Heat adjustment: Modifies the amount of fuel based on the
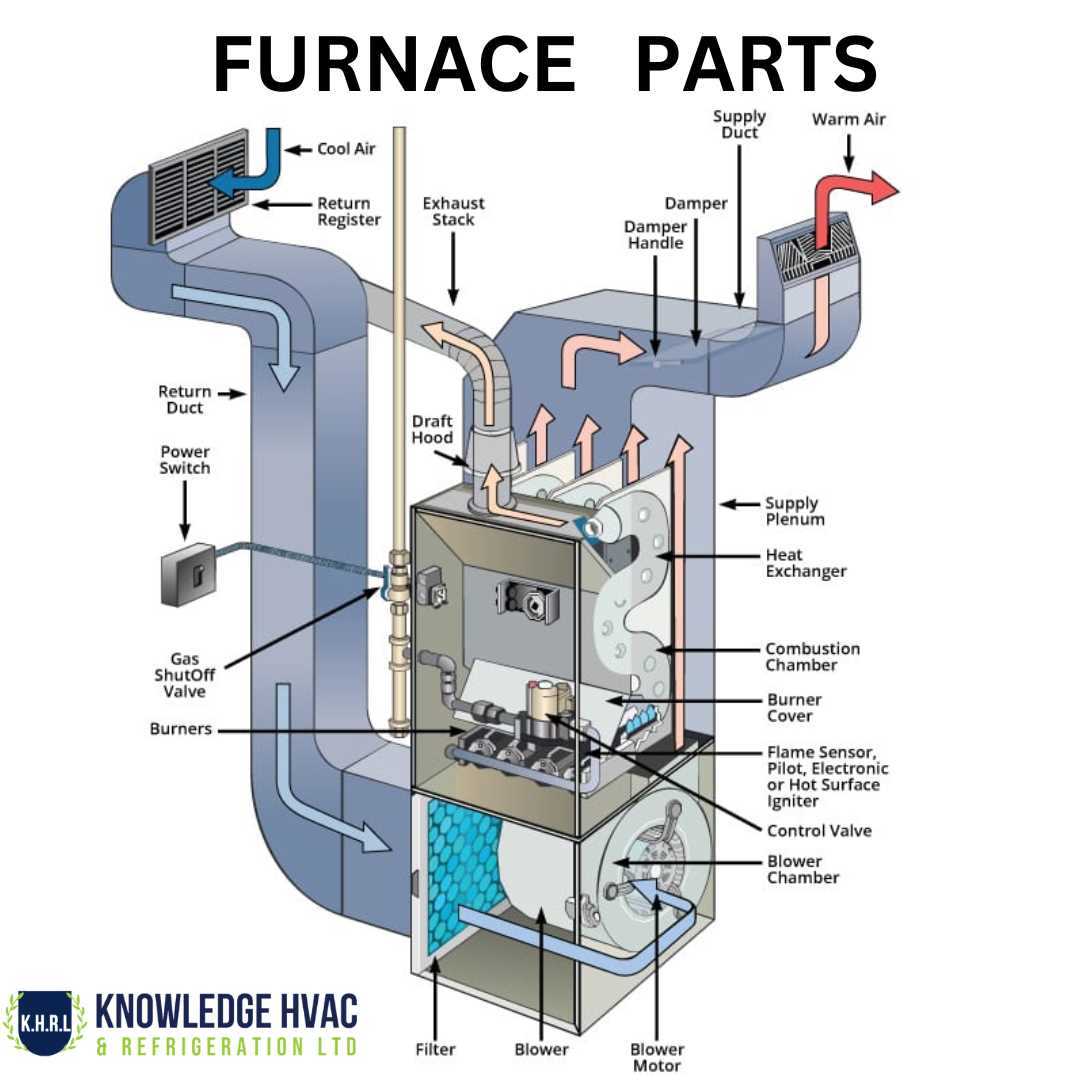
Heat Exchanger Role in Efficiency
The heat exchanger is a critical component in enhancing the overall performance of heating systems. By facilitating the transfer of thermal energy between different mediums, it helps optimize energy use, leading to more efficient heating processes. The design and function of this part play a vital role in reducing energy consumption, as it ensures that minimal heat is wasted, thus contributing to lower operational
