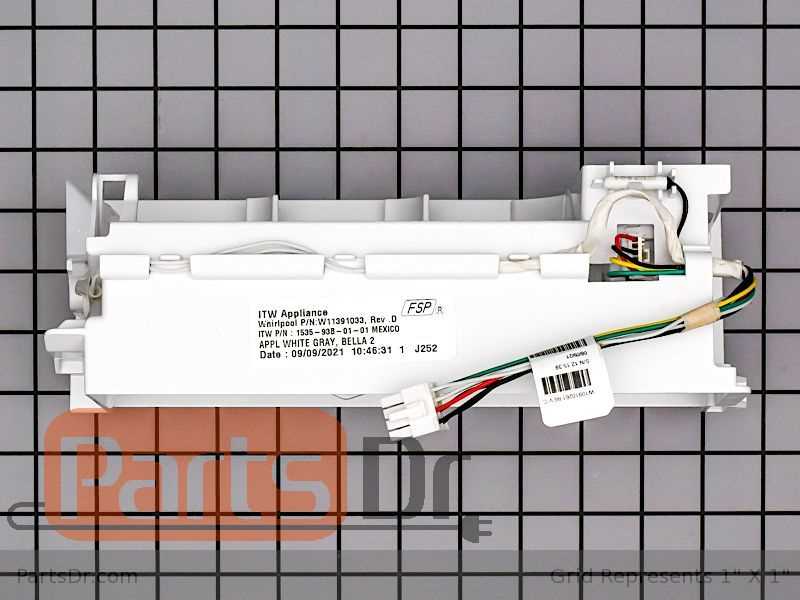
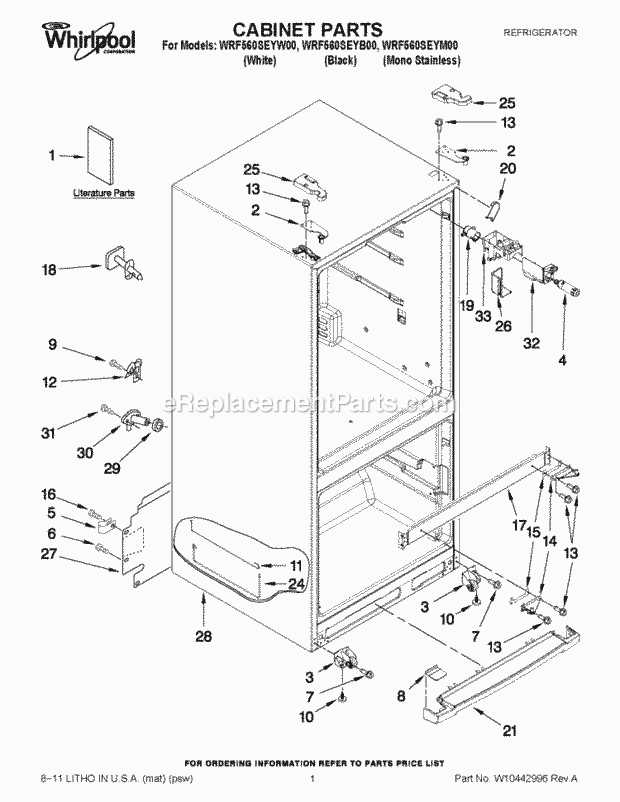
Modern cooling devices have evolved to include various advanced functionalities that simplify daily life. One such feature plays a crucial role in enhancing the overall user experience by offering a convenient way to handle specific tasks within the unit. In this section, we will explore the essential elements that contribute to the smooth operation of this function, focusing on the mechanics behind its reliable performance.
Key elements involved in this process are carefully designed to ensure efficiency and durability. These components are engineered to work together seamlessly, each playing a specific role in the overall functionality. Whether you’re troubleshooting or performing maintenance, understanding the interaction between these core parts can help you keep your device running smoothly for years to come.
