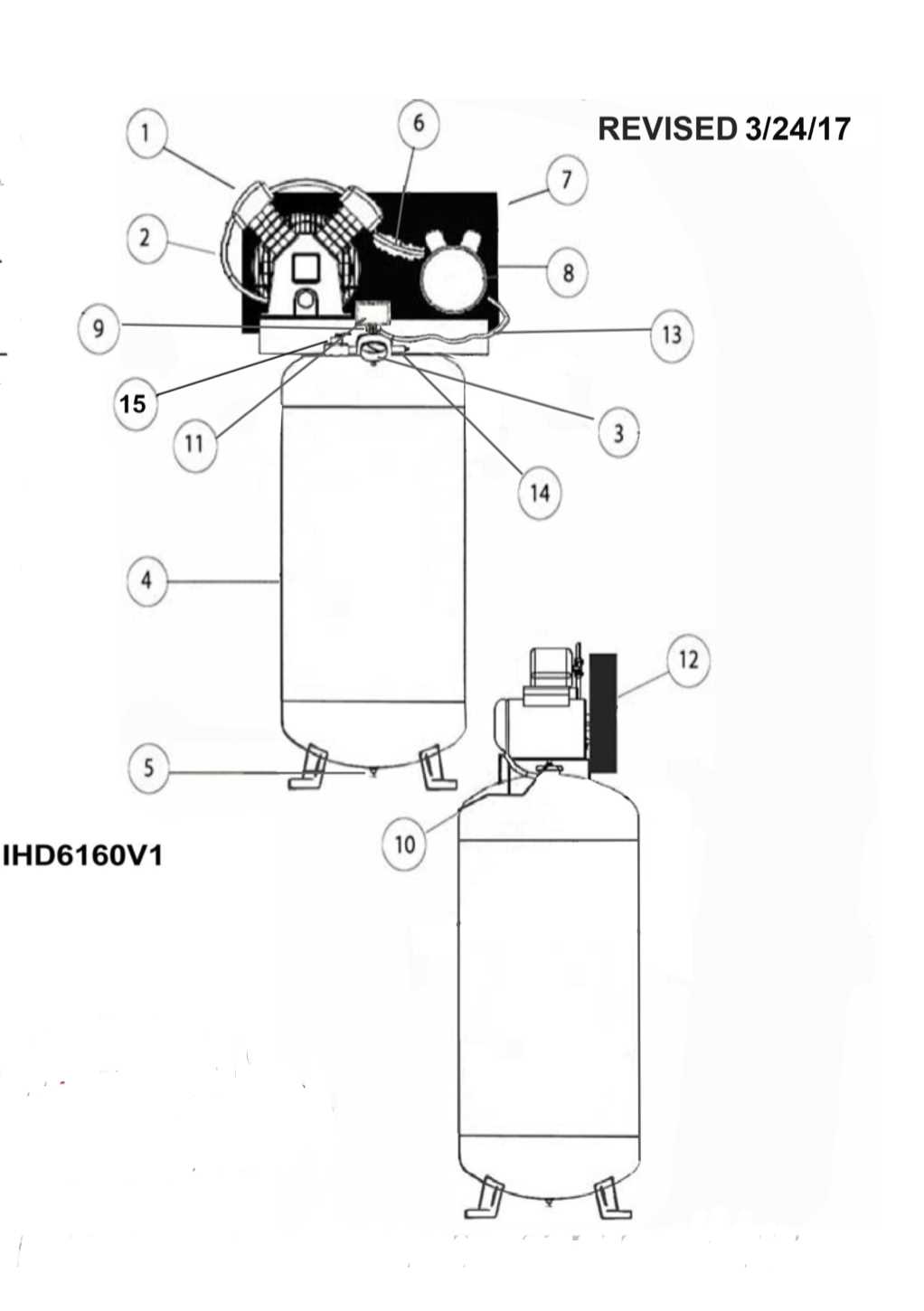
In the world of industrial machinery, the functionality of devices relies heavily on their intricate construction. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring that the entire system operates smoothly and efficiently. By exploring these essential components, one can gain insights into how they interact and contribute to overall performance.
From the basic elements that initiate the process to the sophisticated mechanisms that control it, each piece is crucial. Understanding the layout and connections of these components can illuminate the complexities involved in their operation. This knowledge not only aids in maintenance but also enhances troubleshooting capabilities, making it indispensable for professionals in the field.
Delving deeper into the specifics, one can appreciate the engineering behind each element’s design. Recognizing the unique characteristics and functions of these components provides a clearer picture of how they work together to achieve optimal pressure levels. This understanding is fundamental for anyone looking to optimize the efficiency of their equipment.
