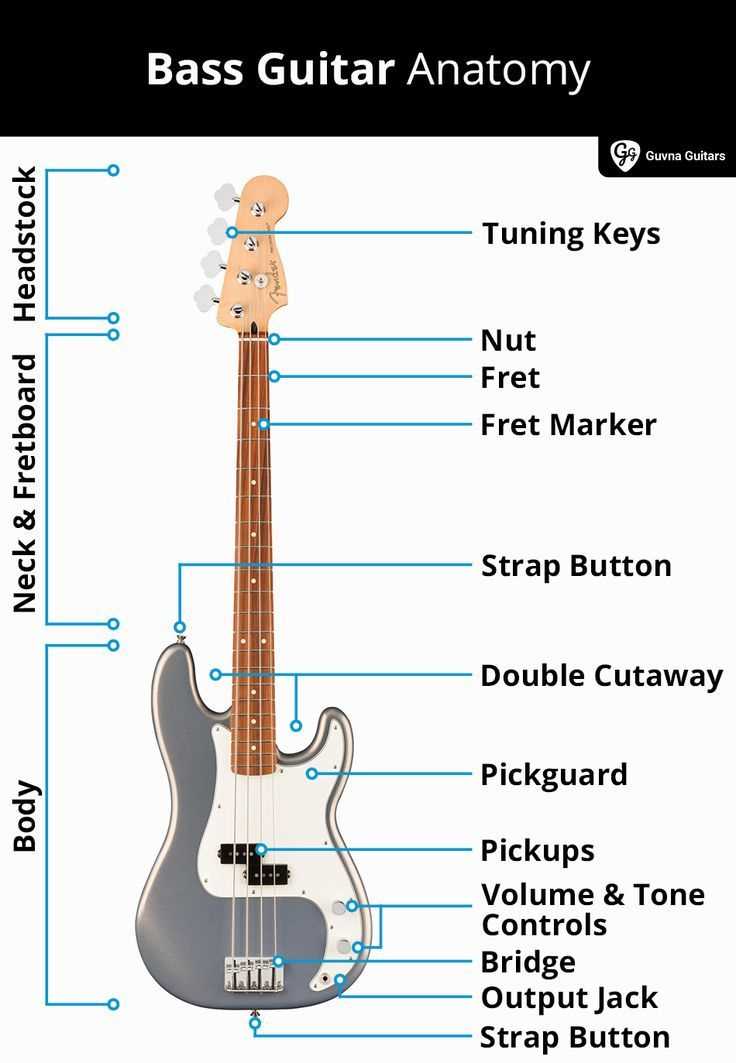
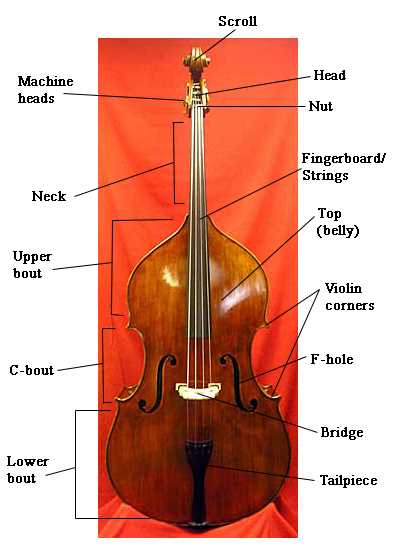
Delving into the construction of a low-end string instrument unveils a world of intricate elements that work harmoniously to create rich, resonant sounds. Each segment contributes uniquely to the overall function and tone, making it essential for players to familiarize themselves with these crucial features. From the body to the tuning mechanisms, each component plays a vital role in shaping the musical experience.
Exploring these essential features offers insights not only into their individual functions but also into how they interact to enhance performance. Knowledge of these elements empowers musicians, helping them make informed decisions about their instrument choices, maintenance, and playing techniques. Understanding this framework paves the way for a deeper appreciation of music and its creation.
Moreover, recognizing the significance of each part encourages players to engage more thoughtfully with their instruments. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned performer, this exploration fosters a connection that transcends mere play, enriching your musical journey and enhancing your skills.
