
The intricate design of flowering plants reveals a fascinating array of elements that contribute to their beauty and functionality. Each component plays a vital role in the overall life cycle, influencing growth, reproduction, and adaptation. This section aims to explore the various sections that make up this botanical masterpiece, highlighting their unique characteristics and purposes.
By examining the specific features found within these elegant organisms, we can gain insight into their ecological significance and evolutionary strategies. Understanding these distinct areas allows us to appreciate not only the aesthetic appeal of blooms but also the intricate processes that sustain their existence. As we delve deeper, we will uncover the ultimate connections between structure and function within these captivating plants.
Understanding Lily Anatomy

Exploring the structure of this beautiful flower reveals a complex arrangement that serves various functions vital for its growth and reproduction. Each component plays a crucial role, contributing to the overall health and beauty of the bloom. A deeper understanding of these elements enhances our appreciation for this exquisite organism.
Key Structures
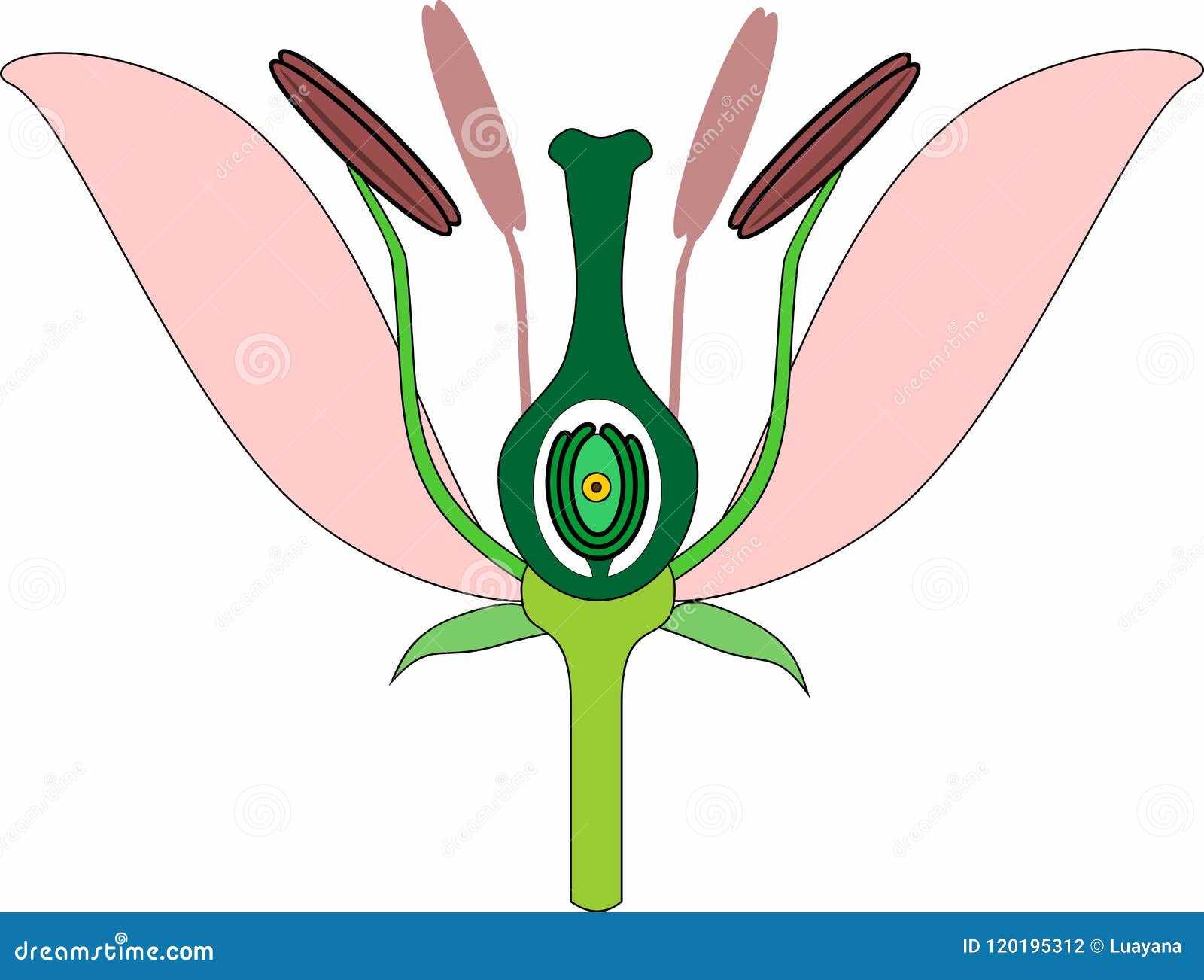

The various components of the flower can be classified into different categories based on their functions. Each category encompasses unique structures that work harmoniously to support the life cycle of the plant.
