
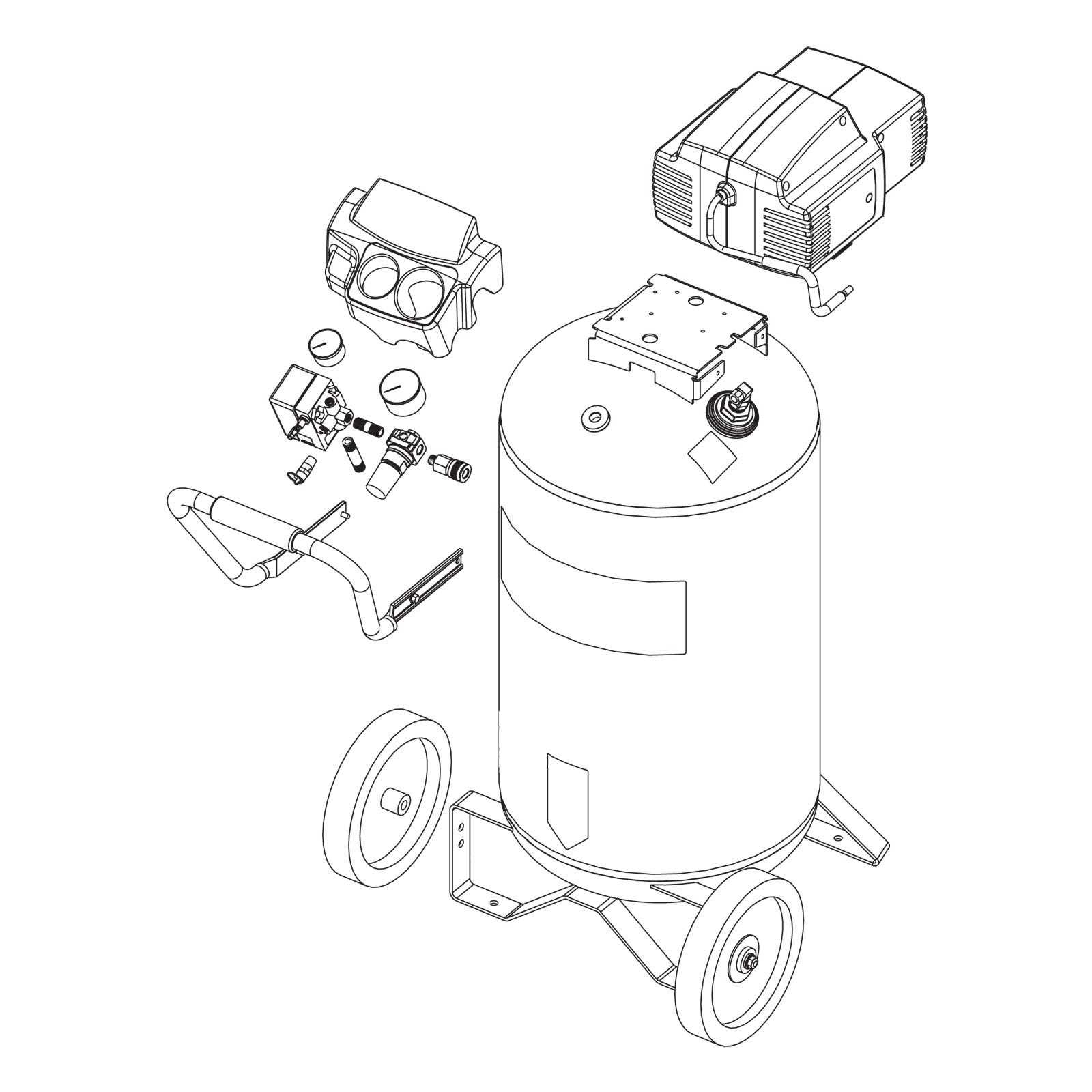
Exploring the functionality of a compact pressure tool involves a detailed look at its various elements. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance, contributing to efficiency and reliability in a range of tasks.
In this section, we will delve into the intricacies of these components, offering insights into their arrangement and significance. By understanding how these parts work together, users can enhance their experience and troubleshoot issues more effectively.
Moreover, having a visual representation of these elements can serve as the ultimate guide for maintenance and repair. Whether you are a seasoned user or a novice, familiarizing yourself with the setup will empower you to make informed decisions.
