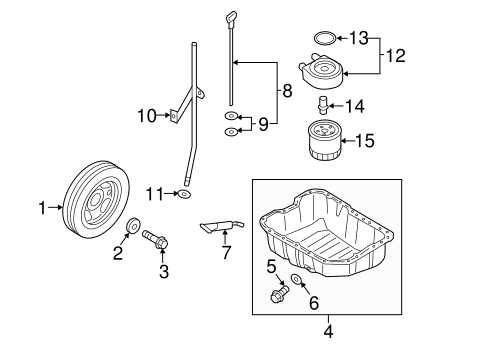
Understanding the structure and arrangement of various elements within a vehicle can be crucial for both routine maintenance and more complex repairs. Each section of the vehicle is meticulously designed, with every element serving a specific purpose. By exploring the overall configuration of essential systems, one can gain insights into how they interact to ensure the smooth operation of the entire machine.
From mechanical to electrical systems, a detailed overview of the internal structure is indispensable for anyone looking to work on their vehicle. Knowing where each element is located and how they connect to one another simplifies troubleshooting and allows for more efficient servicing. This guide will provide a clear understanding of how different systems are organized, offering a practical approach to vehicle upkeep.
Overview of Key Components
In any modern vehicle, various mechanical and electronic systems work together to ensure proper functioning and a smooth driving experience. Understanding the essential elements that contribute to these systems can help with maintenance, troubleshooting, and repairs. Below is an outline of some crucial areas that play a vital role in the vehicle’s overall operation.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Engine Assembly | The core of the vehicle’s propulsion system, responsible for converting fuel into motion, with numerous moving parts working in unison. |
| Transmission System | Manages the power flow from the engine to the wheels, enabling smooth acceleration and control. |
| Suspension | Ensures stability and comfort by absorbing road irregularities and supporting the vehicle’s weight. |
| Braking System | Provides stopping power, ensuring safety through a complex network of hydraulic and electronic components. |
| Electrical Network | Supplies power to vital systems, from lighting and infotainment to sensors and controls, ensuring seamless operation. |
Engine Bay Layout for 2013 Kia Optima
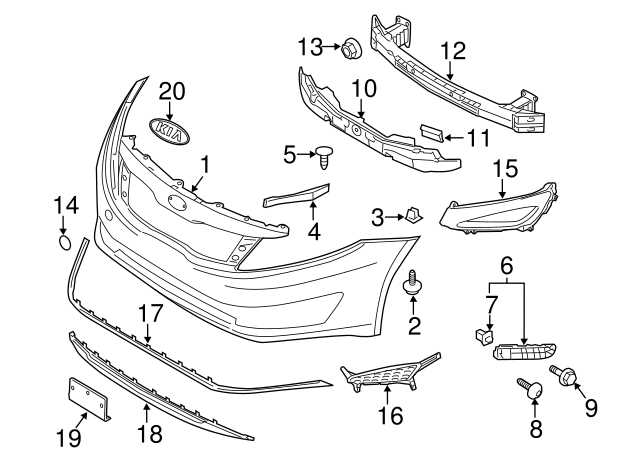
The layout under the hood is designed with practicality and efficiency in mind, ensuring that all components are well-organized and easily accessible for maintenance and inspections. Understanding this layout helps identify key elements of the system, providing insight into how various parts work together to ensure smooth operation.
Main Components Overview
- Power Generation: The section responsible for supplying energy to all systems is centrally located, making it a focal point in the arrangement.
- Cooling System: Positioned near the front, this area houses elements responsible for regulating temperature, ensuring that the mechanical components don’t overheat.
- Fluid Reservoirs: Various containers for essential fluids are distributed in easily accessible locations, allowing for quick refills and checks.
Additional Functional Areas
- The air intake system, which ensures optimal airflow into the mechanism, is placed strategically for maximum efficiency.
- Safety and control systems are located in distinct spots to enhance operational reliability and ease of access.
