performance by maximizing surface area and optimizing airflow. By minimizing resistance and promoting better heat transfer, these systems can achieve higher efficiency levels, leading to reduced energy consumption and lower operational costs. Understanding these advantages can aid in selecting the right systems for residential or commercial applications.
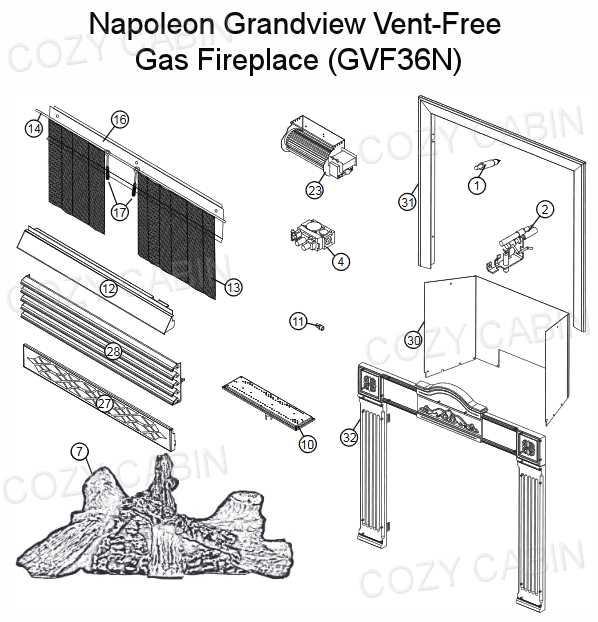
Firebox Design and Materials
The design and materials used in a combustion chamber play a crucial role in ensuring efficiency and safety. A well-constructed chamber not only enhances performance but also contributes to aesthetic appeal. Factors such as heat resistance, insulation, and durability are vital in selecting the right components.
Materials commonly employed include refractory bricks and steel, chosen for their ability to withstand high temperatures and prevent heat loss. The use of ceramic or other insulating materials can further enhance energy efficiency, allowing for optimal heat retention.
Additionally, the design should facilitate proper airflow and combustion, which can significantly impact the overall effectiveness of the heating unit. An effective layout ensures that flames are well-distributed, providing an even warmth and improving the overall experience.
Ignition System Variants
When it comes to initiating combustion in heating units, various methods are employed to ensure reliable operation. Each approach has its unique features and mechanisms that cater to different user preferences and safety standards.
| Type | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Ignition | This method involves a physical trigger, such as a match or lighter, to start the flame. | Simple and cost-effective, providing direct control over the ignition process. |
| Electronic Ignition | Utilizes an electric spark to ignite the fuel, often activated by a switch or remote. | Convenient and efficient, reducing the need for manual intervention. |
| Pilot Light System | A small flame is continuously burning, which can ignite the main fuel supply when needed. | Reliable for consistent operation, ensuring immediate heat availability. |
| Intermittent Pilot | This variant features a pilot light that is only active when the unit is in use. | Enhances energy efficiency by reducing unnecessary fuel consumption when not in use. |
Safety Features in Gas Fireplaces
Ensuring a secure environment is paramount when utilizing heating appliances. Various mechanisms are integrated to prevent hazards and enhance user protection, making the experience enjoyable and worry-free.