Understanding Central Pneumatic Air Compressors
This section delves into the intricacies of a popular tool often employed for various tasks in workshops and home projects. These devices are designed to efficiently convert power into stored energy, allowing users to operate a range of accessories and equipment with ease. By comprehending their components and functionality, users can optimize their performance and maintenance practices.
Key Components
- Motor: Powers the unit and initiates the compression cycle.
- Tank: Stores the pressurized fluid for future use.
- Regulator: Controls the output pressure for different applications.
- Pressure Switch: Automates the start and stop of the motor based on tank pressure.
- Manifold: Distributes the compressed fluid to various outlets.
Benefits of Using These Tools
- Versatility: Suitable for tasks like inflating tires, powering tools, and spray painting.
- Efficiency: Provides consistent power for demanding applications.
- Portability: Many models are compact and easy to transport.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces the need for multiple power sources or tools.
By understanding these essential features and advantages, users can make informed decisions when selecting and utilizing these devices for their projects.
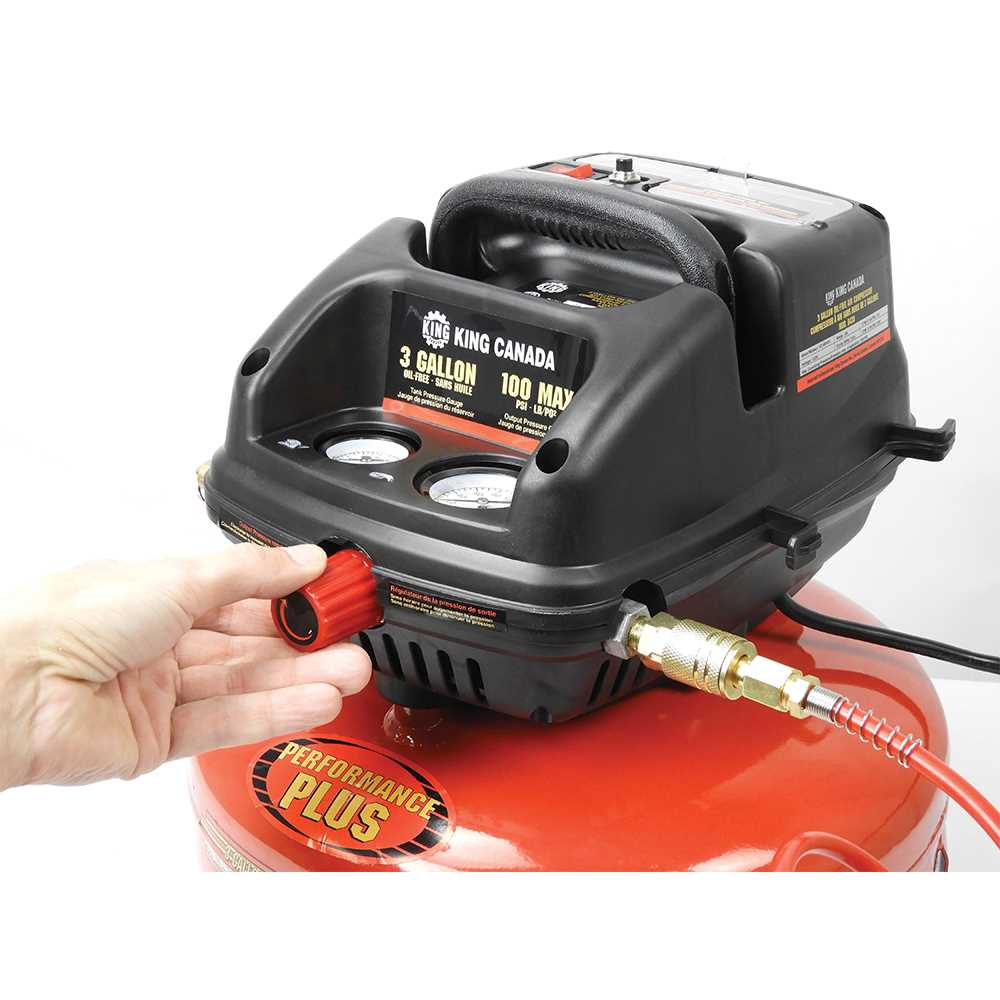
Key Features of 3 Gallon Models
These compact machines are designed to offer versatility and convenience for various tasks. Their lightweight construction and portable design make them ideal for both hobbyists and professionals who require efficient power without occupying much space. Below are some notable attributes that set these models apart in the market.
