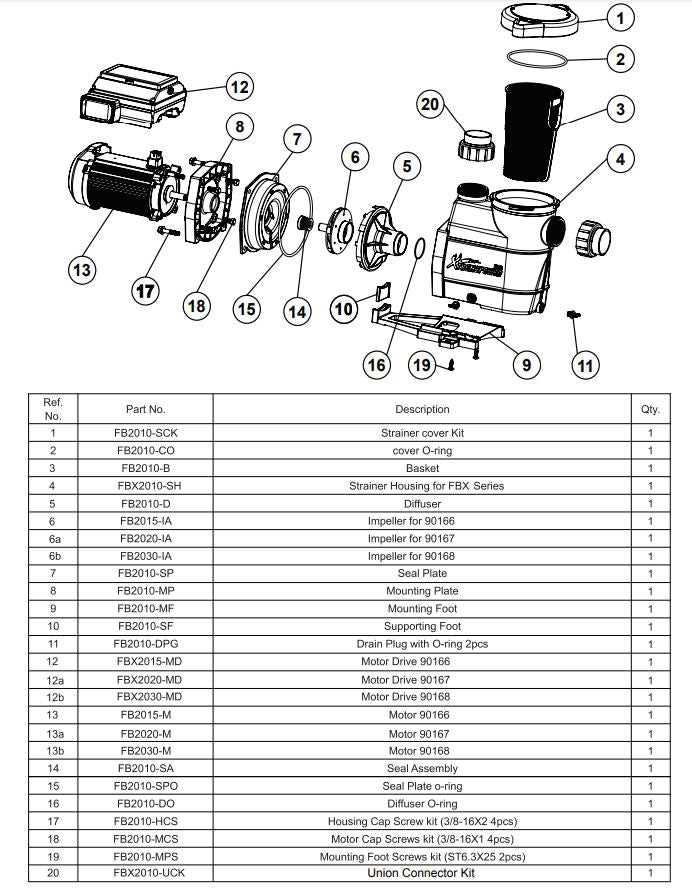
The efficiency of any system designed for the movement of liquids relies heavily on its individual elements and their interactions. A comprehensive grasp of how these components function together can enhance performance and reliability, making it crucial for engineers and technicians alike to familiarize themselves with these intricate designs.
In this section, we delve into the intricate layout of essential components that facilitate the seamless transfer of liquids. By dissecting each element, we can uncover the specific roles they play and the significance of their arrangement, which is vital for optimal functionality.
Furthermore, visual representations serve as valuable tools in understanding these mechanisms. They provide clarity on how each segment contributes to the overall operation, aiding in troubleshooting, maintenance, and improvements. Exploring these visuals allows for a deeper appreciation of the complexity involved in liquid conveyance systems.
Understanding Water Pump Components
Grasping the essential elements of a fluid-moving device is crucial for efficient operation and maintenance. Each component plays a significant role in ensuring optimal performance, and familiarity with their functions can enhance both longevity and effectiveness.
Key elements include:
- Impeller: This rotating element is vital for creating flow and pressure within the system.
- Volute: A casing that helps direct the flow from the impeller, maximizing efficiency.
- Seal: Prevents leakage and maintains pressure within the system.
- Suction Strainer: Filters debris from the fluid, protecting internal components from damage.
- Motor: Provides the necessary power to drive the impeller and initiate movement.
- Bearing: Supports rotating parts, ensuring smooth operation and reducing friction.
Understanding how these components interact is essential for troubleshooting and ensuring reliable function. Regular inspection and maintenance of each element can prevent common issues and extend the lifespan of the entire system.
