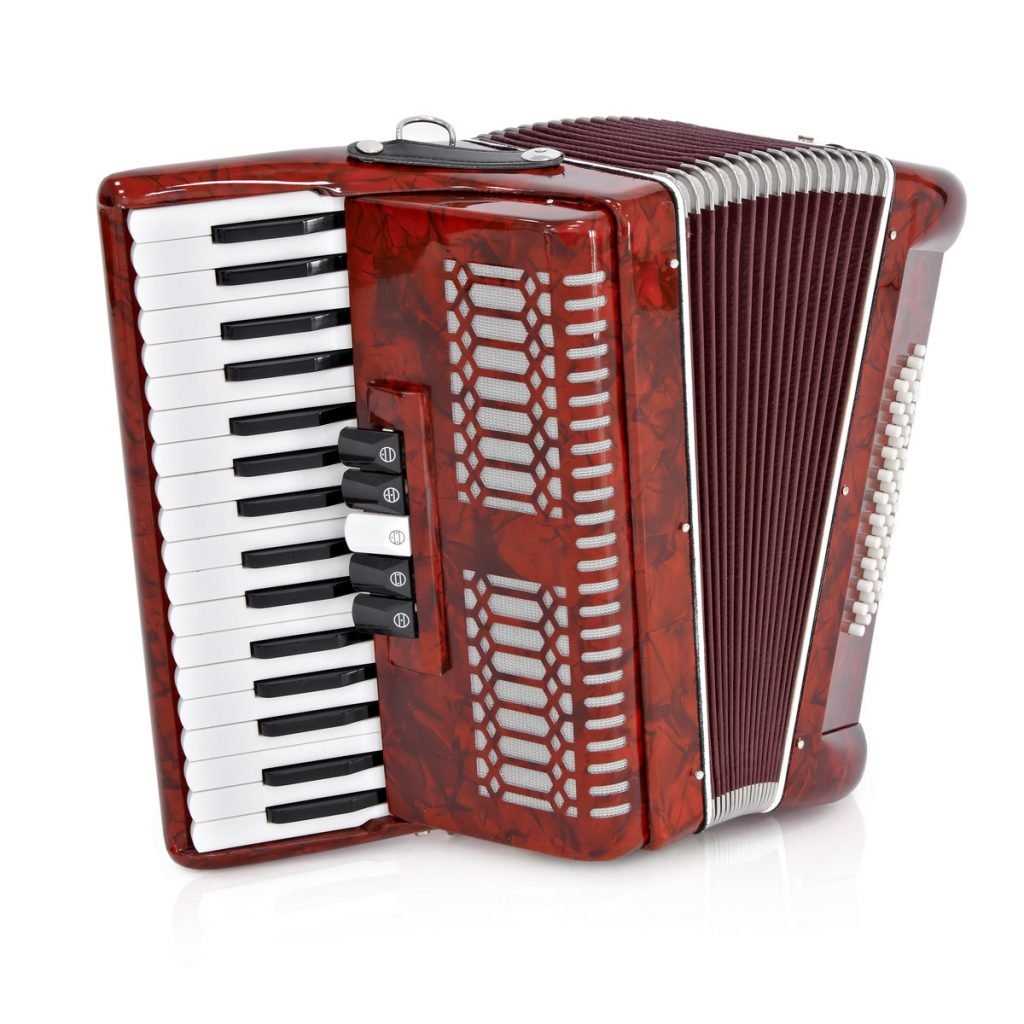

Delving into the mechanics of a beloved musical instrument reveals a fascinating world of sound production and engineering. This exploration uncovers how various components interact to create harmonious melodies, offering both musicians and enthusiasts a deeper appreciation for craftsmanship.
The intricate assembly is designed to facilitate airflow and resonance, crucial elements that define its unique tonal qualities. By examining these elements closely, one can gain insights into the artistry behind the instrument’s creation and the skill required to master its use.
In this discussion, we will break down the essential components that contribute to the instrument’s functionality. Understanding their roles not only enhances performance but also enriches the overall experience of playing and listening.