Portability and Design
The small size of these devices allows for easy transport and storage. Weighing significantly less than larger variants, they can be effortlessly moved around job sites or workshops. Their streamlined design ensures they can fit into tight spaces, making them perfect for projects that demand mobility.
Efficiency and Performance

Despite their compact size, these machines deliver impressive performance. They typically feature powerful motors that enable quick recovery times, allowing users to work continuously without long interruptions. The energy efficiency of these models also contributes to reduced operating costs, making them an economical choice for various applications.
In summary, these compact units offer a blend of portability and efficiency, making them suitable for a wide range of tasks, from home improvement projects to professional use.
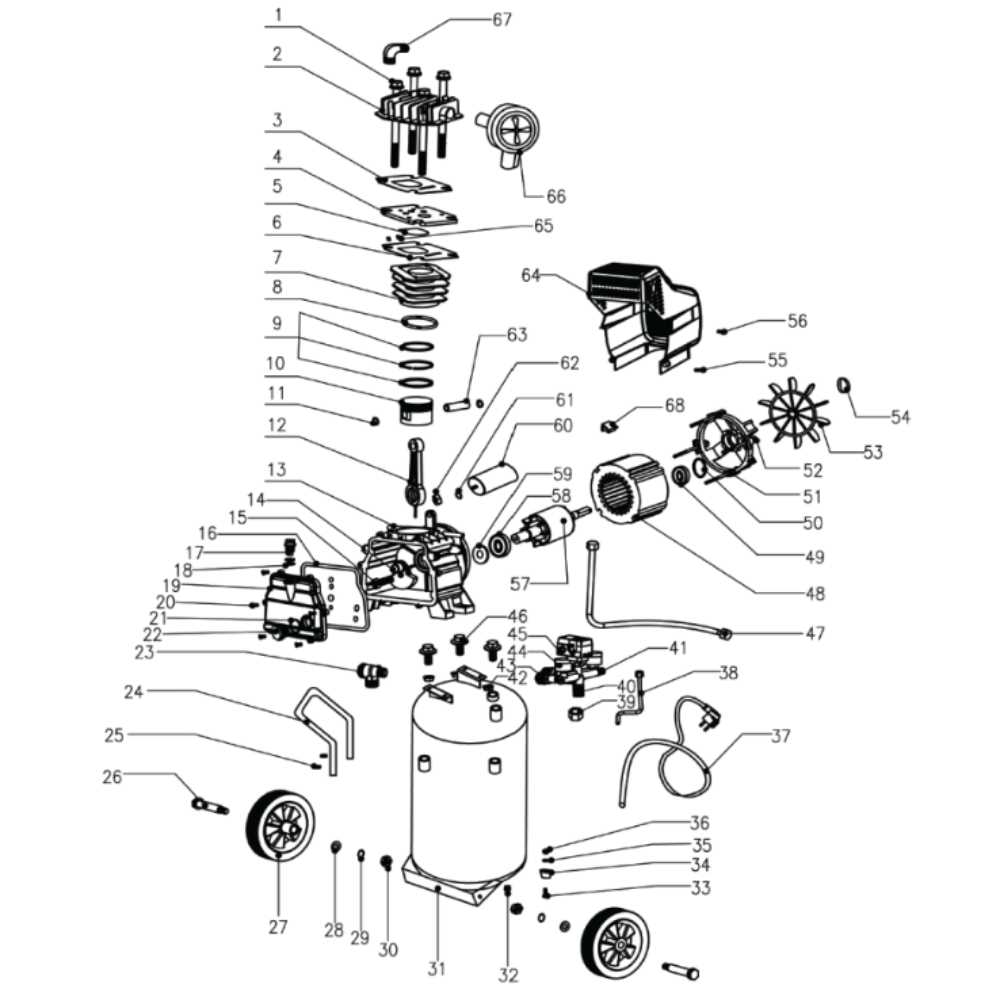
Parts Breakdown for Maintenance
Understanding the components of your equipment is essential for effective upkeep and optimal performance. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring smooth operation and longevity. Regular inspections and maintenance of these components can prevent malfunctions and enhance efficiency.
Below is a detailed overview of key components to focus on during maintenance:
- Motor: Powers the unit and should be regularly checked for any signs of wear or overheating.
- Tank: Holds the compressed substance; inspect for leaks and corrosion.
- Pressure Switch: Regulates the system’s pressure; ensure it is functioning correctly.
