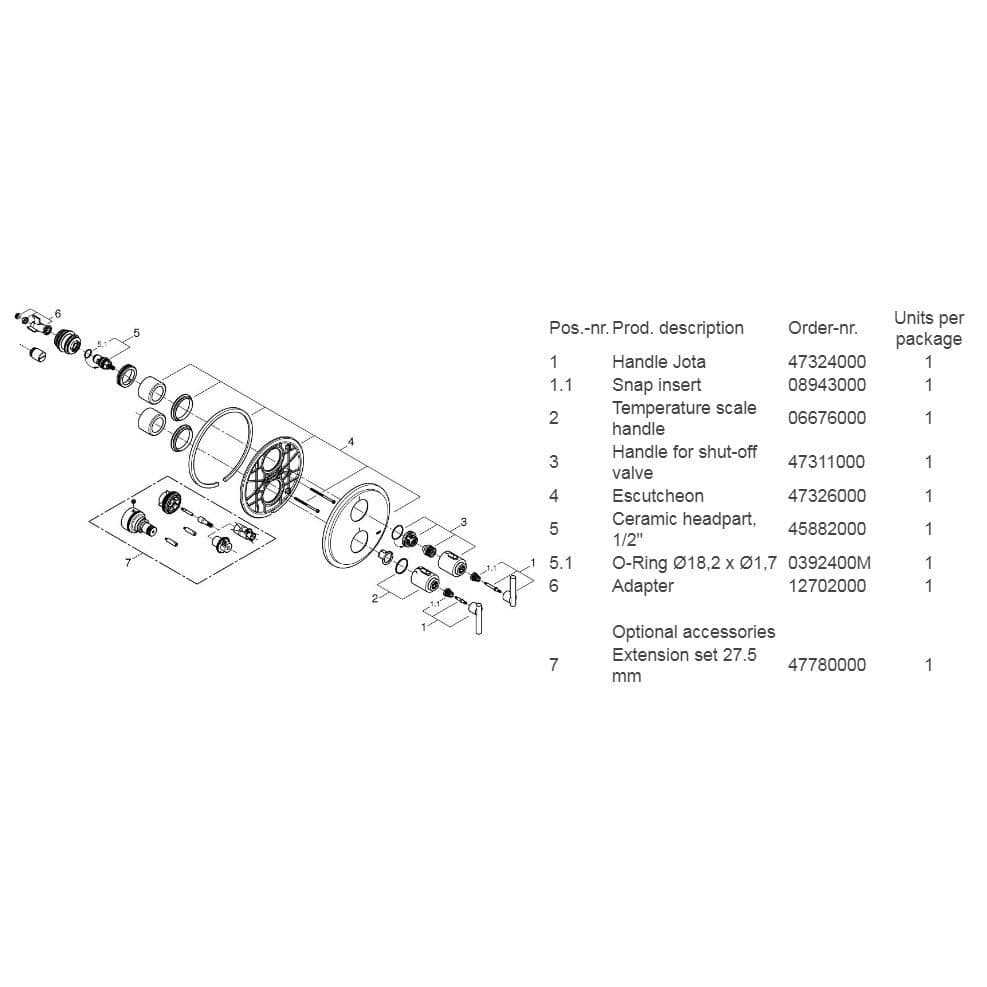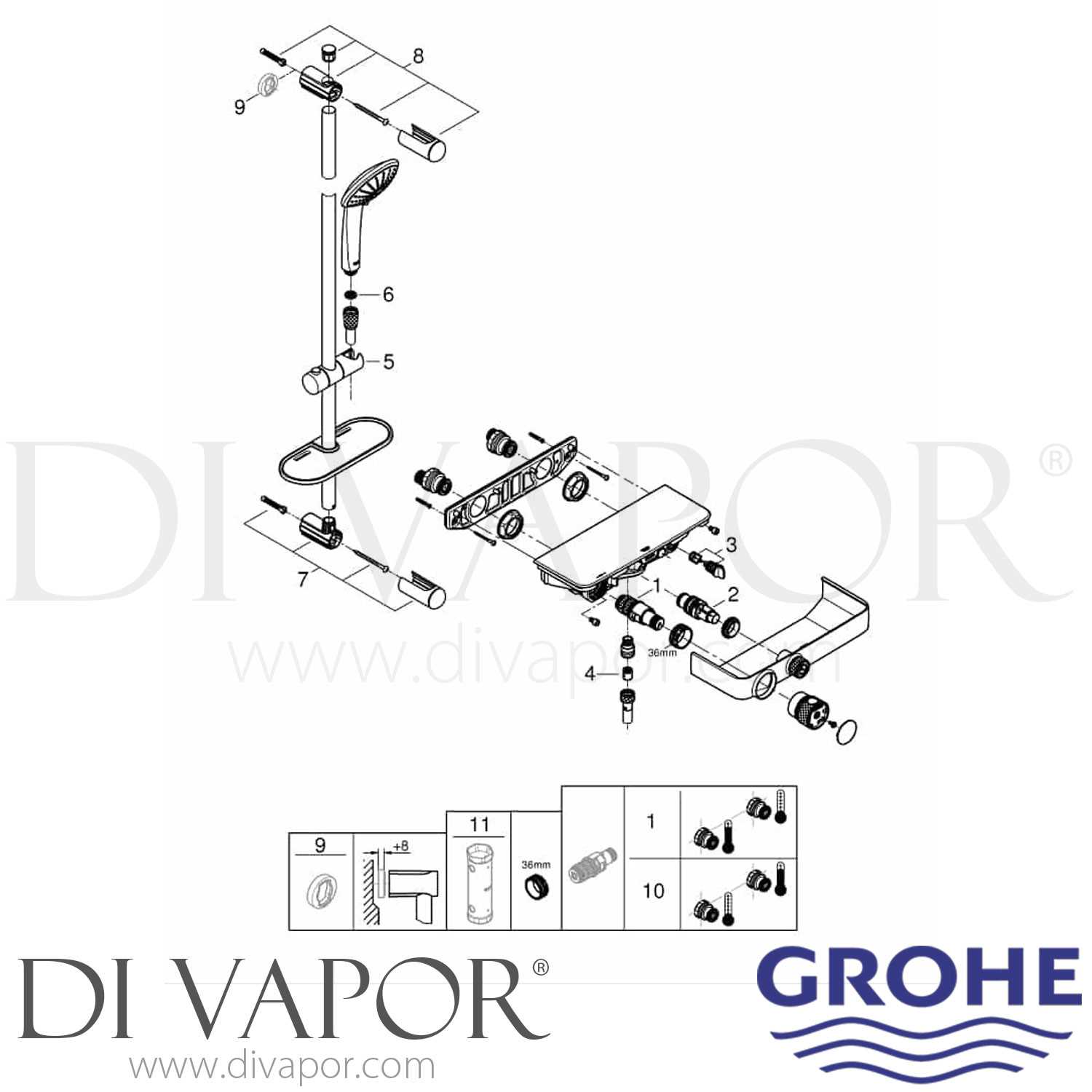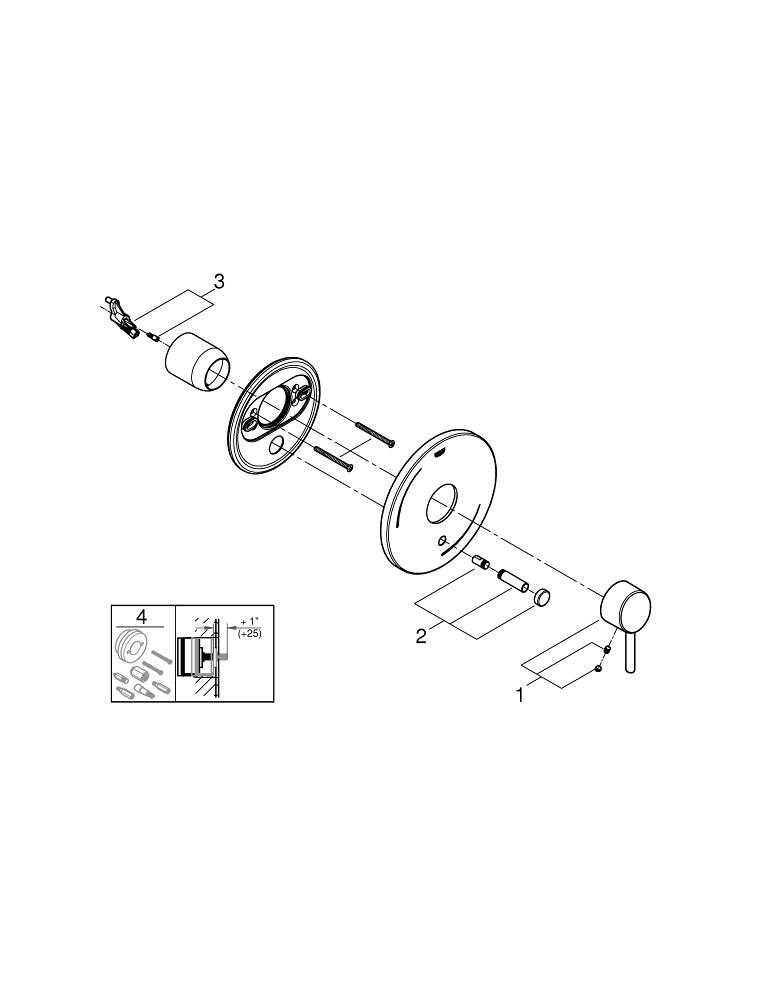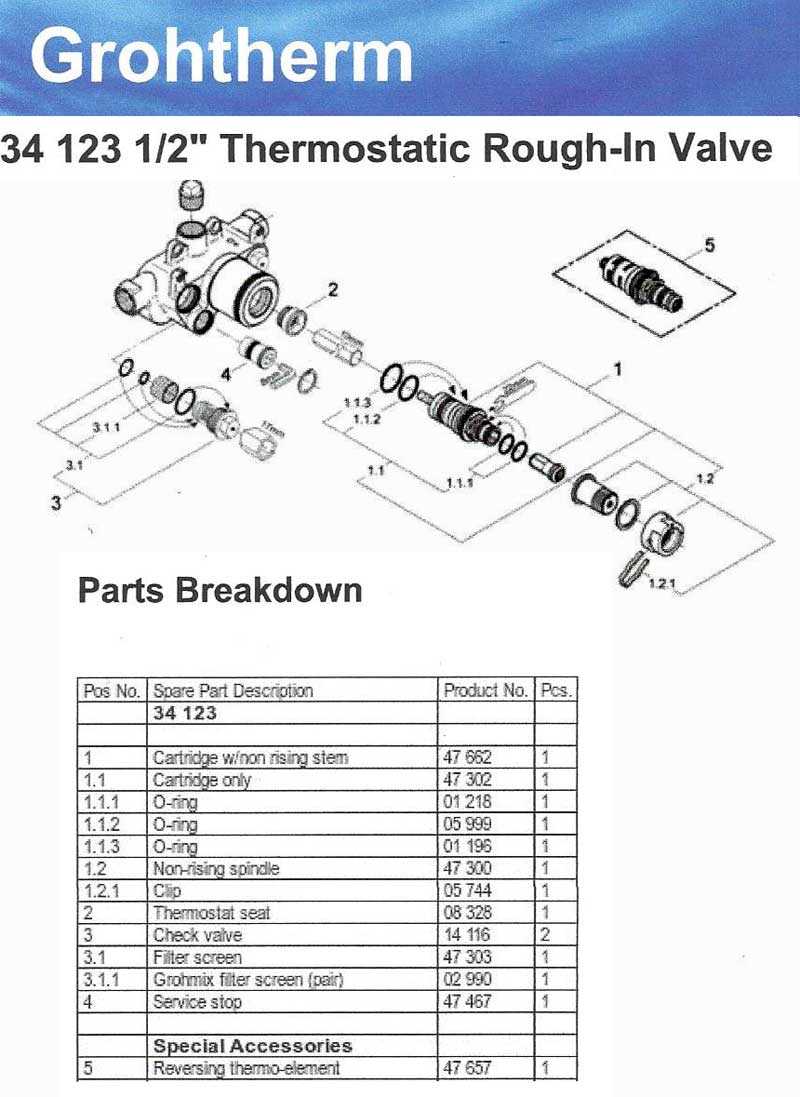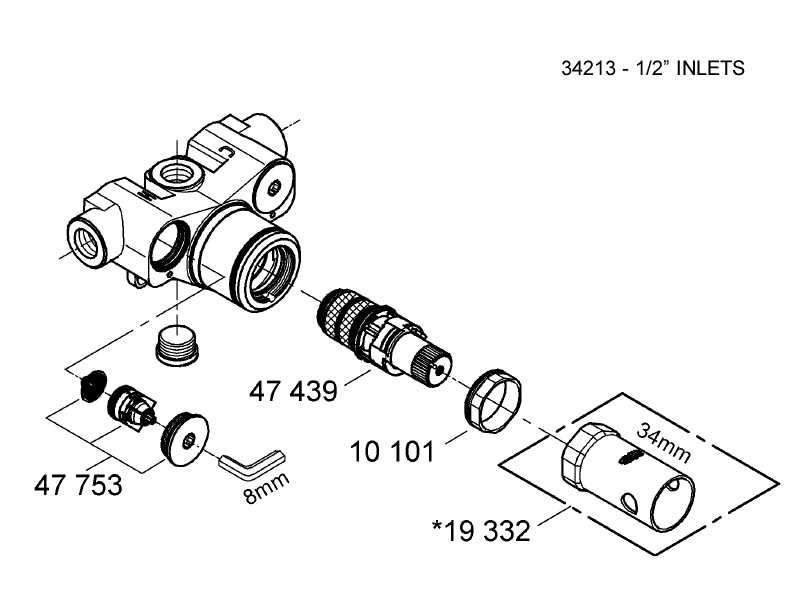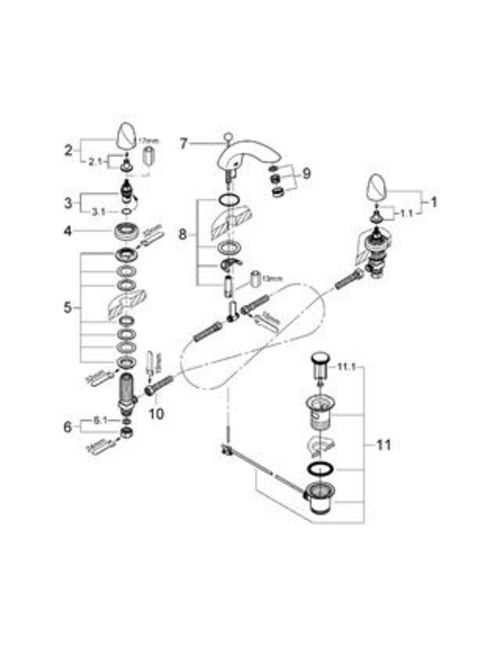
In contemporary water control systems, every element plays a critical role in ensuring smooth operation and efficient flow management. These systems are designed to combine functionality with aesthetics, offering both precision and durability. When looking into the structure of such a system, it becomes important to understand the intricate components that work together to regulate water pressure, temperature, and distribution.
Each individual element within the control mechanism contributes to the overall performance of the system. From the internal mechanisms that allow for easy adjustments to the external fittings that ensure a seamless user experience, all components are interconnected. Examining the detailed structure of these systems can help in troubleshooting, maintenance, and even upgrading the setup to meet specific needs.
Understanding the Components of a Grohe Shower Valve

The intricate mechanisms within this water control device are essential for regulating temperature, water flow, and ensuring a comfortable and consistent experience. Each element plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance, and understanding how these pieces work together is key to troubleshooting and enhancing efficiency.
Internal mechanisms include a balancing component that adjusts the mixture of hot and cold water. This ensures steady pressure and avoids sudden temperature changes, providing a safe and consistent water output. The use of durable materials in this section enhances the longevity and reliability of the overall system.