Suspension System Components Breakdown
The system responsible for ensuring smooth movement and stability on the road consists of several interconnected elements. Each component plays a vital role in absorbing road imperfections, providing control during turns, and maintaining overall ride quality. Understanding how these elements work together can offer insights into vehicle handling and comfort.
- Shock Absorbers: These dampen the impact from bumps, reducing vibrations and ensuring a smoother driving experience.
- Springs: Responsible for supporting the vehicle’s weight and absorbing the initial shock from uneven surfaces.
- Control Arms: These links connect the wheel assemblies to the frame, allowing for controlled vertical movement of the wheels.
- Stabilizer Bar: This bar reduces body roll during sharp turns, enhancing vehicle stability and safety.
- Ball Joints: These spherical bearings act as pivot points, allowing for smooth steering and suspension articulation.
- Wheel Bearings: These components enable the wheels to rotate with minimal friction while supporting the vehicle’s load.
Together, these elements ensure balanced handling, reduce road feedback, and enhance overall safety. Regular maintenance of these parts is crucial for optimal performance.
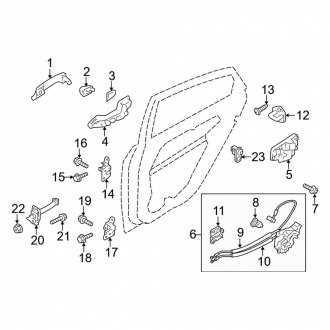
Interior Layout: Seats, Dash, and Console
The inner arrangement of the vehicle’s cabin is carefully designed to enhance comfort and accessibility for both the driver and passengers. The seating arrangement, control interface, and central unit are strategically positioned to ensure an intuitive and ergonomic experience.
Seats and Comfort
The seating layout provides a balance of style and support, with each seat shaped to offer comfort during both short trips and long drives. Adjustable options allow customization of the seating position to suit individual preferences.
- Driver’s seat with height and recline adjustments
- Passenger seats offering spacious legroom
- Rear seating designed with foldable options for extended cargo space
Dash and Console Design
The control center and dashboard present a streamlined interface, ensuring that essential functions are easily within reach. The layout is intuitive, with displays and controls logically organized to reduce driver distraction.
- Central touchscreen for multimedia and navigation controls
- Easy-to-reach climate controls and vehicle settings
- Multiple storage compartments integrated into the
Brake System and Its Main Elements
The braking mechanism in any vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring safety, providing the ability to slow down or stop efficiently under various conditions. This section outlines the core components that work together to achieve optimal control during driving. Understanding how these parts interact is essential for maintaining functionality and avoiding potential issues on the road.
Key Components of the System
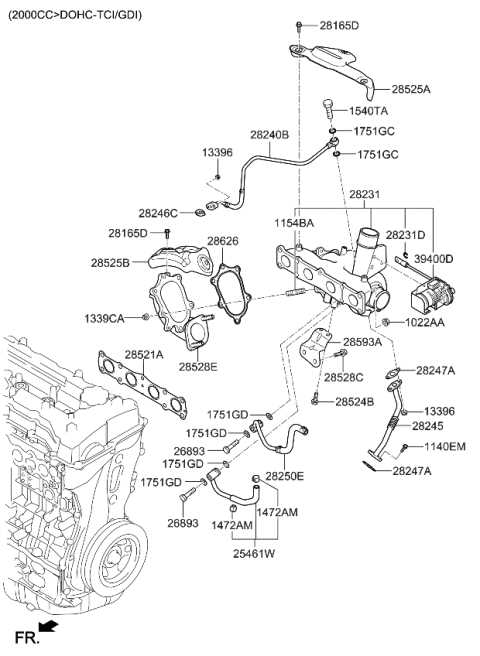
At the heart of the mechanism are several vital elements, including the hydraulic circuit, which transfers force from the pedal to the brakes, and the disc and drum structures, designed to create the necessary friction for stopping. These elements, along with various supporting devices, contribute to smooth deceleration and stability during vehicle operation.
