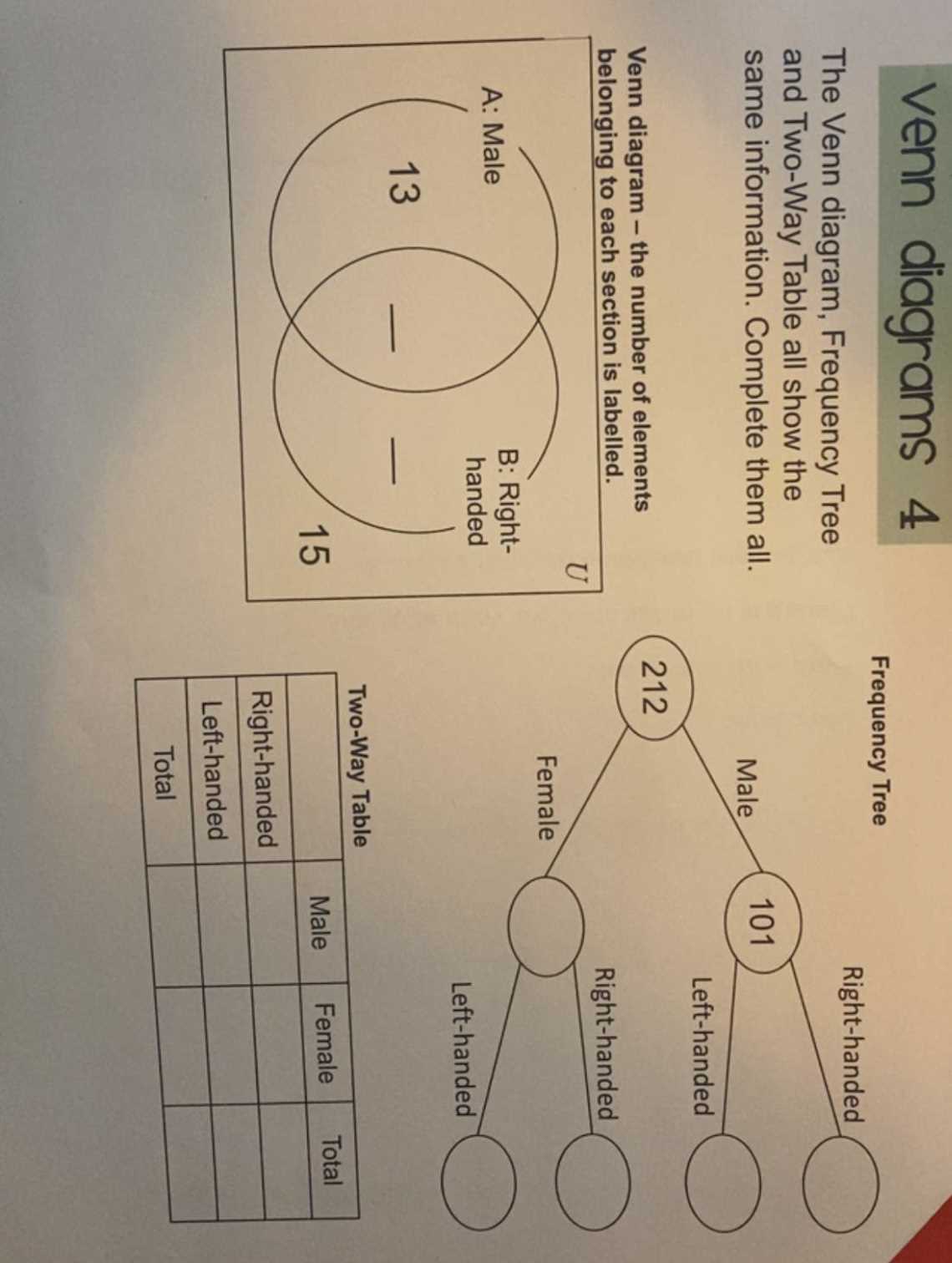
Exploring connections between living organisms and physical structures can reveal fascinating overlaps. These intersections highlight intriguing similarities in form and function, showcasing a unique interplay that exists in our world.