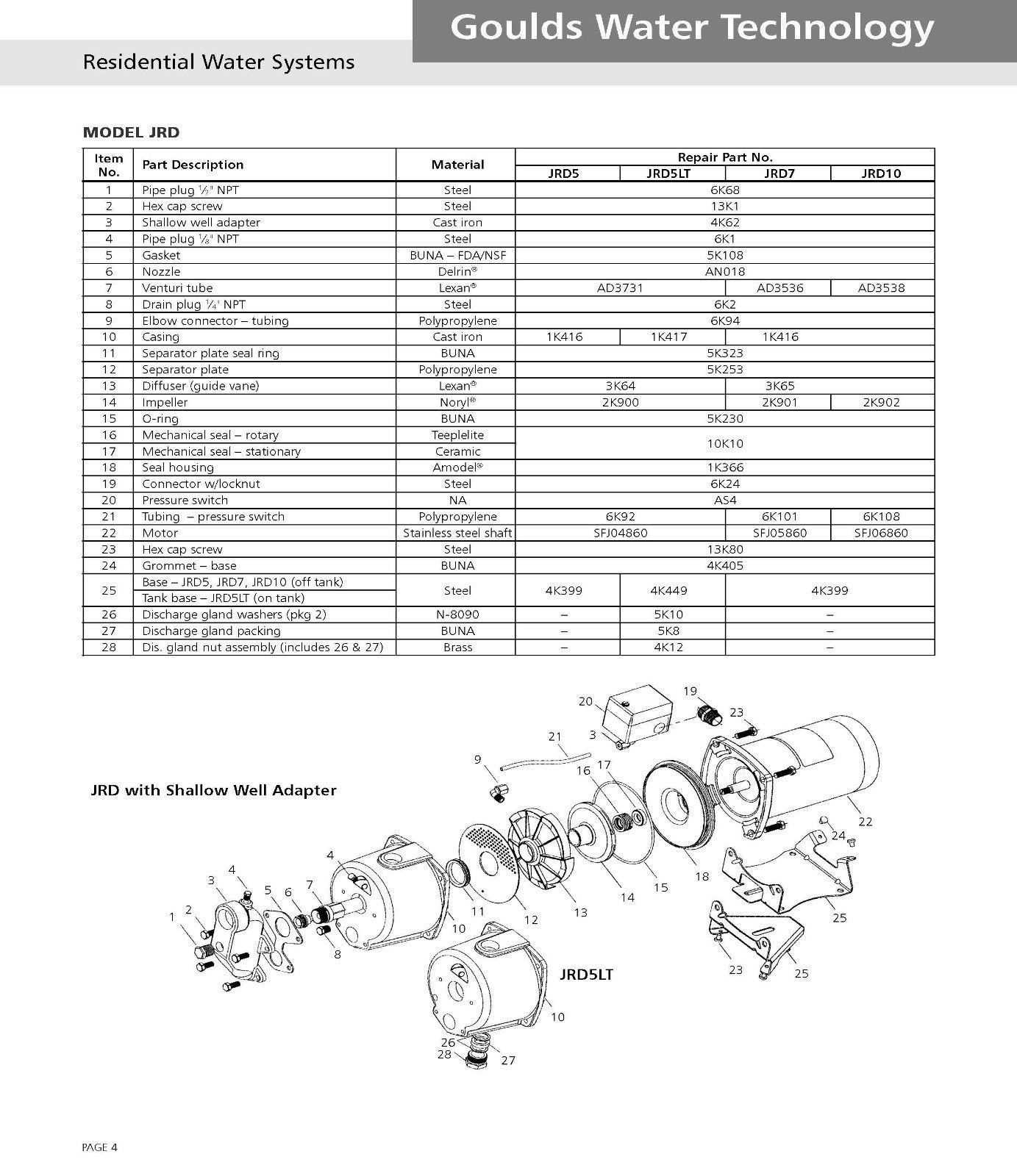
Types of Water Pumps Explained
Understanding the various mechanisms used to move liquids is essential for effective application across different industries. Each design serves a unique purpose and is optimized for specific tasks, showcasing distinct operational principles and efficiencies.
Centrifugal Systems utilize rotational energy to propel fluids. These systems are ideal for applications requiring high flow rates at relatively low pressures. They operate by converting kinetic energy into potential energy, making them widely favored in residential and commercial scenarios.
Positive Displacement Units function by trapping a fixed amount of liquid and forcing it into the discharge pipe. This method is particularly effective for high-viscosity substances and applications that demand consistent flow regardless of pressure variations. Examples include gear and diaphragm mechanisms, each suited for specific contexts.
Submersible Designs are specifically engineered to function while submerged in the fluid being moved. These units are commonly used for draining and sewage applications, where reliability and efficiency are paramount. Their unique construction allows for seamless operation without the need for external components.
Peristaltic Mechanisms work by compressing a flexible tube, effectively pushing the fluid through a series of rollers. This design is often employed in precise dosing applications and is known for its ability to handle shear-sensitive liquids without contamination.
Each of these types has its advantages and limitations, making it crucial to select the appropriate mechanism based on specific requirements and environmental conditions. Understanding these differences enhances operational efficiency and reliability in fluid management systems.
Key Parts of a Water Pump
Understanding the essential components of a fluid-moving device is crucial for effective maintenance and operation. Each element plays a significant role in ensuring efficient performance and longevity of the system. In this section, we will explore the primary elements that contribute to the functionality of such mechanisms.
Impeller: This rotating component is fundamental for creating the flow of the liquid. Its design impacts the efficiency and pressure generated.
Casing: The outer structure houses and protects the internal components, maintaining pressure and directing the fluid flow.
Suction and Discharge Ports: These openings facilitate the entry and exit of the liquid, allowing for seamless operation and transfer.
Seal: A critical element that prevents leaks, ensuring that the fluid remains contained within the system during operation.
Motor: The driving force behind the mechanism, this element powers the impeller and dictates the overall speed and efficiency.
