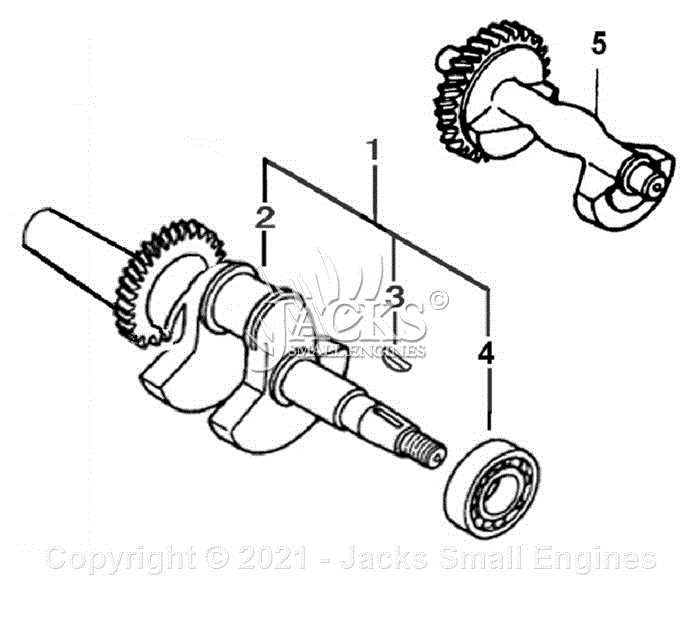
When it comes to ensuring a reliable power source, understanding the intricate elements of a portable energy generator is crucial. This section delves into the various components that contribute to the efficient functioning of these machines, offering insights into their structure and operation.
Each element plays a significant role in maintaining optimal performance, whether it’s the engine that powers the unit, the alternator that converts mechanical energy into electricity, or the control panel that allows users to manage their power supply effectively. By familiarizing yourself with these parts, you can better appreciate how they work together to provide seamless energy solutions during outages or outdoor activities.
This exploration also highlights the importance of regular maintenance and potential replacements, ensuring that your equipment remains in peak condition. A well-informed approach not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of the generator, making it a wise investment for any user seeking dependable energy alternatives.
This section provides a detailed overview of the various elements that constitute a portable power generator. Understanding these components is crucial for both maintenance and troubleshooting. Each part plays a significant role in ensuring efficient operation and reliability.
