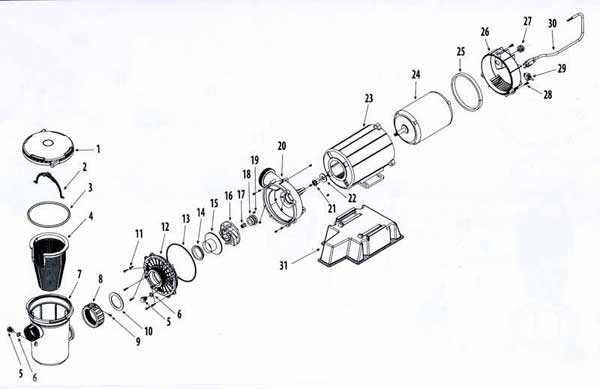
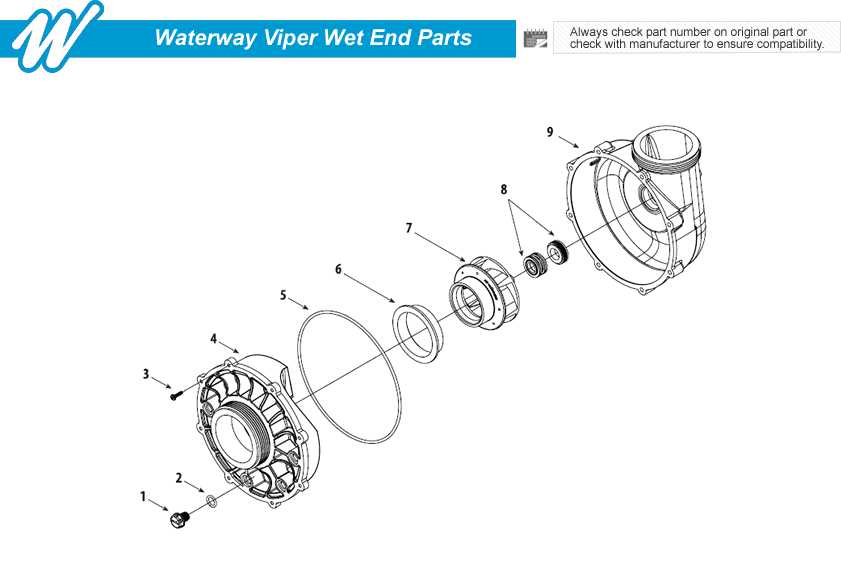
In the realm of liquid management systems, a comprehensive understanding of essential elements is crucial for optimal functionality. Each component plays a significant role in ensuring efficient operation, contributing to the overall performance of the system.
Visual representation of these elements aids in grasping their interconnections and mechanisms. By exploring various segments and their respective functions, one can enhance both knowledge and maintenance practices.
Ultimately, diving into the intricacies of these mechanisms allows for better troubleshooting and optimization, paving the way for enhanced fluid dynamics and longevity of the entire system.
