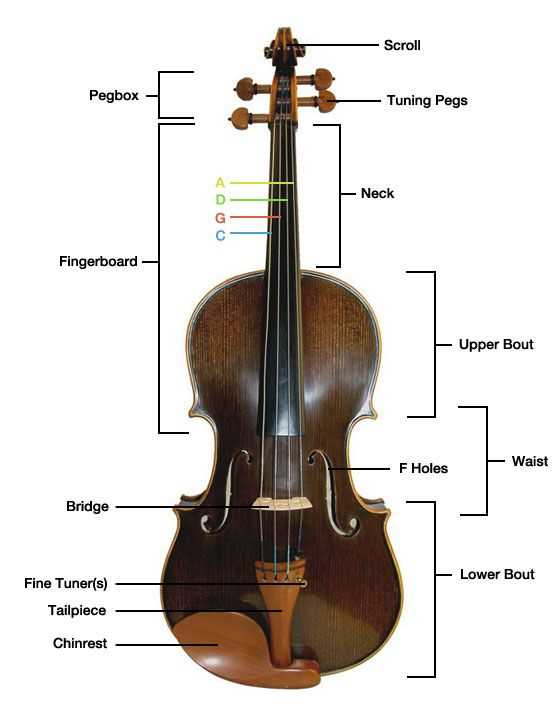
Exploring the intricate structure of a particular stringed instrument reveals a world of craftsmanship and design. Each component plays a crucial role in producing rich tones and maintaining the overall functionality of the musical piece. From the body to the neck, every element contributes to the instrument’s unique voice and character.
As we delve into this fascinating subject, it becomes evident that understanding these components enhances both appreciation and performance. The interplay between various sections influences sound quality and resonance, making knowledge of this anatomy essential for musicians and enthusiasts alike.
Ultimately, recognizing how each section interacts not only enriches one’s musical experience but also deepens the connection to the artistry involved in creating such an instrument. Whether you are a player, a listener, or simply curious, this exploration offers valuable insights into the craftsmanship that brings music to life.
Understanding Cello Anatomy

Exploring the structure of this beautiful instrument reveals the intricate components that contribute to its rich sound. Each element plays a significant role in both the performance and the overall aesthetic, forming a harmonious relationship that defines its character.
