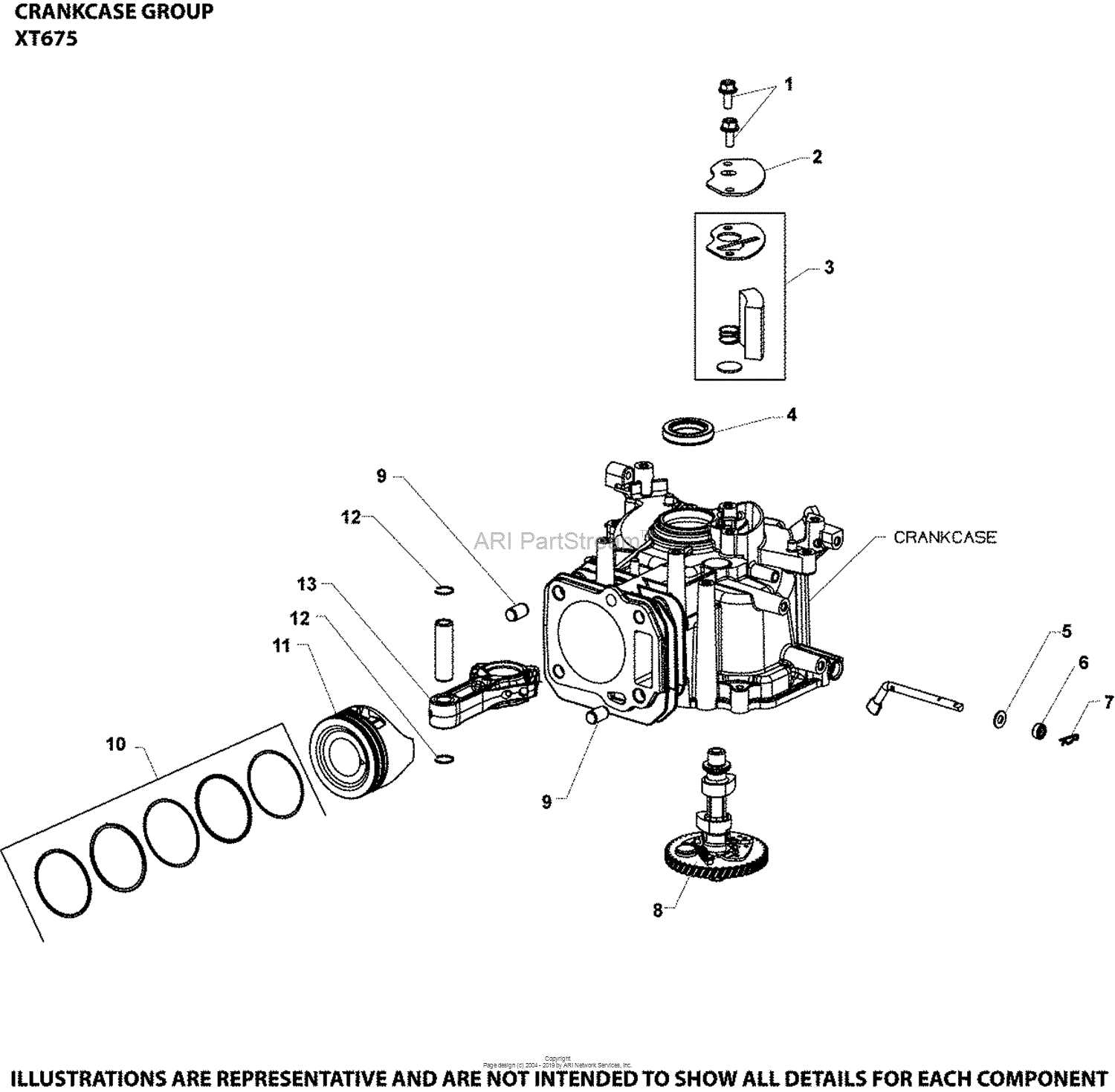
When it comes to maintaining outdoor equipment, understanding how various elements of the system fit together is crucial. Whether you are performing routine maintenance or troubleshooting an issue, a clear view of the system’s structure can be incredibly helpful. Each component serves a specific function, working together to ensure smooth operation and durability over time.
