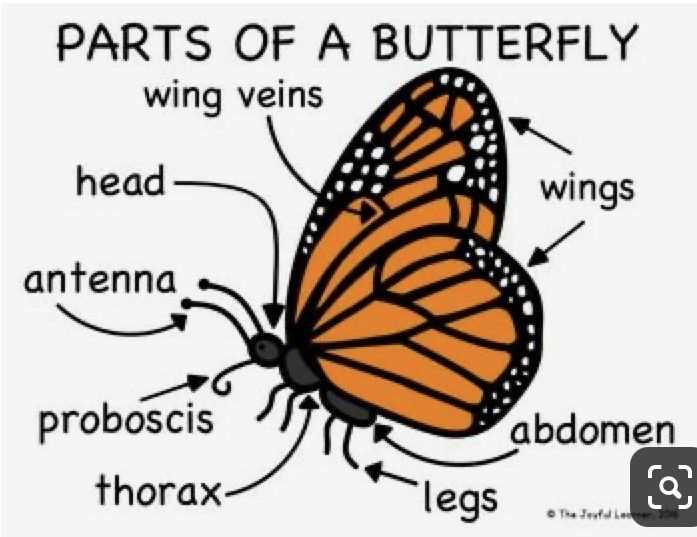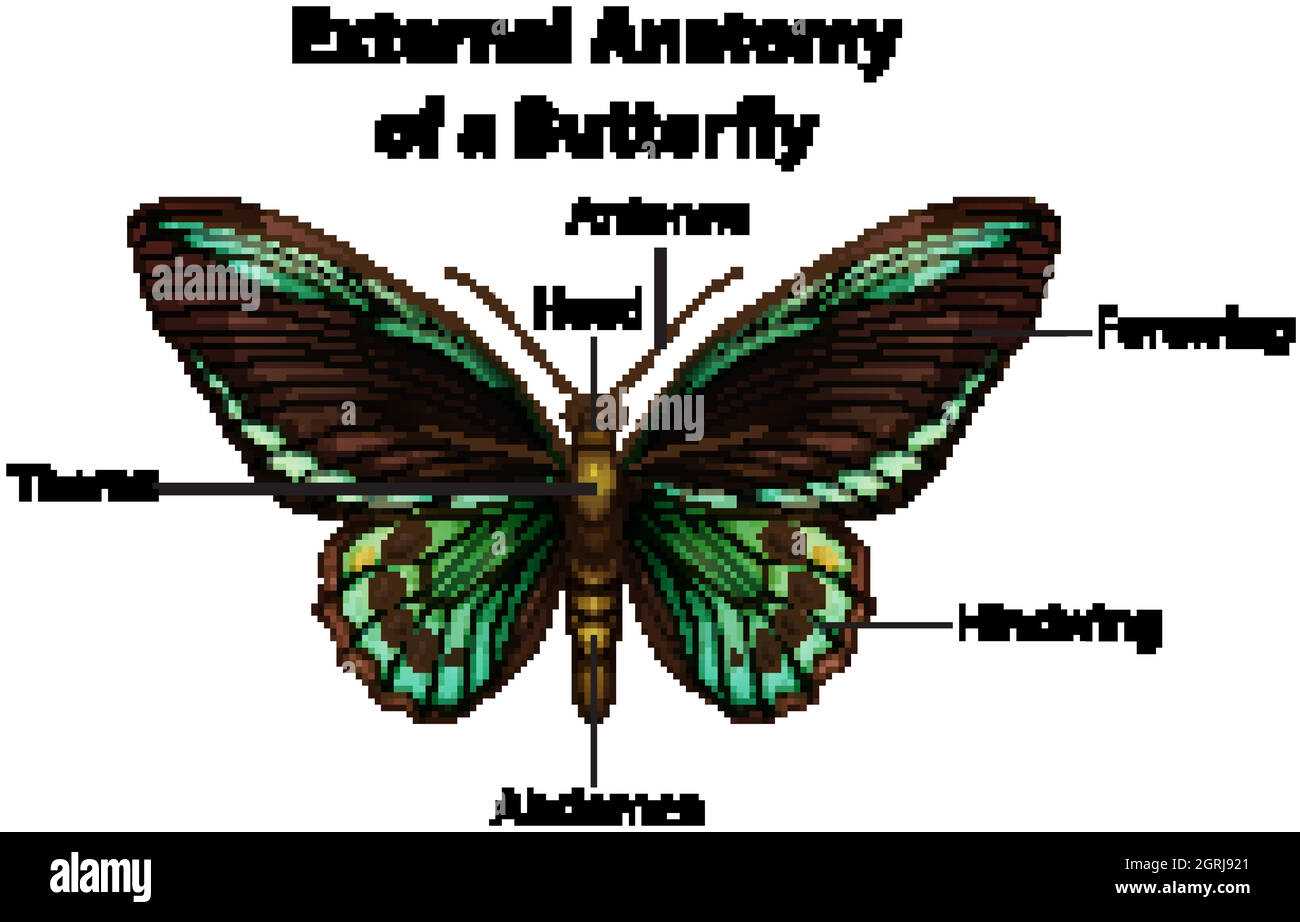
Understanding the structure of flying creatures with colorful wings provides insight into their unique adaptations for survival. Each section of these vibrant beings contributes to their mobility, sensory perception, and interaction with the environment. The complexity of their design is both functional and fascinating, showcasing nature’s ingenuity.