Key Components

At the heart of this musical creation lies the body, crafted to resonate and amplify sound waves. The neck provides a stable foundation for the strings, allowing for precise finger placements and seamless transitions between notes. The scroll, often elaborately designed, not only serves a decorative purpose but also houses the tuning pegs that maintain pitch integrity.
Resonance and Functionality
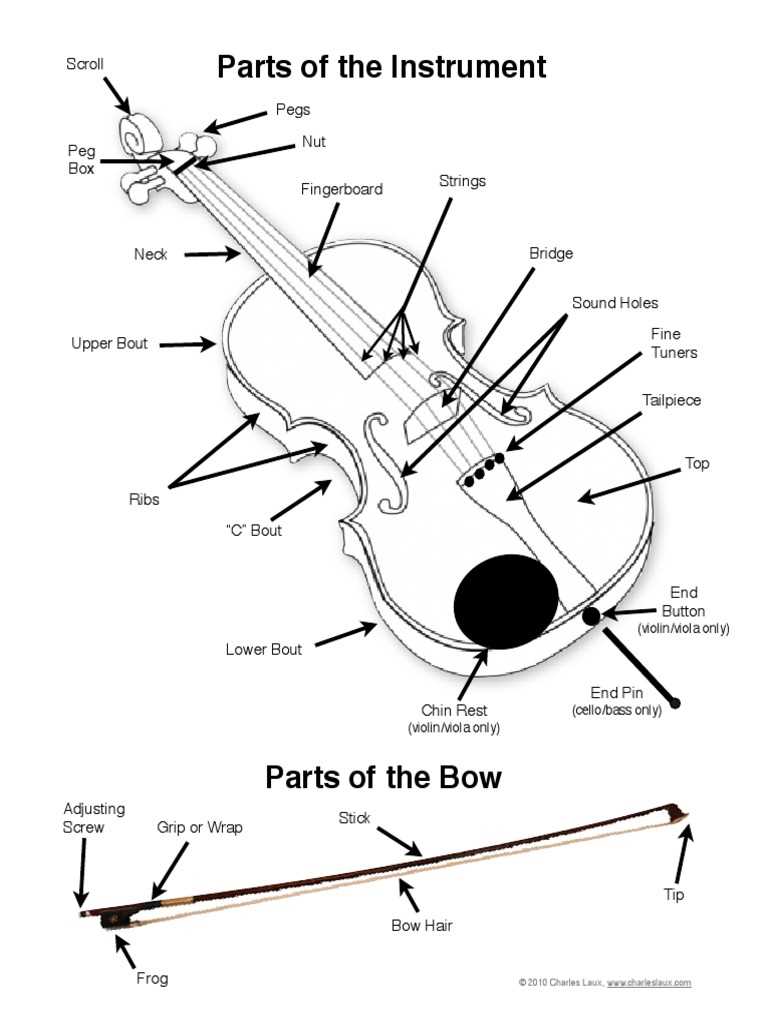
Each segment contributes to the overall functionality and tonal quality. The bridge acts as a crucial conduit, transferring vibrations from the strings to the body, while the sound hole enhances projection. Understanding these elements not only deepens appreciation for the craftsmanship involved but also enriches the experience of playing and listening.
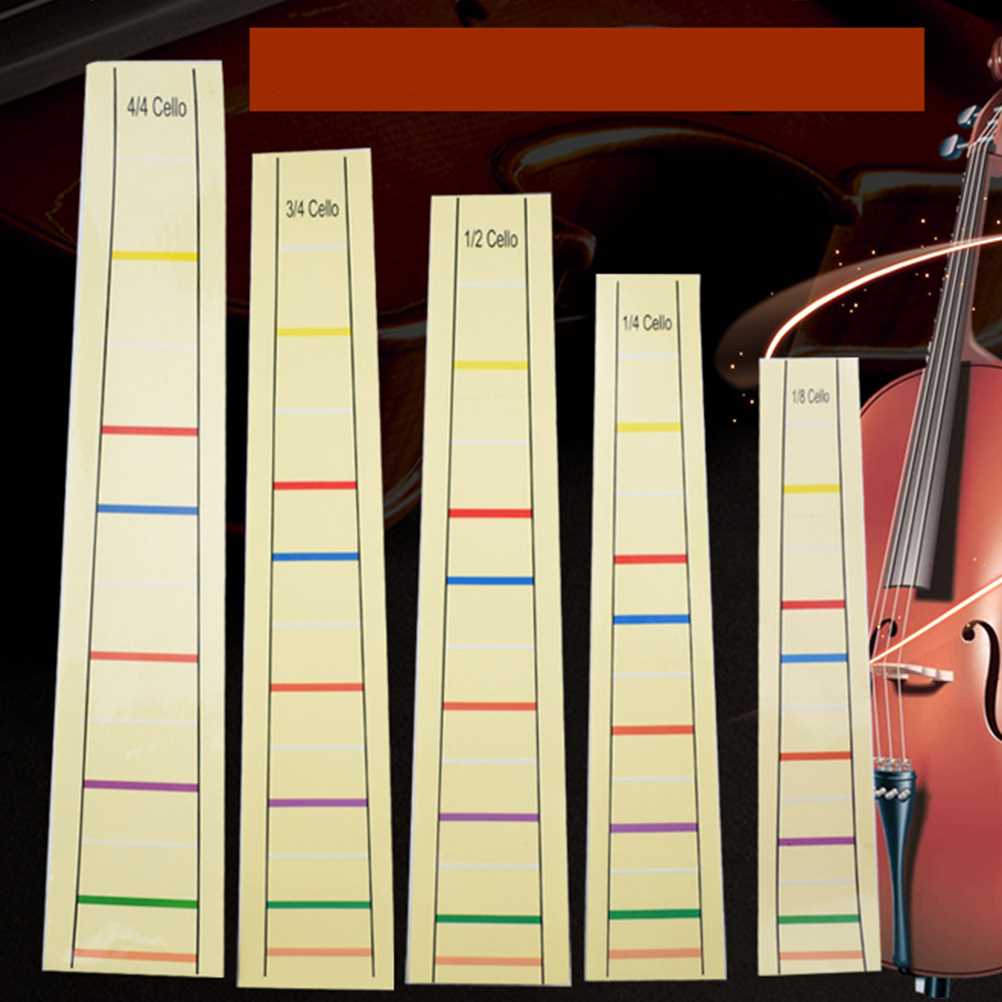
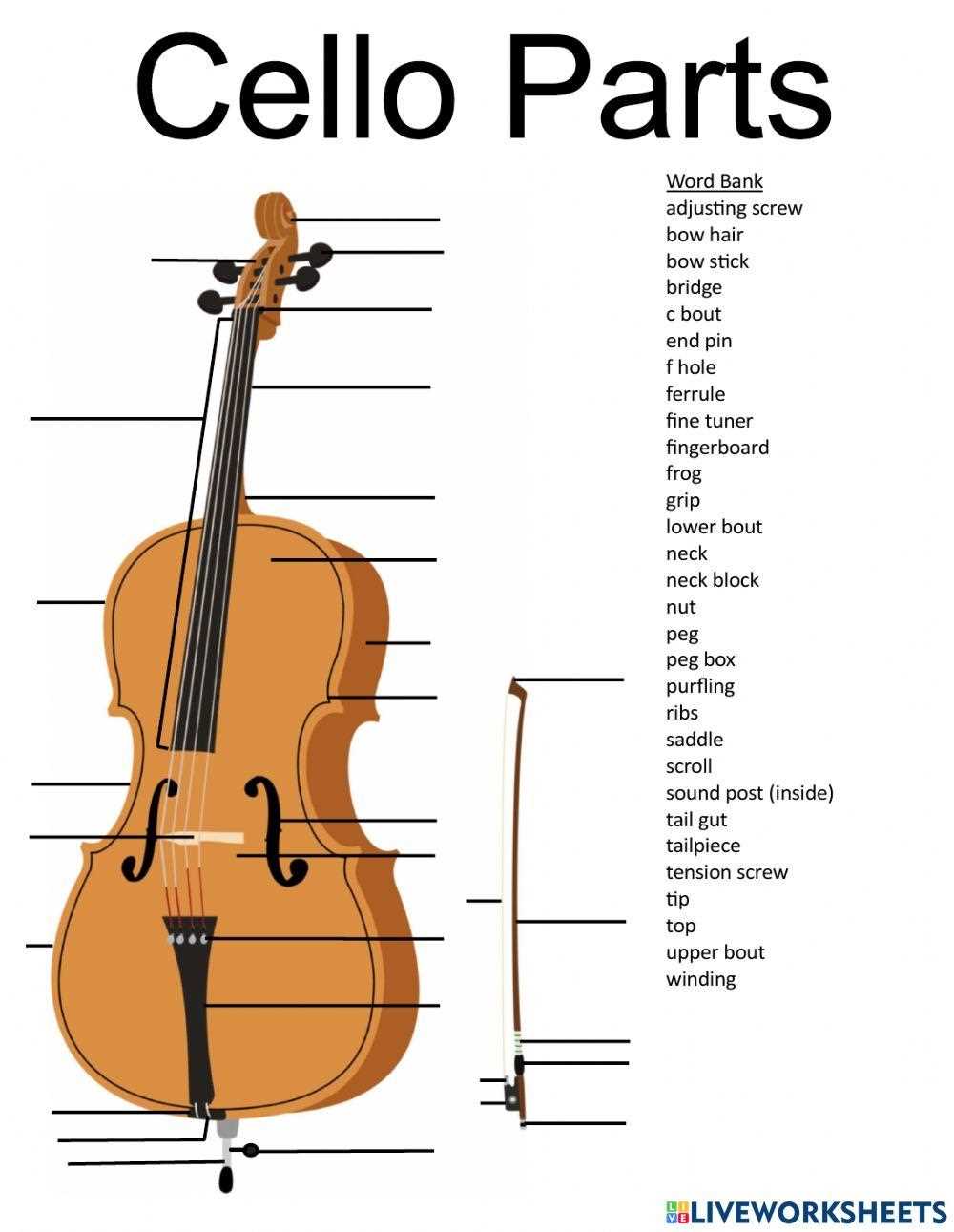
Main Components of a Cello
The structure of this string instrument is composed of several key elements, each contributing to its unique sound and playability. Understanding these components is essential for musicians and enthusiasts alike, as they work in harmony to create the instrument’s rich tonal quality.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Body | The resonating chamber that amplifies sound, crafted from selected woods for optimal acoustics. |
