When it comes to understanding the inner workings of home cooling appliances, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the various elements that make up these complex systems. Each component serves a specific purpose and works in harmony with others to ensure efficient operation. By exploring the layout of key mechanisms, you can gain insight into how the entire system functions and what to look for in case of any issues.
Whether you’re maintaining your appliance or addressing a malfunction, knowing how different elements are organized can make troubleshooting much easier. The ability to recognize the placement and function of different sections can save both time and effort when repairs are needed. This guide aims to provide a clear overview, helping you na
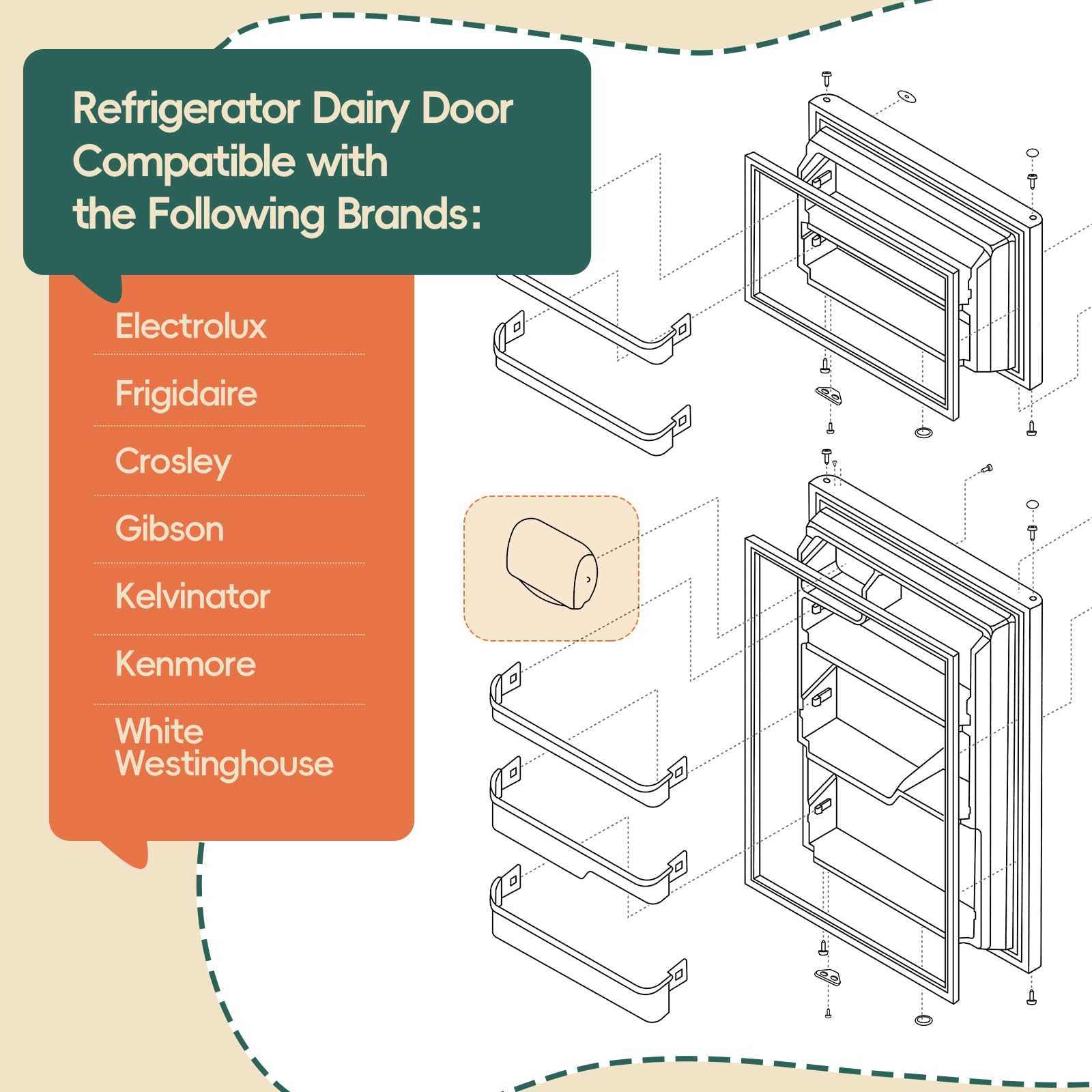
Understanding the Structure of Crosley Refrigerators
The design of cooling appliances involves a careful arrangement of various components working together to ensure optimal performance. Each section of these devices serves a specific purpose, contributing to the overall functionality, from maintaining temperature stability to efficient energy consumption. To fully appreciate how these machines operate, it is essential to examine the core systems that govern their operation.