By exploring the structural overview of such mechanisms, one can better comprehend the interactions between various modules. This deeper knowledge can lead to more effective maintenance and repairs, ultimately extending the lifespan of your equipment. In the following sections, we will explore the essential elements and their roles in the overall functionality, highlighting key areas that require special attention.
With a clear understanding of how everything fits together, you can approach any mechanical task with confidence. A well-organized visual representation not only helps in identifying specific components but also provides insights into how they operate in unison. As we move forward, you’ll gain valuable insights into the most important elements of the system and how they contribute to the smooth functioning of your machine.
Essential Components of the Toro PH-XT675
This equipment is built from several crucial mechanisms that ensure its performance and durability. Understanding these elements helps in maintaining optimal functionality and identifying potential issues during operation.
Key Mechanical Elements
- Engine Unit: The core of the machine, powering all its functions. Proper care of this element is crucial for smooth operation.
- Fuel System: This component controls the delivery of fuel, ensuring consistent energy supply for maximum efficiency.
- Air Filtration: Designed to keep the internal mechanisms clean by preventing debris and particles from entering sensitive areas.
Operational Control Features
- Throttle Control: Allows the user to regulate the power output, ensuring precise adjustments during usage.
- Ignition System: Responsible for initiating the startup process, it
Understanding the Engine Assembly Layout

In order to grasp how the overall engine structure operates, it’s essential to focus on the individual components and their arrangement. The placement and alignment of key mechanical elements play a crucial role in ensuring the engine’s smooth functioning. Each part is strategically positioned to contribute to the efficient movement and power generation, allowing for the system to work seamlessly as a whole.
The engine is composed of interconnected mechanisms that work together to convert energy into motion. These include various rotating, moving, and stationary parts, which must be arranged in a way that minimizes friction and maximizes energy transfer. The correct assembly of these elements is fundamental to ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
By understanding how the different components interrelate and support each other, one can gain insights into both routine maintenance and troubleshooting. Knowing the structure of the engine enables a deeper appreciation of its design and how to address potential operational issues that may arise over time.
Key Features of the Fuel System
The fuel system in modern engines is designed to ensure efficient energy supply, supporting smooth operation and optimal performance. It regulates the intake of liquid energy sources, allowing for consistent combustion and reliable power output under various conditions.
Fuel Delivery Mechanism is essential for maintaining a steady flow of energy to the combustion chamber. This mechanism ensures that the right amount of fuel is supplied based on the engine’s requirements, preventing overconsumption and improving overall efficiency.
Fuel Filtration plays a critical role in preventing impurities from entering the engine. By filtering out particles and contaminants, it protects the sensitive components, prolonging the system’s lifespan and reducing the risk of damage.
Pressure Regulation ensures the energy is delivered at an optimal pressure. Maintaining proper levels is crucial for achieving consistent combustion, especially during varying operational loads.
Air-Fuel Ratio Control is a key factor in enhancing performance and reducing emissions. Bal
Detailed Overview of the Air Filter Design
The air filtration system plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall efficiency and longevity of an engine. Its design is centered around preventing contaminants such as dust, dirt, and debris from entering the engine, which can lead to performance degradation. By ensuring a clean airflow, the engine can function optimally, maintaining consistent performance and reducing wear on internal components.
Key Components of the Filtration System
The filtration unit consists of multiple layers of material that work together to capture impurities. The outer layer typically serves as the first line of defense, blocking larger particles. The inner layers are designed for finer filtration, ensuring that only clean air passes through. The structure is compact yet durable, allowing it to withstand frequent use and environmental challenges without losing its effectiveness.
Maintenance and Replacement Considerations
Over time, the accumulation of debris in the filtration unit can reduce its efficiency, which makes regular maintenance crucial. Depending on environmental conditions and usage, the filter may need to be inspected and replaced to prevent clogging, which could otherwise strain the engine. A clean
Examining the Ignition System Elements
The ignition system is a crucial component in any internal combustion engine, responsible for generating the necessary energy to initiate engine operation. This system operates by creating a high-voltage electrical pulse that ignites the fuel mixture within the combustion chamber. Understanding the key elements within this system helps in identifying potential issues and maintaining optimal performance.