| Neck | The elongated section allowing for finger placement and pitch variation, usually made of strong wood. |
| Fingerboard | A smooth surface affixed to the neck, where the musician presses the strings to alter notes. |
| Strings | The vibrating elements, typically made from gut, steel, or synthetic materials, responsible for sound production. |
| Bows | Tools used to create sound by drawing across the strings, featuring horsehair and a wooden stick. |
| Bridge | A small wooden piece that elevates the strings and transmits vibrations to the body. |
| Tuning Pegs | Mechanisms located on the scroll that adjust string tension to achieve the correct pitch. |
| Chin Rest | A supportive extension that allows players to comfortably hold the instrument while playing. |
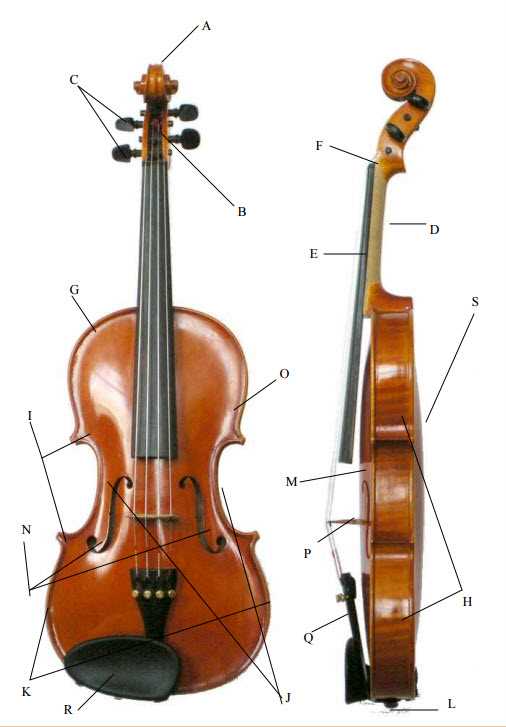
Function of Each Cello Part
Understanding the various components of this string instrument enhances appreciation for its rich sound and intricate design. Each element plays a crucial role in producing the instrument’s unique timbre and facilitating playability. Below, we explore the significance of these essential features.
Body: The resonant structure amplifies sound, shaping the tonal quality. Its curvature allows for optimal vibration, contributing to the overall depth of the notes produced.
Neck: This elongated section provides the necessary support for finger placement, enabling musicians to execute precise techniques. Its length facilitates smooth transitions between notes.
Fingerboard: Positioned atop the neck, this surface allows for the articulation of notes through finger pressure. It plays a vital role in determining pitch accuracy.
Bridge: Acting as a bridge between the strings and the body, this component transmits vibrations effectively, influencing the projection and richness of sound.
Strings: Each string is tuned to specific pitches, essential for harmony and melody. Their material and thickness affect the instrument’s overall voice.
Chin Rest: Providing comfort and stability, this feature allows for better control while playing, ensuring that the musician can focus on technique without physical strain.
Endpin: This component secures the instrument in place during performance, allowing for stability and facilitating a comfortable playing posture.