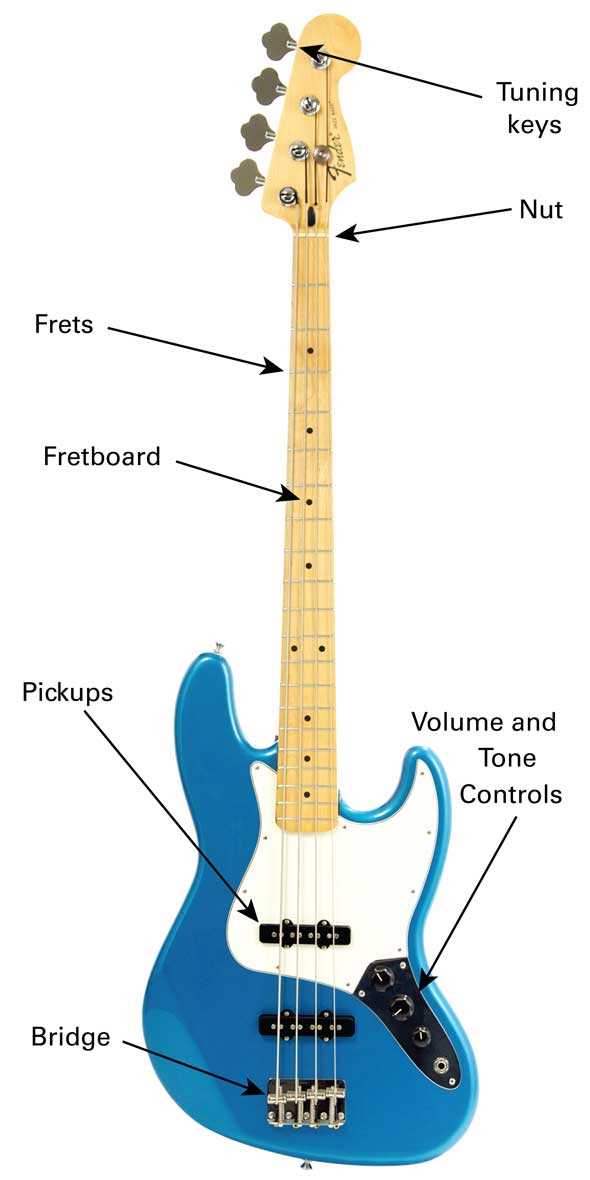
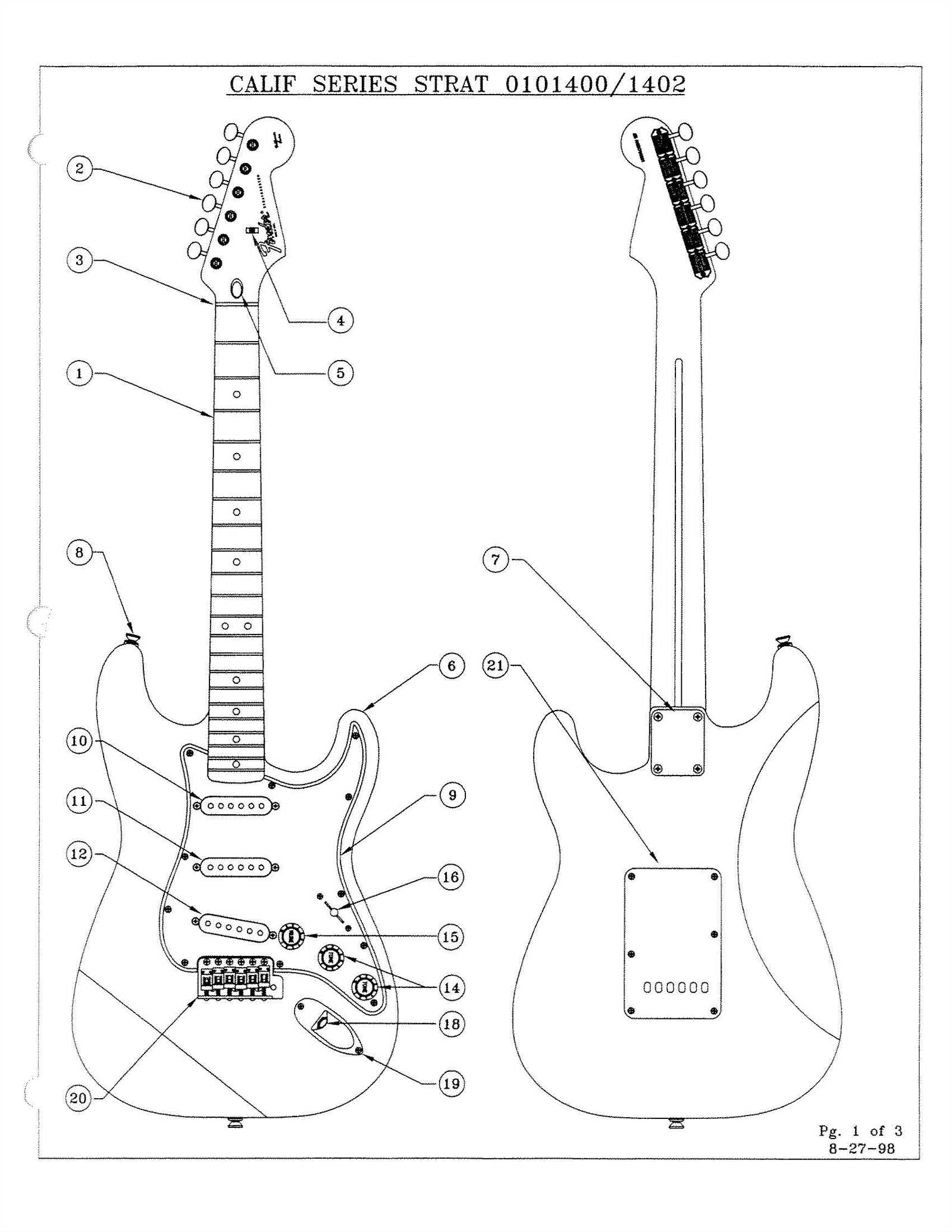
Understanding the Bass Guitar Components
Exploring the various elements that constitute an electric stringed instrument reveals the intricate design and functionality that contribute to its unique sound. Each component plays a vital role in shaping the overall performance and tonal characteristics, making it essential for musicians to grasp their significance.