Role of Friction Materials
The effectiveness of this system largely depends on high-quality friction materials used in specific parts, which directly contact rotating surfaces. These materials must withstand extreme temperatures and wear to ensure reliable performance over time.
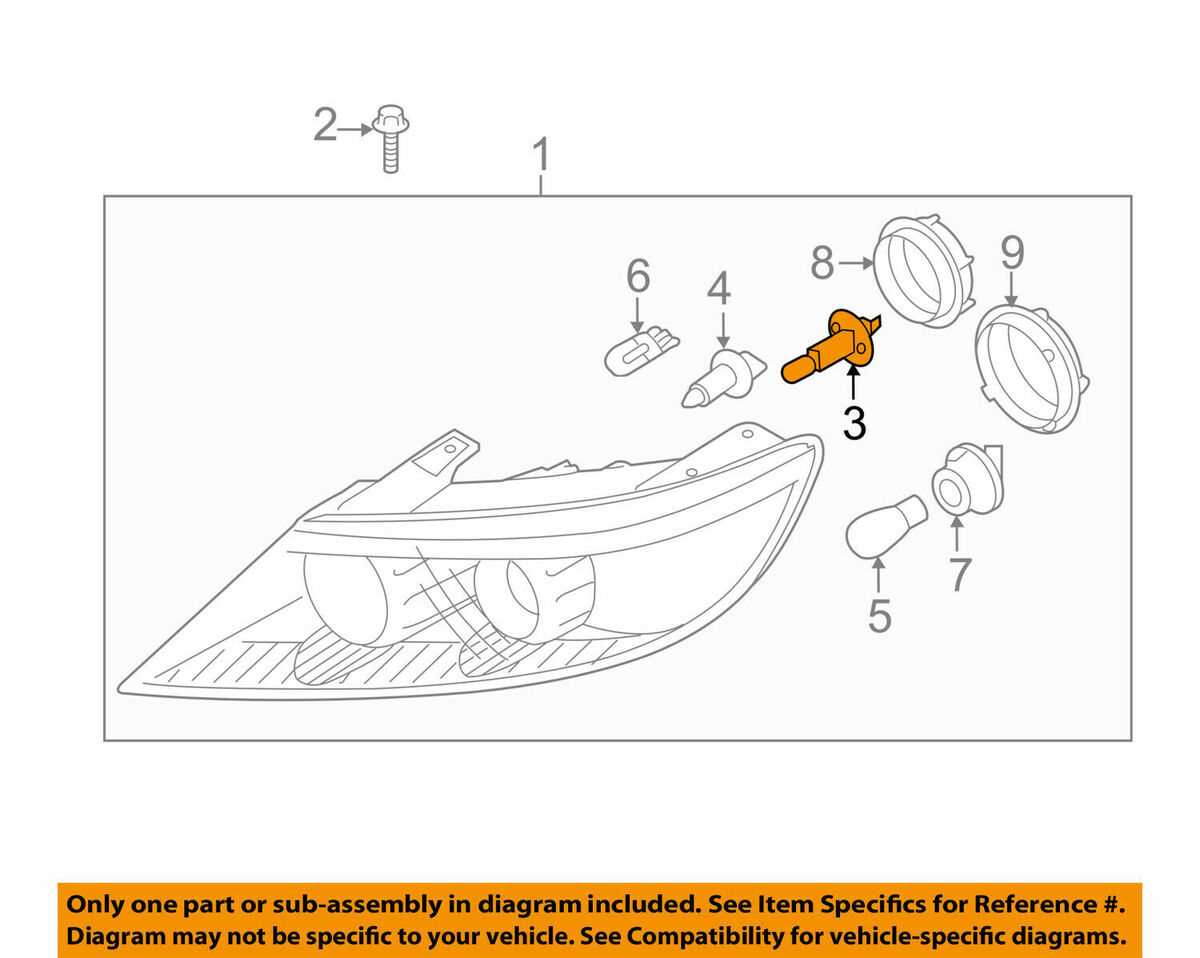
Electrical System Overview and Wiring Pathways
The electrical network in a modern vehicle serves as the backbone of numerous functions, providing the necessary energy and communication for various components. This section delves into the intricacies of the electrical layout and the pathways through which energy flows, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Key Components of the Electrical Network
- Battery: Supplies power for starting the engine and operating electrical devices.