Understanding Accordion Mechanism
The intricate system that powers this unique instrument is designed to produce sound through the interaction of various components. It relies on a combination of air pressure and a series of moving elements that respond to the player’s actions. These elements work in harmony to create both melody and harmony, offering versatility in performance. A clear grasp of how these elements function together can greatly enhance both the player’s experience and understanding of this musical device.
Air Movement and Sound Production
At the core of the system is the flow of air, which is controlled by the user through the expansion and compression of the bellows. As air passes over reeds, vibrations occur, generating sound. The manipulation of the bellows regulates the airflow, while the keys or buttons determine which notes are played. This mechanism allows for dynamic control over pitch and volume, making the instrument highly responsive to the player’s technique.
Interaction of Mechanisms
The keys, buttons, and reed blocks are all linked by a series of levers, springs, and other connecting elements. Each movement of the buttons triggers a lever that opens or closes a valve, allowing air to flow through the corresponding reed. This complex interaction enables a wide range of musical expressions, as the player adjusts both the tempo and the intensity of the sound produced.
Basic Components of an Accordion
Every musical instrument has its own distinct structure, with each element contributing to the overall functionality and sound. In the case of this particular wind-driven instrument, several key elements work together to produce the unique tones and melodies that characterize it. Understanding the main components is essential for mastering its use, as each part plays a crucial role in the instrument’s operation.
The central unit of this instrument consists of a set of bellows, which function by expanding and contracting, forcing air through various reed chambers. These chambers house the reeds, thin metal strips that vibrate when air passes through them, creating sound. The player controls the airflow and pitch by manipulating both the bellows and a set of keys or buttons that open and close specific reed channels, allowing for a wide range of notes to be played.
Additionally, a framework or casing holds all of these components together, providing both structural integrity and ease of handling. The keyboard or button board offers the interface through which the musician interacts with the instrument, allowing for the creation of melody and harmony. Each of these elements combines to form a cohesive whole, allowing for the expression of a broad spectrum of musical genres.
How to Identify Accordion Parts
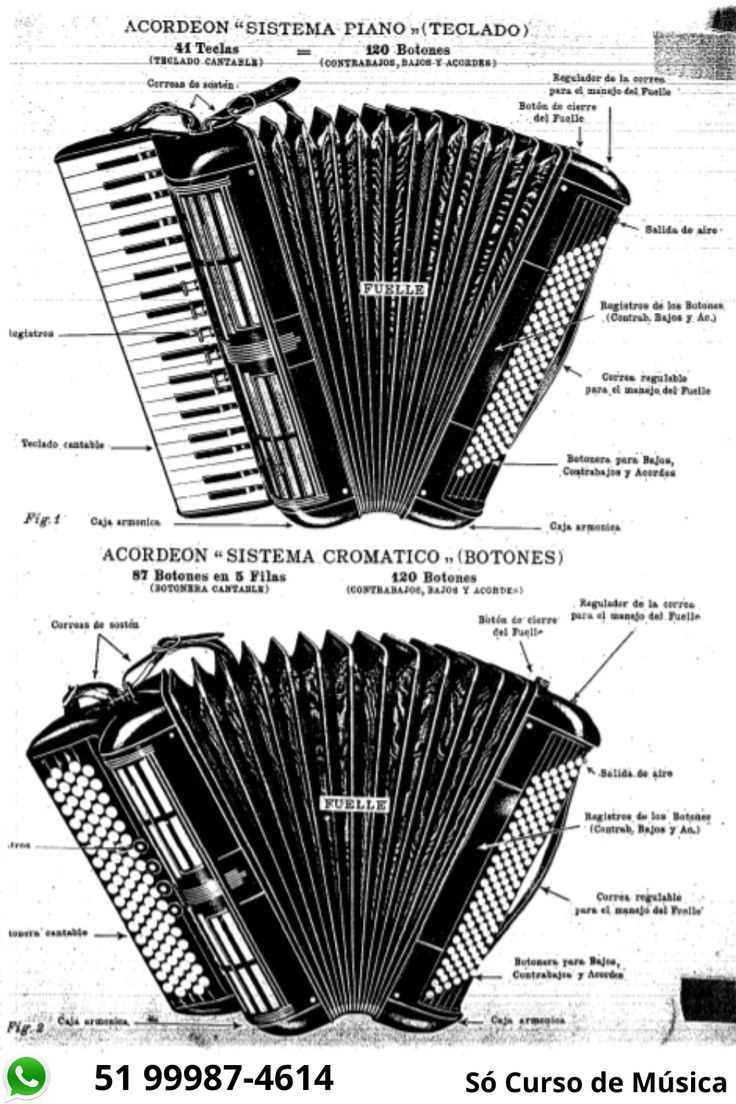
Recognizing the various components of a musical instrument involves understanding its structure and function. Each element plays a crucial role in producing sound, and knowing where to find them can help in tuning, repair, or even learning to play. This section will guide you through the essential parts of the instrument and how to identify them with ease.
