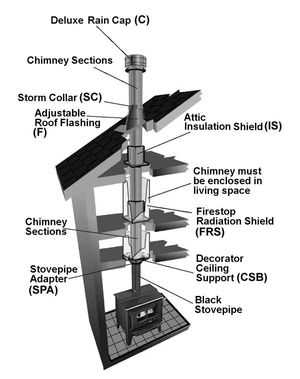
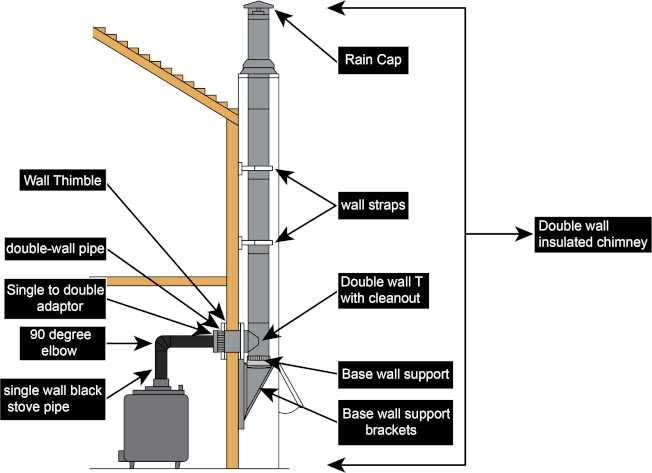
Understanding the configuration of a vertical exhaust structure is essential for ensuring its optimal performance and safety. Each component within this system plays a critical role in directing fumes and gases away from the living space, maintaining proper airflow and preventing hazardous situations.
By examining the various elements that make up this venting structure, we can better appreciate how they contribute to both functionality and long-term durability. Whether it’s about maintaining temperature control, enhancing safety features, or improving energy efficiency, each section has its specific function.
In this guide, we will delve into the primary components, explaining their individual purposes and how they interact within the whole system. This knowledge is key to maintaining a safe and efficient setup in any building where this type of exhaust solution is installed.
Overview of Chimney Components
This section provides a detailed explanation of the key structural elements involved in ensuring efficient air flow and proper ventilation. Each part has a specific role in maintaining safety and optimal performance, contributing to the overall system’s reliability.
Main Structural Elements
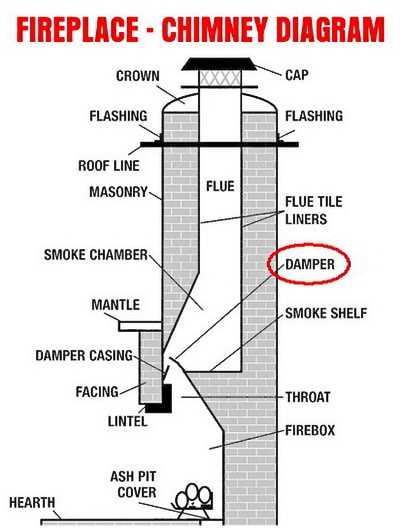
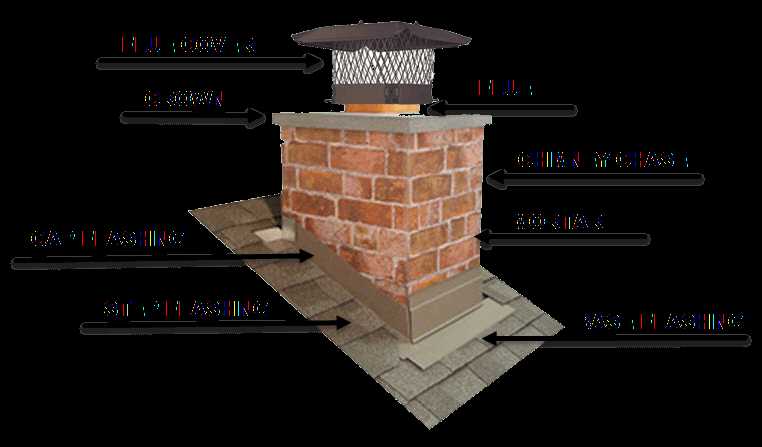
- Flue: This internal passageway guides gases and smoke outside, preventing harmful substances from entering living spaces.
- Crown: A protective layer that covers the top and shields the interior from weather exposure, helping to prevent damage.
- Cap: Positioned on the very top, this accessory prevents debris and animals from entering, while allowing air circulation.
Additional Features
- Damper: A movable barrier that regulates airflow and controls the release of gases, improving efficiency and reducing heat loss.
- Chase: A covering designed to enclose and protect the entire structure, often enhancing both aesthetic appeal and functionality.
