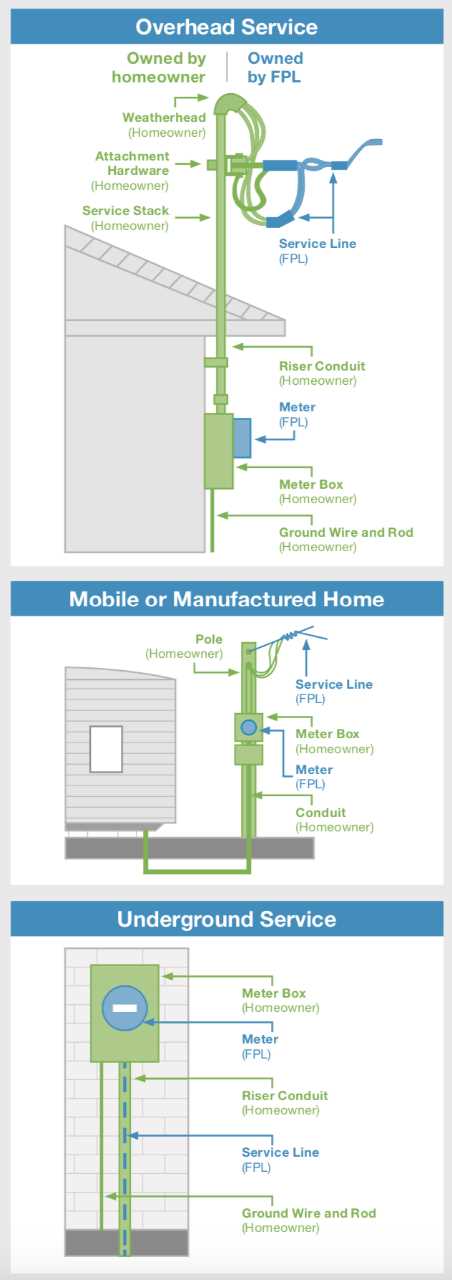
When it comes to electrical systems, the integrity and efficiency of transmission infrastructure are essential. The various components that make up these structures play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and reliable transport of energy across vast distances. Whether you’re dealing with high-voltage lines or distribution networks, understanding the specific elements involved can help demystify how these systems function and contribute to modern society.
In this section, we explore the key elements of these vital frameworks, which support the essential task of connecting power sources with consumers. Each component has a unique function that contributes to the overall stability and performance of the system. By examining these different parts and how they interact, one gains a clearer picture of the engineering marvel that underpins our electrical networks.
Identifying and understanding these elements can aid in troubleshooting, maintenance, and design improvements. It also provides insight into the materials and technologies that have been developed to withstand the harsh environmental conditions they encounter. A detailed look at these structures reveals the complexity and precision required to keep the lights on around the world.
Understanding Power Pole Components
Electricity distribution structures consist of several essential elements that work together to ensure efficient energy transmission. Each component plays a critical role in supporting, protecting, and directing electrical flow across vast distances, connecting power sources with end-users. Recognizing the different functions of these elements can help in maintaining and troubleshooting the overall system.
Main Structural Elements
The foundation of any electrical system lies in its structural components, which provide stability and support. These elements include tall frameworks that elevate electrical conductors, ensuring they remain clear of obstacles. These structures are often made of materials that resist weathering and corrosion, offering long-term durability in various environmental conditions.
Conductive Components
At the heart of these installations are the conductive elements that carry electrical current. These are typically wires or cables that are carefully designed to handle the voltage and power load. Ensuring these conductors are properly insulated and securely attached is vital to prevent accidents and maintain a steady flow of electricity.
Key Parts of a Power Pole System
In any electrical distribution structure, several components work together to ensure reliable transmission and support. Understanding the essential elements of such a setup is crucial for maintaining efficiency and safety. These components are designed to withstand environmental challenges and carry out the system’s intended function without failure.
Below is a list of the core elements typically found in such structures:
- Support Structure: The main framework that holds the entire assembly in place, often made of wood, steel, or concrete.
- Conductors: These are the cables that transmit electricity from one location to another, often suspended between the support framework.
- Insulators: Used to prevent the flow of current into the support framework, ensuring safety and stability of the system.
- Crossarms: Horizontal supports that help in positioning and stabilizing the conductors.
- Brackets and Fasteners: These components secure the other parts in place, ensuring they remain intact and aligned during operation.
- Transformers: Devices used to adjust voltage levels as electricity moves through the system, ensuring safe and efficient distribution.
- Grounding Equipment: Ensures electrical safety by directing any excess electricity safely into the earth in case of a fault.
- Warning Signs: Mark the potential hazards and help in the identification of the structure for maintenance or emergency purposes.
Each of these elements is integral to the overall functionality, making sure that electrical currents flow securely and efficiently to their intended destinations. Proper installation, maintenance, and monitoring are essential for long-term system integrity and safety.
How Power Poles Function in Utility Networks
Utility structures play a crucial role in distributing essential services across urban and rural landscapes. These structures serve as a foundation for connecting various infrastructure elements, allowing energy and communication signals to flow seamlessly through the network. By supporting key components, they ensure the smooth operation of systems that provide daily services to communities.
Transmission of Energy and Communication
These utility structures act as critical pathways for transmitting both electrical currents and communication signals across long distances. Cables and wires attached to them carry these resources efficiently, ensuring that they reach homes, businesses, and other facilities without interruption. The strategic placement of these structures guarantees optimal performance and minimizes disruptions in service delivery.