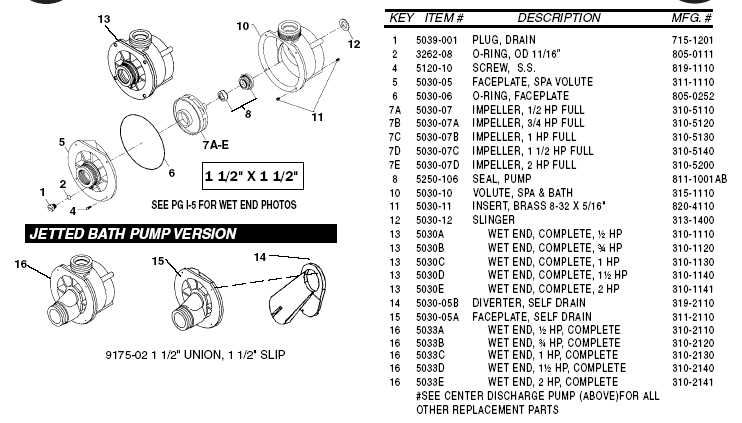
Understanding Waterway Pump Components
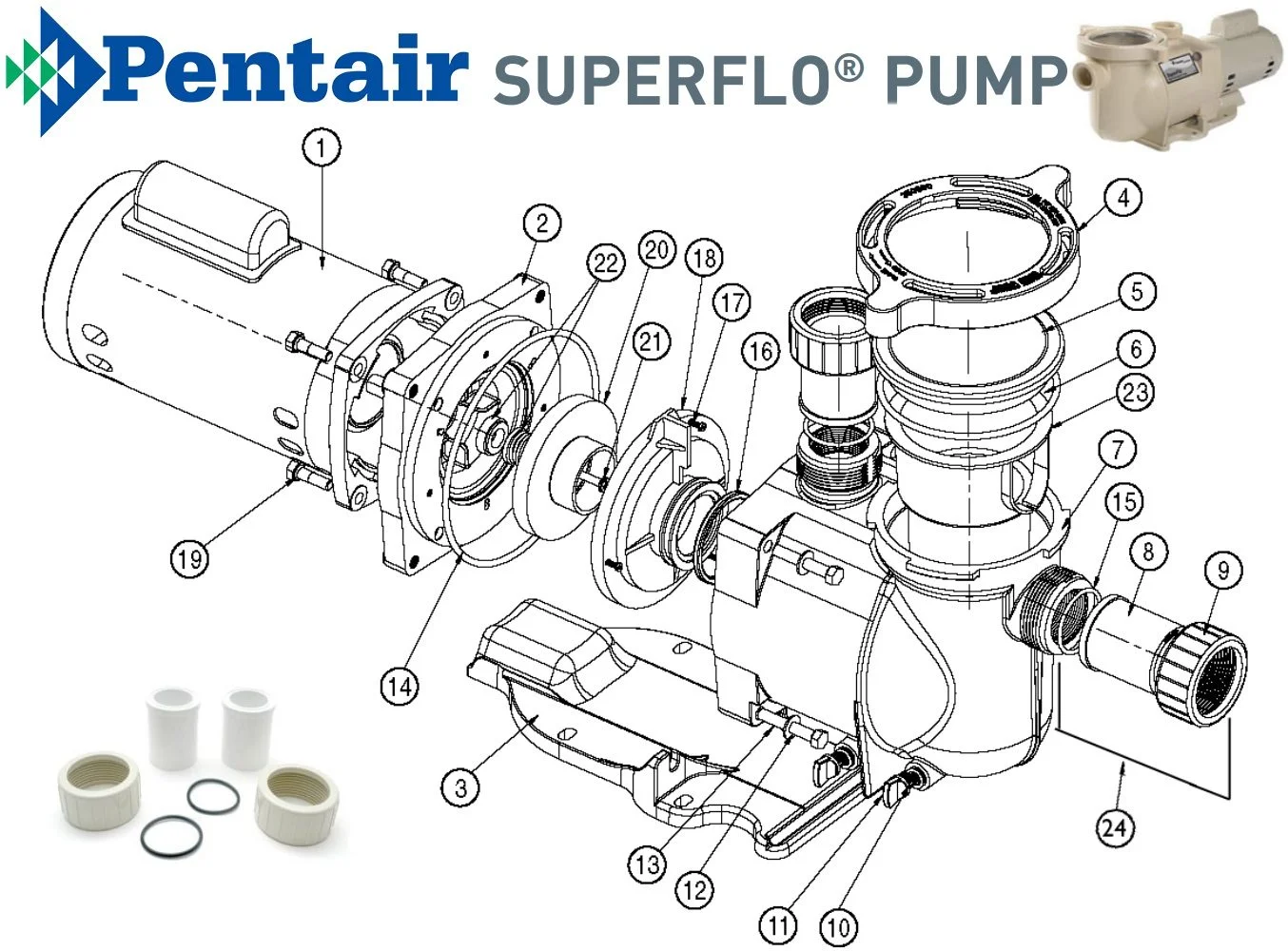
The efficient operation of any fluid-moving system relies on a variety of integral elements working together seamlessly. Grasping the functions and interrelationships of these components is essential for optimal performance and longevity. This section explores the critical elements that contribute to the overall functionality of such systems.