By examining characteristics shared by flora and human anatomy, one can uncover deeper insights into both realms. This exploration not only enhances our understanding of biology but also invites contemplation about the fundamental principles that govern life.
Through this journey, we will delve into various examples that illustrate how these two domains converge, ultimately enriching our appreciation for the intricate designs found in nature and within ourselves.
Understanding Trees and Anatomy
This section explores fascinating connections between various forms of flora and human physical structure. By examining similarities in patterns, functions, and classifications, we can appreciate how nature’s design resonates in both realms.
Commonalities in Structure

Both plant life and human anatomy exhibit intricate frameworks. For instance, roots resemble nerves, grounding essential systems, while branches parallel limbs, extending functionality. This comparison invites deeper reflection on how living entities share fundamental organizational principles.
Functional Analogies
Beyond mere structure, functional roles also align. Just as leaves capture sunlight, lungs facilitate breathing. Exploring these analogies can reveal how ecosystems and biological systems complement each other, showcasing an ultimate harmony within the natural world.
Unique Structures of Tree Species
Exploring various types of flora reveals fascinating features that distinguish each variety. These distinctive characteristics play vital roles in adaptation, survival, and interaction with surrounding environments. By examining these remarkable forms, one can appreciate the intricate relationships present in nature.
| Tree Species | Unique Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Baobab | Thick trunk | Water storage |
| Sequoia | Giant height | Access to sunlight |
| Willow | Flexible branches | Wind resistance |
| Birch | Peeling bark | Pest deterrence |
| Cactus | Succulent stems | Water retention |
Each variety showcases extraordinary adaptations, enhancing its ability to thrive in specific conditions. Understanding these unique forms provides insight into ecological dynamics and highlights the importance of preserving biodiversity.
Common Body Parts and Their Functions
Exploring essential components of human anatomy reveals a fascinating interplay of form and function. Each element contributes uniquely to overall well-being, enabling a variety of activities, from basic movements to complex interactions.
Head: This uppermost section houses vital sensory organs such as eyes, ears, and nose. These structures facilitate sight, hearing, and smell, crucial for perception of the environment.
Heart: Positioned centrally in the chest, this muscular organ is responsible for circulating blood throughout the organism. It ensures that oxygen and nutrients reach tissues while removing waste products.
Lungs: Located on either side of the heart, these spongy organs play a key role in respiration. They enable the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, essential for sustaining life.
Stomach: Found in the upper abdomen, this organ aids in digestion. It breaks down food using acids and enzymes, preparing nutrients for absorption in the intestines.
Hands: At the end of each arm, these versatile appendages allow for manipulation of objects, facilitating tasks from simple grasping to intricate movements.
Legs: Functioning as pillars of mobility, legs support body weight and enable walking, running, and jumping. Their structure provides stability and strength for various activities.
Understanding these fundamental components highlights their significance in maintaining health and facilitating daily functions, demonstrating the remarkable efficiency of human anatomy.
Photosynthesis: Trees and Human Health
This section explores the interconnectedness of nature’s greenery and human well-being, highlighting how natural processes enhance our quality of life. The intricate relationship between flora and human health showcases benefits that extend beyond mere aesthetics.
Photosynthesis plays a crucial role in producing oxygen, which is vital for our survival. As green organisms convert sunlight into energy, they release this essential gas into the atmosphere, contributing significantly to respiratory health. Furthermore, the act of engaging with vibrant landscapes can reduce stress levels, fostering mental clarity and emotional stability.
Additionally, lush environments help filter pollutants, improving air quality and promoting cardiovascular wellness. The presence of vegetation also encourages physical activity, which is beneficial for overall fitness. Therefore, nurturing these vital systems not only supports ecological balance but also enhances our health on multiple levels.
In conclusion, understanding the significance of natural processes reveals their ultimate impact on human vitality. By appreciating and preserving these connections, we ensure a healthier future for ourselves and the planet.