Key Elements of the Generator
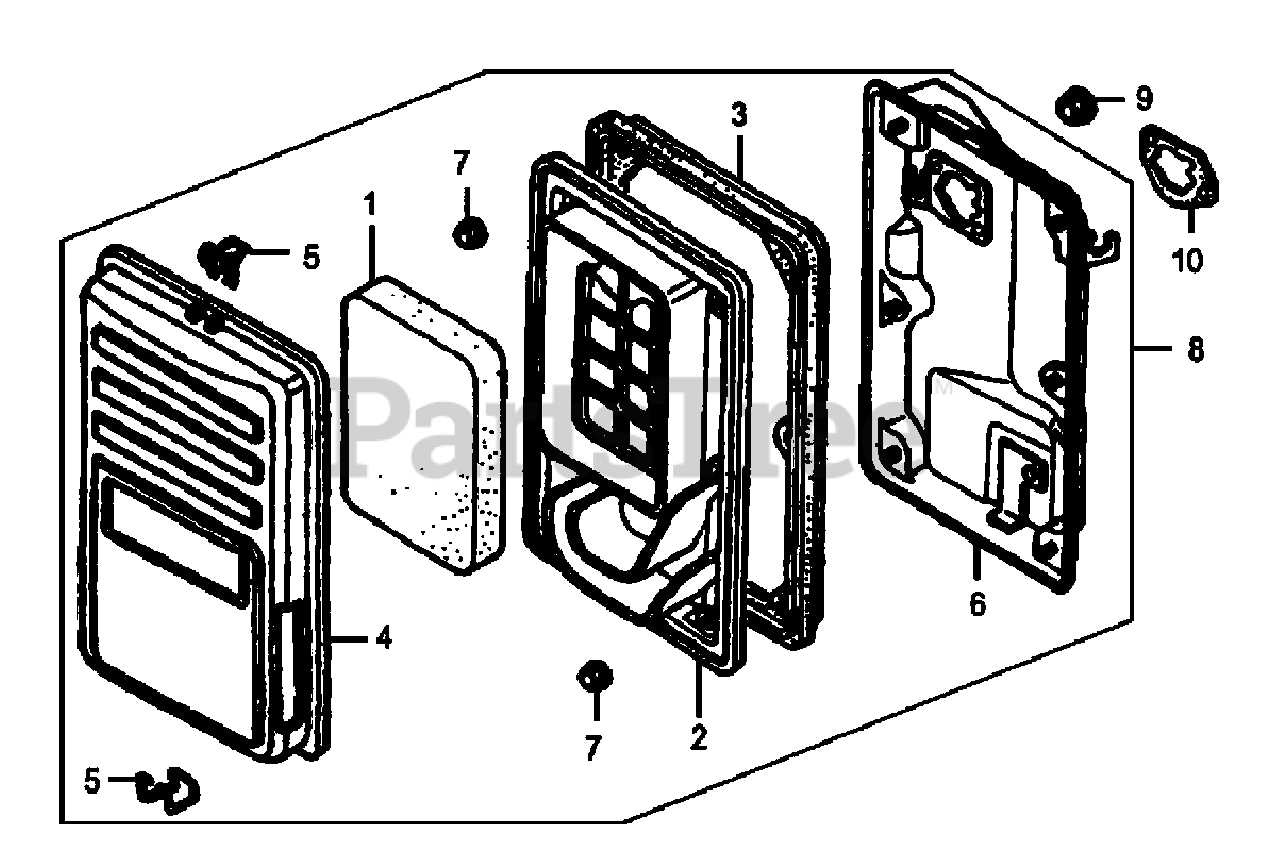
The following table outlines the essential components found within the generator, describing their functions and importance in the overall system.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Engine | The primary source of power generation. | Converts fuel into mechanical energy. |
| Alternator | Transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy. | Supplies electricity to power tools and appliances. |
| Fuel Tank | Stores the fuel required for operation. | Provides the necessary energy to the engine. |
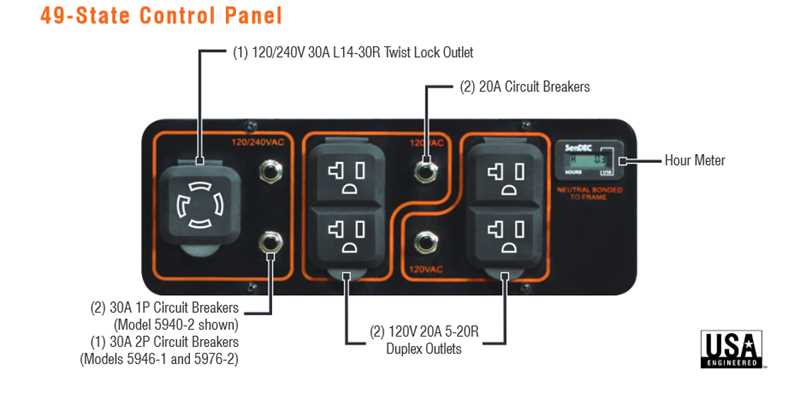
| Control Panel | The interface for operation and monitoring. | Allows users to start/stop the generator and monitor output. |
| Chassis | The framework supporting all components. | Ensures stability and protects internal parts. |
| Cooling System | Regulates the temperature of the engine. | Prevents overheating during operation. |
| Exhaust System | Channels away harmful gases produced during operation. | Improves safety by reducing toxic emissions. |
Understanding these elements is vital for effective maintenance and optimal performance of the equipment. Proper knowledge ensures that users can troubleshoot issues efficiently and enhance the longevity of the machine.