Electrical Control Board Overview
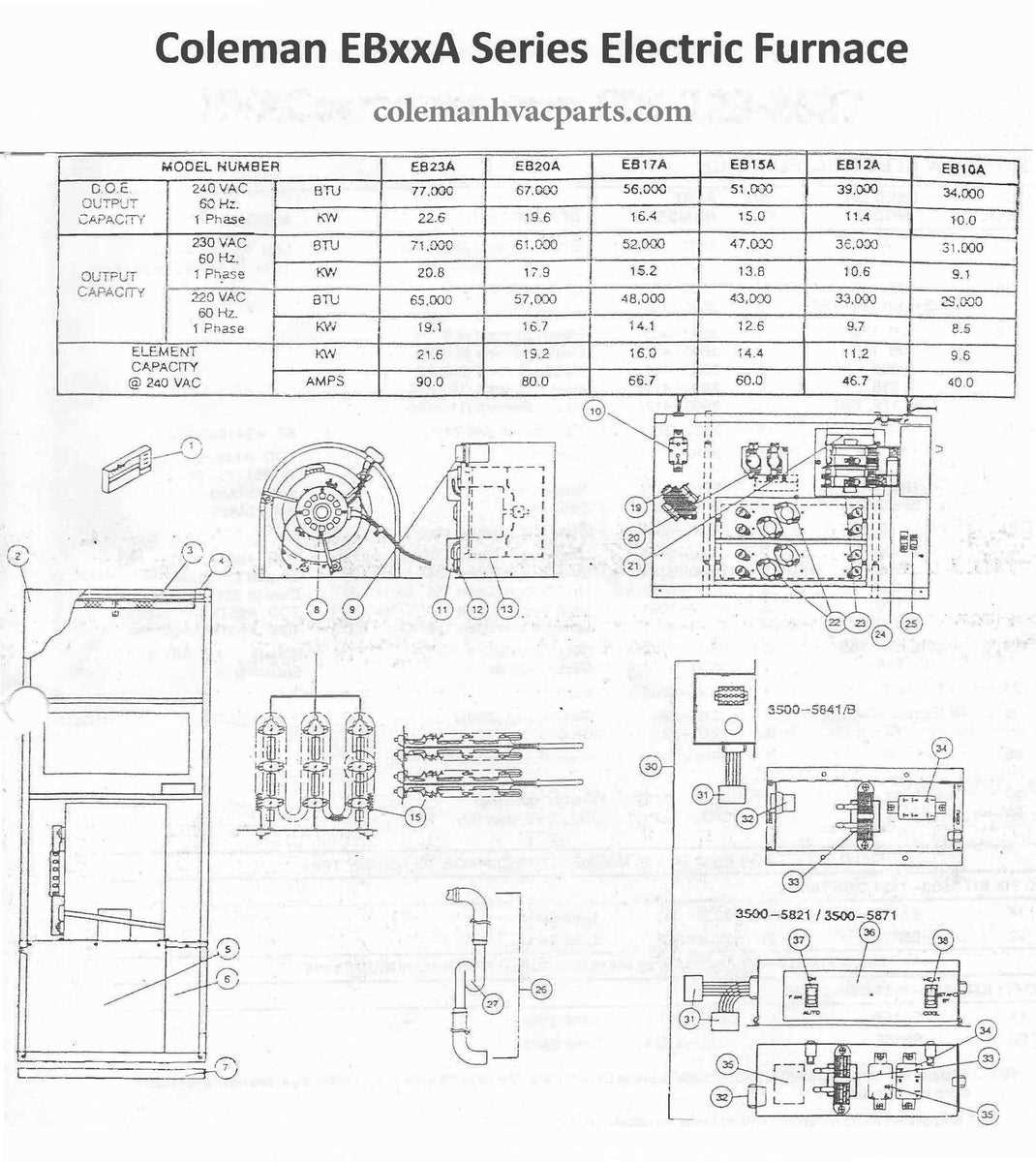
The electrical control board serves as the central processor of the system, overseeing the coordination of various functions to ensure efficient operation. It processes input signals from sensors and user controls, determining when to activate or deactivate specific components. This crucial unit also plays a key role in maintaining safety, preventing malfunctions by monitoring the system’s status.