- Alternator: Recharges the battery and powers the electrical systems when the engine is running.
- Fuses: Protect circuits from overload by breaking the connection when excess current flows.
- Wiring Harness: A collection of wires and connectors that relay power and signals between various components.
- Relays: Electrically operated switches that control high-current circuits with low-current signals.
Wiring Pathways and Their Functions
- Power Distribution: The main wiring pathways connect the battery and alternator to the critical electrical systems.
- Signal Transmission: Wires carry information between sensors, control modules, and actuators to ensure proper operation.
- Grounding: Proper grounding pathways are essential for safety and functionality, providing a return path for electrical currents.
- Connector Points: Various junctions in the wiring harness facilitate easy maintenance and replacement of components.
Exhaust System Parts and Their Placement
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in the overall performance and efficiency of a vehicle. Its components work together to channel harmful gases away from the engine, reduce noise, and minimize emissions. Understanding the arrangement and functionality of these components is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components of the Exhaust Assembly
The exhaust assembly consists of several critical elements, each serving a specific purpose. The manifold collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders and directs them into the system. Following the manifold is the catalytic converter, which transforms harmful pollutants into less toxic emissions. The muffler is responsible for reducing engine noise, while the exhaust pipes transport gases to the rear of the vehicle, ensuring safe dispersion into the atmosphere.
Placement and Configuration
Proper positioning of each component is vital for optimal system performance. The manifold is typically mounted directly to the engine, ensuring a seamless connection. The catalytic converter is located downstream, often within close proximity to the manifold, to allow for effective treatment of gases. The muffler is usually found toward the rear, ensuring that sound is minimized before the gases exit the tailpipe. Each section of the exhaust system is designed to facilitate smooth flow and efficient operation.
Cooling System Structure and Diagrams
The cooling system plays a vital role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures within the engine, ensuring efficiency and longevity. Understanding its configuration and components is essential for diagnosing issues and performing effective maintenance.
Typically, this system comprises various parts, including the radiator, water pump, thermostat, and cooling fans. Each element works in harmony to circulate coolant, regulate temperature, and dissipate heat generated during engine operation. A schematic representation can greatly aid in visualizing the layout and flow of the coolant throughout the system.
Key Components:
- Radiator: Facilitates heat exchange between the coolant and the air.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant through the engine and radiator.
- Thermostat: Regulates coolant flow based on temperature.
- Cooling Fans: Assist in reducing temperature by increasing airflow over the radiator.
Familiarity with these components and their interactions can enhance repair strategies and preventative care, contributing to a reliable performance of the vehicle’s engine.
Transmission Layout and Related Parts
The configuration of the transmission system plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of a vehicle’s drivetrain. Understanding this arrangement and its components is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section delves into the intricacies of the transmission setup, exploring its various elements and their interconnections.
Key Components of the Transmission System
At the heart of the transmission assembly lies the gearbox, which is responsible for regulating the power flow from the engine to the wheels. Key components include the torque converter, which facilitates smooth acceleration, and the valve body, which directs hydraulic fluid to engage the appropriate gears. Additionally, the input and output shafts serve as crucial conduits for transferring torque between different parts of the system.
Understanding Transmission Fluid and Maintenance
Transmission fluid is vital for lubrication and heat dissipation within the system. Regular checks and changes of this fluid can prevent wear and ensure optimal performance. Neglecting this aspect can lead to significant damage over time, emphasizing the importance of routine inspections and timely maintenance to prolong the lifespan of the transmission.