By delving into these components, one can appreciate the intricate design and functionality that enable effective liquid transfer in various applications.
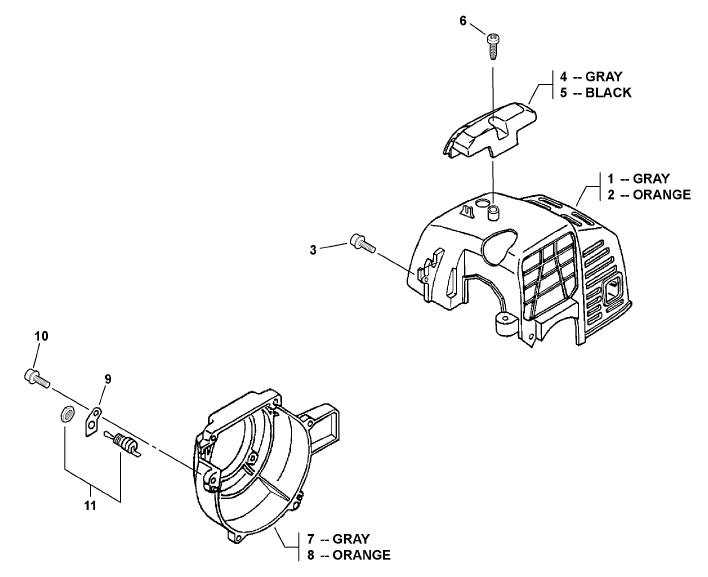
Functionality of Pumping Mechanisms
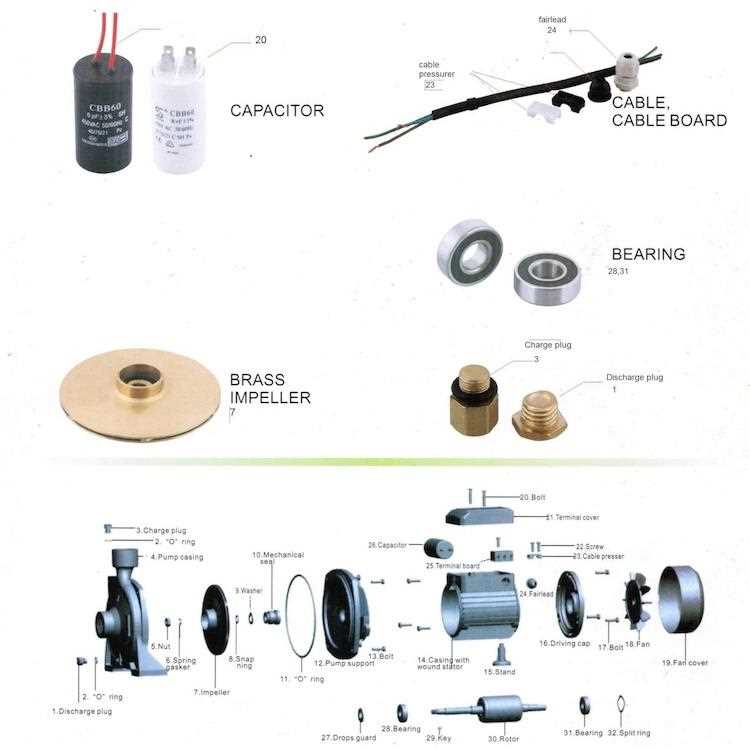
The operation of fluid-moving systems relies on a series of interconnected elements designed to facilitate the transfer of liquids from one location to another. Understanding the intricacies of these mechanisms is crucial for ensuring efficient performance and longevity of the overall assembly. Each component plays a vital role in creating the necessary pressure and flow dynamics.
Key Components and Their Roles
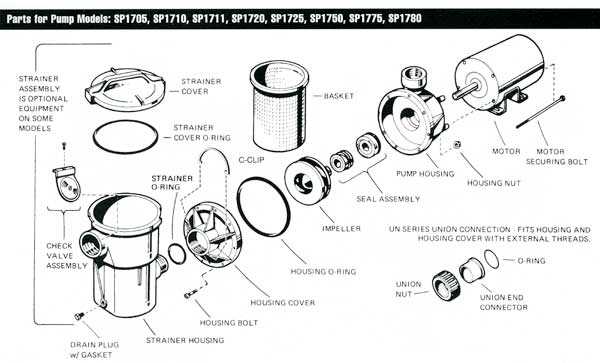
At the heart of these systems lies a series of elements that work harmoniously to achieve fluid movement. The impeller generates kinetic energy, converting it into fluid motion, while the casing contains and directs the flow, optimizing efficiency. Additionally, seals and bearings minimize friction, ensuring smooth operation and preventing leakage.