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Petals | Attract pollinators with vibrant colors and patterns. |
| Stamens | Produce pollen necessary for fertilization. |
| Carpels | House the ovules and facilitate seed development. |
| Sepals | Protect the budding flower before it blooms. |
Significance of Each Element
Understanding the significance of these various structures highlights their interconnected roles within the reproductive system of the flower. This intricate design not only ensures successful reproduction but also plays a part in the plant’s survival in diverse environments.
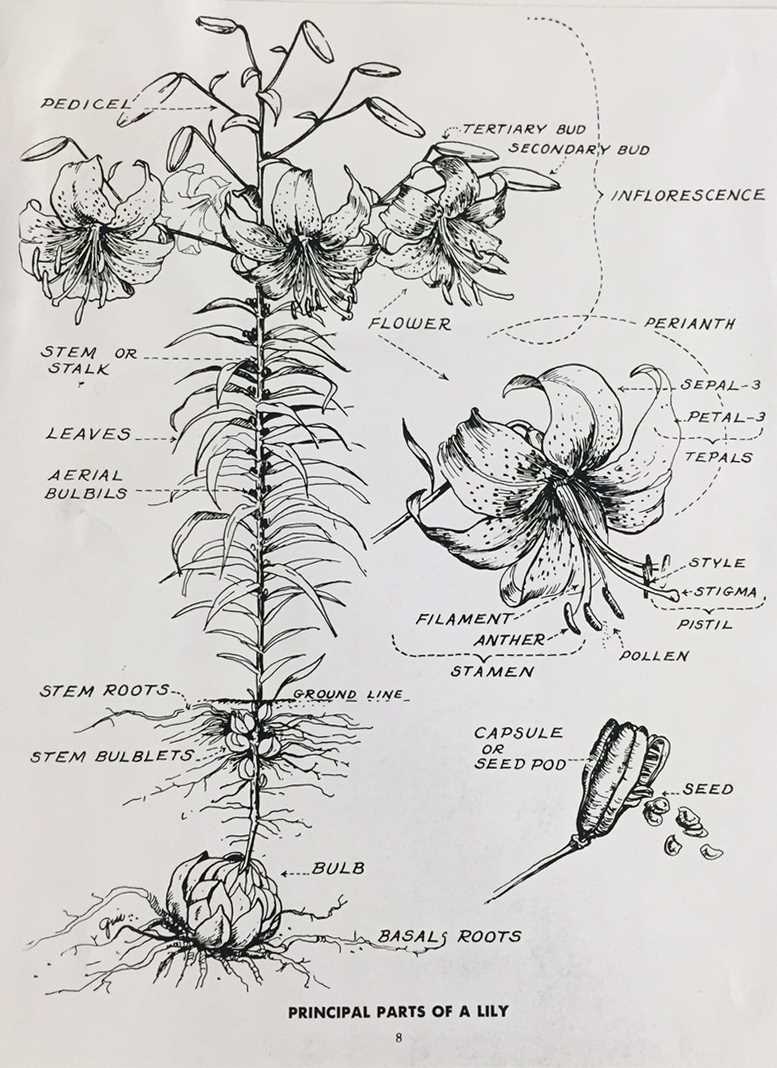
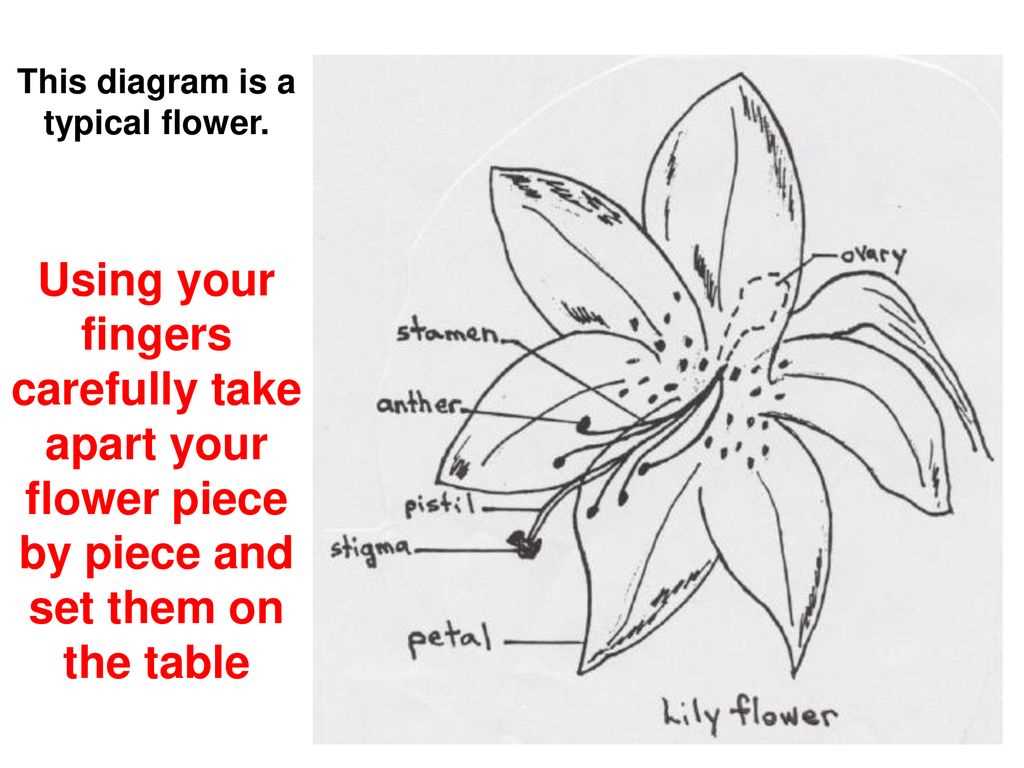
Components of a Lily Flower
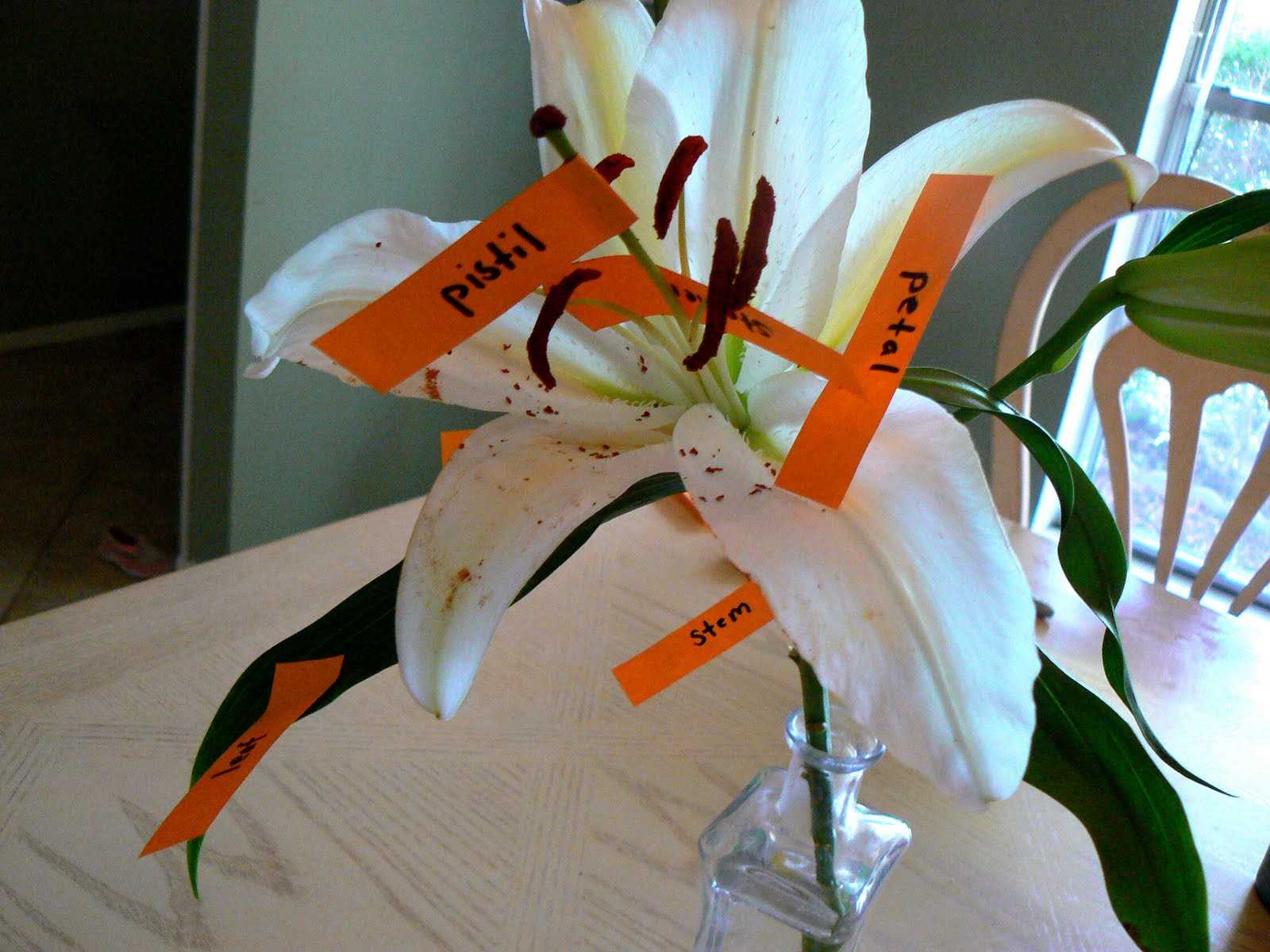

The exquisite structure of this captivating bloom encompasses various essential elements that contribute to its beauty and functionality. Each component plays a vital role in reproduction and growth, showcasing nature’s intricate design.
Stamen serves as the male reproductive part, producing pollen that is crucial for fertilization. This structure is often characterized by its elongated shape, topped with an anther where the pollen grains develop.
Pistil, the female counterpart, is where fertilization occurs. This component consists of several sections: the ovary, which houses ovules; the style, a slender tube leading to the stigma; and the stigma itself, which captures pollen for the fertilization process.