Key Elements of the Instrument
- Body: The main structure that influences resonance and aesthetics.
- Neck: The elongated section where notes are fretted, affecting playability.
- Fingerboard: The surface on the neck where fingers interact with the strings.
- Strings: Essential for producing sound, varying in thickness and material.
Functional Components
- Pickups: Electromagnetic devices that capture string vibrations and convert them into electrical signals.
- Bridge: The point where strings are anchored, crucial for intonation and sustain.
- Tuning Machines: Mechanisms that allow for adjusting string tension to achieve the desired pitch.
- Control Knobs: Elements that enable sound modification through volume and tone adjustments.
Understanding these elements enhances a musician’s ability to choose the right instrument and customize it to their playing style, ensuring a more fulfilling musical experience.
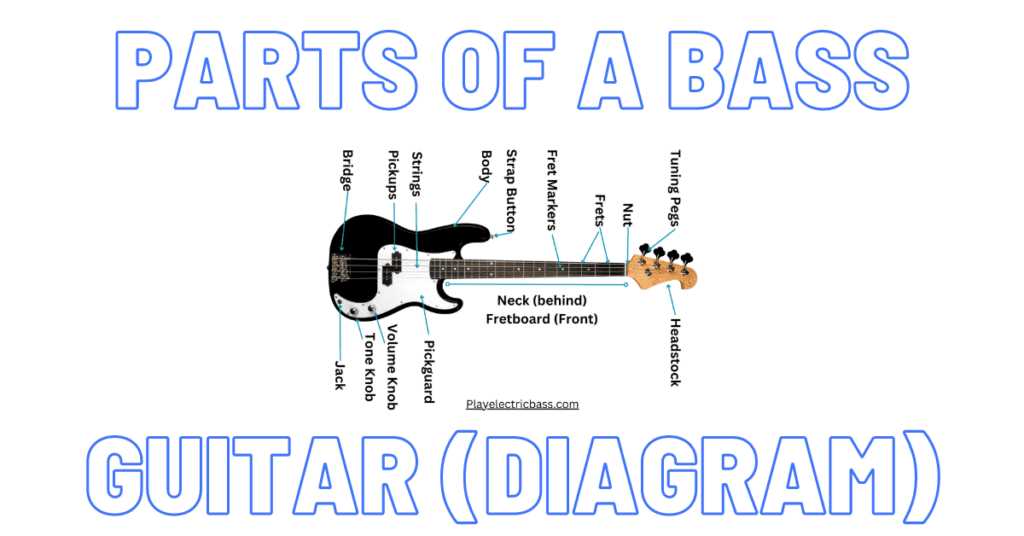
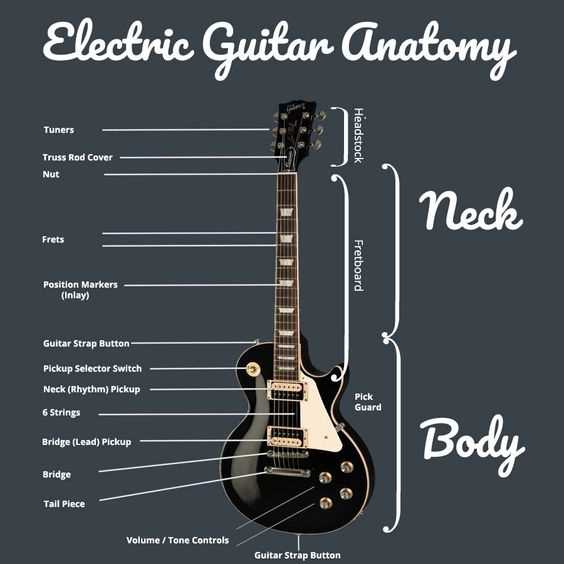
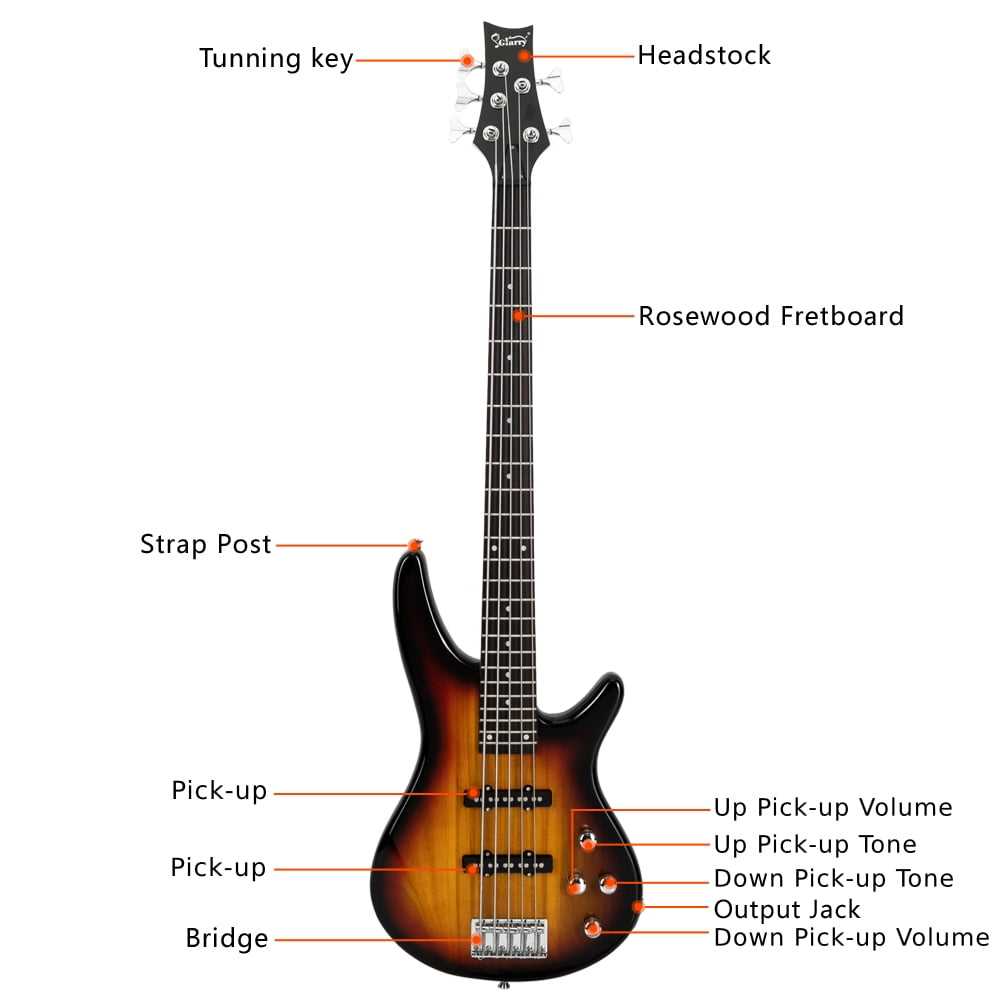
Essential Elements of a Bass Guitar
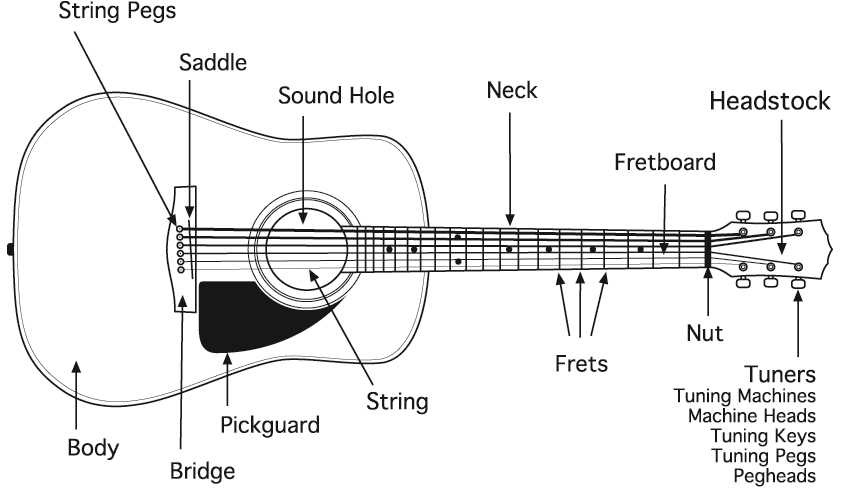
Understanding the fundamental components of this instrument is crucial for musicians who wish to master its unique sound and versatility. Each element plays a vital role in contributing to the overall performance and tone.
- Body: The main structure that influences the instrument’s resonance and weight.
- Neck: The elongated section where the player presses down on the strings to create different notes.
- Headstock: Located at the end of the neck, it houses the tuning mechanisms.
- Strings: The vibrating elements that produce sound, typically thicker than those on other stringed instruments.
- Fretboard: The surface along the neck with marked positions for accurate note placement.
Each of these components interacts to create the distinct voice that characterizes the instrument, allowing for a wide range of musical expression.
- Tuning Pegs: Essential for adjusting string tension and pitch.
- Bridge: The part that anchors the strings and influences sustain and tonal quality.
- Pickups: Magnetic devices that capture string vibrations and convert them into an electrical signal.
- Controls: Knobs and switches that allow adjustments to volume and tone, shaping the overall sound.
By familiarizing oneself with these key components, musicians can better appreciate the artistry involved in crafting and playing this remarkable instrument.