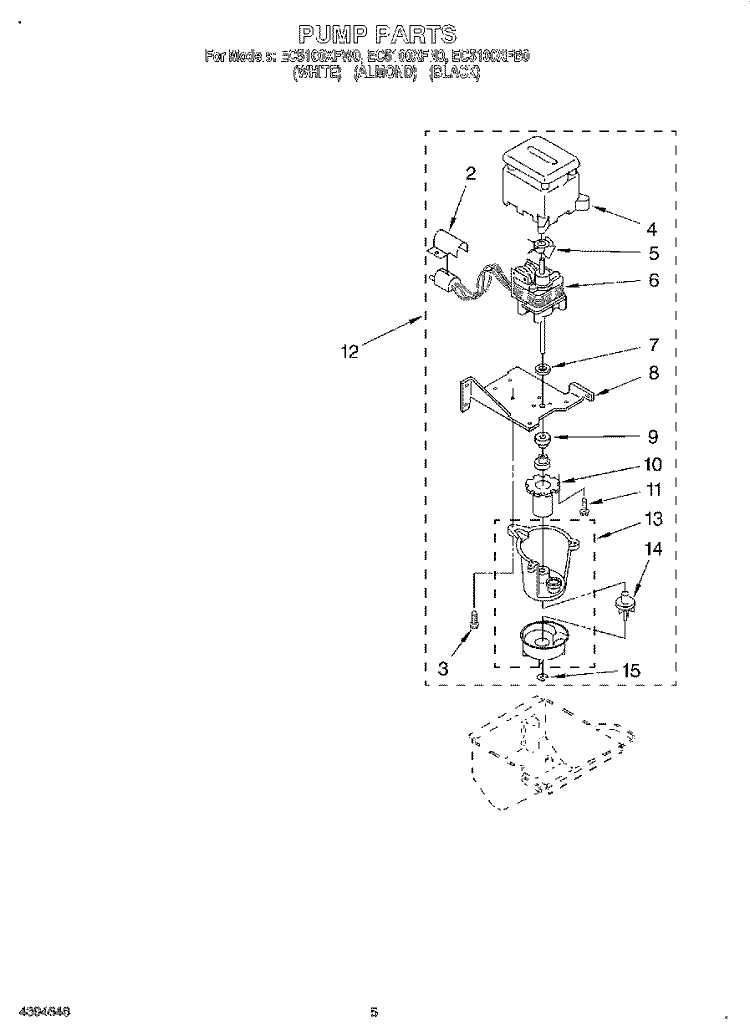
Overview of the Automatic Cooling System Component
The automatic cooling system includes a key feature that enables the efficient production and distribution of frozen water within a household cooling unit. This mechanism operates independently, providing convenience and a steady supply of frozen cubes for daily use. Its design incorporates advanced technology, ensuring reliability and minimal maintenance over time.
Main Functions
- Ensures consistent production of frozen water elements
- Automatically refills and regulates the cooling process
- Integrates with the unit’s temperature control system
Key Components
- Cooling mechanism for freezing the liquid
- Dispenser for easy retrieval
- Control panel for adjusting settings
These essential components work together to create a seamless and efficient process, ensuring that frozen
Understanding the Ice Maker Mechanism
The mechanism responsible for creating frozen cubes in a cooling unit relies on a carefully coordinated process of water intake, freezing, and release. This system ensures that the water is consistently delivered to a tray, where it solidifies before being ejected into a storage bin. Each component works in unison to maintain the seamless production of frozen cubes.
Key Components of the System
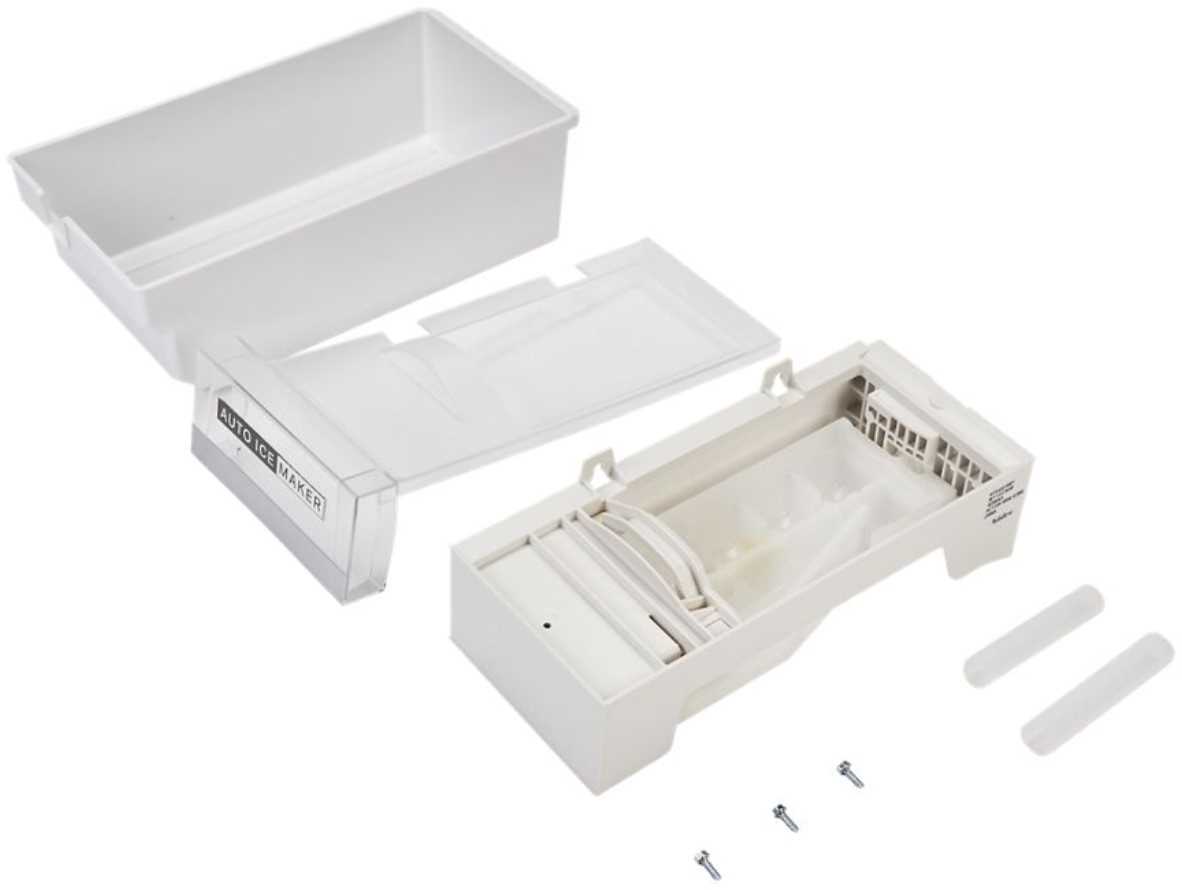

The core of the freezing mechanism involves several critical parts. A water valve controls the flow of water into the system, while the freezing tray holds the liquid until it reaches the proper temperature. Once frozen, a motorized arm or similar component is triggered to release the solidified cubes into a collection area. This process repeats continuously, ensuring a steady supply.