Operational Efficiency and Maintenance
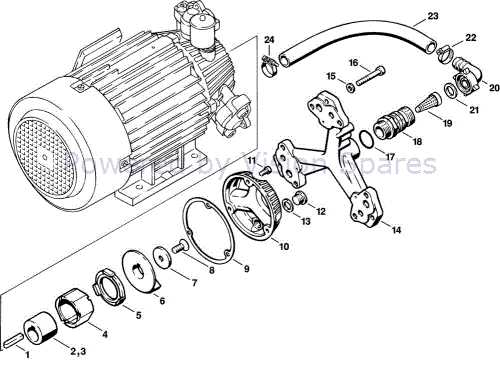
To maintain peak efficiency, regular inspection and maintenance of these components are essential. Issues such as wear and tear can significantly impact performance, leading to reduced flow rates and increased energy consumption. Implementing a proactive maintenance schedule ensures that each element continues to function optimally, prolonging the lifespan of the entire assembly.
Common Issues with Water Pumps
Several challenges can arise when dealing with the machinery responsible for circulating fluid in various systems. These issues can affect efficiency, leading to unwanted downtime or even complete failure if not addressed properly.
1. Overheating
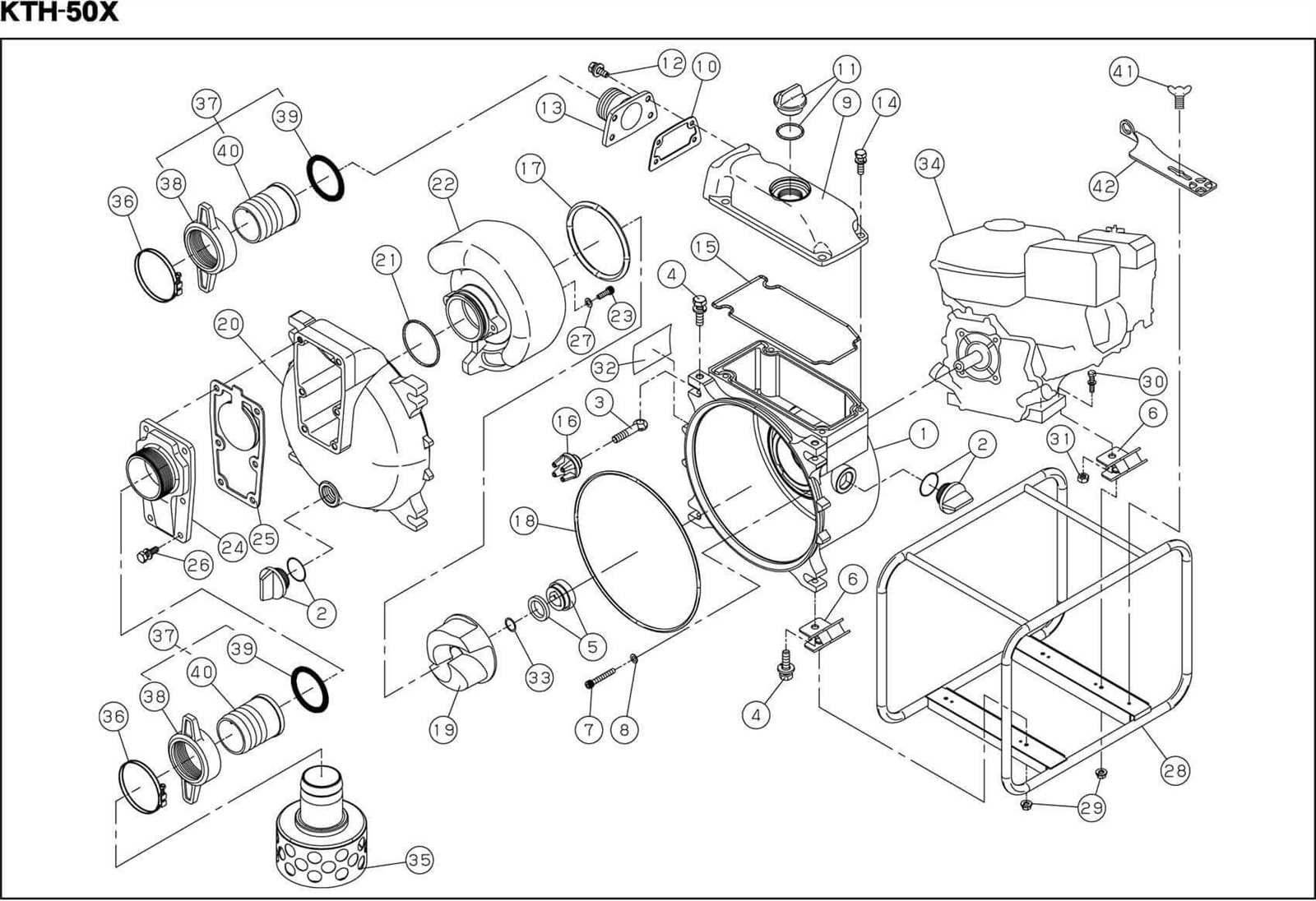
One of the most frequent problems is excessive temperature buildup. When the cooling mechanism is not functioning properly, it can lead to the system’s core components becoming too hot, potentially causing irreversible damage.