To identify the individual components, it’s important to first look at the instrument as a whole. Focus on both the external features and internal mechanisms. Understanding their interactions will give you a clearer picture of how the sound is generated and controlled. Below is a simple guide to help you get familiar with the major sections and their key characteristics.
| Component | Location/Description |
|---|---|
| Bellows | The expandable section, often made from fabric, that contracts and expands to create airflow. |
| Keyboard | Located on the front side, this is the area where you press the keys to produce different pitches. |
| Reeds | Small, thin strips inside that vibrate when air passes through them to create sound. |
| Buttons | For instruments with a button layout, these are located on the side, used for producing notes. |
| Case | The outer shell that houses the instrument, typically made from wood or other materials to protect the internal components. |
| Straps | Used for holding the instrument in place while playing, these are worn around the shoulders or waist. |
By familiarizing yourself with these key sections, you will gain a better understanding of how each contributes to the overall function of the instrument. This knowledge will also prove valuable when troubleshooting or performing maintenance tasks.
The Role of the Reed Blocks
Reed blocks serve a crucial function in the sound production mechanism of musical instruments that utilize this unique system. They act as the housing for the reeds, facilitating the vibration process that generates distinct tones. Understanding their structure and operation is essential for anyone interested in the intricacies of sound creation.
Structure and Function
The configuration of reed blocks influences both the quality and character of the produced sound. Each component is designed to optimize resonance and airflow, contributing to the overall musicality of the instrument.
Impact on Sound Quality
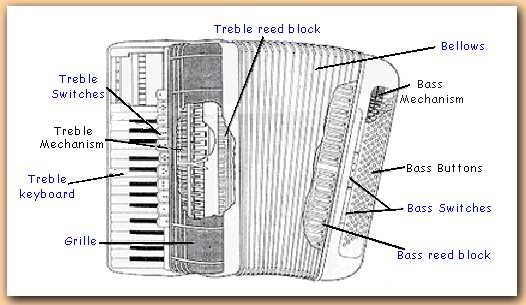
The material and design choices in reed blocks can significantly affect timbre and pitch. Musicians often explore various setups to achieve their desired sound, highlighting the importance of these elements in performance.
| Factor | Influence on Sound |
|---|---|
| Material | Affects resonance and warmth |
| Shape | Modulates airflow and tone |
| Size | Determines pitch range |
Accordion Bellows: Function and Design
The flexible components of this musical instrument play a crucial role in its operation, enabling sound production through controlled airflow. Their unique structure not only supports functionality but also contributes to the aesthetic appeal of the instrument, blending craftsmanship with musicality.
Functionality
These components expand and contract, allowing air to flow through reeds, generating sound. The design must balance durability and flexibility, ensuring that they withstand repeated use while maintaining responsiveness.