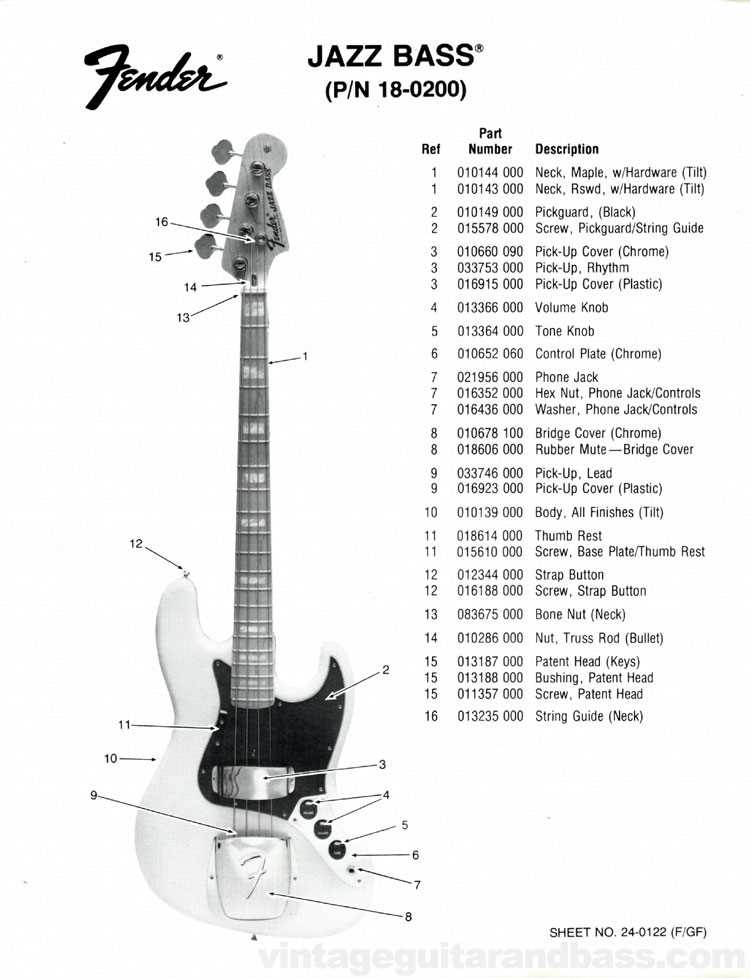
Function of Each Part Explained
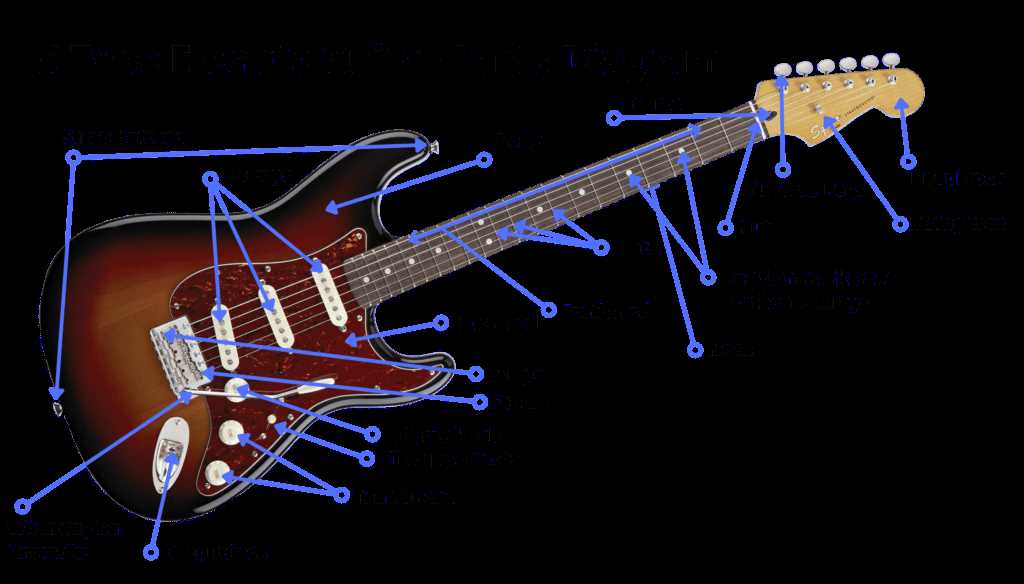
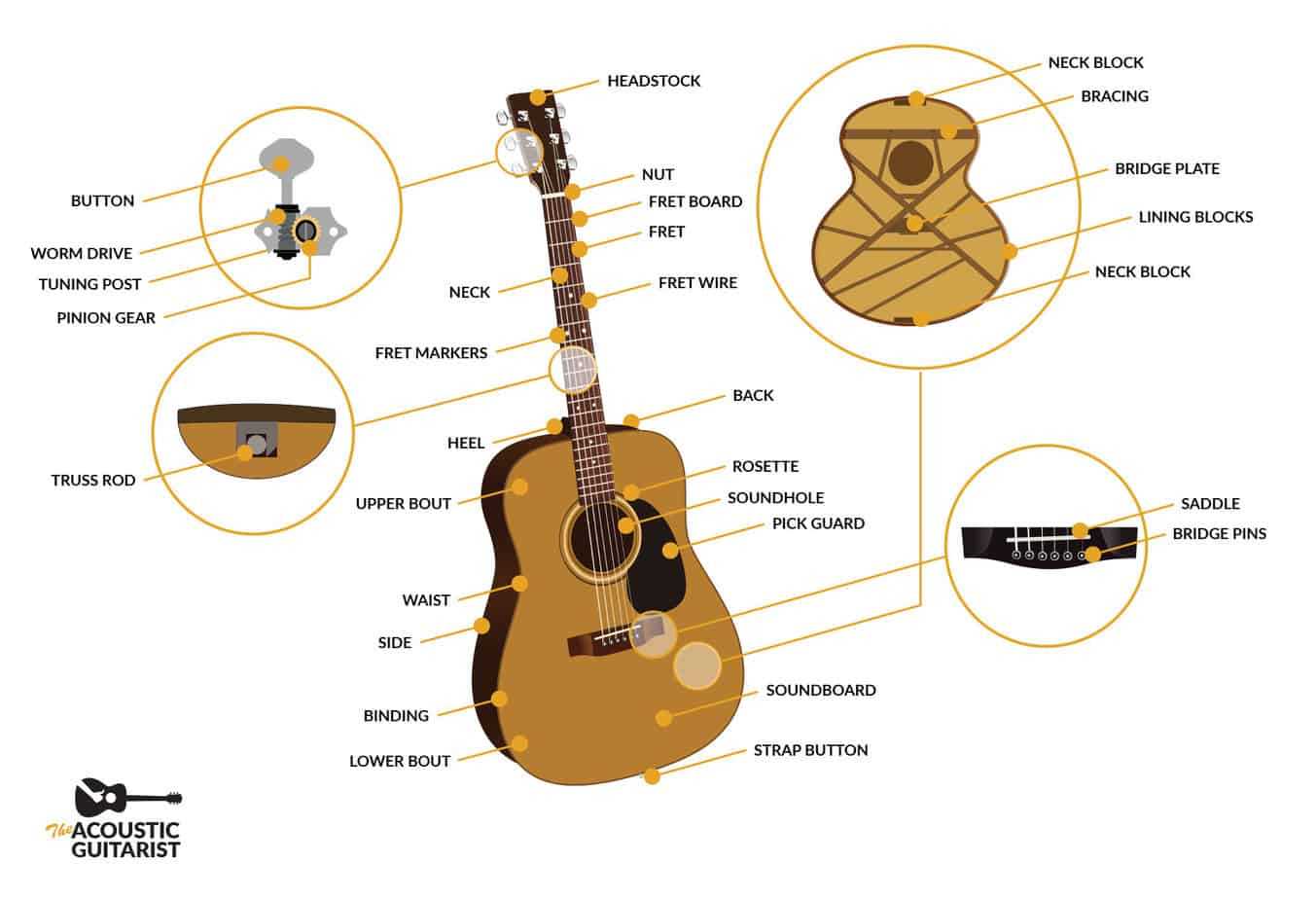
Understanding the various components of a stringed instrument is essential for mastering its sound and playability. Each element plays a unique role, contributing to the overall performance and tonal quality. Here, we will explore the significance of each section and how they work together to create music.
Key Components
- Neck: Provides the framework for finger positioning and is crucial for playability.
- Body: The main structure that resonates sound, influencing tonal depth.
- Strings: Vibrate to produce sound, with thickness affecting pitch.
- Picks: Used for striking the strings, impacting dynamics and attack.
Additional Features
- Bridge: Anchors the strings, affecting sustain and intonation.
- Tuning Pegs: Allow for pitch adjustments, essential for accurate tuning.
- Pickups: Capture string vibrations, converting them into electrical signals for amplification.
Body Types and Their Characteristics
The construction of an instrument greatly influences its sound, playability, and aesthetic appeal. Different shapes and materials create unique tones and feel, allowing musicians to select options that best suit their style and preferences.
Solid Body
Solid body instruments are known for their durability and sustain. These designs typically offer a bright, punchy tone and are favored in genres that require clear articulation, such as rock and metal. The absence of resonating air chambers minimizes feedback, making them ideal for amplified performances.
Hollow Body