- Regulator: Controls the output pressure; verify its settings and responsiveness.
- Hoses: Essential for connection; look for cracks or fraying that may lead to leaks.
- Filter: Maintains cleanliness of the substance; clean or replace as necessary.
- Safety Valve: Prevents overpressure situations; test regularly for reliability.
By routinely examining these components, you can ensure that your equipment operates at peak efficiency and minimize the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
Identifying Common Component Issues
Understanding the typical problems that can arise within your equipment is essential for effective maintenance and performance. By recognizing these issues early, you can ensure longevity and optimal functionality.
Common Problems to Look For
- Noise: Unusual sounds may indicate mechanical wear or misalignment.
- Leaking: Air or fluid leaks can signal seal or connection failures.
- Inconsistent Pressure: Fluctuations may suggest regulator issues or blockages.
Diagnostic Steps
- Inspect connections and fittings for signs of wear.
- Listen for any abnormal noises during operation.
- Check for leaks using soapy water or a dedicated leak detection spray.
- Monitor pressure readings to identify inconsistencies.
Tools Needed for Repairs
When undertaking maintenance or fixes, having the right equipment at your disposal is essential for efficient and effective work. Proper tools not only streamline the process but also ensure safety and enhance the quality of the repair. Whether you’re a seasoned technician or a DIY enthusiast, being prepared with the necessary instruments will make all the difference.
Essential Equipment
To start, a reliable set of wrenches and screwdrivers is crucial for loosening and tightening components. Additionally, a pressure gauge will help monitor levels accurately, ensuring optimal functionality. Having pliers on hand can assist with gripping and maneuvering small parts that may be difficult to handle.
Safety Gear
Don’t overlook the importance of safety gear. Gloves and goggles protect against potential hazards while working on equipment. A sturdy workbench or platform also provides a stable environment for repairs, minimizing the risk of accidents.
How to Replace Worn Parts
Over time, components of your equipment can wear down, affecting its efficiency and functionality. Recognizing the signs of deterioration is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. This guide will help you understand the process of identifying and replacing these aged components effectively.
Identifying Worn Components

The first step in addressing wear is to carefully inspect the unit for signs of damage or fatigue. Look for cracks, leaks, or any irregularities in the structure. Pay attention to areas that experience high stress or frequent movement, as these are often the first to show signs of wear. Regular maintenance checks can help you catch issues before they escalate.
Replacement Process
Once you have identified the faulty components, gather the necessary tools and new replacements. Ensure that the replacements are compatible with your equipment model. Begin by following the manufacturer’s instructions for disassembly, taking care to note the arrangement of each component. After removing the old part, install the new one by reversing the disassembly steps. Finally, test the unit to confirm that it operates smoothly and efficiently.
Safety Precautions During Maintenance
Ensuring safety during the upkeep of machinery is paramount. Proper precautions not only protect the individual performing the maintenance but also enhance the longevity and efficiency of the equipment. Below are key measures to consider before, during, and after maintenance tasks.
Preparation Before Maintenance
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and ear protection.
- Ensure the machine is completely powered down and disconnected from its energy source.
- Familiarize yourself with the user manual and safety guidelines specific to the equipment.
- Inspect the workspace for hazards, such as spills or obstructions, and address them accordingly.
During the Maintenance Process

- Never bypass safety features or guards while working on the machinery.
- Keep tools organized and within reach to prevent unnecessary movement.
- Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling harmful fumes or particles.
- Regularly check for leaks or malfunctions as you perform maintenance tasks.
By adhering to these precautions, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries during maintenance activities.
Upgrading Your Air Compressor Efficiency
Enhancing the performance of your equipment can lead to significant improvements in productivity and cost-effectiveness. By optimizing certain components and practices, you can ensure a smoother operation, reduce energy consumption, and extend the lifespan of your machinery. This section explores various strategies for achieving maximum efficiency.
Key Components to Consider
Identifying and upgrading essential components is crucial for boosting overall functionality. Here are some components that can make a difference:
| Component | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regulator | Improves pressure control, ensuring consistent output. |
| Filter | Enhances air quality, protecting tools and reducing wear. |
| Hoses | Increases airflow, minimizing pressure drops. |
| Lubrication System | Reduces friction, leading to lower energy consumption. |
Best Practices for Maintenance

Regular maintenance can dramatically affect the efficiency of your setup. Implementing best practices such as routine inspections, timely replacements, and proper storage can help maintain optimal performance over time.