Petals adorn the flower, attracting pollinators with their vibrant colors and delicate forms. These elements not only serve an aesthetic purpose but also assist in the reproductive cycle by guiding insects to the reproductive structures.
Sepals protect the developing bud before it blooms, forming a protective layer around the flower. They are typically green and play a crucial role in supporting the petals once the flower opens.
Understanding these fundamental components reveals the remarkable complexity of this enchanting plant and highlights the interdependence of each structure within the ecosystem.
Function of Lily Stamen
The stamen plays a crucial role in the reproductive process of flowering plants. This essential structure is primarily responsible for producing pollen, which is vital for fertilization and the continuation of the species. By facilitating the transfer of male gametes to the female reproductive parts, the stamen ensures successful reproduction and genetic diversity.
Comprising two main components, the filament and anther, this structure supports the overall reproductive system. The filament acts as a stalk, elevating the anther to a position that maximizes exposure to pollinators and wind. The anther, which houses the pollen grains, bursts open when mature, releasing the pollen into the environment. This strategic design aids in the effective dissemination of male gametes, promoting successful fertilization.
Additionally, the presence of various colors and shapes in the stamen can attract pollinators, enhancing the chances of pollen transfer. This attraction is not merely aesthetic; it plays a significant role in the life cycle of these plants, contributing to the overall ecological balance and health of their habitats.
Role of Lily Pistil
The pistil serves a crucial function in the reproductive process of flowering plants. It acts as the central component where fertilization occurs, playing an essential role in the production of seeds and fruit. This structure is designed to facilitate the reception of pollen, ensuring successful reproduction and genetic diversity.
Structure and Function
This reproductive organ typically consists of three main sections: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the receptive surface where pollen grains land, while the style acts as a conduit, allowing pollen to travel to the ovary. The ovary houses the ovules, which develop into seeds upon fertilization.
Importance in Plant Reproduction
Through its specialized structure, the pistil contributes significantly to the overall success of the plant’s reproductive strategy. By ensuring the effective transfer of pollen, it enhances the chances of fertilization and, consequently, the propagation of the species. The intricate design of this organ highlights the evolutionary adaptations that enable plants to thrive in diverse environments.