Support for Multiple Systems
Utility structures are designed to accommodate a variety of systems, including both electrical grids and telecommunication networks. By holding the necessary components in place, they allow for the integration of multiple technologies, ensuring reliable functionality. Their sturdy construction helps withstand external environmental factors, providing a dependable framework for essential utilities.
Essential Tools for Power Pole Maintenance
Regular upkeep of outdoor infrastructure requires the right set of equipment. These tools help ensure efficient, safe, and timely repairs, allowing technicians to address potential issues with minimal downtime. Having the correct gear on hand reduces risks and improves the effectiveness of maintenance efforts.
Basic Hand Tools
For most maintenance tasks, technicians rely on standard hand tools that allow for precise adjustments and quick fixes. Below is a list of essential tools commonly used in the field:
- Wrenches – for tightening bolts and fasteners
- Insulated screwdrivers – designed for electrical safety
- Pliers – useful for gripping and cutting wires
- Measuring tapes – for ensuring proper alignment and dimensions
Safety Equipment
Safety is paramount during any outdoor maintenance work. Essential gear must be worn or used to prevent injuries and ensure compliance with industry standards:
- Insulated gloves – protect against electrical hazards
- Harnesses and lanyards – for secure work at height
- Helmets – safeguard against falling debris and impacts
- High-visibility vests – ensure visibility in all conditions
Common Issues with Power Pole Equipment
When working with large structures and equipment, certain problems may arise over time due to wear and external factors. Recognizing these potential challenges can help in maintaining efficiency and ensuring safety during operations. Below are some of the frequent concerns observed with this type of machinery.
- Corrosion and Rust: Exposure to moisture and harsh weather conditions often leads to metal components deteriorating, reducing their effectiveness and structural integrity.
- Electrical Failures: Equipment that handles high-voltage systems may experience disruptions due to faulty wiring or poor insulation, leading to malfunctions or safety risks.
- Mechanical Wear: Moving parts are prone to wearing down over time, resulting in decreased performance and the need for regular maintenance or replacement.
- Alignment Issues: Shifts in ground conditions or improper installation can cause the equipment to become misaligned, impacting stability and function.
Addressing these common problems promptly can prevent larger malfunctions and extend the lifespan of the equipment.
Materials Used in Power Pole Construction
When constructing support structures for electrical transmission, various materials are selected to ensure durability, reliability, and efficiency. These materials are chosen based on their ability to withstand environmental factors, carry heavy loads, and provide long-term service.
Wood
Wood is often utilized due to its natural strength and flexibility. It is treated to resist decay and insects, making it a popular choice in regions with moderate climate conditions. Properly treated wood can last for several decades, offering a cost-effective and sustainable option.
Steel
Steel is another common material used in construction. It provides greater strength than wood, making it ideal for areas with higher stress factors, such as high winds or heavy loads. Steel is highly resistant to environmental degradation and can be designed to fit various engineering requirements.
Installation Process of Power Pole Parts
The installation of essential structural components involves several steps to ensure stability and longevity. This procedure requires attention to detail and precision at each stage. Proper alignment, secure fastening, and reliable connections are crucial for optimal functionality.
Begin by preparing the foundation, which forms the base for the entire setup. It’s important to ensure that the groundwork is level and solid to avoid any future complications. Afterward, the main support structure is assembled, typically following a specific order to guarantee balance and structural integrity.
Next, the supporting elements are attached, connecting all critical sections. These must be firmly secured to avoid misalignment or instability. Careful adjustment and periodic checks during the process will help maintain accuracy.
Finally, all necessary connections are established, allowing the structure to operate effectively. It’s important to verify that all components are functioning properly before completing the setup. This will prevent potential issues and ensure reliable performance over time.
Safety Measures During Power Pole Repair

Ensuring the well-being of workers and the surrounding area is paramount during maintenance of tall outdoor structures. Various safety protocols must be followed to minimize risks and protect both personnel and equipment involved in the process.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- All workers must wear helmets, gloves, and other safety gear to shield themselves from potential hazards.
- Insulated footwear is crucial to prevent electric shocks in case of accidental contact with live wires.
- High-visibility clothing ensures workers are easily seen in all weather conditions.
Site Preparation and Inspection
- Before any maintenance begins, the area should be cleared of unnecessary items to provide a safe working environment.
- Conduct a thorough inspection of the surroundings to identify possible dangers such as unstable ground or nearby obstacles.
- Ensure proper grounding methods are in place to prevent electrical accidents.
Following these guidelines helps ensure the safety of the team while minimizing the risk of accidents during the maintenance process.
Advancements in Power Pole Technology
Recent innovations in support infrastructure have transformed how utilities manage their systems. New materials, enhanced designs, and integrated technologies are driving improvements in efficiency, durability, and safety. These developments are reshaping the landscape of modern utility networks, creating more resilient and adaptable structures for urban and rural environments alike.
New Materials and Durability
Modern structures now benefit from advanced composites and weather-resistant materials, offering longer lifespans and reduced maintenance. These innovations ensure that infrastructure remains sturdy even in harsh conditions, significantly extending service life.
Smart Integration
Technological advancements have led to the integration of smart monitoring systems within utility structures. These systems allow for real-time data collection, which enhances maintenance planning and minimizes the risk of failures, ensuring greater reliability for communities.