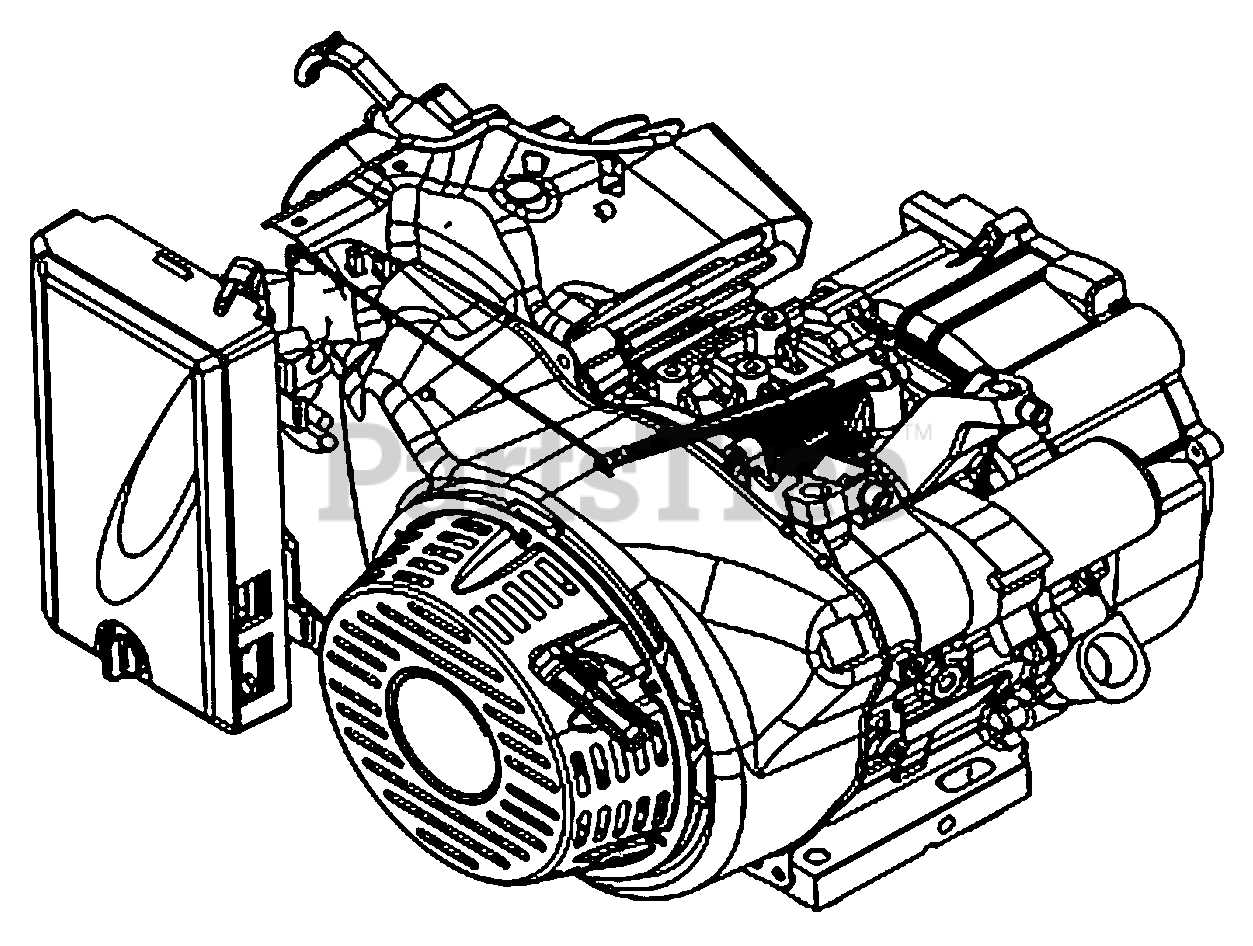
Key Features of the GP6500 Model
This generator model stands out in its class due to its combination of efficiency, reliability, and user-friendly design. Engineered to deliver robust power, it caters to various needs, from home backup to job site use. With a focus on performance and convenience, it ensures that users can depend on it when it matters most.