Another essential part is the flow regulator, which controls the volume of water passing through. This component allows for precise adjustments, ensuring the user can control the desired strength of the water stream. Its design focuses on reducing water waste while maintaining a steady flow.
Finally, the sealing elements prevent leaks, ensuring efficient operation. These parts are designed to fit perfectly, providing a secure closure within the system and helping avoid water wastage or damage over time.
Key Features of Grohe Valve Systems
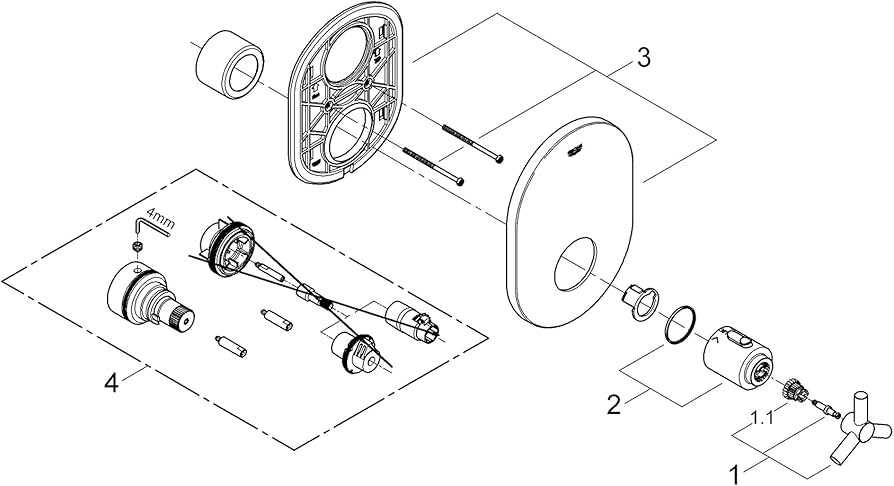
Modern plumbing mechanisms offer exceptional control over water flow, temperature regulation, and ease of installation. With a focus on durability and precision, these systems ensure optimal performance in various environments. Understanding the key characteristics of these components helps in achieving a seamless experience.
Advanced Water Control
- Precise temperature regulation for comfortable use
- Seamless transition between different water modes
- Efficient water flow management to prevent wastage
Durability and Longevity
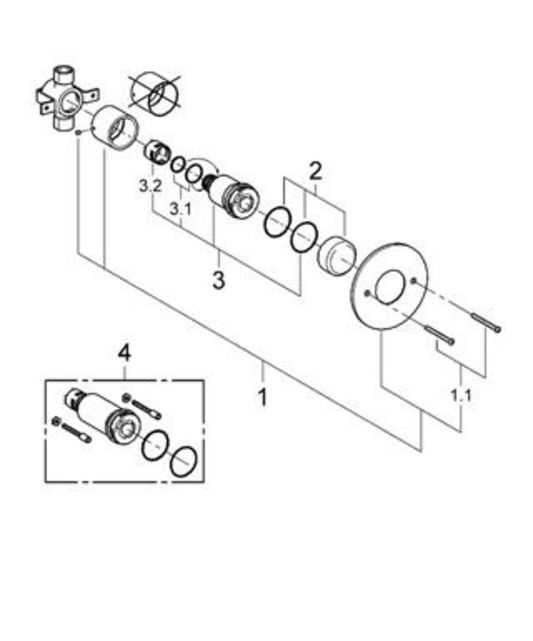
- Built with corrosion-resistant materials for extended life
- Engineered to withstand frequent use without compromising quality
- Minimal maintenance requirements due to robust construction
Exploring the Internal Mechanisms of Shower Valves
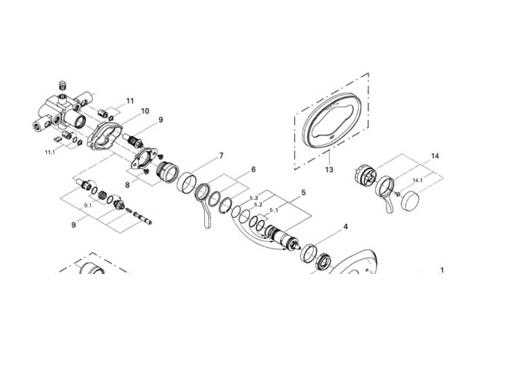
The intricate structure behind water flow control systems plays a crucial role in regulating temperature, pressure, and water direction. Understanding the core components and their interaction helps in diagnosing issues, maintaining optimal performance, and enhancing user comfort. The internal arrangement of these systems involves various mechanisms designed to balance and manage fluid movement seamlessly.