Key Elements
- Motor: The driving force that initiates movement, converting electrical energy into mechanical action.
- Impeller: A rotating component designed to increase the pressure and flow of the fluid.
- Volute: The casing that directs the fluid from the impeller to the discharge pipe.
- Suction Strainer: A filter that prevents debris from entering the system and causing damage.
- Seals: Prevent leaks and maintain pressure within the assembly.
Importance of Each Component
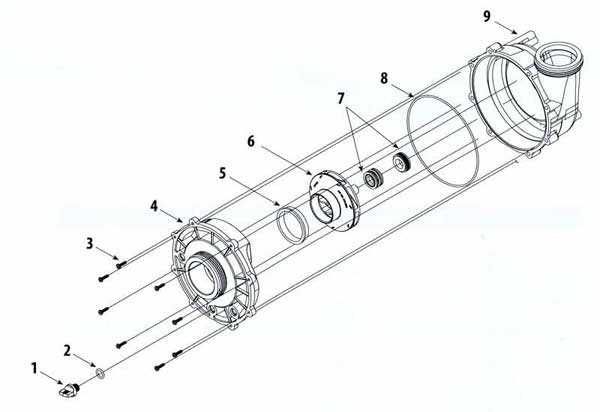
Understanding the role of each component is vital for troubleshooting and maintenance:
- The motor is crucial for initiating fluid movement and must be compatible with the overall system.
- Impellers come in various designs to suit different applications, impacting efficiency and performance.
- Volutes play a key role in directing flow, affecting both velocity and pressure.
- Regular inspection of the suction strainer can prevent costly repairs and downtime.
- Seals require routine checks to ensure they are intact and functioning properly.
By familiarizing oneself with these essential components, one can enhance the reliability and efficiency of the entire system, ensuring that it meets operational demands effectively.
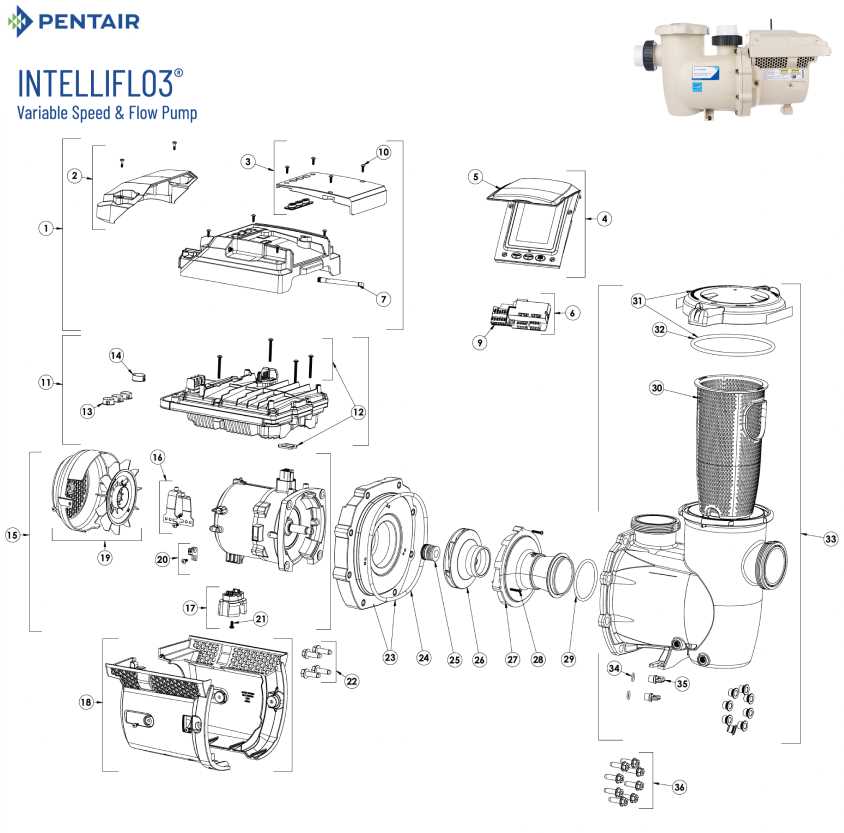
Functionality of Each Pump Part
Understanding the components of a fluid-moving device is essential for effective operation and maintenance. Each element plays a critical role in ensuring the system functions efficiently and reliably. This section delves into the specific functions of each component, highlighting their importance in the overall mechanism.