Power Output and Performance
The unit is equipped with a powerful engine capable of producing ample wattage to run essential appliances during outages or to support tools on worksites. Its ability to handle heavy loads makes it an ideal choice for those requiring consistent performance in demanding situations.
User-Friendly Features

Designed with the user in mind, this generator includes features such as easy-to-read control panels and intuitive start mechanisms. These aspects enhance the overall user experience, allowing for quick setup and operation, even for those unfamiliar with generators. Furthermore, the compact design ensures that it can be easily transported and stored, making it a versatile addition to any toolkit.
Common Issues and Solutions

Operating a portable power generator can sometimes lead to unexpected challenges. Understanding these common problems and their respective solutions can ensure efficient performance and longevity of the unit. Below are some frequent issues encountered by users along with effective remedies.
1. Engine Won’t Start
If the engine fails to start, it can be frustrating. This issue may arise from several factors, including fuel problems, battery issues, or a malfunctioning starter. Here are potential solutions:
| Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
| Insufficient fuel | Check the fuel level and refill if necessary. |
| Dead battery | Test the battery and replace it if it’s no longer functional. |
| Clogged fuel filter | Inspect and replace the fuel filter as needed. |
2. Overheating Issues
Overheating can cause significant damage if not addressed promptly. This problem may result from inadequate ventilation, low oil levels, or debris blocking the cooling system. Here are some solutions:
| Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
| Blocked air intake | Ensure the air intake is clear of obstructions. |
| Low oil level | Check and replenish oil to the recommended level. |
| Dirty spark plug | Clean or replace the spark plug to enhance engine efficiency. |