Below is an overview of key elements within such control mechanisms and their functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cartridge | Regulates temperature by controlling the mix of hot and cold fluids. |
| O-Rings | Provides sealing to prevent leakage between components. |
| Pressure Balancer | Maintains consistent pressure by adjusting to changes in the water supply. |
| Thermostatic Element | Ensures accurate temperature control by responding to temperature shifts. |
Common Issues and Their Causes in Valve Parts
Functional components in water flow control systems are prone to various malfunctions over time. These issues often arise due to regular wear, improper installation, or poor maintenance practices. Identifying the root cause can help prevent more serious problems and ensure the system operates smoothly.
Leaks and Drips
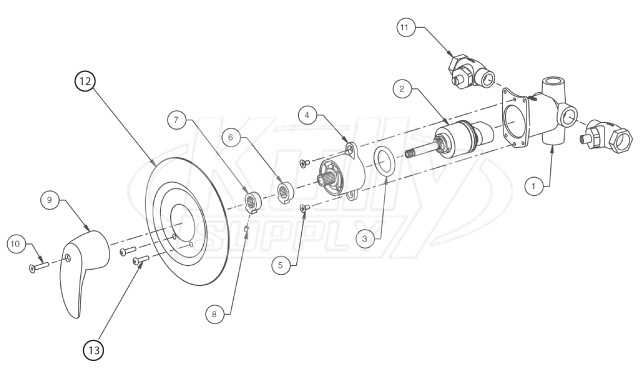
- Worn Seals: Seals tend to degrade over time, allowing water to escape from connections.
- Loose Connections: Inadequate tightening during assembly can result in slow leaks.
- Mineral Buildup: Accumulation of deposits can interfere with proper sealing, leading to drips.
Temperature Inconsistency
- Blocked Cartridges: Obstructions in the control mechanism can prevent smooth temperature adjustments.
- Damaged Components: Broken or faulty internal elements may cause erratic temperature changes.
- Improper Installation: Incorrect setup of system elements can disrupt water temperature control.