Design Considerations
Various materials and construction techniques are employed to enhance both performance and visual elegance. The choice of fabric, reinforcement methods, and overall shape can significantly influence the instrument’s character.
| Material | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Leather | Durable and traditional |
| Plastic | Lightweight and weather-resistant |
| Fabric | Varied textures and colors |
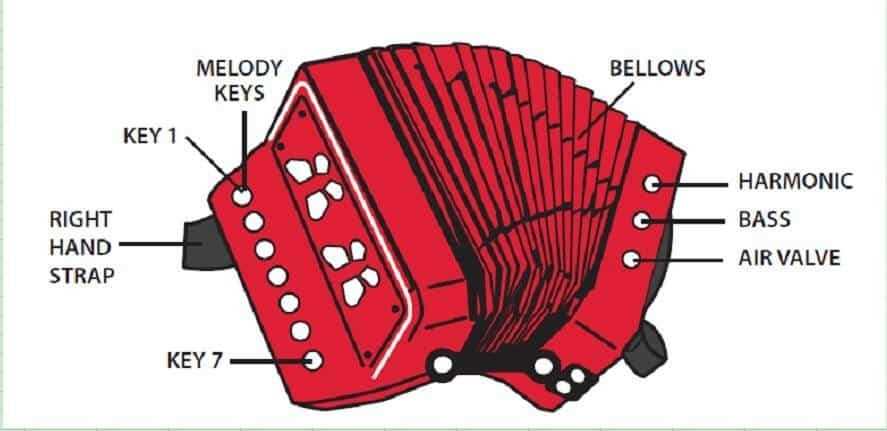
Types of Accordion Keys and Buttons
The diverse components used to create musical sounds in these instruments can significantly influence their playability and sound quality. Understanding the various types available allows musicians to select the right combination for their desired style and expression.
Melody Keys
Melody keys are primarily responsible for producing the main tune. They are typically arranged in a linear fashion and offer a range of pitches that enable players to perform melodies with ease.
Bass Buttons
Bass buttons provide the harmonic foundation and rhythmic support. Positioned differently than melody keys, these buttons allow for chord progressions and bass lines, enhancing the overall musical texture.
Accordion Tuning and Adjustments
Proper tuning and adjustment of musical instruments with bellows are essential for achieving the desired sound quality and performance. This process involves fine-tuning the pitch of each reed and ensuring that the mechanism functions smoothly. Whether you’re restoring an old instrument or maintaining a current one, a proper setup will significantly affect tonal consistency and playability.
Adjustment can be broken down into several key areas, including reed alignment, pressure regulation, and tuning to the desired scale. The fine-tuning of reeds is particularly important, as even minor shifts can alter the instrument’s pitch or cause it to become out of tune. Reeds are carefully adjusted to ensure they vibrate at the correct frequency, creating a harmonious sound when air flows through them. Various factors, such as humidity, temperature, and usage, can affect the tuning, so periodic check-ups are recommended.
Below is a table outlining the key areas of focus during the tuning and adjustment process:
| Adjustment Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Reed Tuning | Fine-tuning of reeds to ensure the correct pitch and tonal quality. |
| Reed Alignment | Ensuring that reeds are properly aligned with the channels to avoid distortion in sound. |
| Bellows Pressure | Adjusting the air pressure to ensure smooth and consistent airflow while playing. |
| Key Sensitivity | Regulating the response of the keys to ensure optimal sound production with minimal effort. |
| Tonality Adjustments | Refining the tonal balance to ensure that the instrument’s sound is clear and vibrant. |
Regular maintenance and expert adjustments not only improve sound but also extend the life of the instrument. By taking care of these aspects, musicians can ensure a smoother, more enjoyable playing experience while maintaining a high standard of sound quality.
Importance of the Accordion Air Valve
The mechanism responsible for airflow regulation plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and performance of a musical instrument. Its effective operation ensures optimal sound production and contributes to the instrument’s dynamic range.
Key reasons for its significance include:
- Sound Quality: Proper airflow leads to a richer, more resonant tone.
- Control: It allows musicians to manipulate volume and expression with precision.
- Durability: A well-functioning valve prevents excess wear on the instrument, enhancing longevity.
- Response: Quick and reliable airflow is essential for maintaining tempo and rhythm during performance.
In summary, the mechanism’s role in sound enhancement, player control, and instrument durability makes it an ultimate component for achieving musical excellence.