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the durability and reliability of your equipment requires consistent and proactive care. Regular maintenance not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of your machinery. Below are essential practices to consider for optimal upkeep.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Change | Every 50 hours | Replace the oil and oil filter to ensure proper lubrication and prevent engine wear. |
| Air Filter Check | Every 25 hours | Inspect and clean or replace the air filter to maintain airflow and efficiency. |
| Spark Plug Replacement | Every 100 hours | Replace the spark plugs to ensure smooth ignition and optimal engine performance. |
| Fuel System Cleaning | As needed | Keep the fuel system clean to prevent clogging and ensure proper fuel flow. |
| Battery Maintenance | Monthly | Check the battery charge and connections to ensure reliable starting and operation. |
Implementing these simple yet effective maintenance tasks can significantly improve the reliability of your equipment, allowing for uninterrupted performance and efficiency over time.
Replacement Parts Overview
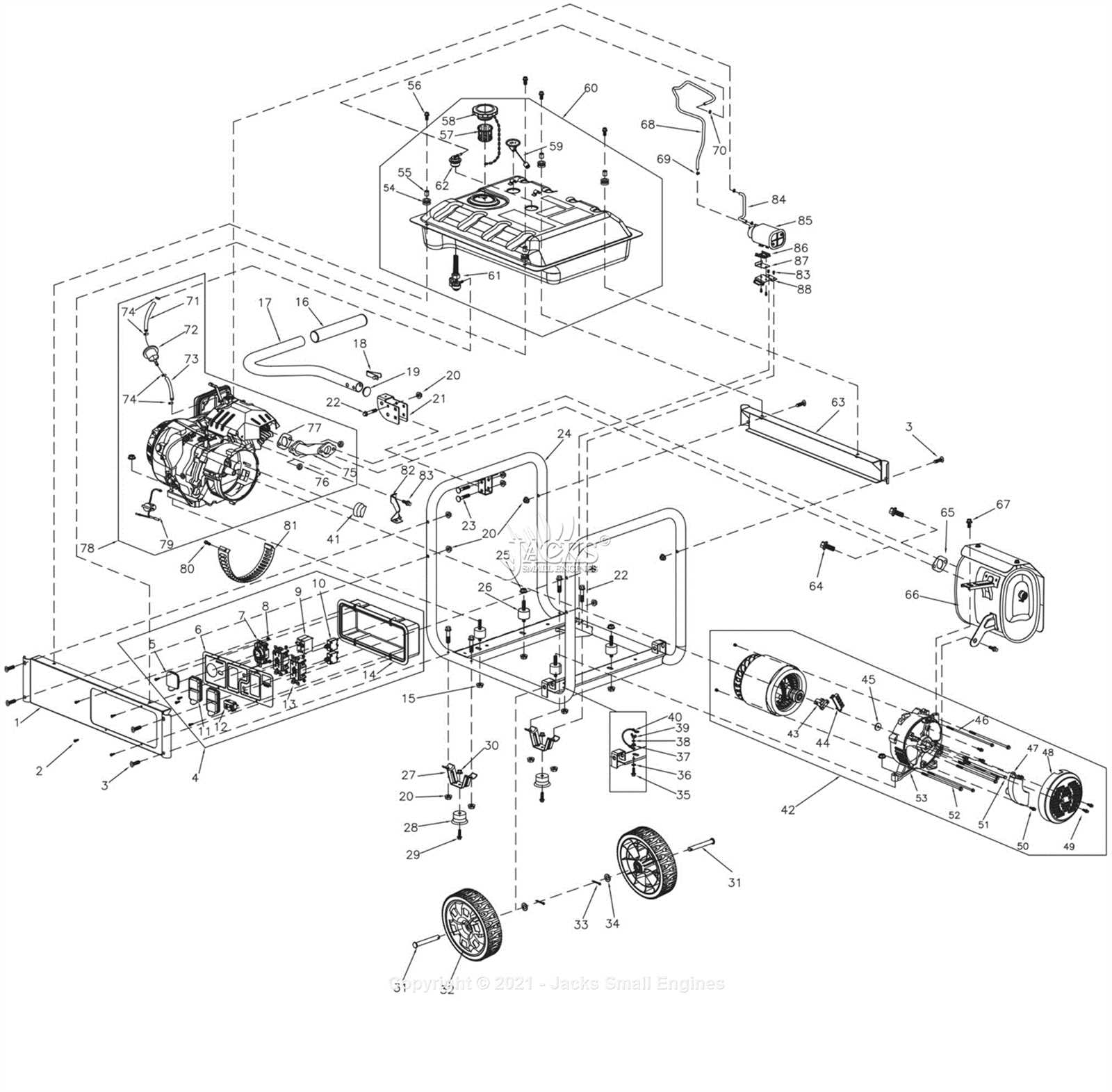
When it comes to maintaining and repairing power generation equipment, understanding the available components is essential. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the necessary elements that ensure optimal performance and reliability. Whether it’s for routine maintenance or unexpected repairs, knowing which components can be replaced helps extend the lifespan of the equipment and enhance its efficiency.
Commonly Required Components
Several key elements are frequently required for maintenance and repair tasks. These include items such as fuel tanks, filters, and starter motors. Each of these components plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of the equipment, and having access to quality replacements can significantly impact performance. Properly functioning filters are vital for maintaining clean fuel flow, while a reliable starter motor is essential for ensuring smooth ignition.