Understanding Air Compressor Components
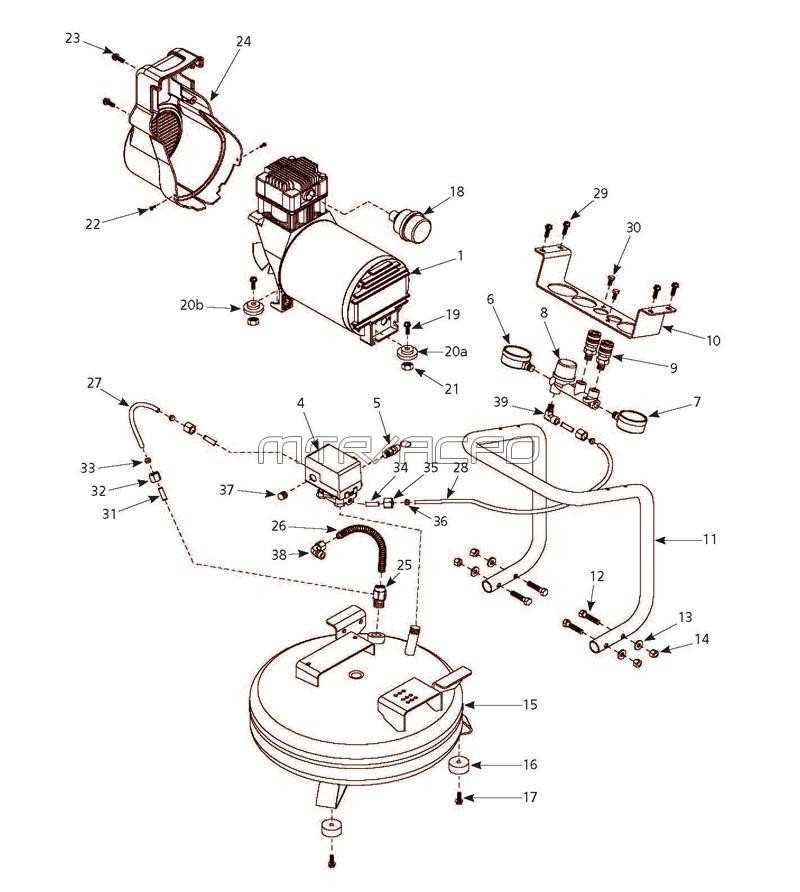
Grasping the elements of a pressurization system is crucial for both optimal performance and longevity. Each component plays a vital role, contributing to the overall efficiency and functionality. Recognizing how these elements interact can enhance maintenance efforts and improve operational reliability.
Main Functional Elements

The primary functional elements include mechanisms responsible for increasing pressure, as well as those that regulate and distribute the generated output. Understanding these roles ensures users can troubleshoot effectively and perform necessary upkeep. For instance, the mechanism that enhances pressure must operate seamlessly with the control units to maintain the desired output level.
Supporting elements, such as filters and coolers, are equally important as they ensure the integrity of the system. Filters remove impurities, while coolers maintain optimal operating temperatures, preventing overheating. Neglecting these components can lead to decreased performance and increased wear. Regular inspection and maintenance of these supportive features are essential for sustaining efficiency and preventing costly repairs.
Key Functions of Compressor Parts
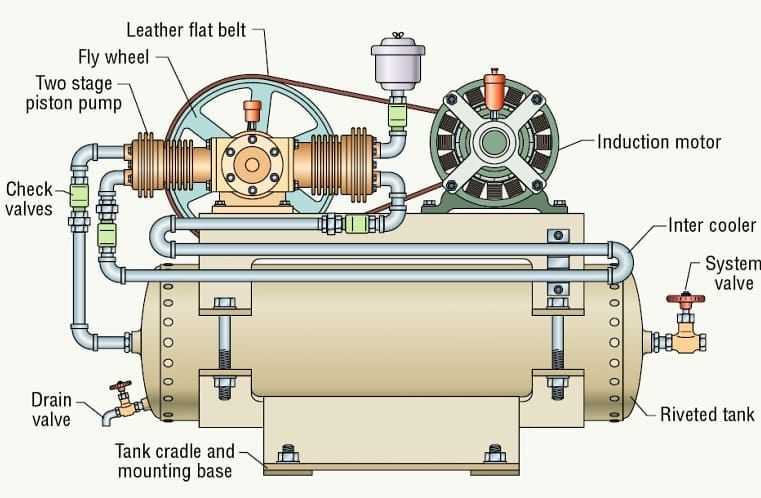
Understanding the essential roles played by various components in a pressurization system is crucial for its efficient operation. Each element contributes to the overall functionality, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the device.
Core Components and Their Roles
- Intake Valve: Responsible for controlling the entry of ambient air, ensuring that the system receives the necessary volume for compression.
- Motor: Acts as the driving force, providing the energy needed to initiate and maintain the compression cycle.
- Piston: Plays a pivotal role in compressing the incoming air, converting mechanical energy into potential energy.
- Exhaust Valve: Facilitates the release of compressed air, allowing it to flow into the storage tank or system.
- Cooling System: Maintains optimal temperature levels, preventing overheating during operation.
