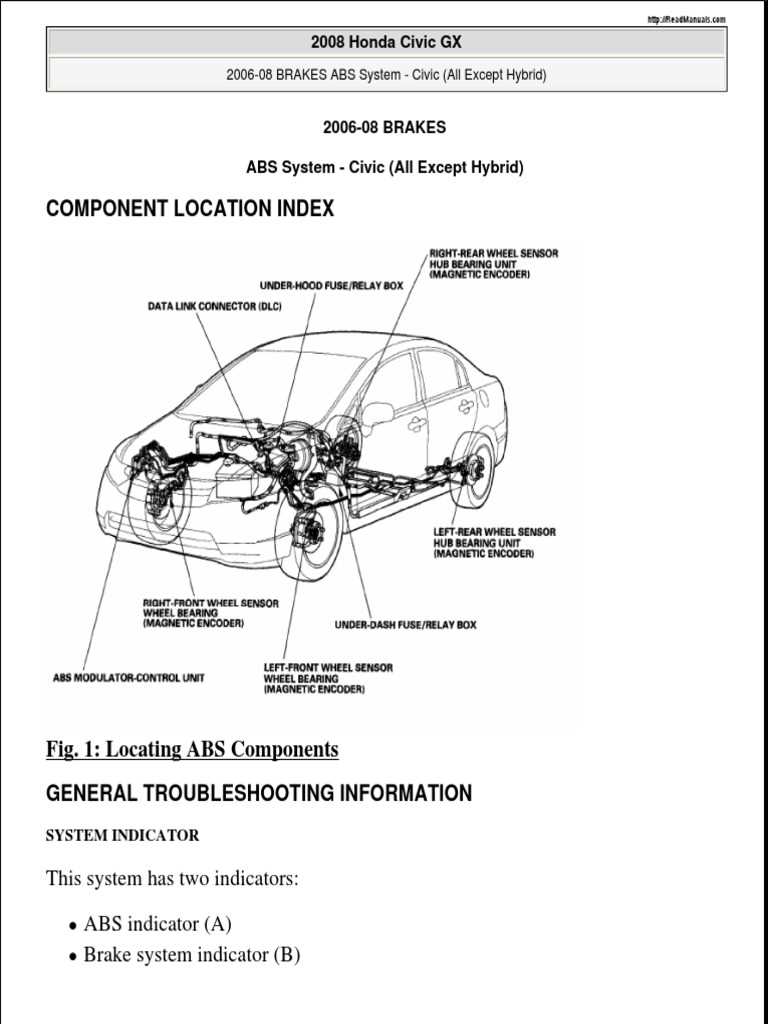
Understanding the layout and structure of various mechanical and electrical systems within a car is essential for maintaining its performance. Each element plays a significant role in ensuring the smooth operation of the vehicle, from the engine to the intricate wiring that connects the systems.
In this section, we explore the relationships between various automotive components. By familiarizing yourself with these elements, you can effectively manage repairs, replacements, and general upkeep. A detailed examination of key assemblies helps in identifying potential issues and maintaining peak efficiency.
Whether you’re focusing on the powertrain, suspension, or electrical systems, having a clear visualization of these connections aids in performing precise interventions, ensuring your vehicle runs smoothly for years to come.
Understanding the 2008 Honda Civic Components
The structure and essential systems of any vehicle are designed to ensure performance, safety, and efficiency. By exploring these elements, we can gain insights into how various mechanical and electrical components work together seamlessly to power the car and maintain its functionality on the road.
Key Mechanical Systems
- Engine and Transmission: The heart of the vehicle, responsible for generating power and transferring it to the wheels.
- Suspension: Ensures a smooth ride by absorbing shocks from uneven road surfaces and improving handling.
- Braking System: Vital for controlling speed and ensuring safety, converting kinetic energy into heat to stop the vehicle.
Electrical and Safety Components
- Battery and Alternator:
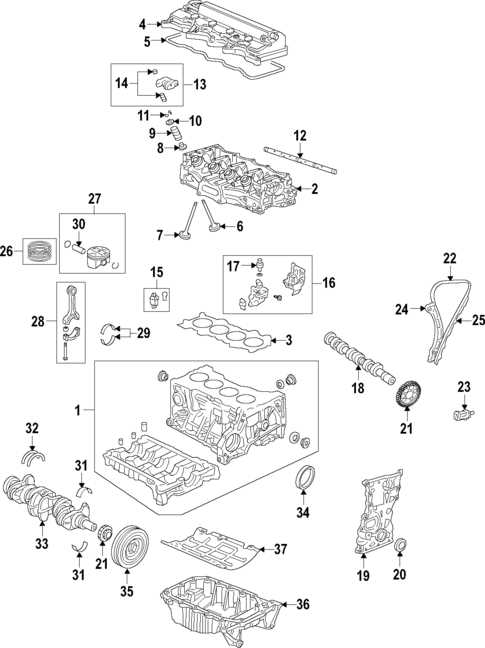
Engine Parts Layout for Honda Civic 2008
The engine of this vehicle is a well-structured mechanism designed for efficient performance. Each component plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall functionality, ensuring smooth operation and long-lasting durability. Understanding the arrangement of these elements is essential for those involved in maintenance or repairs.