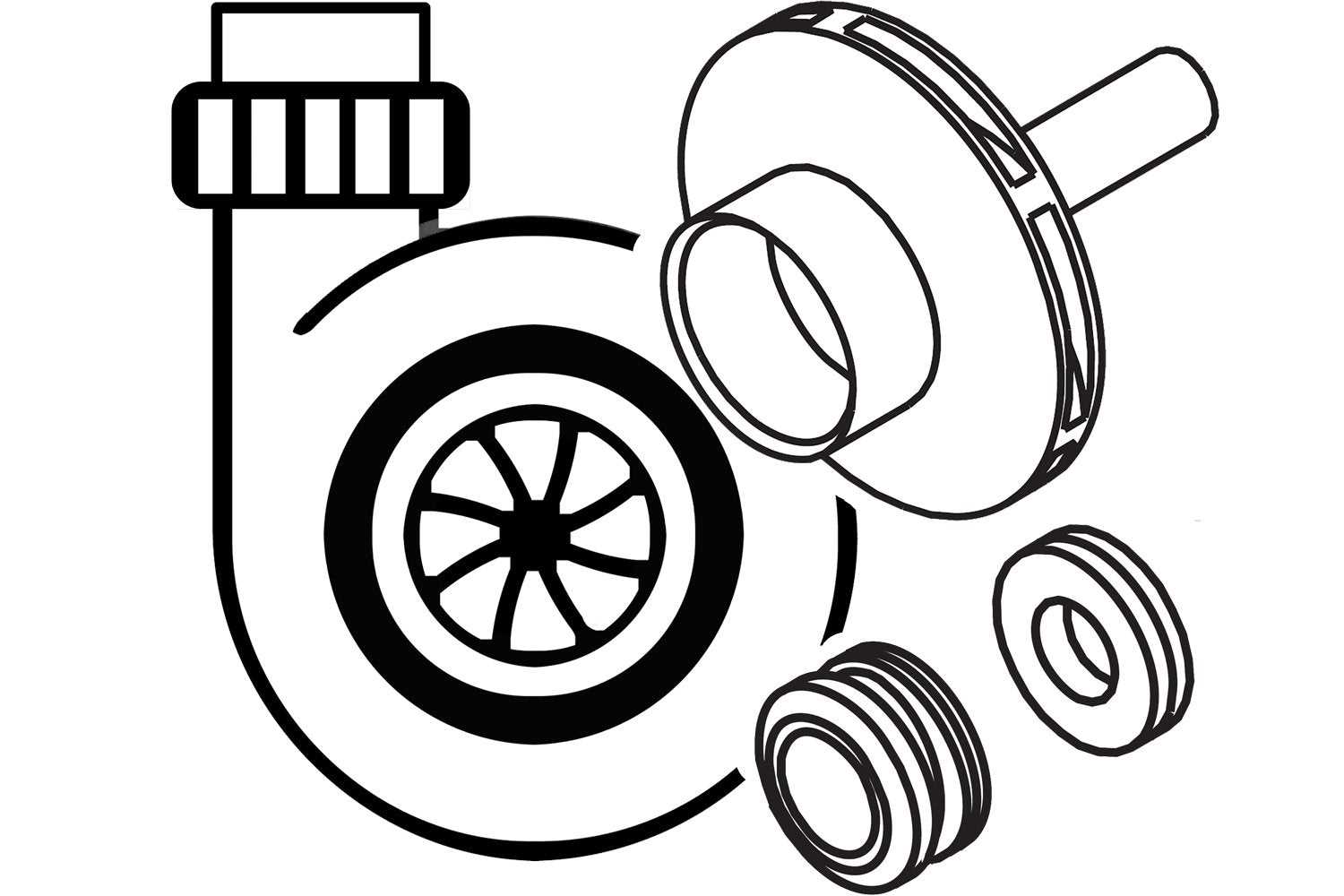
Impeller
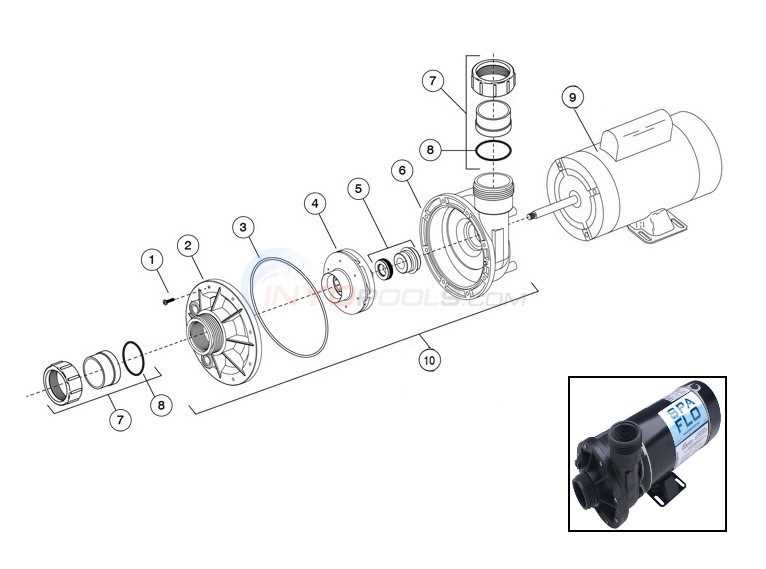
The impeller is the heart of the system, responsible for imparting kinetic energy to the fluid. By rotating rapidly, it creates a low-pressure area that draws in the liquid, converting rotational energy into fluid movement. The design of the impeller directly affects the efficiency and flow rate of the entire assembly.
Volute Casing
The volute casing surrounds the impeller and serves as a pathway for the fluid. Its shape helps convert the high-velocity flow from the impeller into a steady, high-pressure stream. This component also aids in minimizing turbulence, ensuring a smooth transition of the liquid as it exits the device. Proper design and sizing of the volute are crucial for optimal performance.