Automatic Cycle and Temperature Control
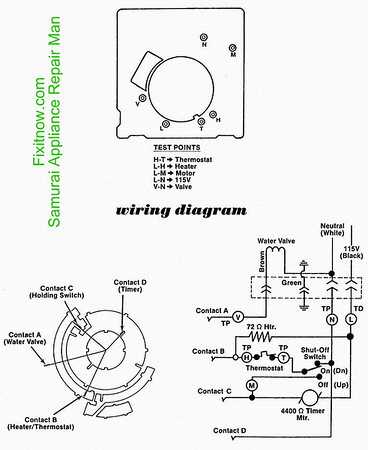
The freezing mechanism operates on an automatic cycle, designed to detect when cubes have been formed and when more water is needed. Sensors within the unit monitor the temperature and ensure that the cubes are released at the right moment. Proper functioning of these sensors is essential for efficient operation, as any disruption could affect the timi
Key Components of the Ice Maker
Understanding the essential elements of the device that produces frozen cubes helps in troubleshooting and maintaining its functionality. Each component plays a crucial role in the process, ensuring efficient operation and consistent results.
- Control Module: This element governs the entire process, coordinating the freezing cycle and ensuring proper timing for dispensing.
- Water Inlet Valve: Responsible for managing the water flow, this valve opens and closes at the right moments to fill the trays with water.
- Thermostat: Monitoring the temperature, the thermostat triggers the freezing cycle once the water reaches the appropriate temperature.
- Heater: To release the frozen cubes, the heater slightly warms the trays, making it easier for the cubes to drop into the storage area.
- Ejector Blades: These blades help push the frozen cubes out of the mold and into the collection bin.
- Water inlet valve: A solenoid valve regulates the flow of water. When needed, it opens to allow water to pass through.
- Water supply line: This is a narrow tube that connects the valve to the freezing section, carrying the water in a controlled manner.
- Fill tube: Water is delivered through a small tube into the tray, where it will be frozen into cubes.
- Unplug the appliance and allow it to thaw if necessary.
- Remove any remaining frozen cubes and empty the water reservoir.
- Use a mixture of warm water and mild detergent to wipe down the interior surfaces.
- Rinse thoroughly with clean water to avoid any detergent residue.
- Dry all surfaces with a clean cloth before reassembling.
- Inspect the water supply line for leaks or kinks.
- Check the filters regularly and replace them as needed.
- Ensure the unit is level to prevent operational issues.
- Monitor the temperature settings for optimal freezing conditions.
How Water is Supplied to the Ice Maker
For the automatic production of frozen cubes, a steady and reliable water supply is essential. The process begins with a connection to the household’s plumbing system, ensuring that fresh water can flow through the necessary components. This supply system works through several steps, ensuring that the liquid reaches the freezing unit efficiently.
The water flow is carefully controlled to ensure that the freezing compartment is filled only to the required level. Any excess water is prevented from entering through the use of sensors and other control mechanisms. This ensures efficiency and prevents leaks or overflows.
Electrical Connections in the Ice Maker System
The electrical system in the cooling unit responsible for producing frozen cubes is a crucial part of its overall operation. The connections ensure that the necessary components function in harmony, delivering power to essential modules and maintaining proper operation. Understanding the wiring and electrical pathways is key to diagnosing potential issues and ensuring smooth performance.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Control Module | Manages the overall process and communicates with the main control system. |
| Water Valve | Regulates the flow of water to the freezing compartment. |
| Heating Element | Prevents the freezing mechanism from getting stuck during operation. |
| Thermostat | Monitors and controls the temperature within the freezing system. |