Main Sections of the Engine
The engine is divided into various sections, each responsible for a specific task. Among the key elements are the combustion area, where fuel is ignited to generate power, and the cooling system, which prevents overheating during operation. These sections work together to deliver optimum performance.
Key Components Overview
Some of the primary components include the cylinders, which form the heart of the system, and the intake manifold, responsible for delivering air to the combustion chambers. Other vital elements, such as the exhaust system and the timing belt, help manage the flow of gases and the synchronization of internal operations.
Detailed Overview of Suspension System
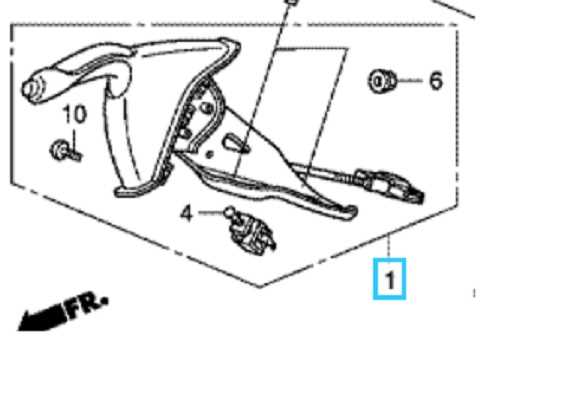
The suspension system is a crucial component that ensures vehicle stability and comfort during movement. It plays a vital role in absorbing shocks and maintaining tire contact with the road surface, contributing to a smooth and controlled ride.
Key Components of the System include various elements that work together to manage the vehicle’s handling. Springs, for instance, help support the weight, while shock absorbers dissipate the energy from road impacts. Control arms and other links maintain the correct alignment of wheels, ensuring proper direction and balance.
Proper maintenance and understanding of the suspension’s mechanics can greatly enhance both safety and driving experience, making it an essential system to regularly inspect and service.
Electrical Wiring Diagram for Civic 2008
The electrical schematic provides a detailed overview of the vehicle’s wiring system. It serves as a guide for understanding the connections and circuits that control various electrical components. This layout helps in troubleshooting and maintaining the system efficiently, ensuring that all functions operate seamlessly.
Main Circuits Overview

The primary circuits in the car include the power supply, lighting, and ignition systems. Each circuit is interconnected through a series of wires and connectors that ensure the smooth flow of electricity. Identifying these circuits is crucial for repairs or modifications.
- Power distribution network
- Lighting and signals layout
- Engine control unit connections
Wiring Components and Functions
The wiring harness consists of various components, each playing a specific role. These components include fuses, relays, and connectors, which protect and facilitate the electrical flow throughout the system. Understanding their function is essential for diagnosing issues.
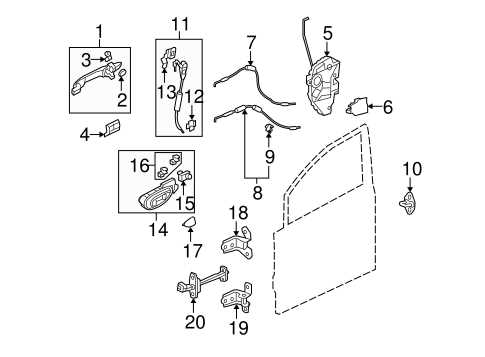
Brake System Structure and Components
The brake system plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe operation of any vehicle. Its structure is designed to control the motion of the car by reducing speed or bringing it to a complete stop. This is achieved through a combination of mechanical and hydraulic elements working together to create friction, which slows down the wheels.
Core components of the brake system include the pedal, which initiates the process, and a master cylinder that transforms the mechanical force into hydraulic pressure. This pressure is then transmitted to the brake calipers, which house the brake pads. These pads press against the rotors, creating the necessary friction to slow the vehicle down. Additionally, brake lines and fluid ensure the hydraulic pressure is maintained throughout the system.
To enhance safety, modern systems are often equipped with anti-lock braking systems (ABS), which prevent the wheels from locking up during sudden stops. This allows
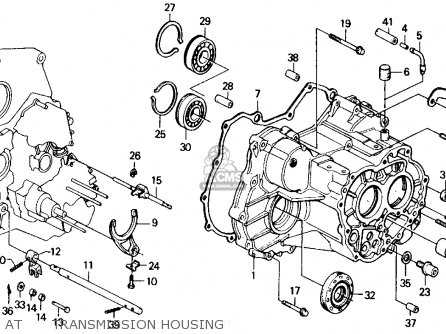
Honda Civic 2008 Transmission Parts Breakdown
The transmission system plays a critical role in ensuring smooth power transfer between the engine and the wheels. Understanding the structure of this mechanism helps in maintaining and troubleshooting any issues that may arise. Each element works in harmony to provide efficient gear shifting and optimal vehicle performance.
Key Components of the Transmission System
The assembly is composed of multiple interconnected elements, each serving a distinct function. The gear sets manage the different speed ratios, while the clutch ensures smooth transitions between these gears. Other elements, like the torque converter and control unit, help regulate power distribution and transmission response.