2. Leakage
Another common issue is the presence of leaks. These can stem from faulty seals or worn-out connections, resulting in the escape of the fluid. This not only reduces operational capacity but also puts the system at risk of malfunctioning.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
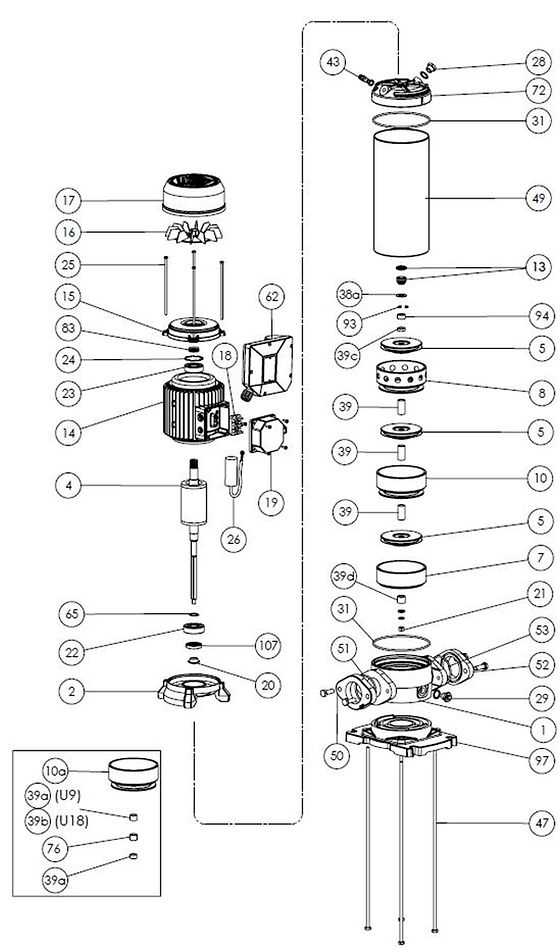
Ensuring the long-term performance of mechanical systems requires consistent care and attention. Regular maintenance helps avoid premature wear and ensures efficient operation over time. By following a few key practices, you can extend the lifespan of your equipment and minimize the need for costly repairs.
- Routine Inspections: Regularly check all components for signs of wear or damage. Identifying issues early prevents bigger problems later.
- Clean Regularly: Keep the internal mechanisms clean from debris and contaminants. This reduces strain and keeps the system running smoothly.