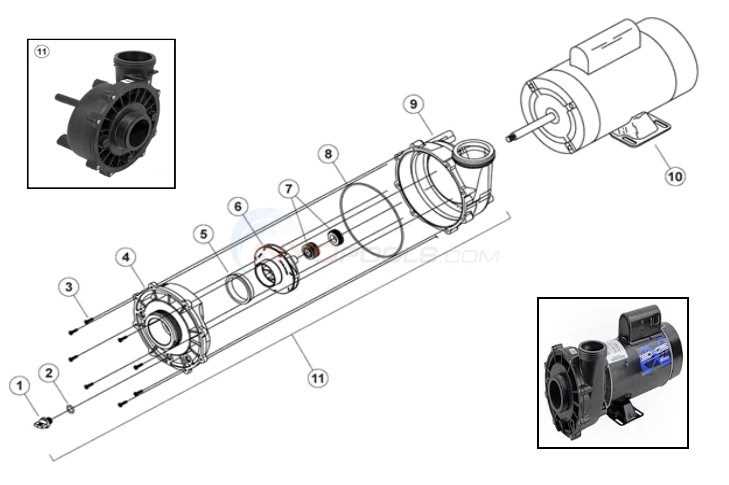
Common Issues in Pump Systems
In any fluid movement system, several challenges can arise that hinder optimal performance. Understanding these common issues is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Below are some frequent problems encountered in these systems.
- Leakage: Fluid leaks can occur at various connection points, leading to decreased efficiency and potential hazards.
- Clogging: Accumulation of debris can obstruct the flow, causing pressure buildup and operational disruptions.
- Noisy Operation: Unusual sounds may indicate mechanical wear, misalignment, or air entrapment, requiring immediate attention.
- Overheating: Excessive heat can result from inadequate lubrication or overloading, risking equipment damage.