Quality and Compatibility
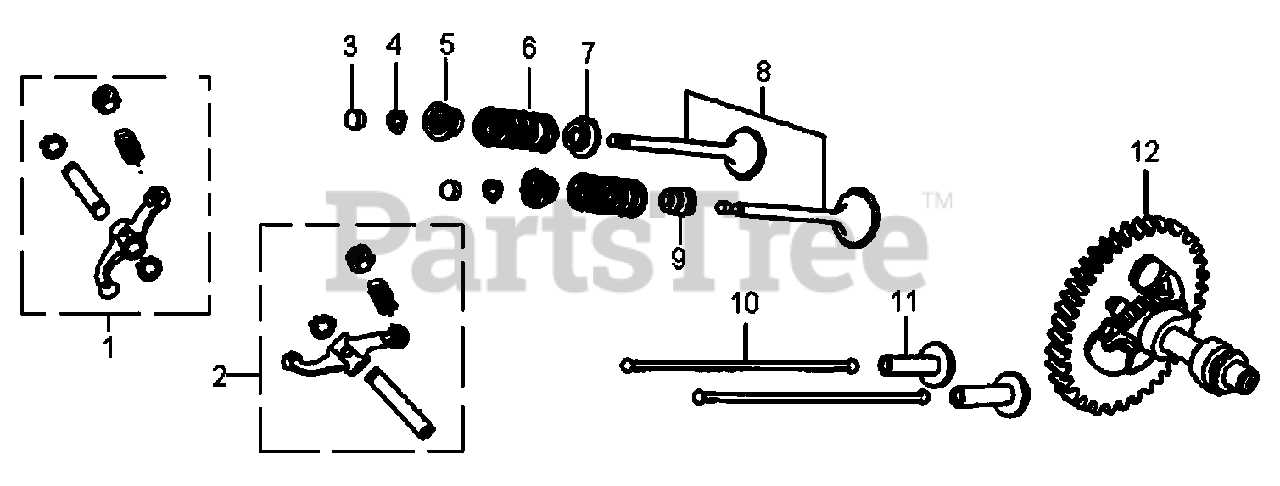
When selecting replacement components, it is important to consider both quality and compatibility. Opting for high-quality parts ensures durability and longevity, while ensuring that the components are compatible with the specific model guarantees optimal performance. Researching and sourcing components from reputable suppliers can help users avoid potential issues that arise from substandard or mismatched parts.
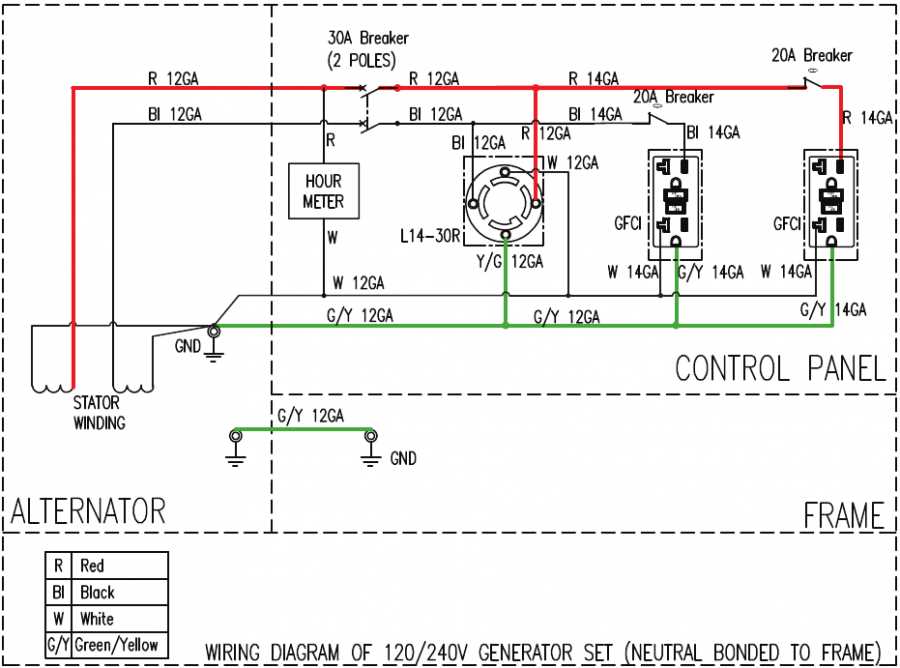
Identifying Electrical Components
Understanding the various electrical components within a power generator is essential for efficient operation and maintenance. Recognizing these elements helps users troubleshoot issues, perform repairs, and ensure safety during usage. This section will guide you through the primary electrical components commonly found in portable generators.