Tree Growth and Human Development
This section explores the fascinating parallels between the growth patterns of flora and the evolution of human beings. Both processes reflect adaptation, resilience, and the complex interplay of internal and external factors. Understanding these similarities can offer insights into biological systems and the interconnectedness of life.
| Aspect | Flora Growth | Human Development |
|---|---|---|
| Stages | Seedling, maturity, reproduction | Childhood, adolescence, adulthood |
| Influencing Factors | Soil quality, climate, light | Nutrition, environment, education |
| Resilience | Adapting to seasons, diseases | Overcoming challenges, learning |
| Growth Patterns | Branching, leaf expansion | Physical, cognitive, emotional growth |
Both organisms require nurturing conditions to thrive. Just as a sapling needs water, sunlight, and nutrients, individuals flourish in supportive environments that promote their potential. Observing these connections can enhance our appreciation of life’s complexities.
Ecological Benefits of Trees

Numerous advantages arise from the presence of these vital organisms in our environment. Their contributions significantly enhance both natural ecosystems and human well-being, fostering a more balanced planet.
Key ecological benefits include:
- Air Quality Improvement: These entities absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, purifying the atmosphere.
- Soil Erosion Prevention: Roots stabilize soil, reducing erosion and promoting nutrient retention.
- Habitat Creation: They provide shelter and food for various species, supporting biodiversity.
- Water Cycle Regulation: Through transpiration, they influence local weather patterns and maintain hydrological balance.
- Climate Regulation: By sequestering carbon, they play a crucial role in mitigating climate change effects.
Incorporating these vital entities into urban planning not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also promotes healthier living environments for communities. Their strategic placement can lead to improved public health outcomes and increased quality of life.
Recognizing and preserving these organisms is essential for sustainable development and ecological resilience.
Symbolism of Trees in Culture

In various societies, certain flora hold deep significance, embodying values, beliefs, and narratives that shape collective identity. These plants are often seen as powerful symbols, representing life cycles, growth, and connections to nature. Their presence in folklore and art reflects humanity’s relationship with the natural world and its mysteries.
Spiritual Connections
Many cultures regard these organisms as sacred, linking them to divine forces or ancestral spirits. Rituals and ceremonies frequently involve these natural entities, symbolizing renewal, wisdom, and strength. This spiritual dimension enhances their role as vital elements in cultural practices.
Representation of Life and Growth
Beyond spirituality, these organisms often symbolize personal growth, resilience, and the passage of time. They serve as reminders of continuity and change, illustrating how life evolves through various seasons. This duality reflects the ultimate journey of existence, resonating with human experiences and emotions.
Anatomy: Lessons from Nature’s Design
Nature offers a fascinating blueprint that intertwines various life forms, showcasing intricate patterns that resonate across different domains. This interconnectedness reveals profound insights into functionality, structure, and adaptability. By examining these natural designs, we can glean valuable knowledge that informs our understanding of biological frameworks and their efficiency.
Both flora and living organisms exhibit remarkable parallels in their construction and operational principles. Studying these relationships not only enhances our appreciation for biodiversity but also inspires innovative approaches in fields such as medicine, engineering, and environmental science.
| Nature’s Element | Biological Insight |
|---|---|
| Branches | Circulatory pathways |
| Roots | Neural networks |
| Leaves | Skin structures |
| Trunks | Spinal columns |
Embracing these analogies fosters a deeper comprehension of both natural phenomena and human anatomy. By recognizing how life evolves and adapts through similar mechanisms, we can cultivate innovative solutions that harmonize with our environment.
Interconnectedness of Life Forms
Life manifests in a multitude of forms, each intricately linked to others within ecosystems. These connections illustrate a profound relationship among living entities, showcasing how existence relies on cooperation and mutual influence. Understanding these bonds enriches our appreciation of biodiversity and emphasizes the importance of every organism in maintaining balance.
Examples of Connections
- Symbiosis: Mutual relationships enhance survival, such as between fungi and plants.
- Pollination: Insects play a crucial role in the reproduction of flowering plants.
- Food Chains: Predators and prey illustrate energy transfer and dependency.
Implications for Conservation
Recognizing these interrelations is essential for effective conservation efforts. Protecting one species can have a ripple effect, benefiting others and the environment as a whole. Strategies should include:
- Habitat preservation to maintain ecosystem integrity.
- Restoration projects to revive damaged environments.
- Educational programs to raise awareness about ecological significance.