Hollow designs produce a warm, rich tone due to their resonating chambers. They are popular in jazz and blues genres, where a softer, more organic sound is desired. However, they may be more prone to feedback when played at high volumes, which can be both a challenge and a characteristic feature for certain musicians.
Neck Variations and Their Impact
The design and structure of the elongated section of stringed instruments significantly influence playability and tonal characteristics. Different configurations can cater to various musical styles and personal preferences, ultimately shaping the overall sound and feel for the musician.
Types of Neck Designs
- Straight Neck
- Curved Neck
- Fretless Neck
Each design offers distinct advantages, affecting how notes are articulated and the ease of playing across different registers.
Effects on Performance
- Comfort: The shape can enhance or hinder the player’s technique.
- Tone: Variations impact resonance and sustain, altering the instrument’s voice.
- Versatility: Certain designs accommodate a wider range of musical styles.
Ultimately, the choice of neck structure is crucial in achieving the desired sound and performance experience.
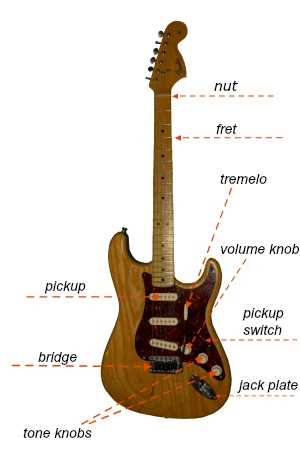
Pickups: Types and Sound Differences
In the world of stringed instruments, the choice of electromagnetic sensors plays a crucial role in shaping the overall tonal character. Each type of sensor has its unique qualities, contributing to a wide range of sounds, from punchy and aggressive to smooth and mellow. Understanding these variations helps musicians select the right tool for their creative expression.