Supporting Elements for Efficiency
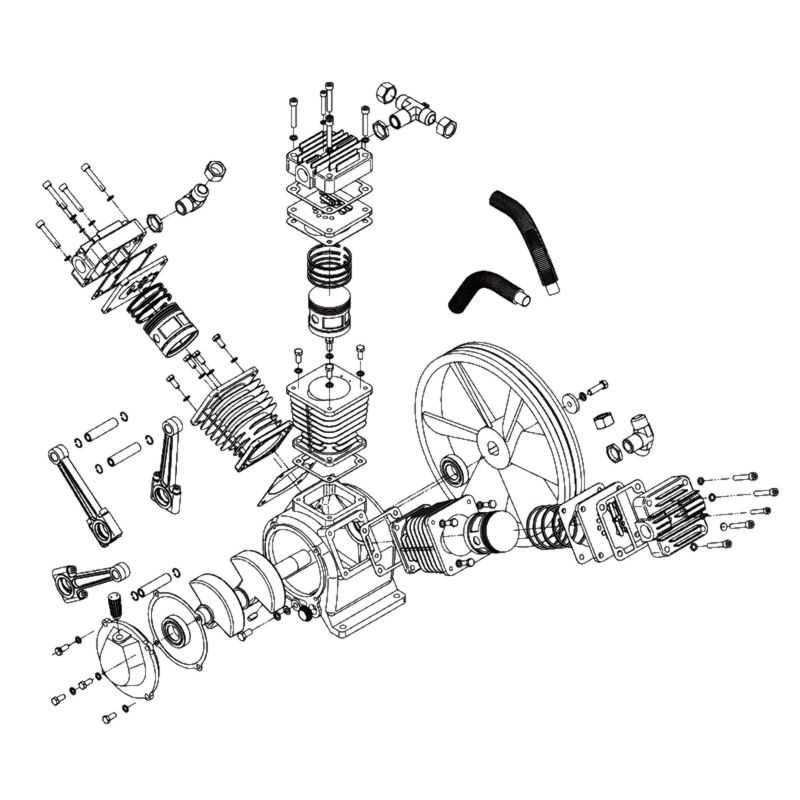
- Filters: Remove impurities from the intake air, protecting internal components from damage.
- Pressure Switch: Monitors and regulates pressure levels, ensuring safe and effective operation.
- Reservoir: Stores compressed air, providing a steady supply for various applications.
By understanding these functions, users can better appreciate how each element contributes to the overall effectiveness and reliability of the system, enabling informed decisions regarding maintenance and upgrades.
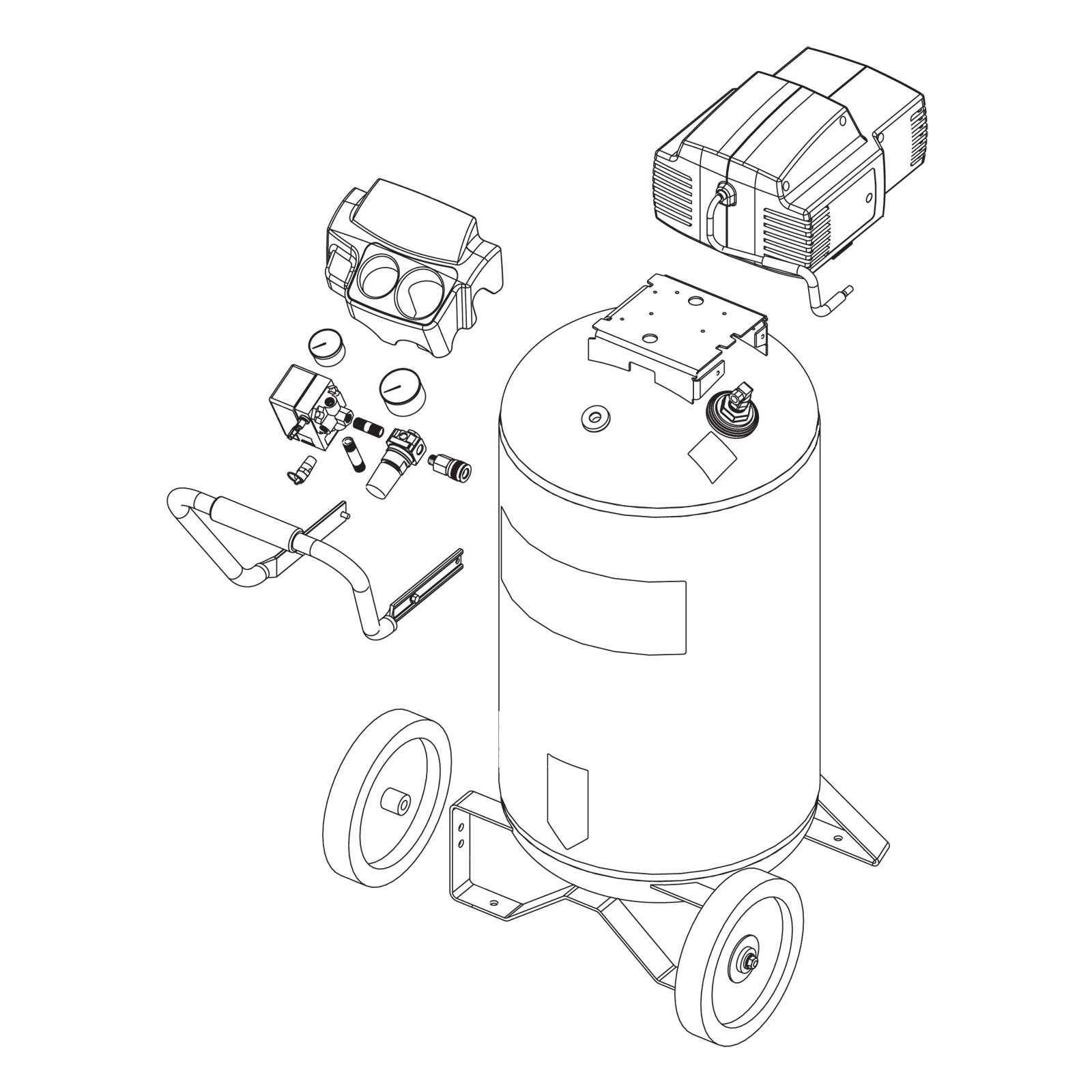
Common Types of Air Compressors
In various industries and applications, different methods are utilized to convert power into potential energy. This section will explore the prevalent variations that cater to specific needs and preferences, highlighting their unique characteristics and functionalities.