From their delicate, patterned wings to the small, intricate appendages that allow them to explore their surroundings, every aspect of their form has a specific purpose. Examining these structures can reveal much about their behavior, life cycle, and role in the ecosystem.
Appreciating the beauty and functionality of these airborne insects requires a closer look at the various segments that enable flight, nourishment, and reproduction. By exploring their intricate physical features, we gain a deeper understanding of the delicate balance they maintain within nature.
Butterfly Anatomy Overview
Insects of this category exhibit a complex structure that enables their graceful movement and survival in various environments. Their bodies are divided into distinct sections, each serving a specialized purpose, from navigation to nourishment. These creatures are known for their delicate and colorful appearance, supported by a series of intricate systems working in harmony.
Their upper extremities are often characterized by vibrant patterns, which play a role in both attraction and defense. The central part, which connects these sections, is crucial for maintaining balance and movement, while the lower segment houses the tools for sustenance. Together, these features form an efficient and elegant organism, capable of adapting to its surroundings with ease.
Key Features of Butterfly Wings
Wings of these delicate insects are renowned for their intricate patterns and vibrant colors. They play a crucial role not only in movement but also in survival, providing camouflage and signaling to potential mates or predators. The surface of each wing is covered in tiny scales that create the illusion of different hues, contributing to their striking appearance.
One of the most notable characteristics is their lightweight structure, which allows for effortless flight. These wings also have a unique design that helps in thermoregulation, absorbing sunlight to maintain body temperature. Additionally, their flexible and durable nature helps these creatures navigate through various environments with ease.
The symmetrical design is another essential aspect, ensuring balance during flight. These wings are more than just tools for movement; they serve as an integral part of the survival and adaptation mechanisms in a diverse range of habitats.
Functions of Butterfly Antennae
The slender, sensory organs located on the head play a crucial role in navigating the environment. These appendages help detect various signals from the surroundings, which assist in daily activities and survival. Their ability to sense both physical and chemical changes allows them to effectively interact with the world.
Orientation is one of the key functions, as these structures aid in determining direction. They are sensitive to airflow, enabling precise adjustments during flight.
Another important role is in chemical detection. They are equipped with specialized receptors that can pick up on different scents and pheromones, which is vital for locating food sources and potential mates.
Leg Structure and Movement
The intricate design of the limb system is vital for both locomotion and interaction with the surrounding environment. Each component is specifically adapted to support various activities, from walking and gripping to fine-tuned sensory input. The overall organization ensures flexibility, balance, and precision during movement.
Main Sections of the Limb

Each limb consists of multiple segments that are connected by flexible joints. These sections allow for a wide range of motion, making it possible to navigate different surfaces and perform complex tasks. The segments are typically elongated, providing reach and leverage, while the joints offer smooth articulation.
Movement Mechanism
Movement is coordinated through a combination of muscle contractions and joint rotations. Fine control is achieved through specialized muscles that manage delicate
Role of the Proboscis in Feeding
The proboscis plays a crucial function in the nourishment process, allowing the insect to access liquid sustenance from various sources. This elongated structure is highly specialized for extracting fluids, enabling efficient feeding in diverse environments.
Structure and Flexibility

The proboscis consists of a flexible, coiled tube that extends when needed. Its design allows it to reach deep into flowers or other sources, ensuring efficient extraction of nectar or other liquids. The structure’s ability to coil and uncoil adds to its versatility in accessing food in various locations.
How the Proboscis Works
During feeding, the tube unfurls and is inserted into a liquid source. Muscular actions enable the movement of fluids through the proboscis, ensuring a steady intake of nutrients. The specialized tip ensures precise access, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
| Key Features | Description |
|---|---|