The table below provides an overview of key elements found in these appliances, highlighting their role and interaction within the system:
| Component | Function | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cooling Unit | Regulates internal temperature by extracting heat. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Thermostat | Controls and monitors
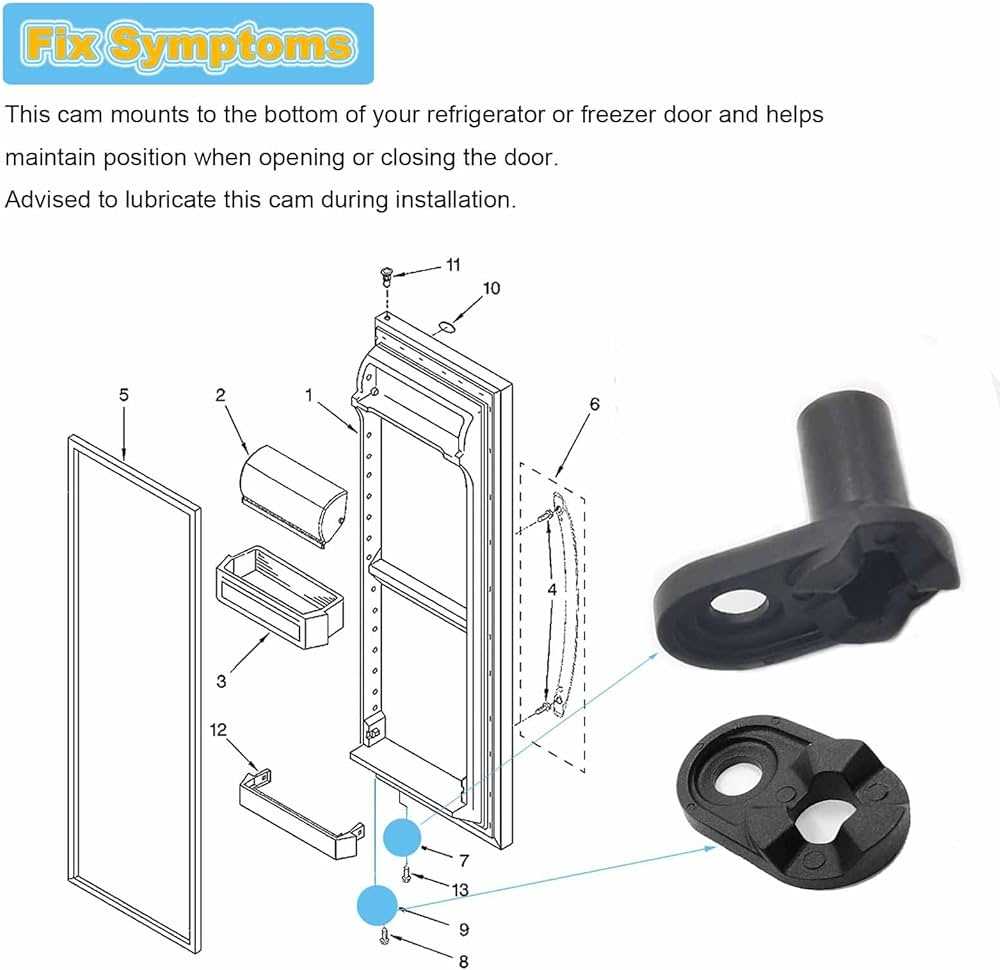
Key Components of the Cooling SystemThe cooling mechanism relies on several essential elements working together to regulate and maintain optimal temperature levels. Each component plays a specific role in the process of absorbing and expelling heat, ensuring efficiency and consistent performance. Compressor: Often referred to as the heart of the system, this part circulates the cooling medium, creating the necessary pressure to facilitate heat transfer. Condenser: This element aids in releasing absorbed heat into the surrounding environment, allowing the cycle to continue smoothly by condensing the refrigerant back into liquid form. Evaporator: The evaporator is responsible for absorbing heat from the interior, allowing the cooling medium to evaporate and lower the overall temperature. Expansion Device: This component controls the flow Interior Layout and Shelving OptionsThe design inside is thoughtfully structured to provide maximum storage efficiency and flexibility. With multiple levels and adjustable elements, it allows users to organize items in a way that best suits their needs, ensuring easy access and proper utilization of space. Adjustable Shelves: One of the standout features is the ability to modify the height of the shelves. This ensures that items of varying sizes, from tall containers to smaller packages, can be easily stored without any wasted room. Specialized Compartments: Additional sections are dedicated to specific types of items, providing tailored storage for products that require unique conditions, such as fresh produce or beverages. Overall, the internal configuration prioritizes both functionality and customization, offering a versatile solution for a wide range of storage preferences. How Temperature Control Mechanisms WorkThe regulation of coolness within a cooling system is essential for maintaining optimal conditions. A key component responsible for this balance ensures that items remain at their desired levels, preventing unwanted fluctuations in the environment. This process relies on a combination of sensors and control units that communicate to keep everything stable. Thermostatic Functions: A thermostat plays a pivotal role in the system by constantly monitoring internal conditions. When changes are detected, it signals adjustments, either increasing or decreasing the cooling effect to maintain balance. Sensor Accuracy: Sensors located throughout the unit are critical for detecting the exact current status. These sensors feed information back to the central control unit, ensuring adjustments are made efficiently and precisely, based on the data they gather. Automatic Adjustments: When temperatures shift beyond the ideal range, the system automatically activates or deactivates cooling elements, ensuring the internal atmosphere remains steady without manual intervention. This automation is what makes the system reliable and efficient in energy usage. Defrosting System and Its OperationThe process of removing accumulated ice is essential for ensuring efficient cooling. Over time, ice buildup can hinder the airflow, causing a decrease in overall performance. A well-designed system prevents this by regularly melting ice before it affects functionality. The mechanism typically involves a set of components that work together to manage the melting process. Sensors detect when a specific temperature is reached, triggering a controlled process that eliminates frost. Heating elements, along with timing devices, ensure this occurs in cycles to maintain optimal performance.
|