Reciprocating Units
This category is characterized by its piston-driven mechanism, which compresses gas through a back-and-forth motion. These units are widely favored for their efficiency and ability to generate high pressure, making them suitable for tasks requiring significant force. They come in both single and multi-stage configurations, allowing for flexibility depending on the operational demands.
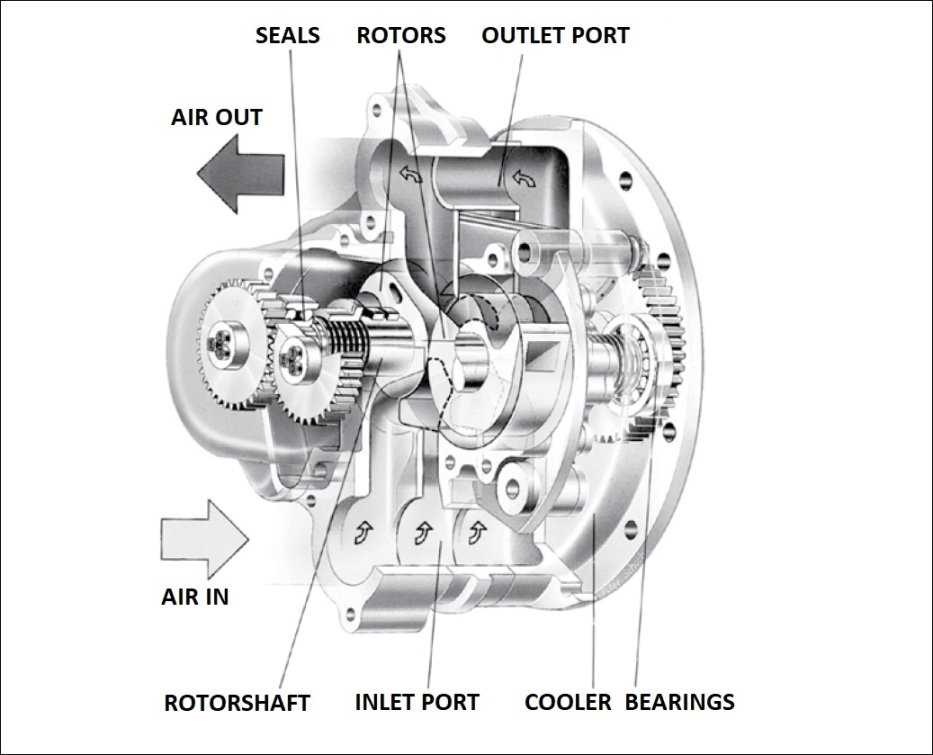
Rotary Screw Mechanisms
These devices employ two interlocking helical rotors to compress gas continuously. Their design provides