Component Function Spark Plug Converts electrical energy into a spark that ignites the fuel mixture in the engine. Ignition Coil Transforms low-voltage power from the battery into a high-voltage charge needed for the spark plug. Flywheel Provides momentum and regulates engine speed while also generating electric pulses for the ignition coil. Magneto Generates current for the ignition system in some engines, ensuring a reliable spark delivery. Role of the Governor Mechanism
The governor mechanism plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and efficiency of various machinery. Its primary function is to regulate the speed of an engine or motor by adjusting the fuel supply, ensuring that the system operates within optimal parameters. This self-regulating feature helps to prevent over-revving, which can lead to damage and decreased performance.
Functionality and Importance
The mechanism works by sensing the rotational speed of the engine and making real-time adjustments. When the speed exceeds a predetermined threshold, the governor restricts fuel flow, effectively reducing power output and stabilizing the engine speed. Conversely, if the speed drops below the desired level, it allows more fuel to flow, promoting increased power and maintaining operational efficiency.
Impact on Performance
A well-functioning governor mechanism not only enhances the longevity of machinery but also improves overall performance. By ensuring that the engine operates smoothly and efficiently, it reduces fuel consumption and emissions, contributing to a more environmentally friendly operation. Additionally, it provides a consistent power output, which is essential for tasks requiring precision and reliability.
Exploring the Exhaust System Configuration
The configuration of the exhaust mechanism plays a crucial role in enhancing engine performance and ensuring efficient operation. This system is designed to channel gases away from the engine, minimizing emissions and optimizing fuel consumption. Understanding its layout and functionality can significantly aid in maintenance and troubleshooting processes, leading to improved longevity and effectiveness of the overall equipment.
Components of the Exhaust Mechanism
Key elements within the exhaust assembly include the manifold, which collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders, and the muffler, responsible for reducing noise levels. Additionally, catalytic converters are essential for minimizing harmful emissions, converting toxic substances into less harmful compounds before they exit into the atmosphere. Each component must function harmoniously to maintain optimal engine efficiency.
Maintenance and Optimization
Regular inspection of the exhaust configuration is vital to identify potential issues such as leaks or blockages. Ensuring that all parts are in good condition can prevent performance degradation. Adjustments and replacements should be made as necessary to guarantee that the system operates at peak efficiency, contributing to the overall performance of the machine.
Common Parts in the Carburetor Setup
The carburetor assembly plays a vital role in the efficient operation of an engine by mixing air and fuel in the correct proportions. Understanding the various components involved can aid in troubleshooting and maintenance. This section highlights key elements typically found within this assembly.
Component Description Float Chamber Holds a reserve of fuel and regulates its flow into the mixing area. Needle Valve Controls the entry of fuel into the float chamber based on the fuel level. Main Jet Allows fuel to enter the air stream, influencing the engine’s performance during acceleration. Choke Valve Restricts air flow to enrich the fuel mixture during starting, especially in cold conditions. Throttle Valve Regulates the amount of air-fuel mixture entering the engine, controlling engine speed. Air Filter Removes impurities from the incoming air, ensuring clean airflow for efficient combustion. Guide to the Starter Mechanism Components
The starter mechanism is a crucial assembly responsible for initiating the operation of small engines, particularly in outdoor power equipment. Understanding its components and their functions is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section outlines the key elements of the starter system, providing insights into their roles and interconnections.
Key Components of the Starter Assembly
- Starter Motor: This electric device converts electrical energy into mechanical motion, providing the necessary torque to crank the engine.
- Solenoid: Acting as a switch, it engages the starter motor when the ignition is activated, allowing the flow of current to the motor.
- Flywheel: A heavy rotating component that stores kinetic energy, enabling the engine to start smoothly and maintain momentum.
- Starter Gear: This gear interacts with the flywheel, helping to transfer the rotational force generated by the starter motor to the engine.
- Pull Cord: A manual mechanism that allows users to start the engine by pulling on a cord, which engages the starter system.
Functions of the Starter Mechanism
- Initiates engine operation by providing the necessary cranking speed.
- Ensures a reliable and consistent start for various outdoor equipment.
- Facilitates user engagement through both electric and manual starting options.
- Contributes to the overall efficiency and performance of the engine.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components can prevent starting issues and extend the lifespan of the equipment. Familiarity with the starter assembly will empower users to troubleshoot problems effectively and make informed decisions regarding repairs and replacements.