Maintenance Tips for Long-Lasting Valve Functionality
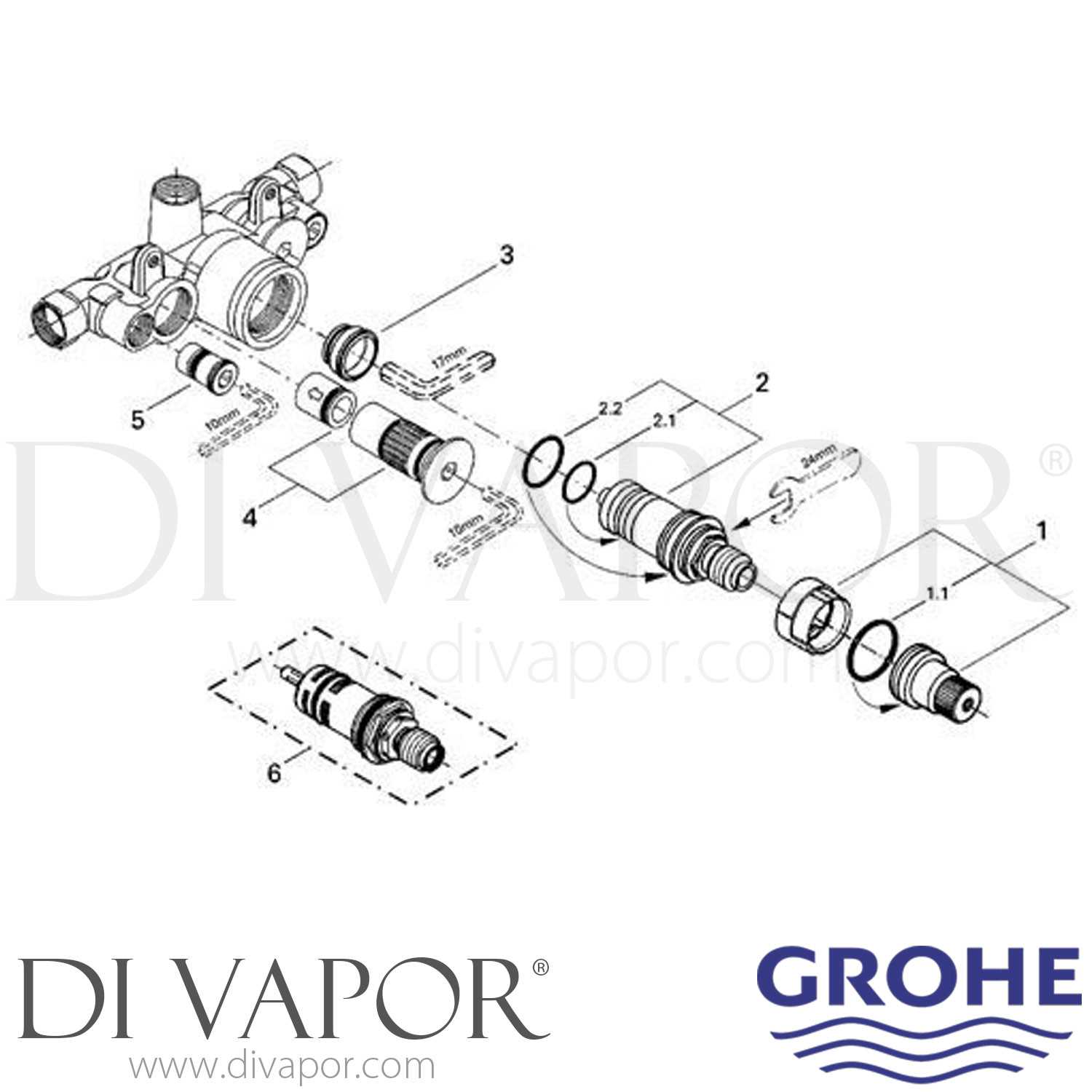
Ensuring the durability of your system requires regular upkeep and attention to key components. By following a few simple steps, you can avoid premature wear and ensure optimal performance over time. Proper care will help maintain the integrity and smooth operation of the mechanism, allowing it to function efficiently for years to come.
Inspect Seals and Gaskets Regularly: Periodically check the seals for signs of damage or wear. Replacing them when necessary can prevent leaks and ensure tight connections, which are essential for a well-functioning system.
Clean Internal Components: Over time, mineral deposits and debris can build up inside, leading to blockages or reduced flow. Regular cleaning of the internal parts will help maintain proper water flow and pressure, ensuring efficient operation.
Lubricate Moving Parts: Proper lubrication of the moving components reduces friction, allowing for smoother operation. Use a suitable lubricant recommended for such mechanisms, applying it during regular maintenance to prevent stiffness or sticking.
Avoid Excessive Force: When adjusting or using the mechanism, avoid applying unnecessary force. Gentle operation reduces stress on internal parts, prolonging the system’s life.
By incorporating these simple maintenance practices into your routine, you will significantly extend the life of your system and avoid common issues associated with neglect.