a steady flow and is particularly advantageous for large-scale applications that require consistent performance. The durability and reduced maintenance needs make them an ideal choice for industrial settings.
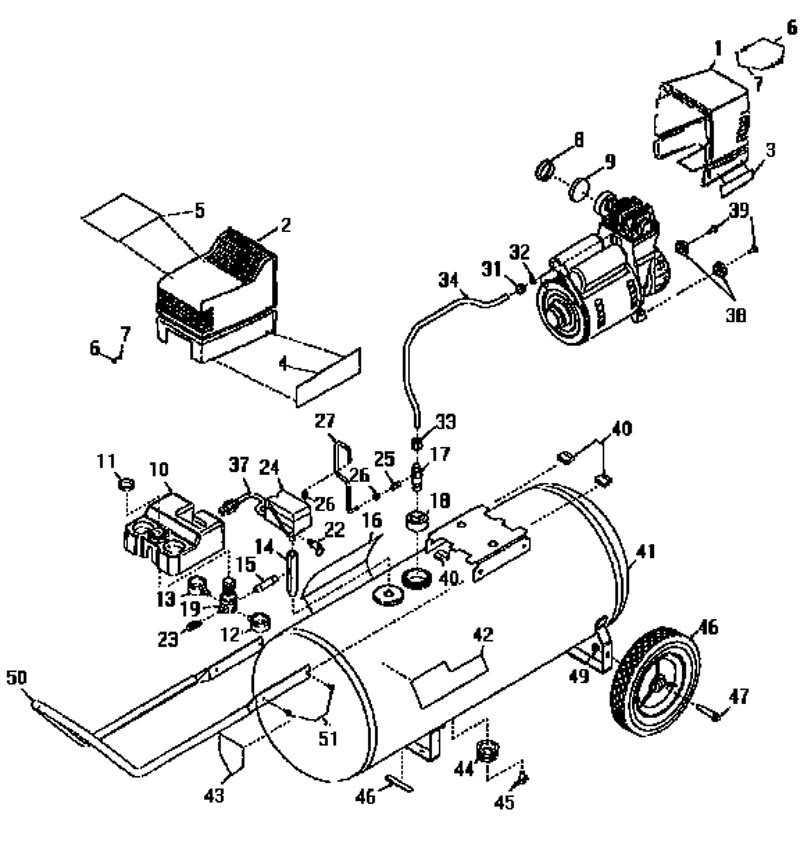
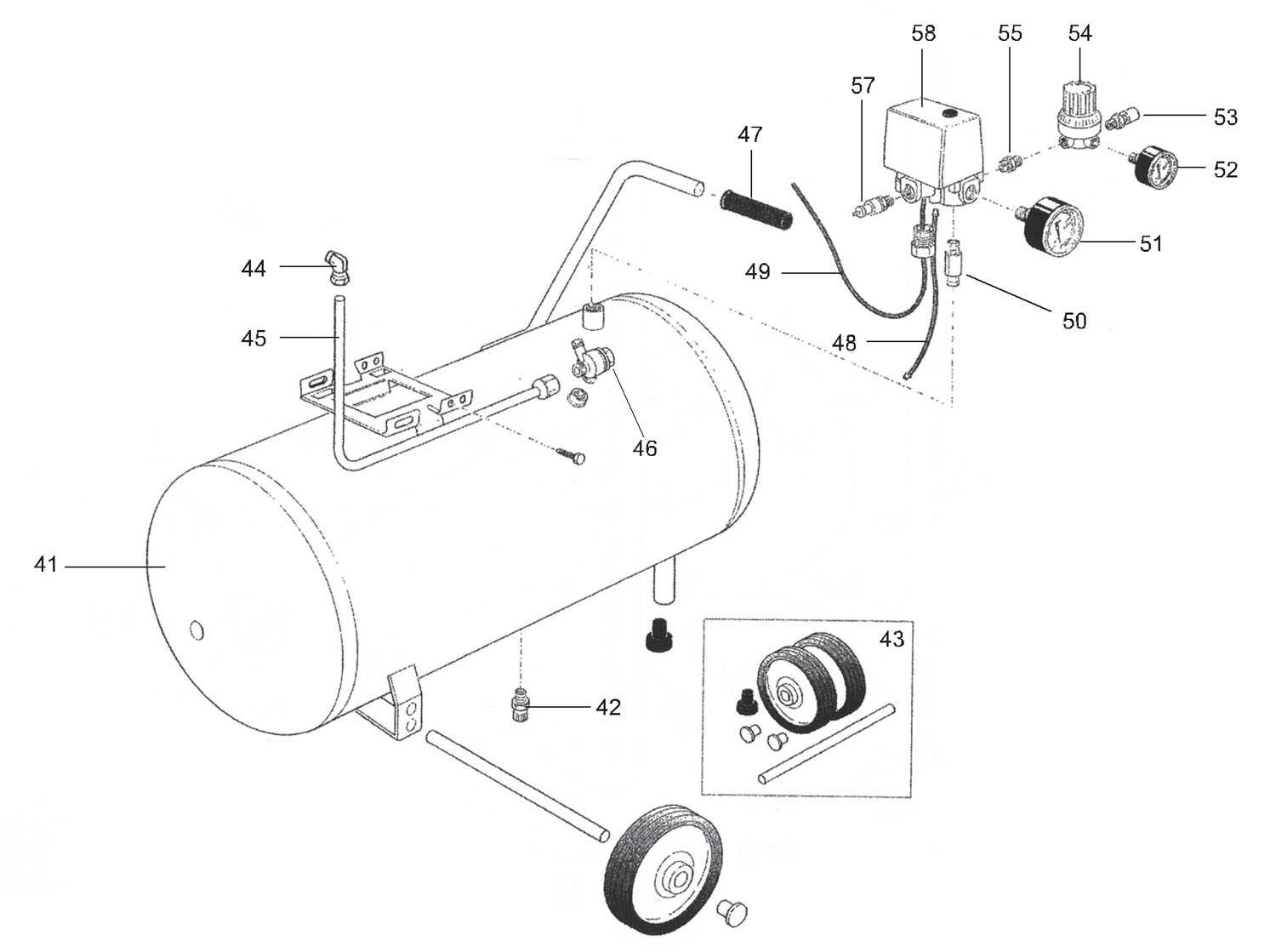
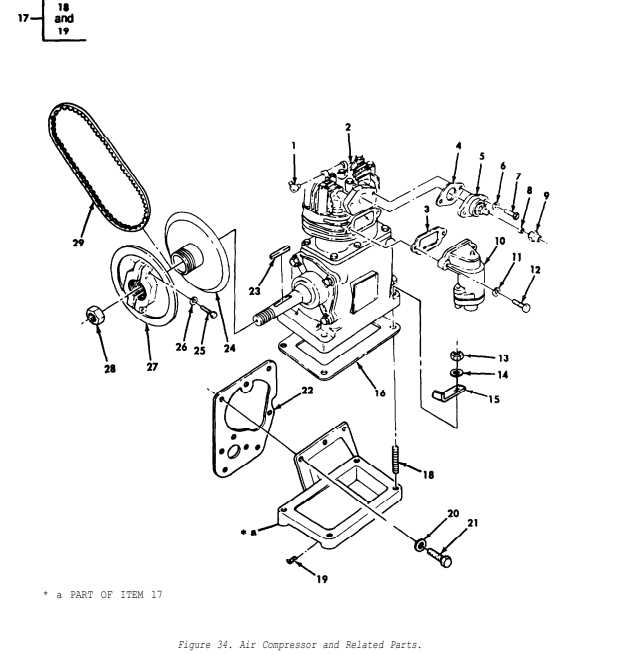
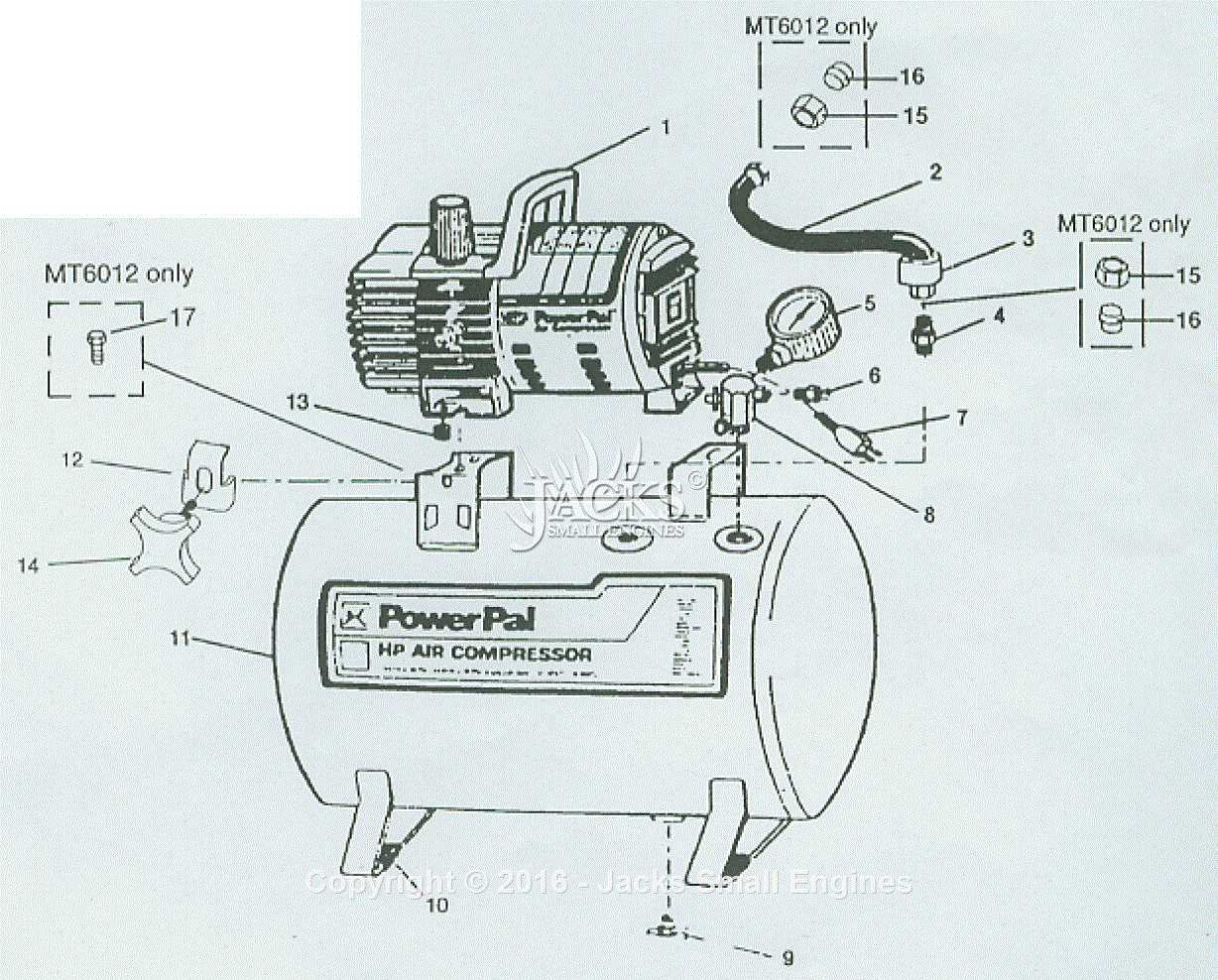
How to Read a Parts Diagram
Understanding the visual representation of mechanical components is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. These illustrations provide a detailed overview of various