Addressing these issues promptly can prolong the lifespan of the equipment and ensure reliable operation. Regular inspections and proper maintenance practices play a vital role in preventing these common challenges.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Routine care and inspection are crucial for ensuring optimal functionality and longevity of equipment. Neglecting these practices can lead to inefficiencies, costly repairs, and unexpected downtime, impacting overall performance.
Benefits of Consistent Upkeep
Regular servicing helps identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring smooth operation and reducing the risk of major failures. Additionally, it can enhance energy efficiency, saving costs over time.
Maintenance Checklist
| Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Monthly | Check for leaks and wear |
| Lubrication | Quarterly | Ensure moving parts are well-greased |
| Filter Replacement | Every 6 months | Keep systems clear of debris |
| Calibration | Annually | Maintain accuracy in operations |
How to Read Pump Diagrams
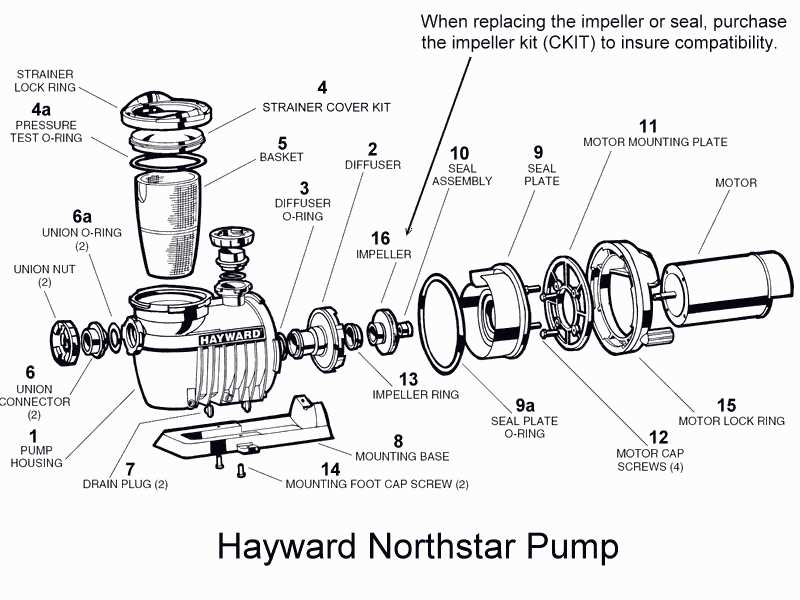
Understanding schematics is essential for anyone working with fluid movement systems. These illustrations provide a visual representation of the components and their relationships within the system, allowing for easier troubleshooting and maintenance. By grasping the symbols and conventions used, one can effectively interpret the layout and functionality of the assembly.
Begin by familiarizing yourself with the common symbols used in these representations. Each icon typically corresponds to a specific component, such as valves, filters, or motors. Learning these symbols can significantly enhance your ability to decipher the overall configuration. Additionally, pay attention to the lines and arrows, which indicate the flow direction and connections between elements.
Next, look for annotations that often accompany the visuals. These notes may include specifications, such as sizes, materials, or operational guidelines. Understanding these details is crucial, as they provide insights into the performance characteristics and limitations of the system.
Finally, practice by analyzing various schematics. Start with simpler designs before progressing to more complex ones. With time, your ability to read and interpret these technical illustrations will improve, allowing you to efficiently address any issues that may arise in the fluid movement system.