Exploring Lily Petals
Delving into the delicate structures of floral beauty reveals fascinating aspects of their design and function. These vibrant elements play a crucial role in the life cycle of their species, attracting pollinators and providing a stunning visual display. Understanding their intricate details enhances our appreciation for nature’s artistry and complexity.
Structure and Function
Each petal is uniquely shaped and colored, serving not just aesthetic purposes but also practical ones. The anatomy of these floral components often includes a waxy surface, which helps in retaining moisture. Additionally, the arrangement of these elements can significantly influence pollinator behavior, leading to effective reproduction.
Color and Attraction
The hues found in these floral structures are not merely for decoration; they are essential for attracting specific pollinators. Bright shades and intricate patterns act as signals, guiding insects towards the reproductive organs. This symbiotic relationship showcases the brilliant strategies evolved over time to ensure the survival of various plant species.
Significance of Lily Sepals
These outer floral structures play a crucial role in the overall health and aesthetic appeal of the bloom. They serve not only as protective coverings for the inner components but also contribute to the plant’s reproductive success.
First and foremost, these elements shield delicate reproductive parts from environmental stressors such as pests, weather, and disease. By providing this defense, they enhance the likelihood of successful pollination and seed formation.
Additionally, their vibrant colors and shapes attract pollinators, making them essential in the process of fertilization. The interaction between these structures and their surroundings illustrates the intricate balance of nature and the importance of each component in a plant’s life cycle.
Lily Leaves: Structure and Purpose
The foliage of these elegant plants plays a vital role in their overall health and functionality. Each element is designed to optimize photosynthesis, water retention, and nutrient absorption, contributing to the plant’s growth and resilience.
Structure is fundamental to understanding how the leaves operate. The broad, flat shape maximizes sunlight capture, while the arrangement facilitates efficient airflow. This design not only enhances light absorption but also aids in reducing water loss, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
In terms of function, the leaves serve multiple purposes. Primarily, they engage in photosynthesis, transforming light energy into chemical energy, which fuels the plant’s development. Additionally, the surface area is adapted to minimize moisture evaporation, allowing the organism to thrive in diverse habitats. The unique adaptations also help protect against herbivores and environmental stressors.
Overall, the combination of structure and function in the leaves underscores their importance in sustaining life and promoting growth, reflecting the intricate relationship between morphology and ecological success.
Roots and Their Functions in Lilies

The underground structures of flowering plants play a vital role in their overall health and development. These systems serve multiple purposes, ensuring the organism remains stable, nourished, and capable of thriving in its environment.
Primarily, the anchoring function of these structures is crucial. They secure the plant in the soil, providing stability against environmental forces. Additionally, they are responsible for nutrient and water absorption, drawing essential elements from the soil to support growth. This interaction with the surrounding substrate also facilitates the storage of energy, which can be vital during periods of dormancy.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Anchorage | Stabilizes the plant in the soil, preventing displacement. |
| Nutrient Absorption | Absorbs minerals and nutrients necessary for growth. |
| Water Uptake | Draws moisture from the soil to sustain the plant. |
| Energy Storage | Stores carbohydrates and other compounds for future use. |
In summary, the foundational components not only anchor the organism but also play a critical role in its nutrition and energy management, contributing to the plant’s vitality and resilience in various conditions.
Life Cycle of a Lily Plant
The development of this exquisite flowering species is a fascinating journey through various stages, each playing a crucial role in its growth and reproduction. Understanding these phases reveals the intricate processes that sustain its life and enable it to thrive in diverse environments.
Stages of Development

- Seed Germination: The cycle begins with a seed, which requires moisture, warmth, and light to sprout. During this phase, the outer shell breaks open, allowing the young plant to emerge.
- Vegetative Growth: Following germination, the plant enters a period of active growth. It develops roots, stems, and leaves, which are essential for photosynthesis and nutrient absorption.
- Flowering: As the plant matures, it produces blooms. This stage is crucial for reproduction, attracting pollinators and facilitating fertilization.
- Seed Production: Once pollination occurs, the plant develops seeds, ensuring the continuation of its species. These seeds are eventually dispersed to new locations.
- Dormancy: After the growing season, the plant may enter a dormant phase, conserving energy and resources until the conditions are favorable for regrowth.
Environmental Influences
Several factors impact the development cycle of this species, including:
- Soil quality and type
- Availability of water
- Sunlight exposure
- Temperature variations
Each of these elements plays a vital role in determining the health and vigor of the plant, influencing its ability to complete the cycle successfully.