elements and their interconnections, allowing users to identify each component’s function and placement. Familiarity with these visuals can greatly enhance your ability to service and repair machinery.
Identifying Components
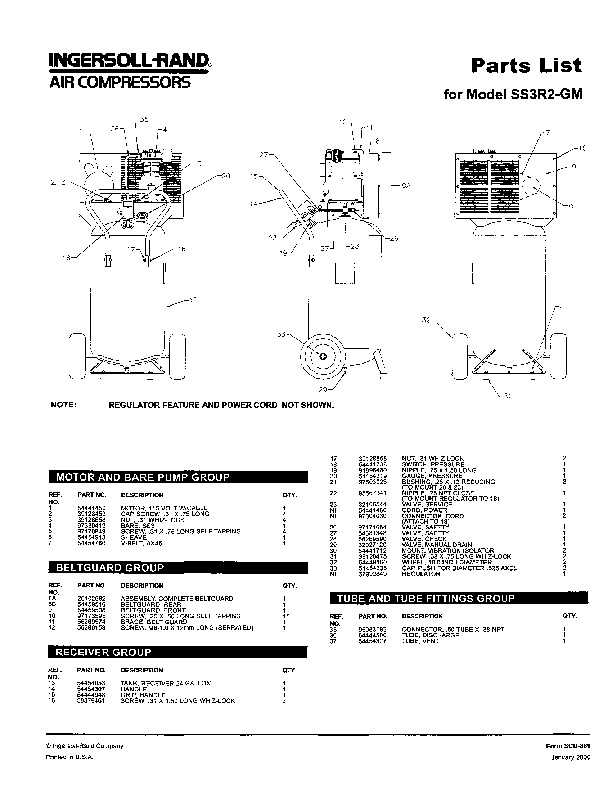
Each symbol or number on the visual guide corresponds to a specific element. It is essential to familiarize yourself with the legend or key that often accompanies these representations. This will help you match each label to its physical counterpart, ensuring accurate identification of all elements involved.