Tools Needed for Pump Repairs
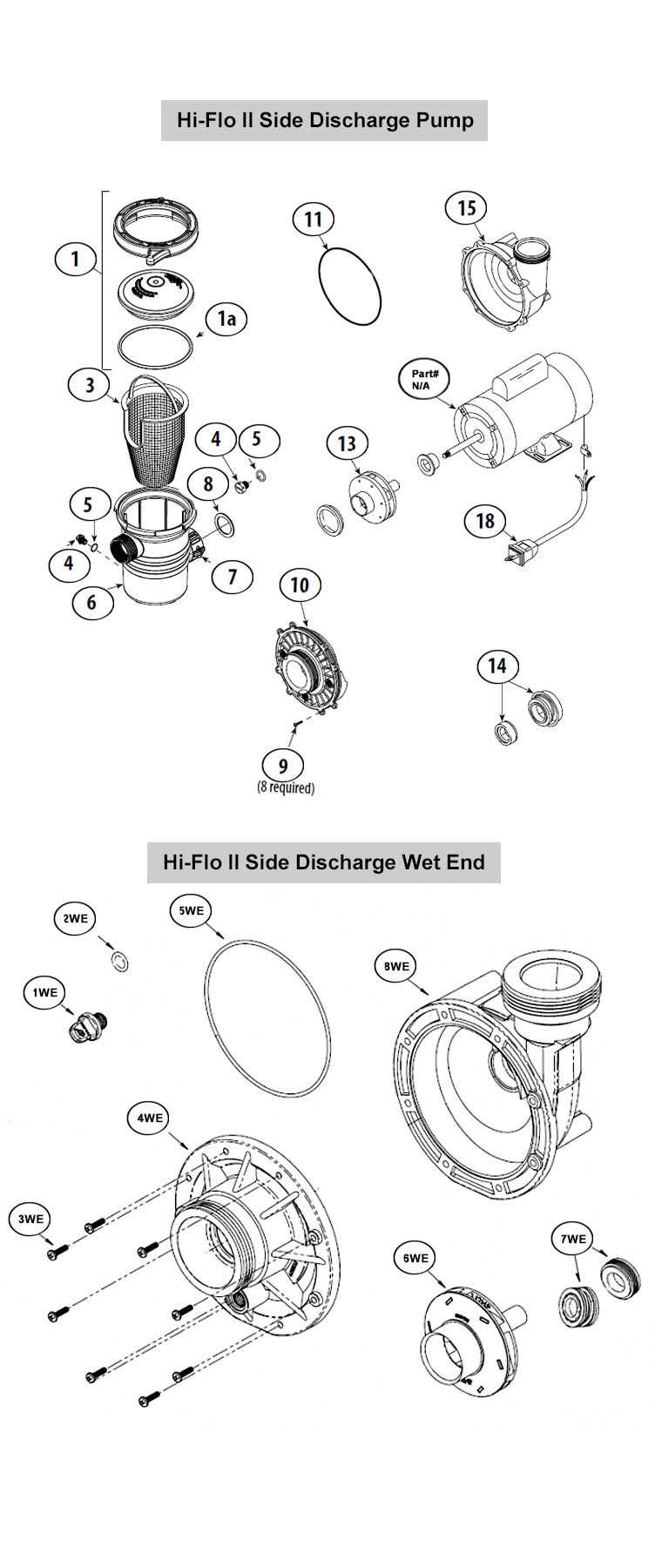
When it comes to maintaining and fixing various systems, having the right equipment is crucial for ensuring effective and efficient repairs. A well-equipped toolkit can significantly streamline the process and enhance the overall outcome, allowing for timely interventions and minimizing downtime.
Here is a list of essential tools that are commonly required for these types of maintenance tasks:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Screwdriver Set | Used for loosening and tightening screws in assembly and disassembly. |
| Wrench Set | Necessary for gripping, fastening, and turning various fittings and components. |
| Pliers | Helpful for holding and bending materials as well as removing stubborn parts. |
| Socket Set | Provides versatility for working with different bolt sizes and types. |
| Sealant | Used for ensuring airtight and watertight seals during reassembly. |
| Cleaning Supplies | Essential for maintaining cleanliness and proper functionality of components. |
| Lubricants | Facilitate smooth operation of moving parts by reducing friction. |
| Safety Gear | Protective equipment like gloves and goggles to ensure safe working conditions. |
Choosing Quality Replacement Parts
When it comes to maintaining your system, selecting high-grade components is essential for ensuring longevity and optimal performance. The right choices can significantly impact efficiency and reliability, while subpar alternatives may lead to frequent failures and additional costs. This guide outlines key considerations for identifying superior replacements.