How the Cello Produces Sound
The creation of sound in this string instrument is a fascinating interplay of physical elements and techniques. When a bow is drawn across the strings, it generates vibrations that resonate through the body of the instrument, transforming these motions into audible tones. The unique shape and materials of the instrument play a crucial role in amplifying and enriching these vibrations.
Vibration Mechanics
Initially, the friction between the bow and the strings causes them to oscillate. This action produces sound waves that travel through the instrument’s structure. The tension and thickness of the strings, along with their length, influence the pitch, enabling a wide range of musical expression.
Resonance and Amplification
The hollow body of the instrument is designed to enhance sound quality. As the strings vibrate, these movements cause the air inside the chamber to vibrate as well, creating a resonant sound that is both rich and full. The curvature and materials used in the construction further refine the tonal qualities, allowing for a warm and resonant sound.
Player’s Technique
The way a musician interacts with the instrument also significantly impacts sound production. Various techniques, such as bowing speed, pressure, and angle, can alter dynamics and expression. Additionally, the use of finger placement on the strings allows for different pitches and harmonics, showcasing the versatility of this beautiful instrument.
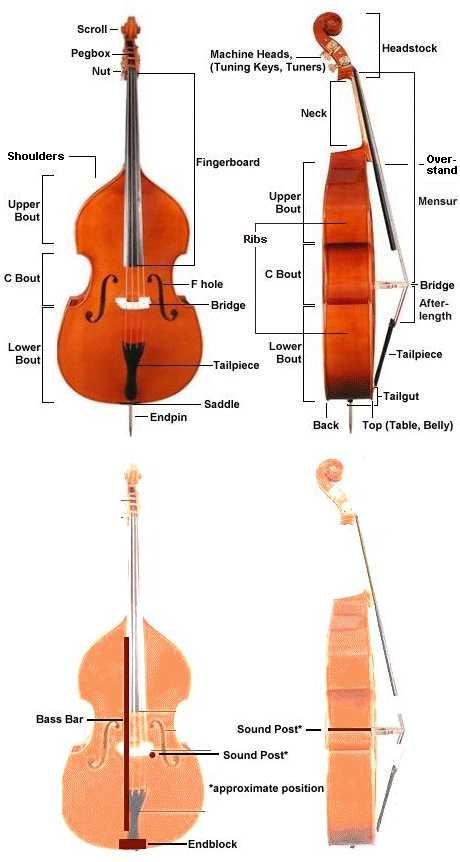
Materials Used in Cello Construction
The selection of materials plays a crucial role in the creation of string instruments, impacting their sound quality and overall aesthetics. Various elements contribute to the unique characteristics of these instruments, each chosen for its specific properties and influence on performance.
- Wood: The primary material used for the body, providing warmth and resonance. Common types include:
- Spruce for the top
- Maple for the back and sides
- Varnish: Applied to enhance appearance and protect the wood, often made from natural resins.
- Strings: Typically made from gut, steel, or synthetic materials, each offering distinct tonal qualities.
- Bow Hair: Generally sourced from horsehair, essential for producing sound when drawn across the strings.
- Fittings: Composed of various materials such as ebony or rosewood, used for pegs, tailpieces, and chin rests.
phpCopy code
Understanding these materials allows enthusiasts to appreciate the craftsmanship involved in creating high-quality instruments.
Common Cello Accessories Explained

In the world of string instruments, various supplementary tools play a crucial role in enhancing the overall experience for musicians. These essentials not only contribute to sound quality but also aid in maintenance and comfort during practice and performances.
Bows are perhaps the most significant accessory, as they directly influence the instrument’s tone. Made from wood and horsehair, the right bow can dramatically improve playability and expression. Musicians often choose between different types based on their playing style and the genre of music.
Rosin is another vital item, applied to the bow hair to create friction. This sticky substance ensures that the bow can grip the strings effectively, producing a clear and resonant sound. Regular application is necessary for optimal performance.
Endpins provide stability by anchoring the instrument to the ground, allowing for greater control during play. These come in various materials and designs, enabling players to select one that best suits their needs.
Shoulder rests enhance comfort by providing support and stability during play. By allowing the instrument to rest securely on the shoulder, they help reduce fatigue, enabling longer practice sessions without discomfort.