Types of Sensors
There are primarily two categories of electromagnetic sensors: single-coil and humbucker. Single-coil sensors offer a bright, clear tone with a pronounced high end, making them ideal for styles that require precision and articulation. However, they can sometimes pick up unwanted noise, which may be a drawback in certain environments.
On the other hand, humbuckers are designed to cancel out interference, resulting in a thicker, warmer sound. This makes them popular for genres that demand a heavier, more powerful output. Their construction allows for a richer midrange, giving depth to the overall sound profile.
Sound Differences
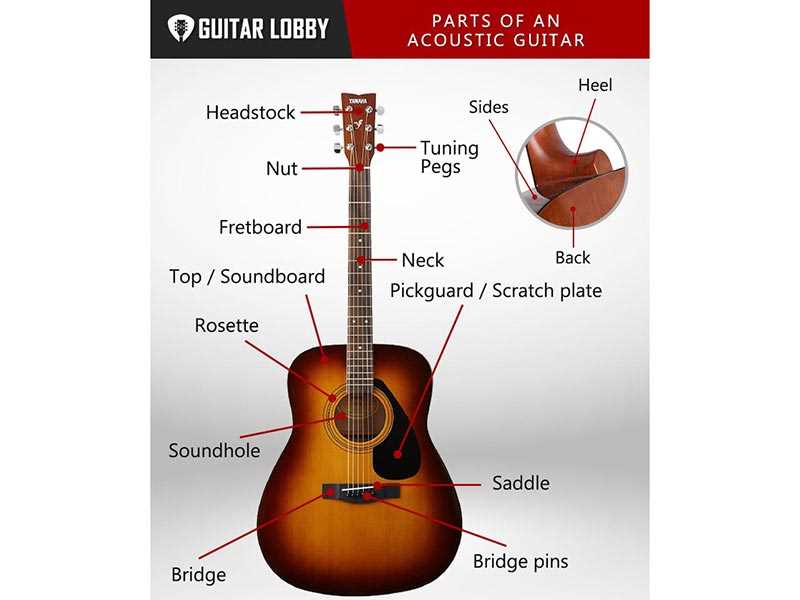
The sonic distinctions between these types of sensors are significant. Single-coils tend to produce a bright, snappy attack that can be ideal for funk and slap techniques. Their clarity shines in clean settings, allowing for intricate playing to be heard distinctly. In contrast, humbuckers deliver a more robust and full-bodied tone, often preferred in rock and metal genres for their ability to sustain notes and create a more pronounced low end.
Ultimately, the choice of electromagnetic sensors influences not just the sound but also the playing experience. Musicians should consider their preferred styles and settings when selecting the appropriate option to achieve their desired soundscape.
Hardware: Bridges and Tuners Overview
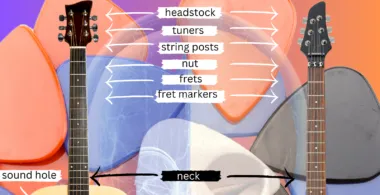
The fundamental components that contribute to the instrument’s playability and sound quality play a crucial role in enhancing overall performance. Understanding the functions and variations of these essential elements is vital for musicians looking to optimize their experience.
Bridges serve as the critical interface between the strings and the body, influencing sustain and tone. There are several types, including fixed, adjustable, and floating bridges, each offering unique advantages that can alter the instrument’s sound and playability.
Tuners, on the other hand, ensure precise string tension and pitch. Available in various styles, such as open-gear and sealed, they provide stability and reliability, allowing players to maintain perfect tuning during performances.
Both bridges and tuners are integral to achieving the ultimate sound and feel, making it essential for players to delve into their characteristics when choosing their equipment.
Electronics and Wiring Basics
This section delves into the essential concepts behind the electrical components and connections that play a crucial role in sound production and manipulation. Understanding these fundamentals is key for anyone looking to enhance their instrument’s performance or troubleshoot issues effectively.
Key Components
At the heart of the system are several vital elements, including pickups, potentiometers, and output jacks. Pickups capture the vibrations of the strings and convert them into electrical signals, while potentiometers adjust volume and tone. Output jacks serve as the final point of connection, allowing the generated signals to flow to amplifiers or effects units.
Wiring Techniques
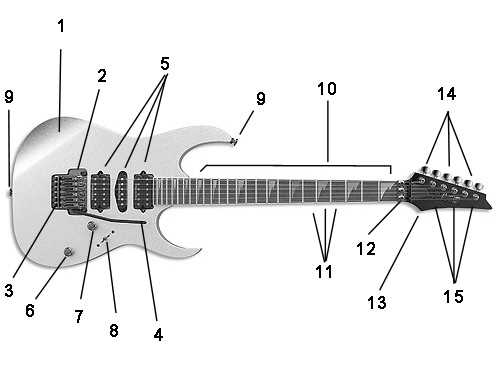
Proper wiring techniques are essential for achieving optimal performance. Utilizing high-quality cables and connectors ensures minimal interference and signal loss. Additionally, following standardized color codes for wiring helps prevent confusion during assembly or repairs. Mastering these techniques not only improves reliability but also opens doors for customization and enhancement of the instrument’s capabilities.