- Check for Leaks: Inspect connections and seals to prevent any leaks, which can lead to reduced efficiency and potential damage.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication is essential for reducing friction and preventing premature wear of moving elements.
- Monitor Performance: Keep track of the system’s performance, noting any irregularities or changes that could indicate the need for maintenance.
Adopting these habits will help you maximize the lifespan and efficiency of your system, ensuring it operates at its best for years to come.
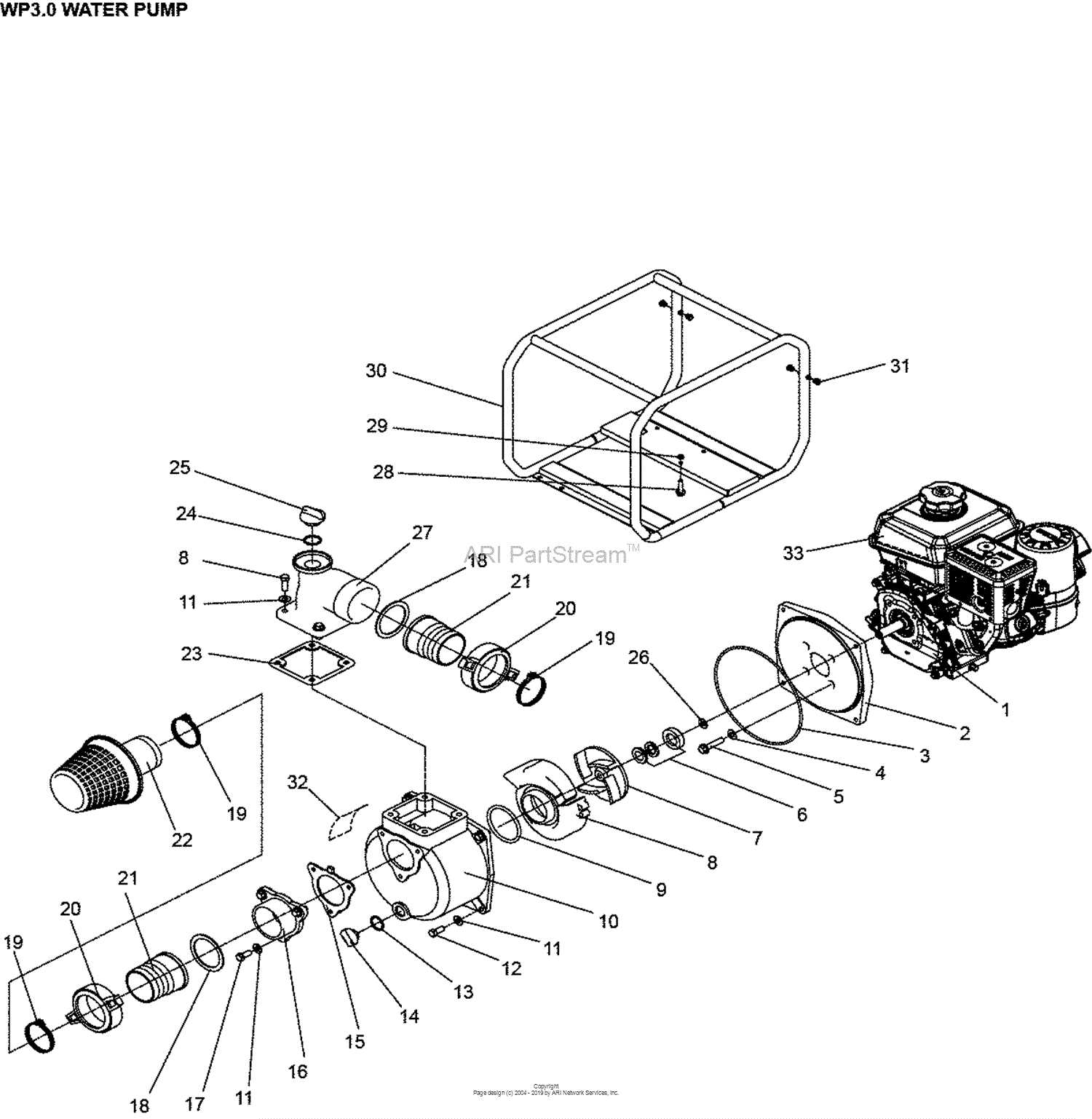
How to Read a Parts Diagram
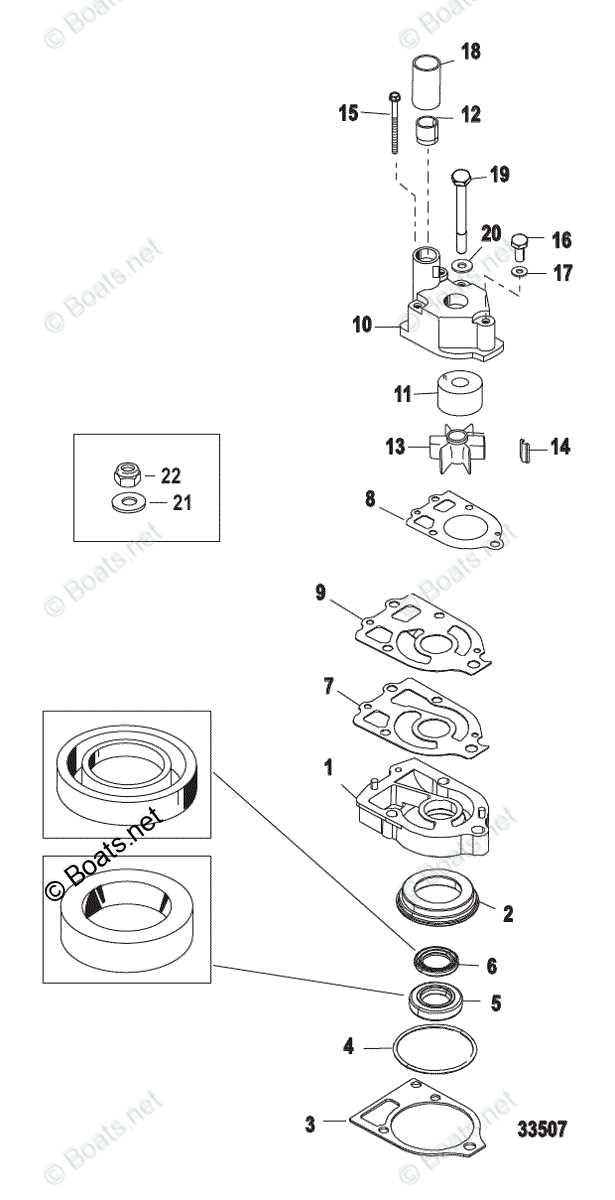
Understanding the layout of components within a mechanical system is essential for efficient maintenance and assembly. Each element is represented in a clear and organized manner, providing a visual guide to their arrangement and interaction. Mastering the interpretation of these visuals allows for easier identification of the individual elements, their functions, and their proper connections.