Key Functions of the Control Board
Limit Switch and Its Importance

The limit switch serves a crucial function in various mechanical systems, ensuring safety and operational efficiency. This device monitors specific parameters within the equipment, enabling automatic responses to prevent malfunctions. By detecting the position or state of moving parts, it helps maintain optimal performance and guards against potential hazards.
Functionality of the Limit Switch
A limit switch operates by responding to predetermined conditions, such as movement or pressure. When these conditions are met, it triggers an action, such as stopping or starting a process. This automatic response is vital for maintaining safe operating environments and preventing damage to machinery.
Benefits of Implementing Limit Switches
Incorporating limit switches into equipment provides numerous advantages. First, they enhance safety by minimizing the risk of accidents caused by equipment overreach or failure. Second, they contribute to increased efficiency by ensuring processes run smoothly without unnecessary interruptions. Additionally, the reliability of limit switches reduces maintenance costs and extends the lifespan of machinery.
How the Ignition System Operates
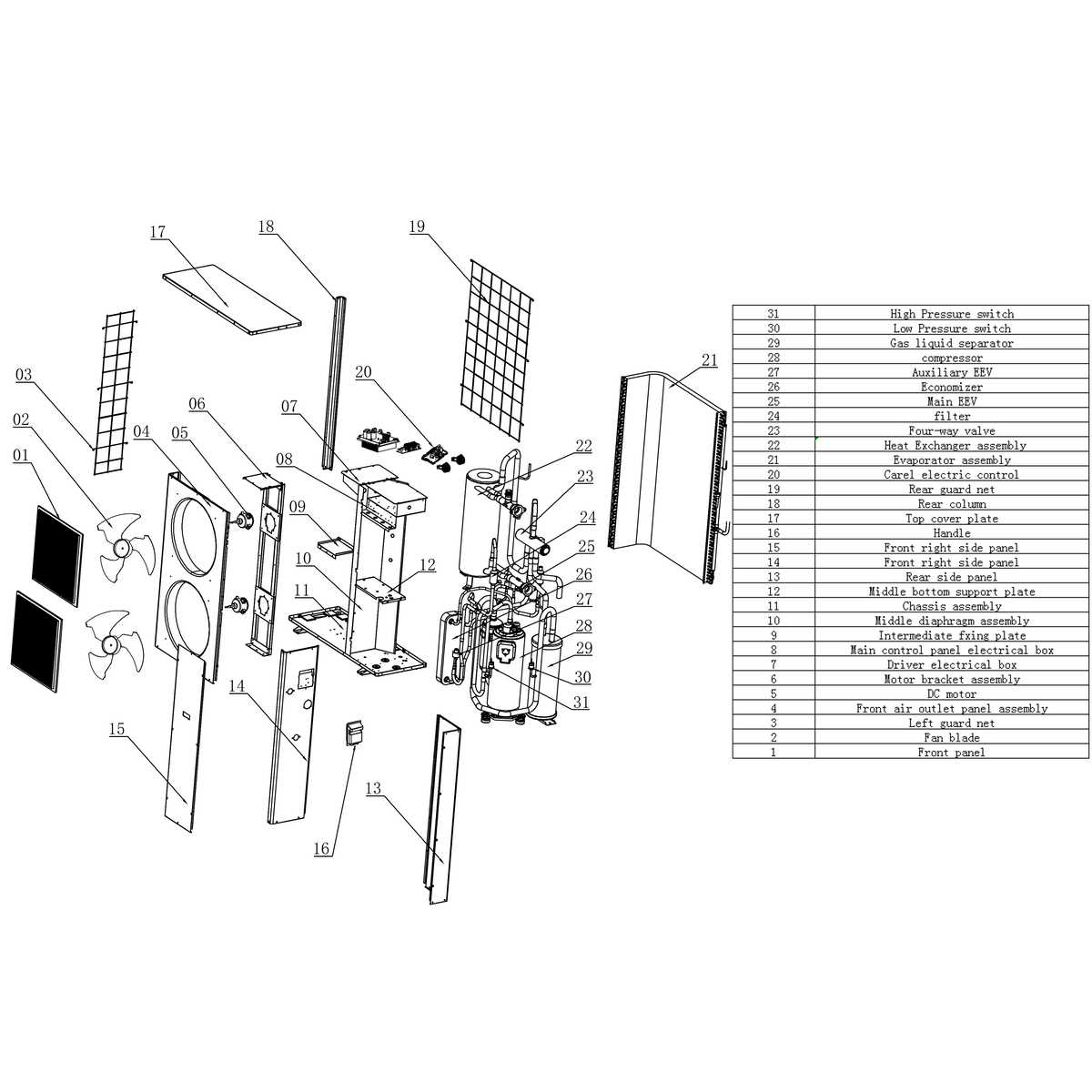
The ignition mechanism plays a crucial role in initiating the combustion process within heating equipment. This system is designed to produce a reliable flame to ensure optimal operation and efficiency. Understanding its components and functioning is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components of the Ignition Mechanism
The ignition system comprises several key elements that work together to create a stable flame. These components include:
- Spark Generator
- Electrode
- Gas Valve
- Control Module
Operating Principles
When the heating unit is activated, the control module signals the gas valve to open. Subsequently, the spark generator ignites the gas emitted from the valve, creating a flame. This process is monitored to ensure safety and efficiency, enabling adjustments as necessary to maintain consistent performance.
| Component |
Function |
| Spark Generator |
Creates the initial ignition spark. |
| Electrode |
Conducts the spark to ignite the fuel. |
| Gas Valve |
Regulates the flow of gas for combustion. |
| Control Module |
Monitors and controls the ignition process. |
Filters and Air Quality Improvement