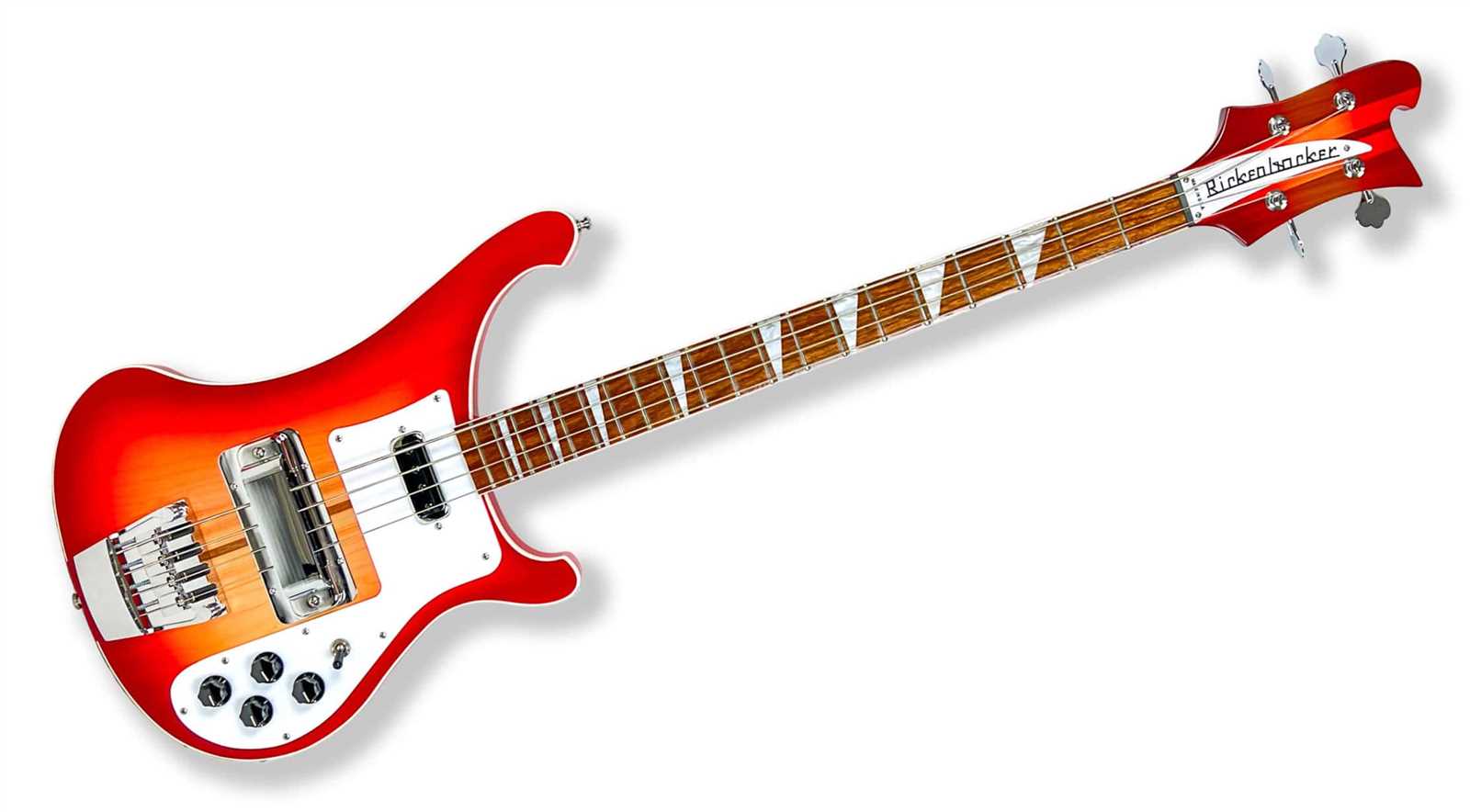
Maintaining Your Bass Guitar Parts

Proper care and regular upkeep of your instrument can significantly enhance its performance and longevity. By focusing on the various components, you ensure that each element functions harmoniously, contributing to a more enjoyable playing experience. Implementing a consistent maintenance routine will keep your setup in optimal condition and prevent potential issues down the road.
Cleaning and Inspection
Regularly clean the surface and fretboard to remove dirt and grime. Use appropriate cleaners and soft cloths to avoid damaging the finish. During this process, inspect the hardware for any signs of wear or corrosion. Addressing these concerns early can prevent larger problems that might affect sound quality and playability.
String Care and Replacement

Strings are crucial for sound production, so changing them periodically is essential. Depending on your playing frequency, you might consider replacing them every few weeks or months. Keep them clean by wiping them down after each session to prolong their life. Fresh strings not only sound better but also enhance the overall feel of the instrument.