Identifying Key Symbols and Labels
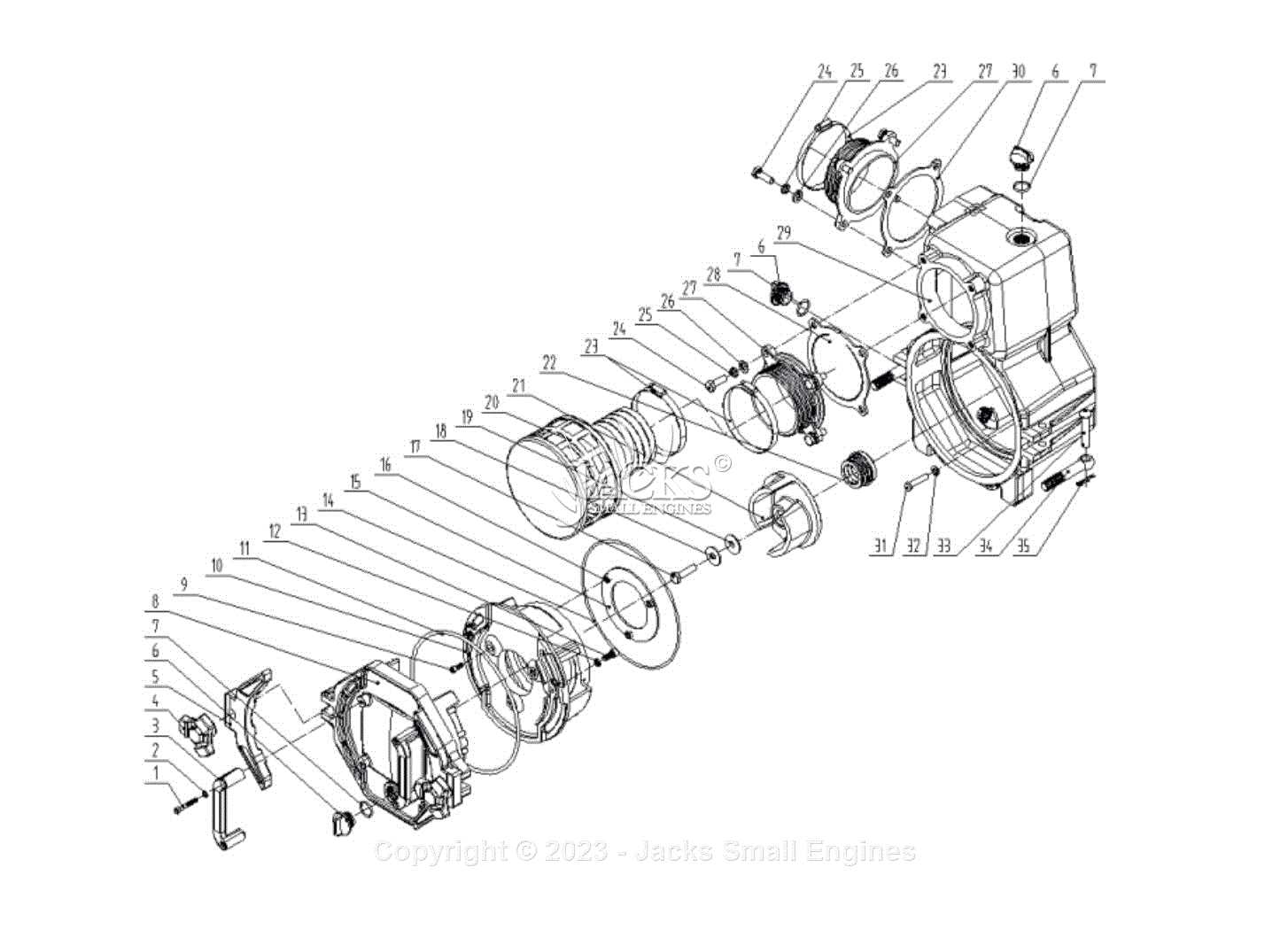
Each component in the visual representation is marked with specific symbols or labels that correspond to their respective names and functions. These symbols often use standardized shapes to depict different types of elements, making it easier to distinguish between them. The labels provide crucial information about size, material, or orientation, aiding in precise assembly or troubleshooting.