Replacing Worn-Out Grohe Shower Valve Components
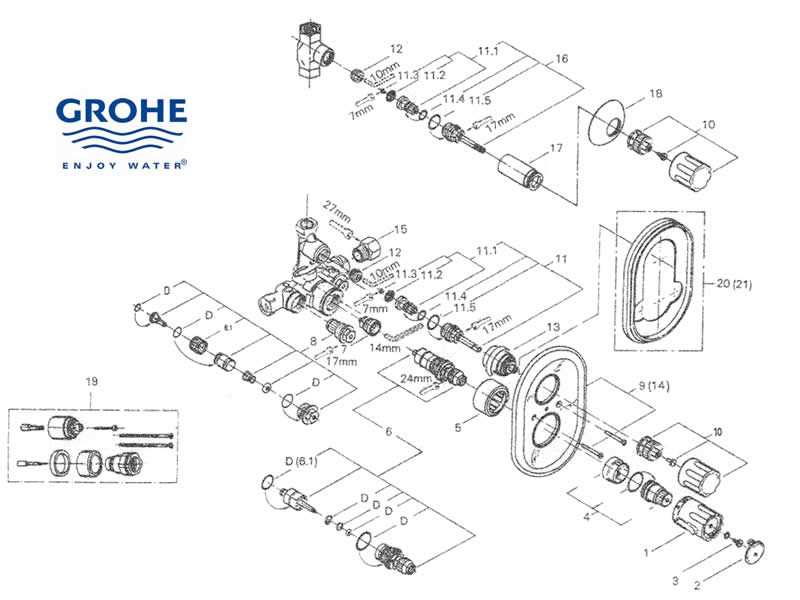
Over time, components within water control systems can deteriorate, leading to performance issues. Timely replacement of these worn elements is crucial to ensure smooth operation and prevent leaks. This guide provides an overview of the steps involved in removing old parts and installing new ones, focusing on key areas that commonly require attention.
Identifying Signs of Wear
Before replacing any elements, it’s important to recognize the common signs of aging components. Decreased water flow, difficulty in adjusting temperature, or small leaks around connection points are usually the first indicators. Early detection can prevent more serious issues and prolong the lifespan of the entire system.
Step-by-Step Replacement Process
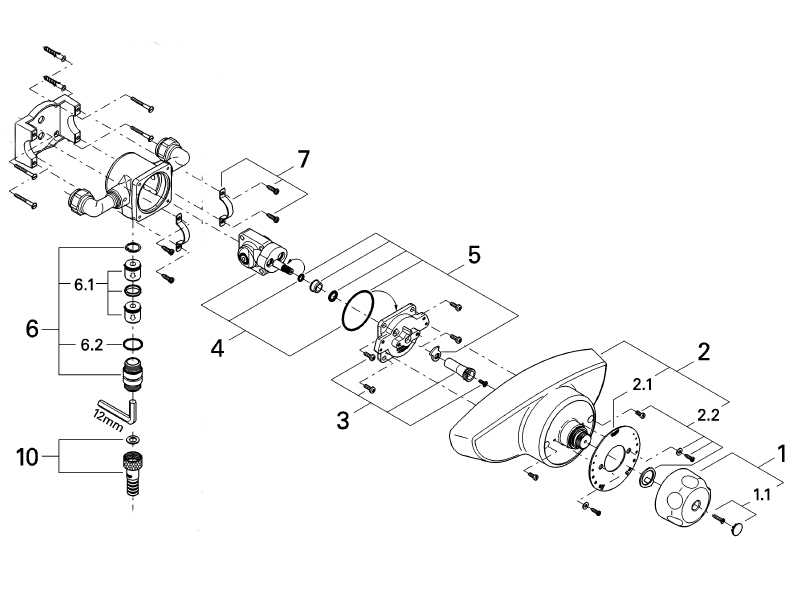
Once the problem areas are identified, follow a systematic approach to replace the necessary parts. Ensure that the water supply is turned off before starting. Using the correct tools, carefully disassemble the unit, removing any damaged or corroded parts. Clean the areas where new components will be installed, then proceed with reassembly. Make sure all connections are secure before restoring water flow.
| Component | Common Issues | Replacement Tips | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cartridge | Water leaks, uneven temperature control | Ensure compatibility with your model |
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Low Water Pressure | Clogged aerator or cartridge | Remove and clean or replace the affected part. |
| Leaking | Worn seals or fittings | Inspect seals and replace if necessary. |
| Temperature Fluctuations | Faulty temperature control mechanism | Check the control unit and replace if faulty. |
| Unusual Noises | Loose or damaged components | Tighten or replace any damaged parts. |
By following these steps and maintaining regular inspections, you can ensure that your plumbing fixture operates effectively and prolong its lifespan.