Automatic Shut-off Systems
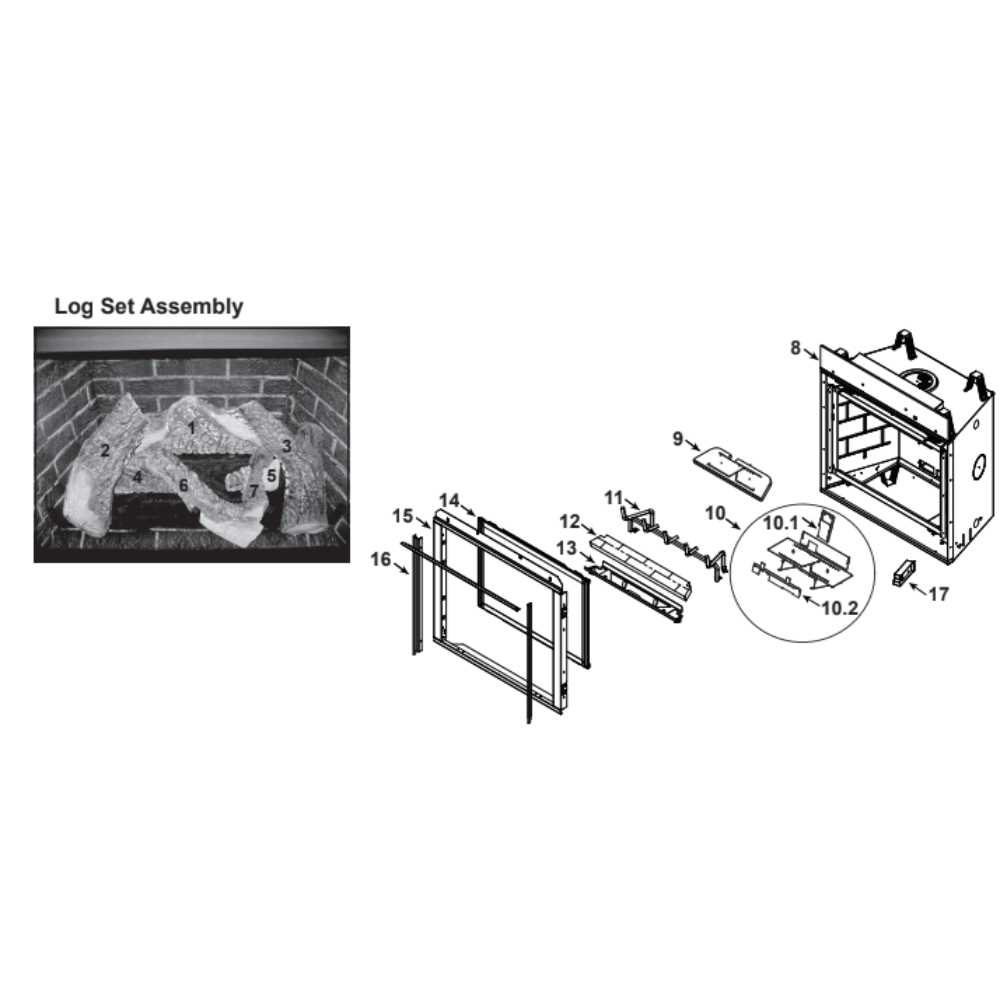
Many modern units are equipped with automatic shut-off mechanisms that activate in case of irregularities. This feature significantly reduces the risk of overheating or gas leaks, providing peace of mind to users.
Ventilation and Oxygen Depletion Sensors
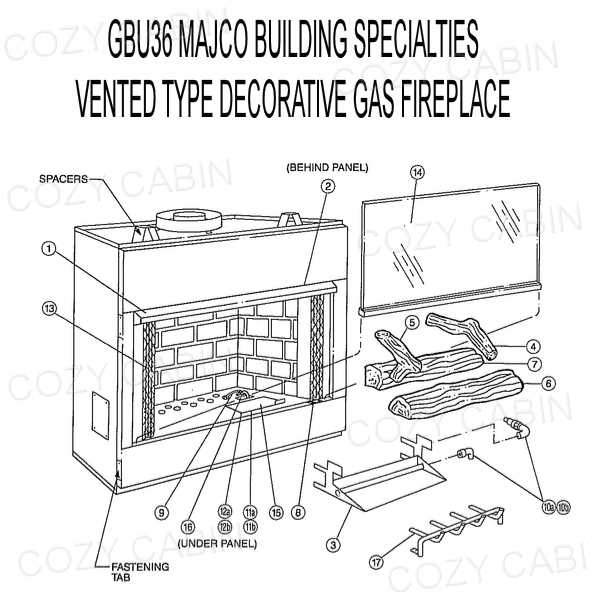
To maintain safe air quality, certain models include ventilation systems and sensors that monitor oxygen levels. These technologies automatically adjust operations to prevent harmful situations, ensuring a healthy atmosphere.
Maintenance of Fireplace Parts

Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring the efficient operation and longevity of your heating appliance. Proper care helps prevent malfunctions and enhances safety. Engaging in routine checks can lead to a cozy and reliable atmosphere during chilly days.
Essential Maintenance Steps
- Inspect for any wear and tear.
- Clean components to prevent buildup.
- Check connections and seals for leaks.
- Ensure proper ventilation is maintained.
Frequency of Maintenance
- Monthly: Visual inspections and basic cleaning.
- Seasonal: Comprehensive checks and deep cleaning.
- Yearly: Professional evaluation and servicing.