Understanding Relationships
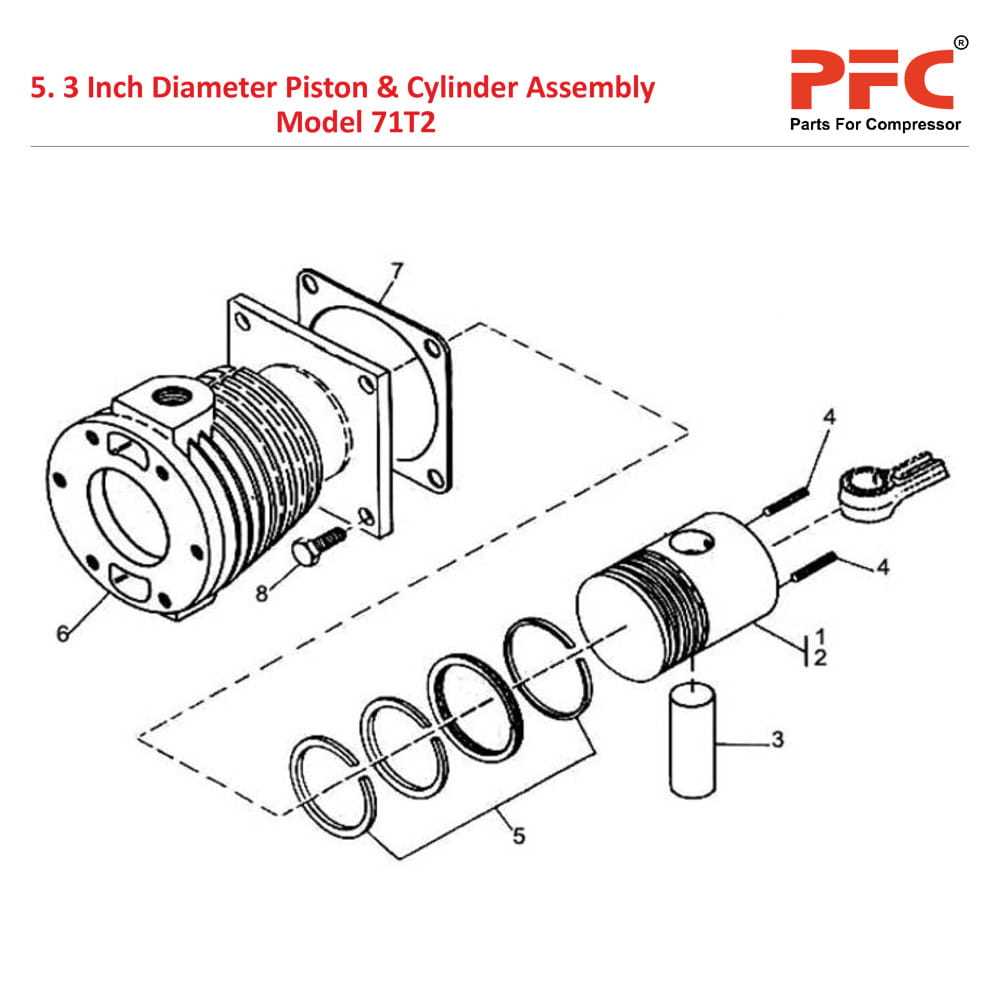
Beyond mere identification, it’s important to grasp how different components interact. Pay attention to lines and arrows that indicate connections, flow, or movement. This knowledge will assist in diagnosing issues and planning repairs effectively, as you’ll better understand how each element contributes to the overall functionality.
Maintenance Tips for Compressor Parts

Regular upkeep of mechanical systems is crucial for their longevity and optimal performance. Proper attention to components can prevent costly repairs and ensure smooth operation. Below are essential strategies for maintaining various elements of your machinery.
- Routine Inspections: Conduct frequent checks to identify wear and tear early. Look for signs of damage, leaks, or corrosion.
- Cleaning: Keep components free of dust and debris. Use appropriate cleaners to avoid damaging surfaces.
- Lubrication: Apply lubricant to moving parts as recommended by the manufacturer. This helps reduce friction and prolongs lifespan.
- Replace Worn Elements: Schedule replacements for items that show significant signs of wear. Waiting too long can lead to failure.
- Monitor Performance: Keep an eye on operational efficiency. Any decline may indicate an underlying issue that needs addressing.
By following these tips, you can enhance the reliability of your equipment and avoid unexpected downtimes.