Effective filtration systems play a crucial role in enhancing indoor air quality. By trapping pollutants and particulates, these mechanisms contribute significantly to a healthier environment. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of filters are essential for optimal performance and to ensure that harmful substances are minimized.
Implementing high-quality filtration can lead to several benefits:
- Reduction of Allergens: Filters capture dust, pollen, and other allergens, providing relief for individuals with sensitivities.
- Minimized Odors: Advanced filtering technologies can eliminate unpleasant smells from various sources.
- Enhanced System Efficiency: Clean filters allow air circulation systems to operate more efficiently, reducing energy consumption.
To further improve air quality, consider the following strategies:
- Regular Inspection: Periodically check filters for clogging and wear to maintain effective airflow.
- Choose Appropriate Filters: Opt for filters with the right MERV (Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value) rating to suit specific needs.
- Incorporate Additional Purification: Utilize air purifiers or UV light systems alongside filters for enhanced protection against pathogens.
In conclusion, prioritizing air filtration not only enhances comfort but also supports overall health and well-being in indoor spaces.
Thermostat Wiring and Troubleshooting
Understanding the connection and functionality of temperature control devices is essential for maintaining an efficient heating system. Proper wiring ensures that the system operates effectively and responds accurately to the desired temperature settings. This section provides insights into the wiring process and common issues that may arise during operation.
Wiring Connections
Correct wiring is crucial for seamless communication between the thermostat and the heating unit. Here are the typical connections to consider:
- R Wire: Connects to the power source.
- W Wire: Controls the heating element.
- Y Wire: Engages cooling systems, if applicable.
- G Wire: Manages the fan operation.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When problems arise, the following steps can help diagnose and resolve them:
- Ensure all connections are secure and free from corrosion.
- Verify that the power supply to the thermostat is functional.
- Check the calibration of the temperature sensor.
- Examine the device for any visible damage or wear.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that the temperature control mechanism operates efficiently, enhancing the overall performance of the heating system.