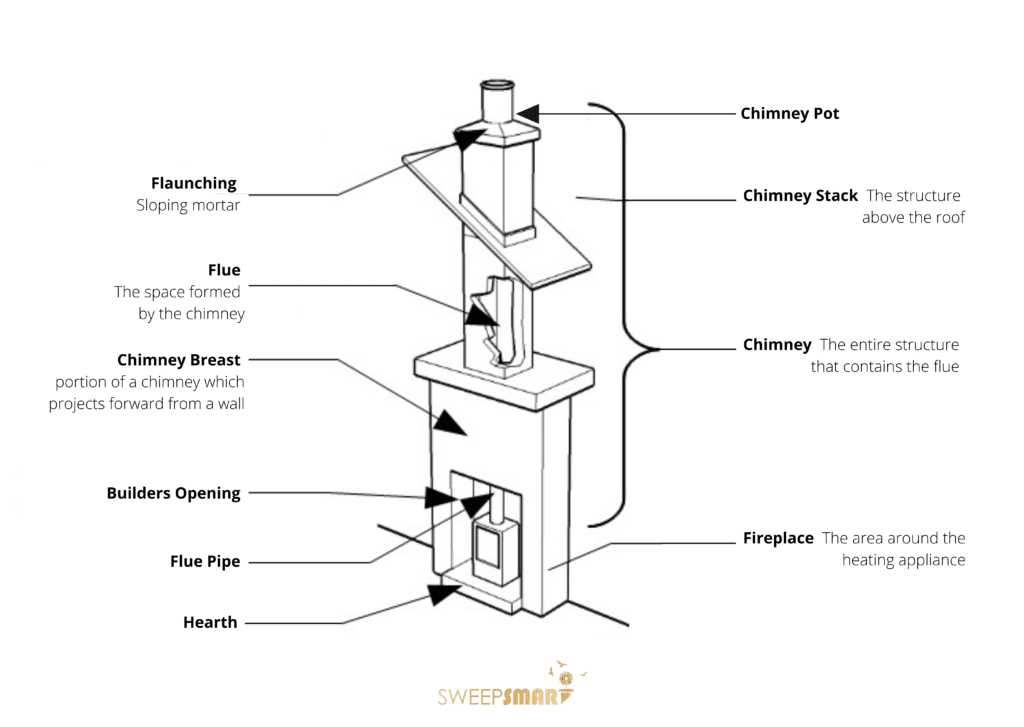
Main Structural Elements of a Chimney
The vertical structure responsible for directing gases and smoke outside consists of several crucial components. Each element works together to ensure efficient operation and safety. Understanding these individual sections allows for better maintenance and overall performance.
- Base Foundation: This is the lower section that provides support and stability to the entire structure. It must be robust and secure to withstand external conditions.
- Vertical Channel: This long, hollow column serves to guide the gases upwards. Its construction ensures the safe removal of fumes and heat, protecting the interior.
- Protective Cover: Positioned at the top, this component prevents debris and precipitation from entering the system while still allowing smoke to escape freely.
- Insulating Layers: These sections are added to protect the system from extreme temperatures, preventing heat loss and safeguarding nearby materials.
- Exhaust Cap: This uppermost section serves to enhance the safe release of smoke and gases, ensuring optimal airflow and preventing backflow into the building.
Chimney Crown and Its Role
The uppermost surface that protects the entire venting structure plays a crucial part in shielding the system from various external factors. It acts as a barrier against weather elements, preventing moisture and debris from entering the system and ensuring its longevity.
Key Features of the Protective Cap
The protective cap is typically crafted from durable materials to withstand harsh conditions. Its slightly sloped design allows rain and snow to drain away, preventing water from seeping into the inner structure and causing potential damage over time.
Importance for Overall Functionality
The protective top ensures that the air flows properly, maintaining the overall efficiency of the venting process. By keeping out unwanted elements, it supports the system’s smooth operation, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and repairs.
| Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| Material | Resistant to weather and corrosion |
| Design | Sloped for water runoff |
| Protection | Prevents debris and moisture infiltration |
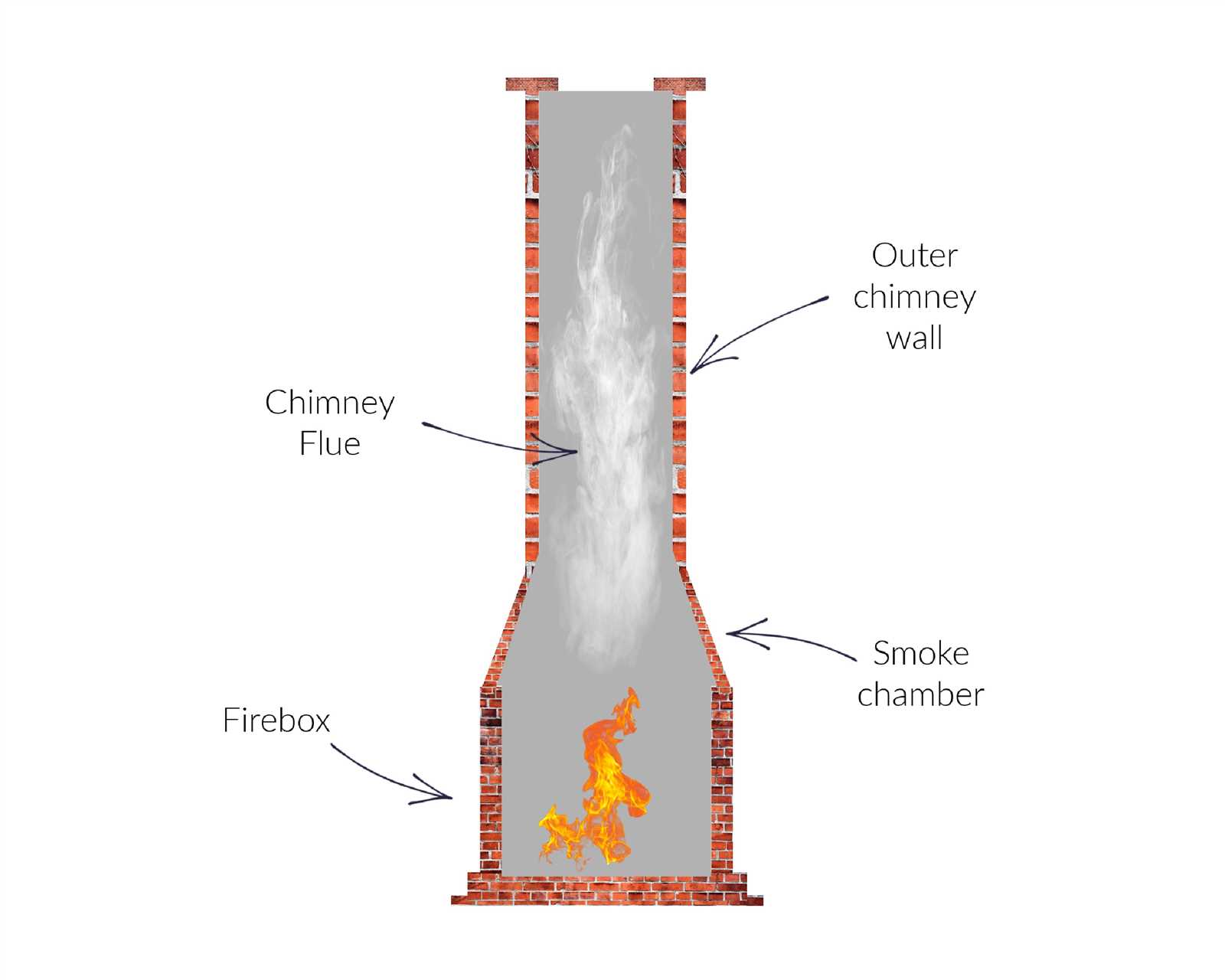
Importance of the Chimney Flue
The flue plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient expulsion of gases produced during combustion. Its design and functionality significantly impact the overall performance of the entire system, directly affecting safety and energy efficiency in residential and commercial settings.
Key Functions of the Flue
- Ensures proper ventilation of harmful gases
- Maintains optimal draft for combustion
- Prevents backflow of smoke into the living space
Impact on Safety and Efficiency
A well-constructed flue enhances safety by minimizing the risk of carbon monoxide buildup. Furthermore, it optimizes energy use, reducing costs associated with heating. Regular maintenance and inspection are vital to preserving its integrity and functionality.
- Check for blockages regularly.
- Inspect for cracks and damage.
- Ensure proper insulation to prevent heat loss.
Understanding Chimney Liner Materials
Lining materials play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of your venting system. The choice of lining can affect everything from performance to longevity, making it an essential aspect to consider. There are several options available, each offering different benefits depending on the installation environment and maintenance needs.
Common Types of Liner Materials
There are several popular options for lining materials, each suited to different heating methods and construction types. These include metal, clay, and composite linings, which offer various levels of durability and resistance to heat. Selecting the right material can ensure long-lasting service and minimize potential hazards.
Comparison of Liner Materials
| Material Type | Durability | Heat Resistance | Maintenance Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal | High | Excellent | Low |
| Clay | Moderate | Good | Medium |
| Composite | Variable | Good |