Cases serve as protective carriers, safeguarding the instrument from environmental factors and physical damage. A quality case not only ensures safe transport but also offers additional storage for accessories.
Understanding these accessories can significantly impact a musician’s performance and overall enjoyment. By choosing the right tools, players can elevate their practice sessions and performances, ensuring a more fulfilling musical journey.
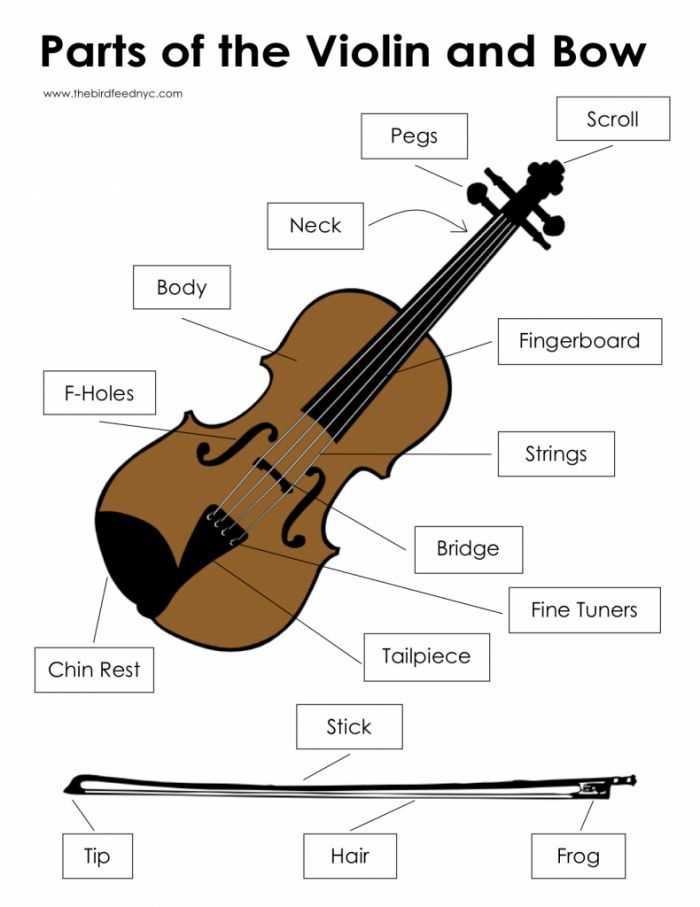
Visual Guide to Cello Parts
This section offers an insightful exploration into the various components that create the unique essence of a string instrument. Understanding these elements enhances appreciation and mastery, as each plays a crucial role in the overall performance and sound quality.
Body: The main structure that resonates with sound, crafted to amplify vibrations.
Fingerboard: The smooth surface where fingers press down the strings, influencing pitch.
Bridge: A critical piece that supports the strings, transferring vibrations to the body.
Soundhole: An opening that allows sound to project, essential for tonal quality.
Scroll: The ornate top end of the neck, often elaborately designed, serving both aesthetic and functional purposes.
Understanding these components is the ultimate key to appreciating the intricate craftsmanship and artistry involved in creating a remarkable musical experience.
Differences Between Cello Models

Various string instruments exhibit distinct characteristics that affect their sound quality, playability, and overall aesthetic. Understanding these differences is crucial for musicians when selecting an instrument that best suits their needs and preferences. Each design and construction technique contributes to the unique tonal qualities and responsiveness of the instrument.
| Model | Wood Type | Sound Quality | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Student | Spruce and Maple | Bright, focused sound | $500 – $1,500 |
| Intermediate | Solid Wood | Warm, balanced tone | $1,500 – $3,500 |
| Professional | Premium Woods | Rich, complex resonance | $3,500 and above |
In addition to the choice of materials, the craftsmanship and finishing techniques also play a significant role in determining the overall quality and performance of the instrument. As musicians advance in their skills, they often seek models that can enhance their expressive capabilities and provide a richer tonal palette.