Key Considerations
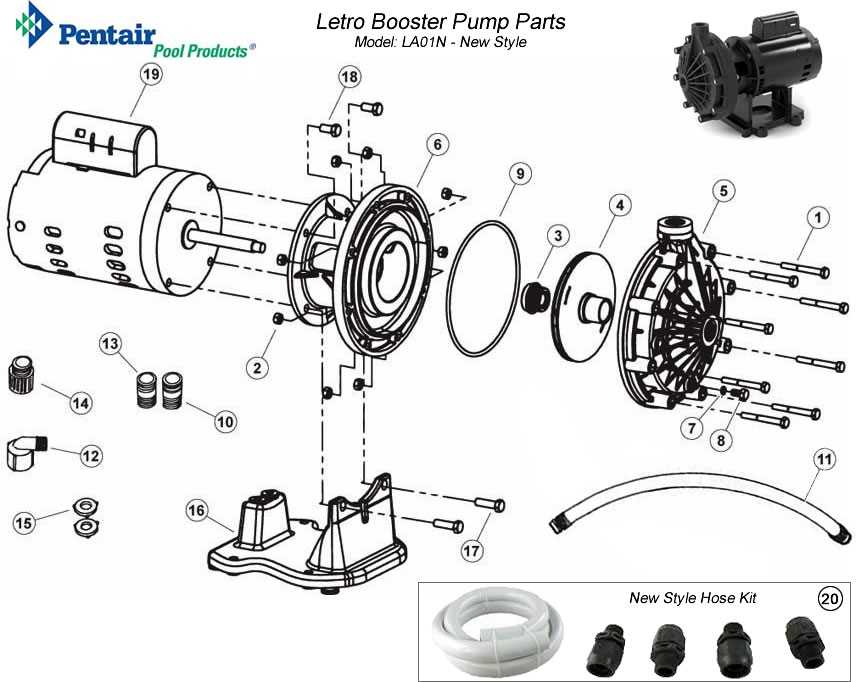
Before making a purchase, assess the following factors to guarantee that your selections meet quality standards:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Quality | Opt for components made from durable materials that resist wear and corrosion. |
| Compatibility | Ensure that the chosen items are fully compatible with your existing setup to avoid operational issues. |
| Manufacturer Reputation | Research manufacturers with a proven track record in producing reliable and high-performance components. |
| Warranty | Look for items that come with a warranty, indicating confidence in their durability and functionality. |
Conclusion
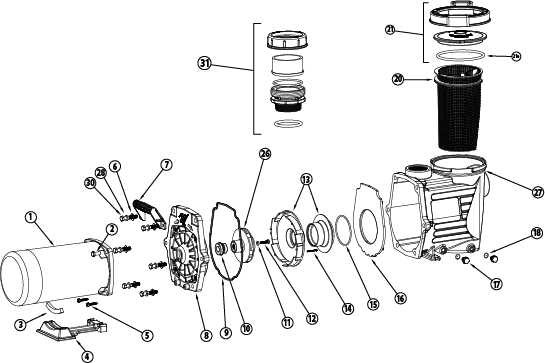
Investing time in selecting high-quality components pays off in the long run. Prioritize materials, compatibility, manufacturer credibility, and warranty options to enhance the overall functionality and lifespan of your system.
Trends in Pump Technology Advancements
Recent innovations in fluid transport mechanisms have led to significant improvements in efficiency, sustainability, and automation. As industries seek to optimize their operations, the focus has shifted towards integrating advanced materials, smart controls, and energy-efficient designs. These trends not only enhance performance but also contribute to reducing environmental impact.
One of the most notable advancements is the adoption of smart technology. Incorporating sensors and IoT capabilities allows for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and extending equipment lifespan. This shift towards connectivity enhances operational insights, enabling users to make informed decisions quickly.
Another critical trend is the development of eco-friendly materials. Manufacturers are increasingly utilizing sustainable options that reduce waste and lower the carbon footprint. Innovations such as biodegradable composites and recycled metals are becoming more common, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Energy efficiency remains a top priority, driving the creation of designs that consume less power while maintaining high output levels. Techniques like variable frequency drives (VFDs) are gaining traction, allowing for precise control of flow rates and reducing energy consumption significantly.
Overall, the ongoing evolution in fluid handling technologies reflects a commitment to efficiency and sustainability, positioning industries for future challenges while supporting environmental stewardship.