- Alternator: This component generates electrical energy by converting mechanical energy. It is crucial for providing power to connected devices.
- Voltage Regulator: Responsible for maintaining a consistent output voltage, this part protects electrical devices from voltage fluctuations.
- Starter Motor: This motor initiates the engine’s operation. A reliable starter is vital for the generator’s functionality.
- Fuel System: This includes the fuel tank, lines, and filters that supply fuel to the engine. Proper maintenance of this system ensures optimal performance.
- Control Panel: The interface for the user, it typically includes gauges and switches to monitor and manage the generator’s operations.
- Battery: Provides the necessary power to start the generator. A well-maintained battery is crucial for reliable performance.
- Wiring Harness: Connects all electrical components, facilitating communication between them. Proper wiring is essential for safety and efficiency.
By familiarizing yourself with these essential elements, you can enhance your understanding of how the equipment operates and address potential issues effectively.
Fuel System and its Components
The fuel system is a crucial element in any engine, responsible for delivering the right amount of fuel to ensure optimal performance. This system includes several interconnected parts that work together to store, transport, and regulate fuel supply. Understanding these components helps in diagnosing issues and maintaining efficiency.
Key Components of the Fuel System
- Fuel Tank: Stores fuel safely and provides a reservoir for the system.
- Fuel Pump: Transfers fuel from the tank to the engine, ensuring a steady supply.
- Fuel Filter: Removes impurities and debris from the fuel before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel Lines: Flexible hoses that transport fuel between components, designed to withstand pressure.
- Carburetor: Mixes fuel with air for combustion, crucial for engine performance.
Functionality and Maintenance
Each component plays a vital role in the overall functionality of the fuel system. Regular maintenance, including filter replacement and checking for leaks, is essential to ensure the longevity and reliability of the system. Neglecting these parts can lead to performance issues and increased fuel consumption.
Safety Mechanisms in Generac GP6500
Safety features play a crucial role in ensuring the reliable operation of power equipment. These mechanisms are designed to prevent accidents and protect users from potential hazards. In the case of portable generators, a variety of safeguards are integrated to enhance user safety and equipment longevity.
One of the primary safety components is the overload protection system, which automatically shuts down the generator when it exceeds its load capacity. This feature helps prevent overheating and potential damage to both the unit and connected devices. Additionally, an automatic voltage regulation system ensures that the output remains stable, safeguarding sensitive electronics from power surges.
Another significant aspect is the inclusion of low oil shutdown. This mechanism detects when oil levels drop below a safe threshold, triggering an automatic engine shutdown to prevent severe engine damage. Furthermore, safety indicators and warning lights provide users with critical information regarding the operational status, allowing for timely maintenance and intervention.
Finally, the presence of robust housing and grounding features further enhances safety. These elements protect users from electric shock and ensure stable operation on various surfaces. By incorporating these essential mechanisms, the equipment promotes safe usage and peace of mind for operators.
How to Read Parts Diagrams
Understanding component illustrations is essential for effective maintenance and repair of various equipment. These visual representations provide a clear layout of the different elements, their arrangement, and how they interact within the machinery. By familiarizing yourself with the structure of these illustrations, you can enhance your ability to troubleshoot issues and order the necessary components.
Key Elements of Component Illustrations

- Labels: Each part typically has a unique identifier or label associated with it, which helps in pinpointing the exact component needed.
- Numbers: Numerical designations often correspond to a list of items, detailing specifications and quantities.
- Lines: Connecting lines may indicate relationships or assembly order between different elements.
Steps for Decoding Illustrations
- Start by identifying the legend or key, which explains symbols and labels used throughout the representation.
- Familiarize yourself with the layout to understand how components fit together.
- Cross-reference labeled parts with the accompanying list to ensure correct identification.
- Use the information to assess the condition of each component and plan for any necessary replacements.