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular inspection and upkeep of the system’s components are essential for the longevity of the vehicle. Worn gears, fluid leaks, or damaged control units can lead to significant performance issues. It’s important to check the condition of each part and replace any worn elements to avoid costly repairs in the future.
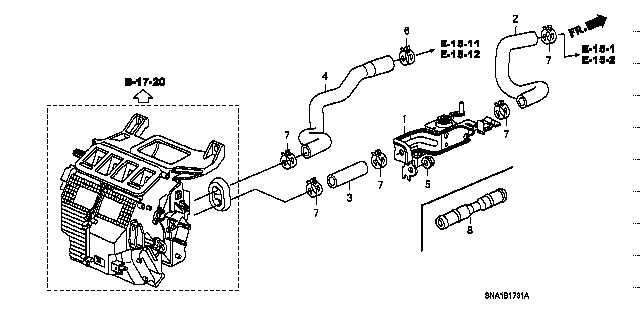
Cooling System Components and Flow Diagram

The cooling system in a vehicle is designed to regulate the temperature of the engine, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance. By circulating coolant through various components, the system maintains a balanced temperature, dissipating excess heat and enabling the engine to run efficiently. Understanding the key elements of this system and how they interact is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Elements of the Cooling System
The primary components include a radiator, which acts as the core heat exchanger, transferring heat from the coolant to the air. The water pump circulates the coolant through the system, while the thermostat controls the flow of coolant based on engine temperature. Hoses and connections ensure the coolant flows smoothly between each part.
Coolant Flow and Operation
Coolant flows from the engine to the radiator, where it releases heat before being pumped back to the engine. The thermostat opens and closes depending on temperature, allowing the coolant to flow through the radiator when needed. This continuous cycle keeps the engine from overheating, maintaining its efficiency.
Fuel System Schematic for Efficient Repairs
The fuel delivery setup is critical for the optimal performance of any vehicle. Understanding its layout allows for more precise and effective maintenance. This guide provides an overview of the key elements involved in the fuel system, helping ensure reliable performance and simplified troubleshooting.
Key Components of the Fuel Delivery Network
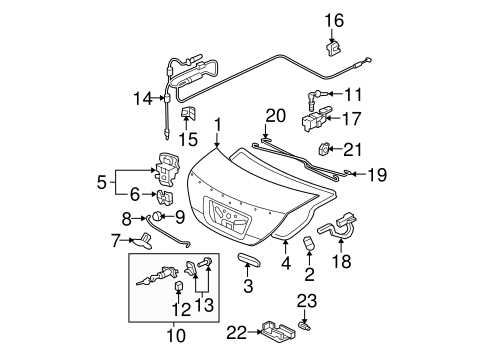
- Fuel Tank: Stores and supplies the necessary fuel to the engine.
- Fuel Pump: Ensures the correct pressure is maintained for smooth fuel delivery.
- Fuel Injectors: Spray fuel into the engine cylinders for combustion.
- Fuel Filter: Removes impurities from the fuel to prevent engine damage.
Steps for Identifying Common Issues
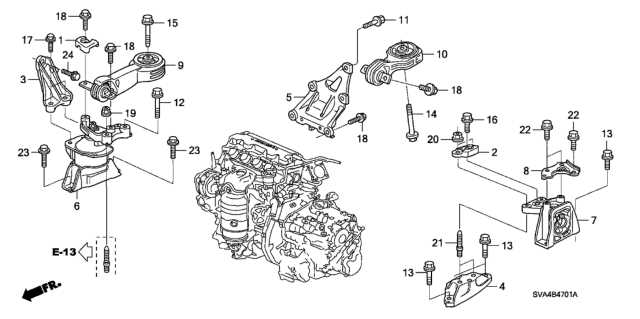
- Inspect the fuel pump for pressure inconsistencies or noise.
- Check for blockages or debris in the fuel filter.
- Examine fuel injectors for signs of clogging or leaks.
- Ensure proper connections between all fuel lines and components.
Interior Components and Dashboard Layout
This section provides an overview of the interior structure and control arrangement within a compact vehicle. The focus lies on the functionality and design of various elements that contribute to an optimal driving experience. Understanding these components is essential for maintenance and customization, ensuring comfort and accessibility for all occupants.
Main Dashboard Features
The dashboard houses several critical features that enhance driver interaction and vehicle operation. These components include gauges, control knobs, and infotainment systems. Each element is strategically positioned for easy access while driving, promoting safety and efficiency.
Seating and Storage Solutions
In addition to the dashboard, the interior design incorporates seating and storage solutions that maximize space and comfort. The layout is designed to provide adequate legroom and accessibility to personal items. This thoughtful arrangement contributes to an enjoyable journey.
Component Description Instrument Cluster Displays critical information such as speed, fuel level, and engine temperature. Center Console Hosts controls for audio, climate settings, and additional storage compartments. Seating Ergonomically designed seats providing support and comfort for occupants. Storage Compartments Includes glove box, cup holders, and side pockets for convenient storage.