Understanding the Flow and Connections
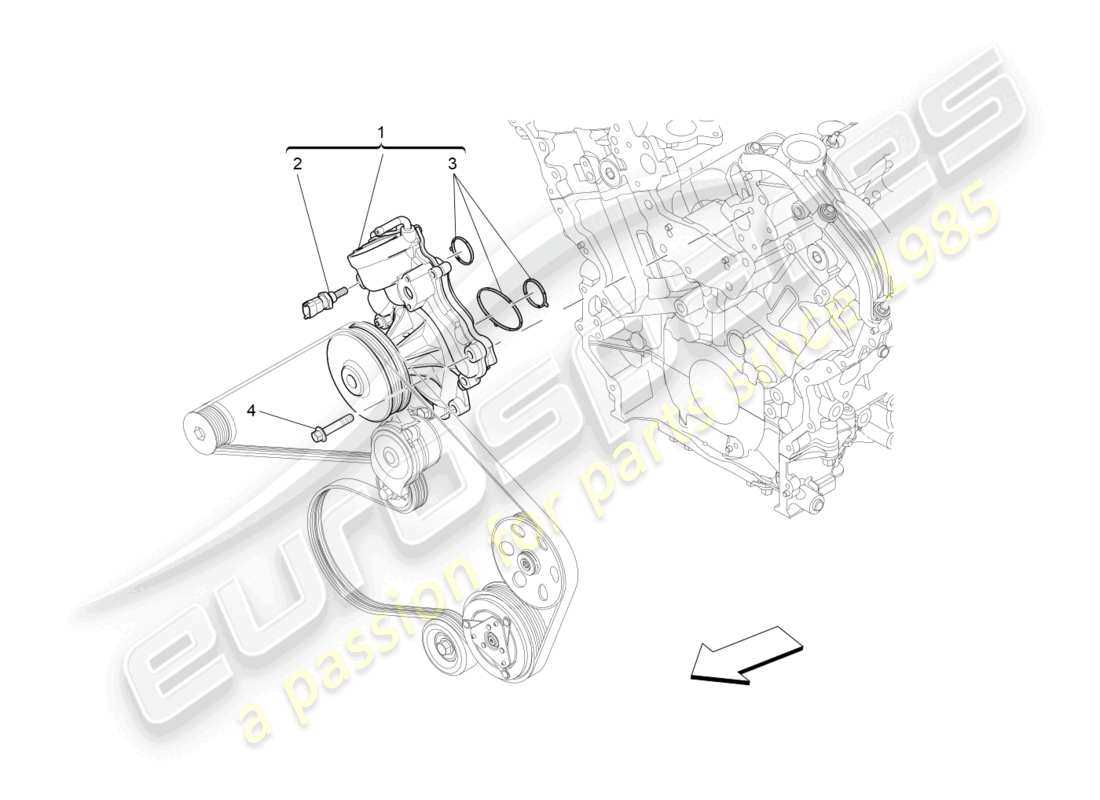
In these visuals, the flow of the system is often illustrated with arrows or lines that show how different elements work together. Recognizing these connections helps to understand the overall functioning of the assembly. Following the paths can ensure that all pieces are correctly aligned and functioning in harmony.
Importance of Accurate Diagrams
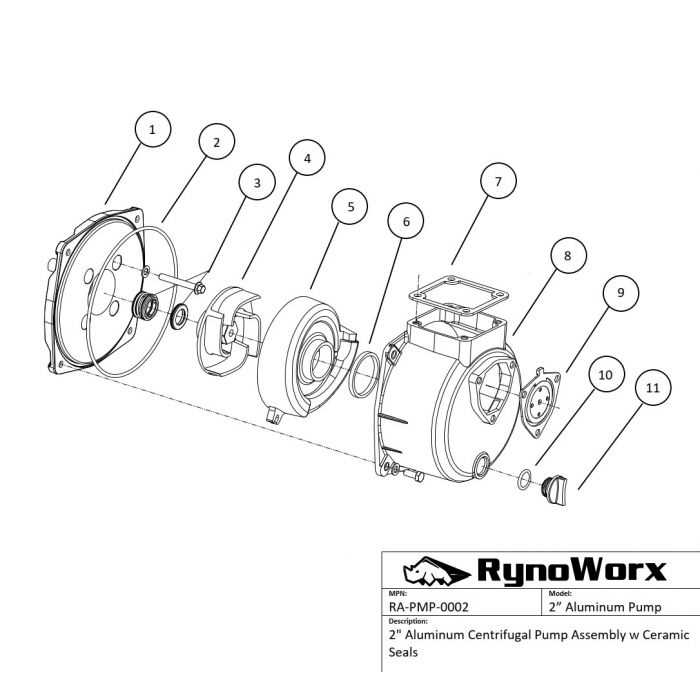
Precision in technical illustrations is essential for understanding the function and assembly of mechanical systems. Clear and detailed visuals ensure that each component is identified correctly, allowing for seamless repairs and maintenance. This accuracy minimizes the risk of errors and enhances the efficiency of both installation and troubleshooting processes.
Without well-detailed visuals, users may struggle to locate the correct elements, leading to potential malfunctions or damage. Accurate representations also aid in communication between engineers, technicians, and operators, fostering a smoother workflow and reducing downtime.