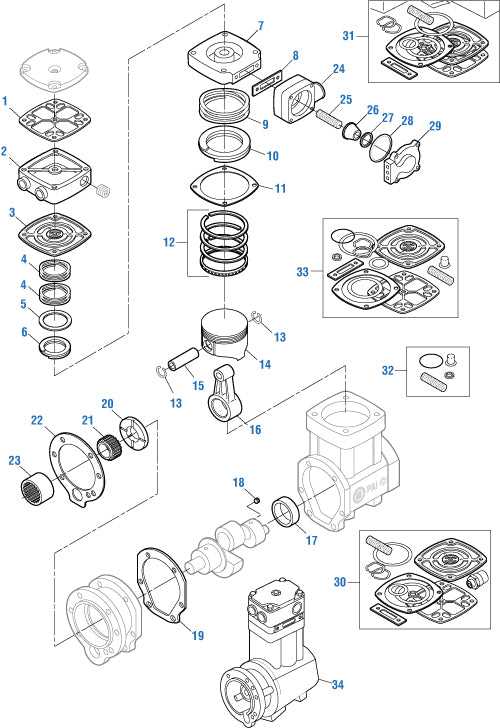
Identifying Wear and Tear Signs
Recognizing the indicators of deterioration is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of any machinery. Over time, components may exhibit signs of fatigue due to constant use and environmental factors. Early identification of these signs can prevent more severe damage and costly repairs.
Key indicators to observe include unusual noises, vibrations, and changes in performance. Regular inspections will help ensure that any issues are detected promptly, allowing for timely interventions.
| Sign | Description | Possible Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Unusual Noises | Sounds that deviate from normal operation | Worn bearings or loose fittings |
| Excessive Vibration | Increased movement or shaking during operation | Imbalance or misalignment of components |
| Reduced Efficiency | Decline in output or performance | Clogged filters or failing elements |
| Visible Damage | Cracks, wear marks, or corrosion on surfaces | Environmental exposure or material fatigue |
Regular monitoring and maintenance can help mitigate the effects of wear, ensuring that your machinery remains reliable and effective over its operational lifespan.
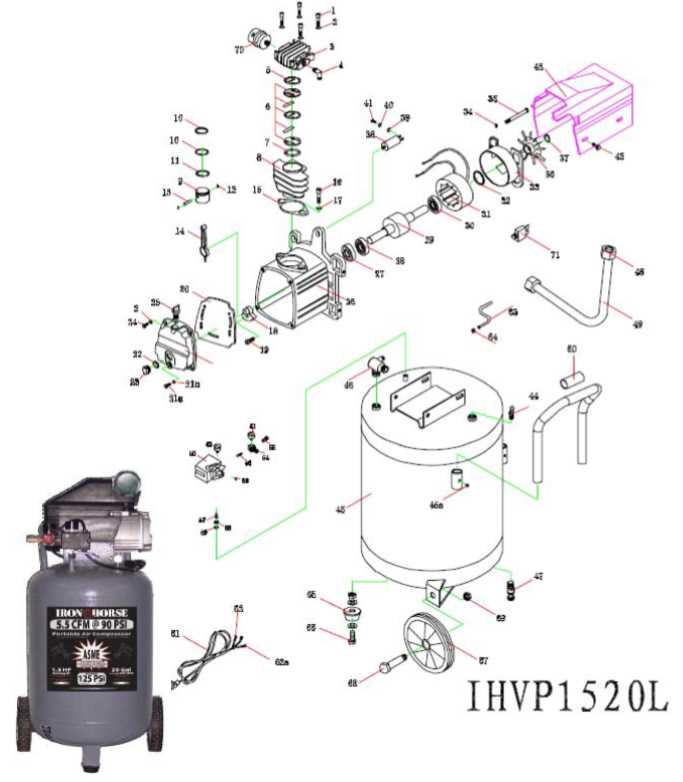
Replacement Parts: When and Why

Understanding the necessity for replacement components is crucial for maintaining efficiency and longevity in machinery. Regular wear and tear can lead to diminished performance, increased energy consumption, and potential breakdowns. Recognizing when to replace specific elements can save time and costs in the long run.
Signs You Need Replacement
- Decreased efficiency: If the system is not performing as expected.
- Unusual noises: Strange sounds can indicate issues with specific components.
- Leaks: Visible leaks are often signs that seals or other items need attention.
- Increased energy costs: A spike in utility bills may signal that parts are struggling to function properly.
Importance of Timely Replacement
Addressing the need for new components promptly can prevent more extensive damage and costly repairs. The benefits include:
- Enhanced performance: New elements can restore optimal operation.
- Reduced downtime: Quick replacements minimize interruptions in use.
- Improved safety: Functional equipment reduces risks associated with failure.
- Cost efficiency: Investing in new components is often more economical than extensive repairs.
Safety Precautions During Repairs
When undertaking maintenance tasks, it is crucial to prioritize safety to prevent accidents and injuries. Implementing proper protocols ensures that individuals remain protected while addressing mechanical issues. Adhering to guidelines not only fosters a secure work environment but also enhances the efficiency of the repair process.
Personal Protective Equipment
Utilizing appropriate protective gear, such as gloves, goggles, and masks, is essential. These items shield against potential hazards, including sharp edges and harmful substances. Always inspect your equipment before starting any repair to ensure it is in good condition.
Work Area Organization
Maintaining a clean and organized workspace minimizes risks. Clear any clutter and ensure that tools are readily accessible. Proper lighting is also vital, as it enhances visibility and reduces the chance of accidents during repairs.